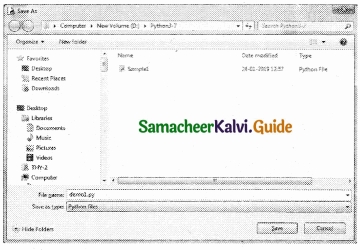
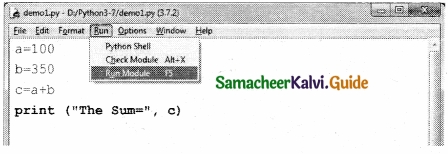
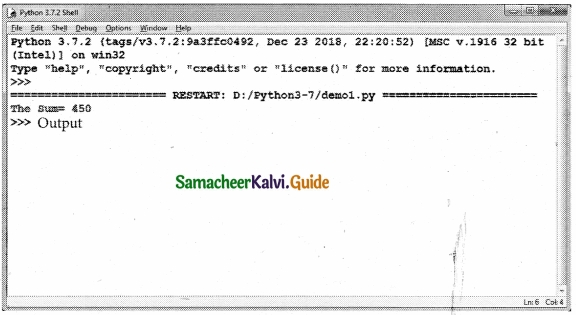
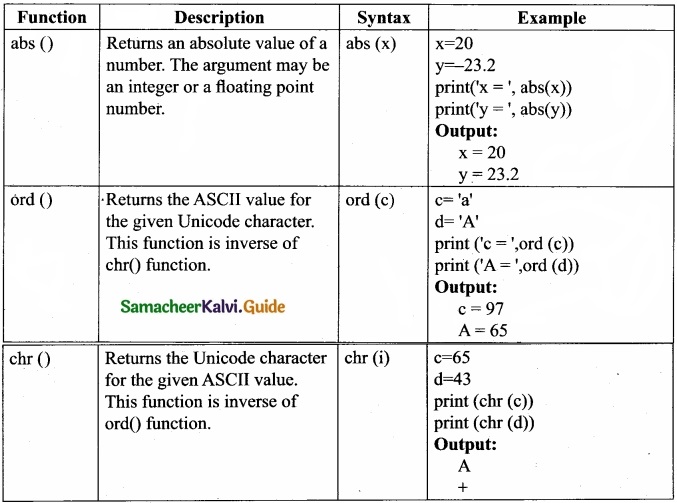
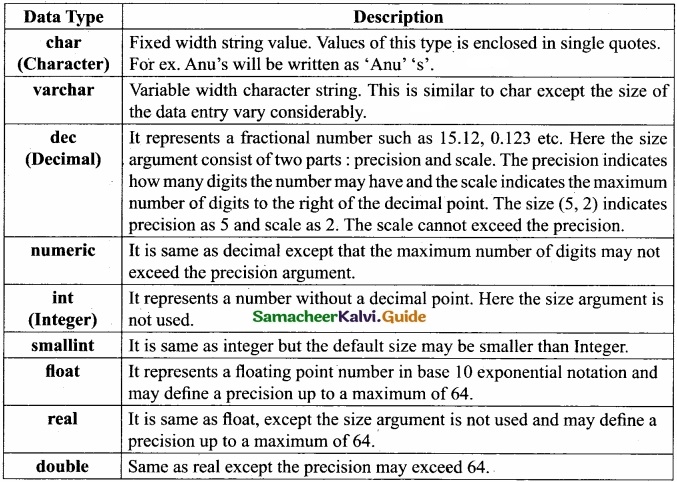
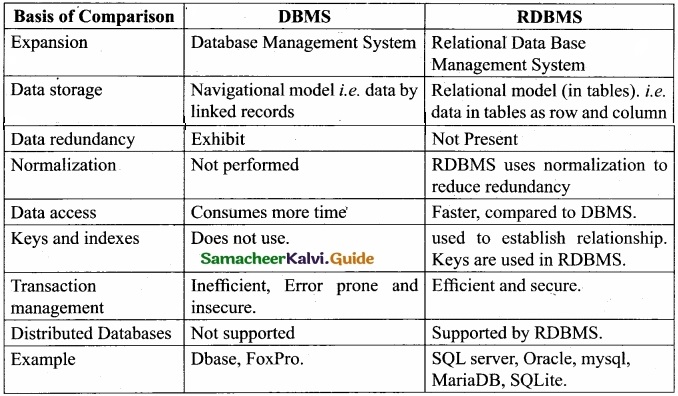
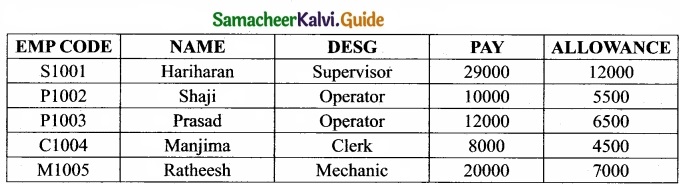
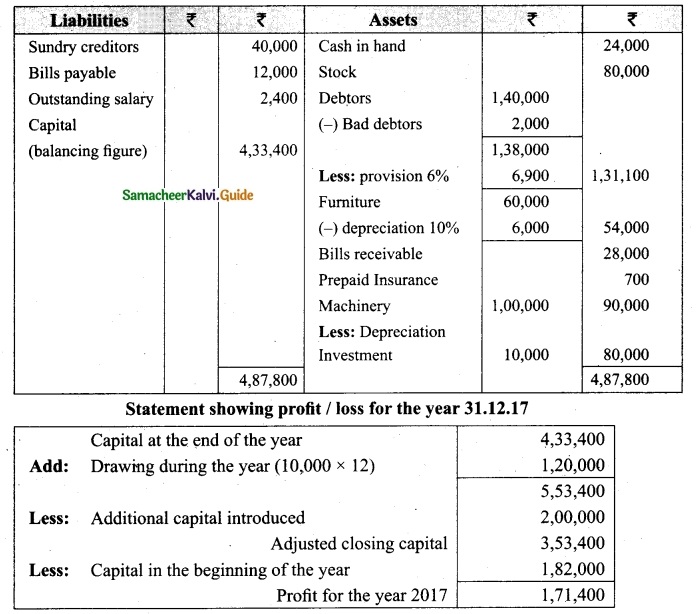
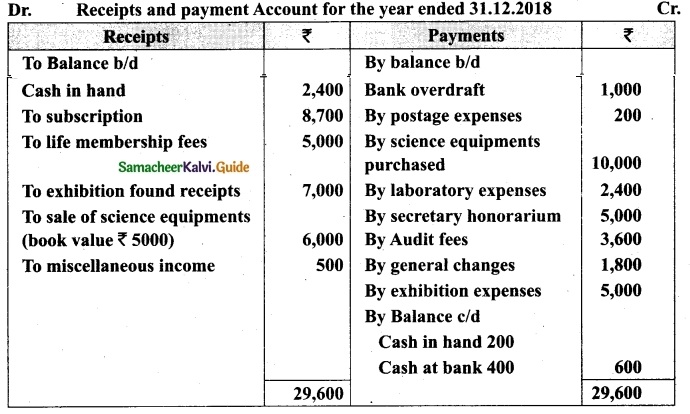
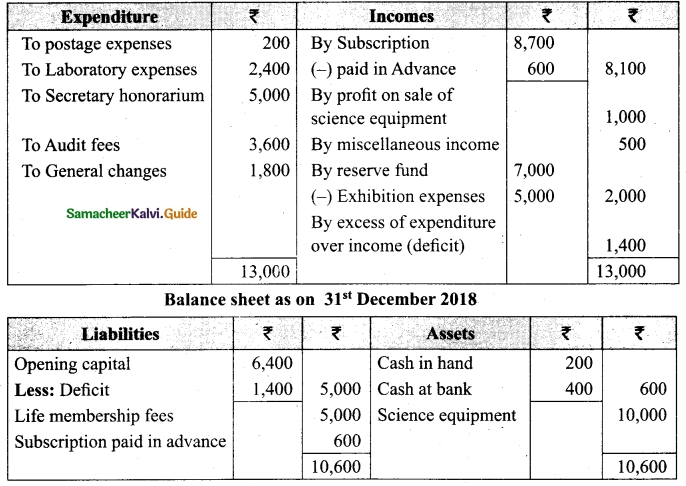
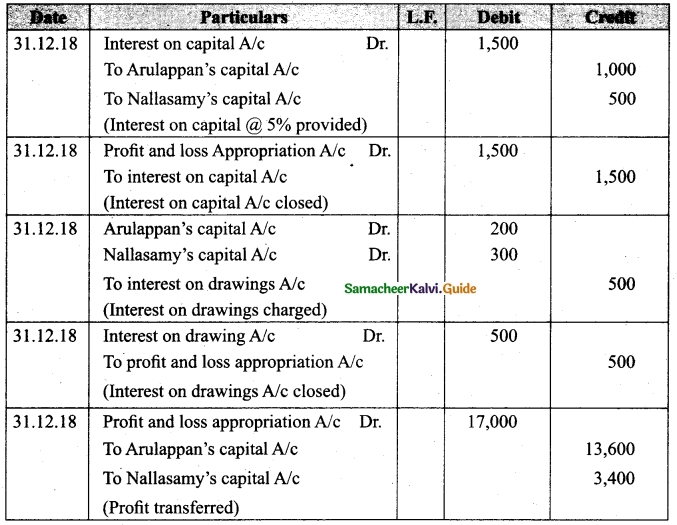
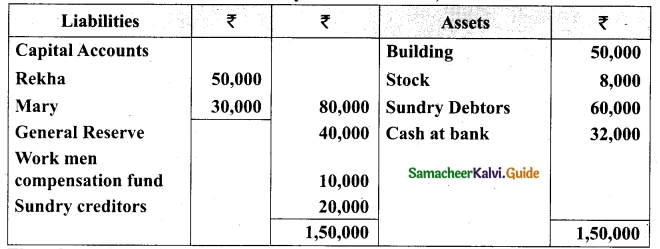
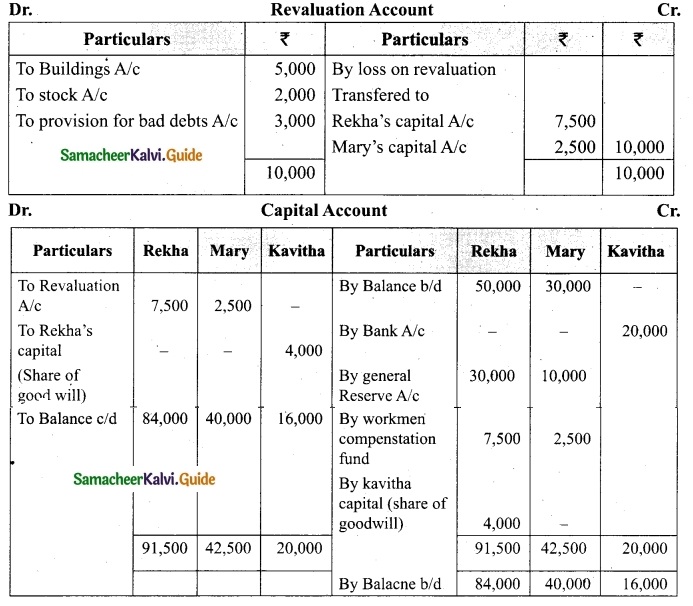
