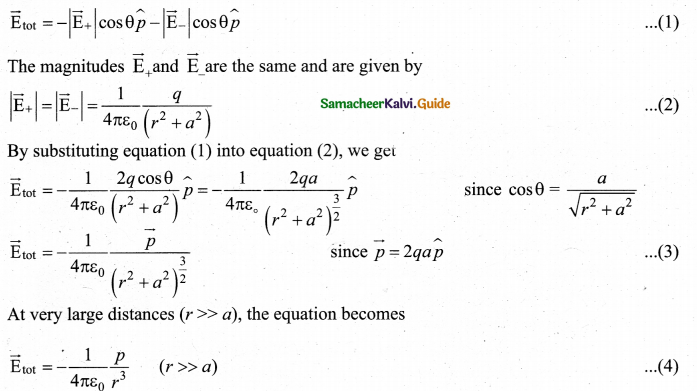Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 3 Theory of Equations Ex 3.1 Textbook Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Theory of Equations Ex 3.1
Question 1.
If the sides of a cubic box are increased by 1, 2, 3 units respectively to form a cuboid, then the volume is increased by 52 cubic units. Find the volume of the cuboid.
Solution:
Let the side of the cube be ‘x’
Sides of cuboid are (x + 1) (x + 2) (x + 3)
∴ Volume of cuboid = x3 + 52
⇒ (x + 1) (x + 2) (x + 3) = x3 + 52
⇒ (x2 + 3x + 2)(x + 3) = x3 + 52
⇒ x3 + 3x2 + 3x2 + 9x + 2x + 6 – x3 – 52 = 0
⇒ 6x2 + 11x – 46 = 0 (÷2)
⇒ (x – 2) (6x + 23) = 0
⇒ x – 2 = 0 or 6x + 23 = 0
⇒ x = 2 or x = \(-\frac{23}{6}\) (not possible)
∴ x = 2
Volume of cube = 23 = 8
Volume of cuboid = 52 + 8 = 60 cubic units
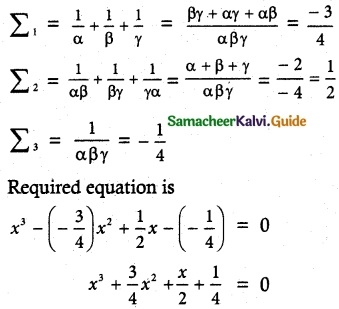
Question 2.
Construct a cubic equation with roots
Solution:
(i) 1, 2, and 3
α = 1, β = 2, γ = 3
α + β + γ = 6
αβ + βγ + γα = 2 + 6 + 3 = 11
αβγ = 6
x³ – (α + β + γ)x² + (αβ + βγ + γα)x – αβγ = 0
x³ – 6x² + 11x – 6 = 0
(ii) 1, 1, and -2
α = 1, β = 1, γ = -2
α + β + γ = 1 + 1 – 2 = 0
αβ + βγ + γα = 1 – 2 – 2 = -3
αβγ = 1(1)(-2) = -2
x³ – 0x² – 3x + 2 = 0
∴ x³ – 3x + 2 = 0
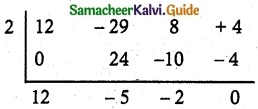
(iii) 2, \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\), and 1.

Multiplying by 2
2x³ – 7x² + 7x – 2 = 0
![]()
Question 3.
If α, β and γ are the roots of the cubic equation x³ + 2x² + 3x + 4 = 0, form a cubic equation whose roots are
(i) 2α, 2β, 2γ,
(ii) \(\frac{1}{α}\), \(\frac{1}{β}\), \(\frac{1}{γ}\)
(iii) – α, – β, – γ
Solution:
(i) Given that α, β, γ are the roots of x3 + 2x2 + 3x + 4 = 0
Compare with x3 + bx2 + cx + d = 0
b = 2, c = 3, d = 4
α + β + γ = -6 = -2
αβ + βγ + γα = c = 3
αβγ = -d = -4
Given roots are 2α, 2β, 2γ
2α + 2β + 2γ = 2 (α + β + γ)
= 2 (-2)
= -4
(2α) (2β) + (2β) (2γ) + (2γ) (2α) = (4αβ + 4βγ + 4γα)
= 4(αβ + βγ + γα)
= 4(3)
= 12
(2α) (2β) (2γ) = 8(αβγ)
= 8(-4)
= -32
The equation is
x3 – x2 (2α + 2β + 2γ) + x (4αβ + 4βγ + 4γα) – 8 (αβγ) = 0
⇒ x3 – x2 (-4) + x (12) – (-32) = 0
⇒ x3 + 4x2 + 12x + 32 = 0
(ii) The new roots are \(\frac{1}{α}\), \(\frac{1}{β}\), \(\frac{1}{γ}\)
⇒ 4x³ + 3x² + 2x + 1 = 0
(iii) The given roots are -α, -β, -γ
The cubic equation is
x3 – x2 (-α – β – γ) + x (αβ + βγ + γα) + (αβγ) = 0
⇒ x3 + x2 (α + β + γ) + x (αβ + βγ + γα) + (αβγ) = 0
⇒ x3 + x2 (-2) + x (3) – 4 = 0
⇒ x3 – 2x2 + 3x – 4 = 0
![]()
Question 4.