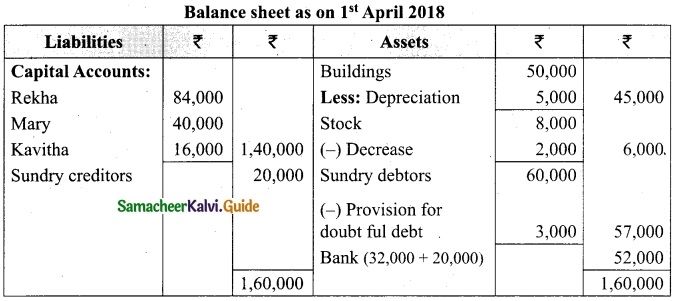
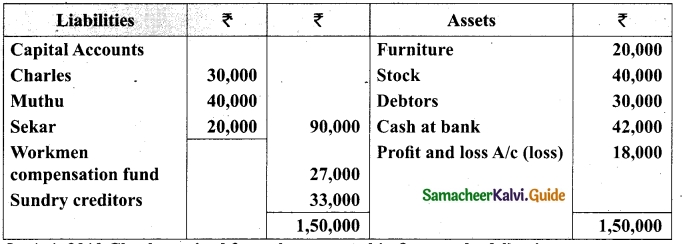
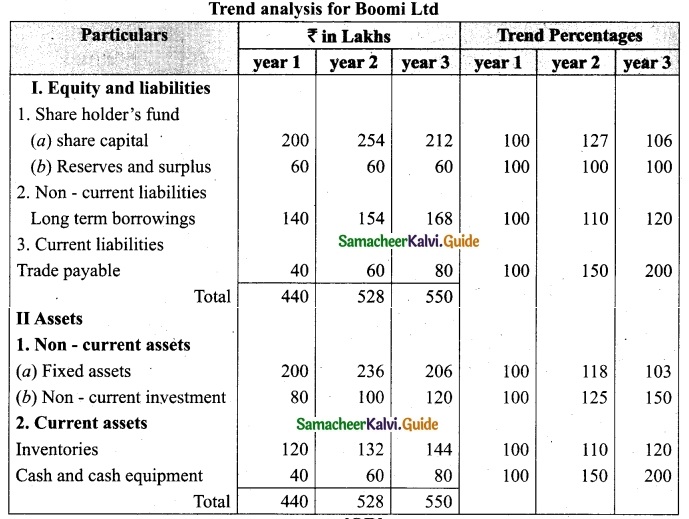
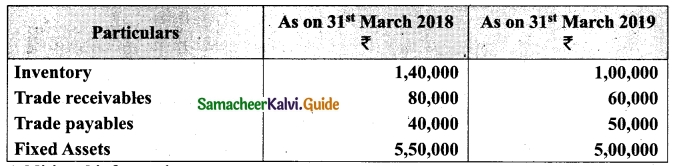
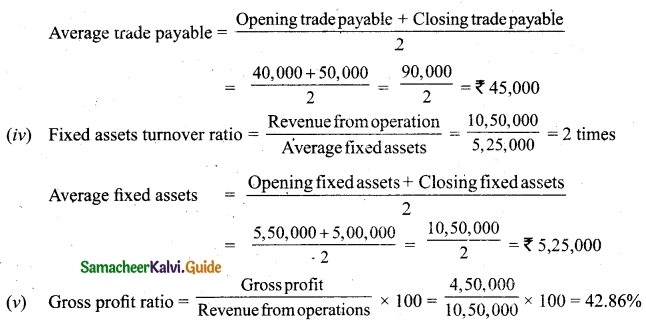
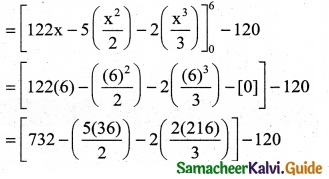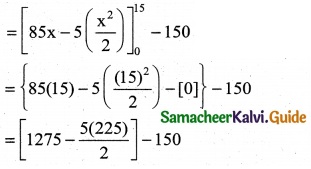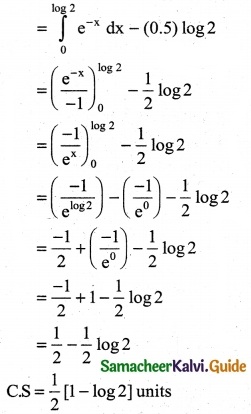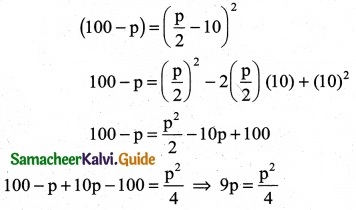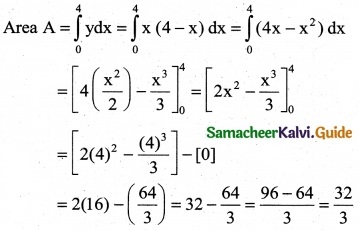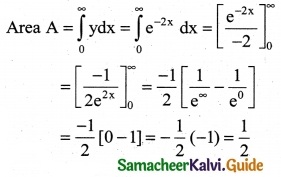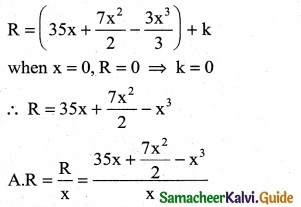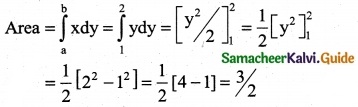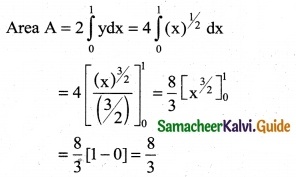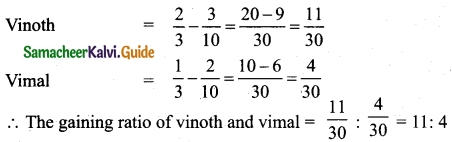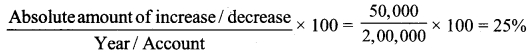Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Business Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 3 Integral Calculus II Miscellaneous Problems Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Business Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Integral Calculus II Miscellaneous Problems
Question 1.
A manufacture’s marginal revenue functional is given by MR = 275 – x – 0.3x². Find the increase in the manufactures total revenue if the production increased from 10 to 20 units.
Solution:
MR = 275 – x – 0.3x²
The increase in the manufactures total revenue 20
T.R = ∫MR dx = (275 – x – 0.3x²) dx
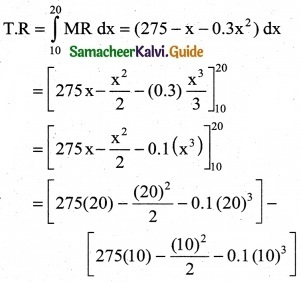
= [5500 – 200 – 0.1 (8000)] – [2750 – 50 – 0.1(1000)]
= [5500 – 200 – 800] – [2750 – 50 – 100]
= 4500 – 2600
= Rs 1900
![]()
Question 2.
A company has determined that marginal cost function for product of a particular commodity is given by MC = 125 + 10x – \(\frac { 8 }{3}\). Where C is the cost of producing x units of the commodity. If the fixed cost Rs 250 what is cost of producing 15 units.
Solution:
MC = 125 + 10x – \(\frac { x^2 }{9}\)
Fixed cos t K = Rs 250
C = ∫MC dx – ∫(125 + 10x – \(\frac { x^2 }{9}\)) dx
C = 125x + \(\frac { 10x^2 }{9}\) – \(\frac { x^3 }{9×3}\) + k
C = 125x + 5x² – \(\frac { x^3 }{27}\) + 250
when x = 15
C = 125(15) + 5(15)² – \(\frac { (15)^3 }{27}\) + 250
= 1875 + 1125 – 125 + 250
C = Rs 3,125
Question 3.