Solve the equation 3x³ – 16x² + 23x – 6 = 0 if the product of two roots is 1.
Solution:
Let the roots be α, β, γ
Given αβ = 1, β = \(\frac{1}{α}\)
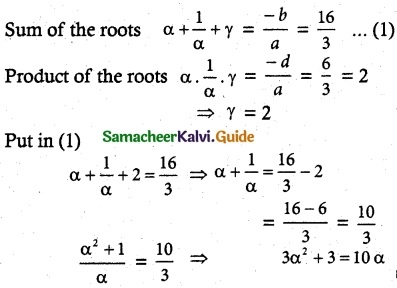
⇒ 3α² – 10α + 3 = 0
3α² – 9α – α + 3 = 0
3α(α – 3) -1(α – 3) = 0
(3α – 1) (α – 3) = 0
α = 3 or α = \(\frac{1}{3}\)
If α = 3, β = \(\frac{1}{3}\), γ = 2 (or)
α = \(\frac{1}{3}\), β = 3, γ = 2
⇒ [α, β, γ] = (\(\frac{1}{3}\), 3, 2)
Question 5.
Find the sum of squares of roots of the equation 2x4 – 8x³ + 6x² – 3 = 0.
Solution:
The given equation is 2x4 – 8x3 + 6x2 – 3 = 0.
(÷ 2) ⇒ x4 – 4x3 + 3x2 – \(\frac{3}{2}\) = 0
Let the roots be α, β, γ, δ
α + β + γ + δ = -b = 4
(αβ + βγ + γδ + αδ + αγ + βδ) = c = 3
αβγ + βγδ + γδα = -d = 0
αβγδ = \(\frac{-3}{2}\)
To Find α2 + β2 + γ2 + δ2 = (α + β + γ + δ)2 – 2 (αβ + βγ + γδ + αδ + αγ + βδ)
= (4)2 – 2(3)
= 16 – 6
= 10
![]()
Question 6.
Solve the equation x³ – 9x² + 14x + 24 = 0 if it is given that two of its roots are in the ratio 3 : 2.
Solution:
Let the roots are 3α, 2α, β
sum of the roots are
3α + 2α + β = 9
5α + β = 9 ………. (1)
Product of two roots
3α(2α) + 2α(β) + β(3α) = 14
6α² + 5αβ = 14 ……… (2)
Product of three roots
(3α) (2α)β = -24
α²β = -4 ………. (3)
(1) ⇒ β = 9 – 5 α
(2) ⇒ 6α² + 5α (9 – 5α) = 14
6α² + 45α – 25α² = 14
-19α² + 45α – 14 = 0
19α² – 45α + 14 = 0
(α – 2) (α – \(\frac{7}{19}\)) = 0
α = 2 or α = \(\frac{7}{19}\)
If α = 2, β = 9 – 5 (α) = 9 – 5(2) = 9 – 10 = -1
roots are 3α, 2α, β
3(2), 2(2), -1 (i,e.,) 6, 4, -1
If α = \(\frac{7}{19}\), β = 9 – 5(\(\frac{7}{19}\)) = (\(\frac{136}{19}\))
roots are 3α, 2α, β (i,e.,) \(\frac{21}{19}\), \(\frac{14}{19}\), \(\frac{136}{19}\)
Question 7.
If α, β, and γ are the roots of the polynomial equation ax³ + bx² + cx + d = 0, find the value of Σ\(\frac{α}{βγ}\) terms of the coefficients.
Solution:
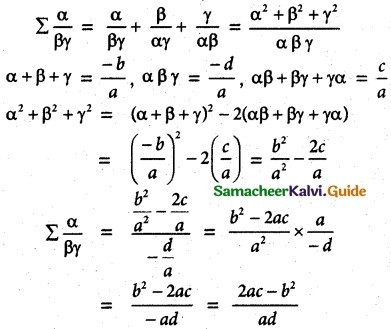
![]()
Question 8.
If α, β, γ and δ are the roots of the polynomial equation 2x4 + 5x³ – 7x² + 8 = 0, find a quadratic equation with integer coefficients whose roots are α + β + γ + δ and αβγδ.
Solution:
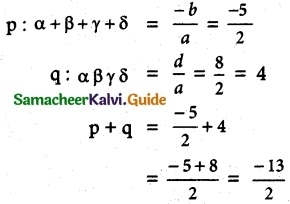
pq = (\(\frac{-5}{2}\))(4) = -10
x² – (p + q)x + pq = 0
x² – \(\frac{3}{2}\)x – 10 = 0
2x² – 3x – 20 = 0
Question 9.
If p and q are the roots of the equation lx² + nx + n = 0,
show that, ![]()
Solution:
p and q are the roots of the equation lx² + nx + n = 0
p + q = –\(\frac{n}{l}\), pq = \(\frac{n}{l}\)
LHS
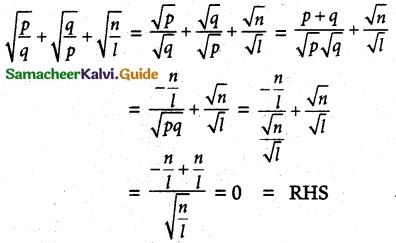
Question 10.
If the equations x² + px + q = 0 and x² + p’x + q’ = 0 have a common