The marginal revenue function for a firm given by MR = \(\frac { 2 }{x+3}\) – \(\frac { 2x }{(x+3)^2}\) + 5. Show that the demand function is P = \(\frac { 2x }{(x+3)^2}\) + 5
Solution:

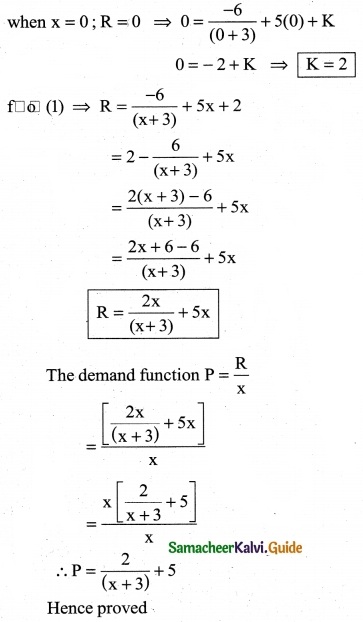
![]()
Question 4.
For the marginal revenue function MR = 6 – 3x² – x³, Find the revenue function and demand function
Solution:
MR = 6 – 3x² – x³
Revenue function R = ∫MR dx
R = ∫(6 – 3x² – x³)dx
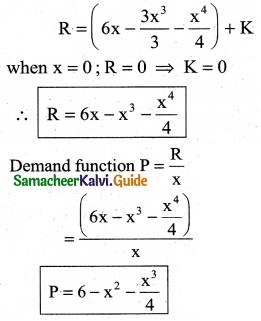
Question 5.
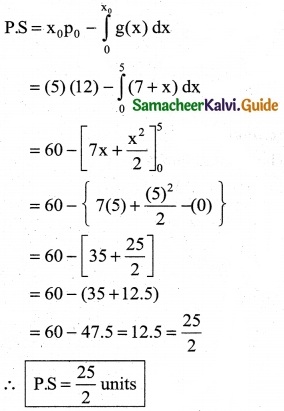
The marginal cost of production of a firm is given by C'(x) = 20 + \(\frac { x }{20}\) the marginal revenue is given by R’(x) = 30 and the fixed cost is Rs 100. Find the profit function.
Solution:
C'(x) = 20 + \(\frac { x }{20}\)
Fixed cost k1 = Rs 100
C(x) = ∫C1(x) dx + k1
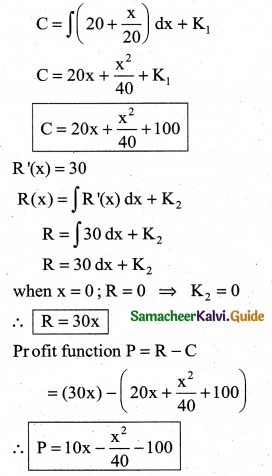
![]()
Question 6.
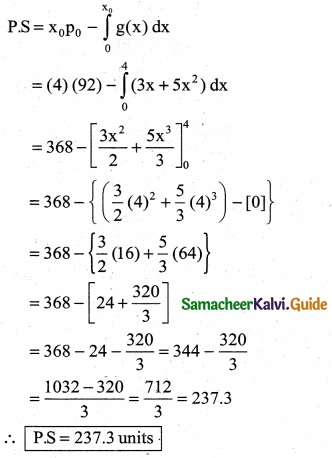
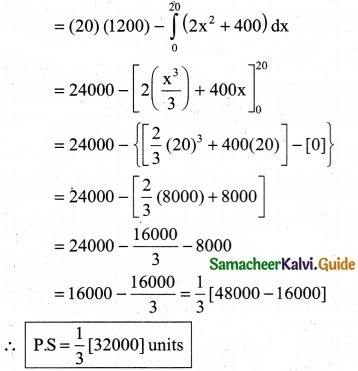
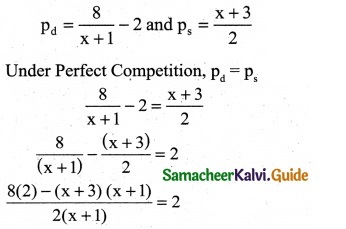
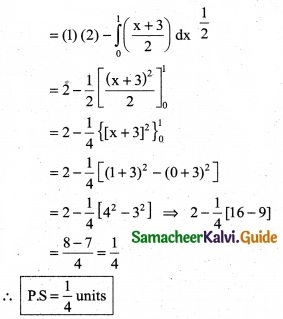
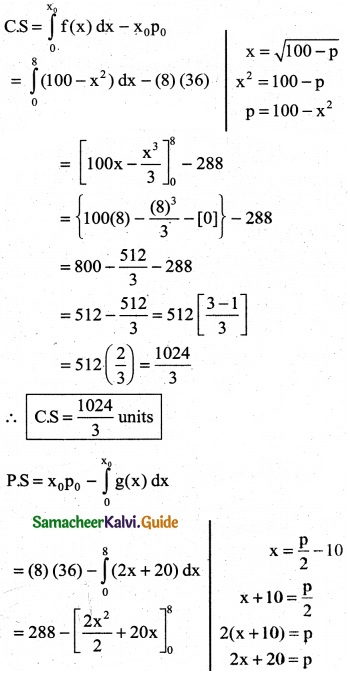
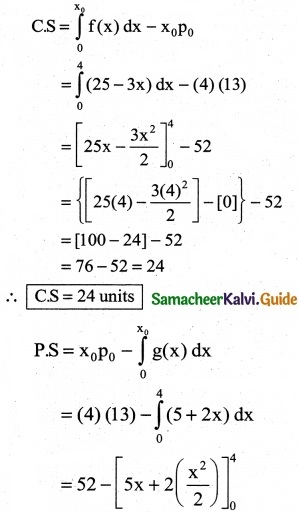
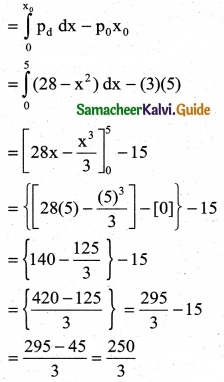
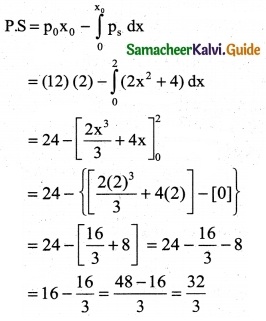
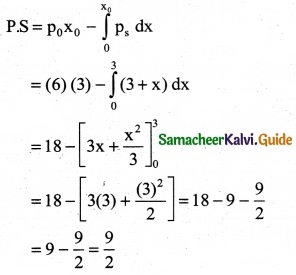
The demand equation for a product is Pd = 20 – 5x and the supply equation is Ps = 4x + 8. Determine the consumers surplus and producer’s surplus under market equilibrium.
Solution:
Pd = 20 – 5x and Ps = 4x + 8
At market equilibrium
Pd = Pd
20 – 5x = 4x + 8 ⇒ 20 – 8 = 4x + 5x
9x = 12 ⇒ x = \(\frac { 12 }{9}\)
∴ x = \(\frac { 4 }{3}\)
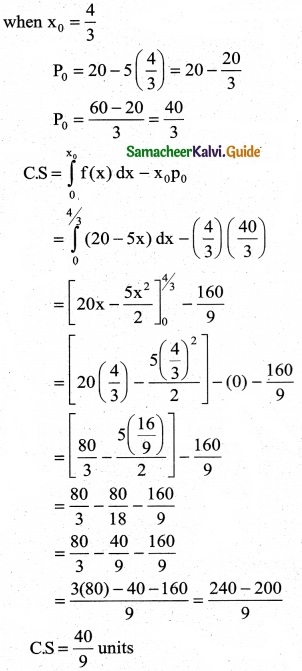
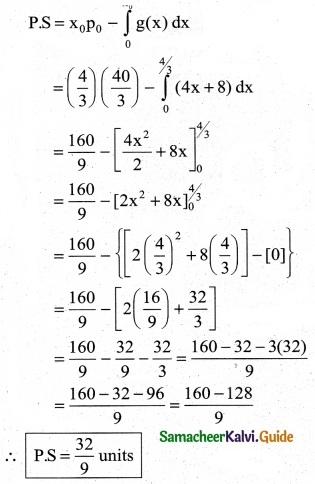
![]()
Question 7.
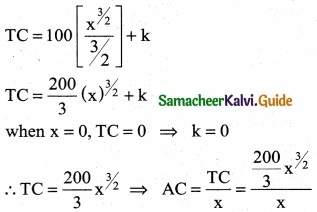
A company requires f(x) number of hours to produce 500 units. lt is represented by f(x) = 1800x-0.4. Find out the number of hours required to produce additional 400 units. [(900)0.6 = 59.22, (500)0.6 = 41.63]
Solution:
f(x) number of hours to produce 500
f(x) = 1800 x-0.4
The number of hours required to produce additions
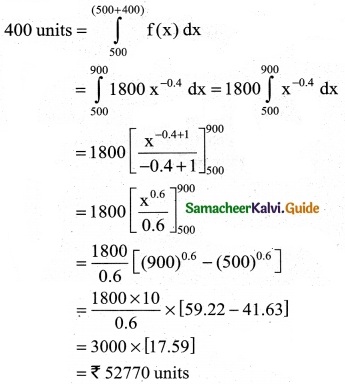
Question 8.
The price elasticity of demand for a commodity is \(\frac { p }{x^3}\). Find the demand function if the quantity of demand is 3, When the price is Rs 2.
Solution:
Price elasticity of demand
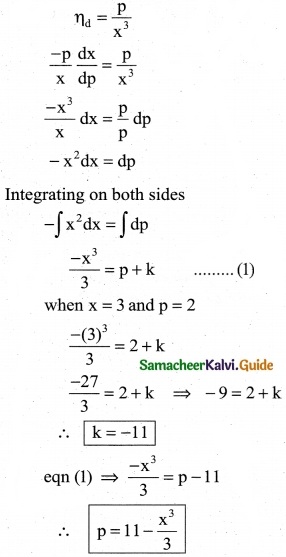
![]()
Question 9.
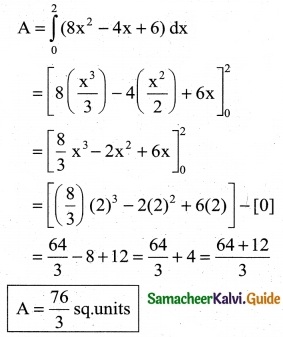
Find the area of the region bounded by the curve between the parabola y = 8x² – 4x + 6 the y-axis and the ordinate at x = 2.
Solution:
Equation of the parabola
y = 8x² – 4x + 6
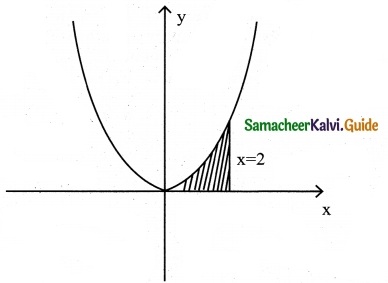
The required region is bounded by the y-axis and the ordinate at x = 2.
∴ Required Area A = \(\int_{0}^{2}\)ydx
Question 10.
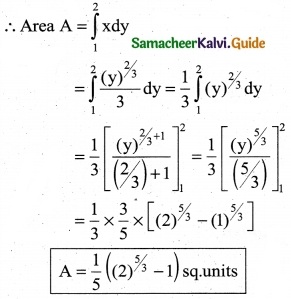
Find the area of the region bounded by the curve y² = 27x³ and the line x = 0, y = 1 and y = 2
Solution:
Equation of the curve is y² = 27x³
⇒ x³ = \(\frac { y^2 }{27}\) = \(\frac { y^3 }{3^3}\)
∴ x = \(\frac { (y)^{2/3} }{3}\)
Since the Area of the region bounded by the given curve and the lines x = 0, y = 1 and y = 2
![]()
Read Once: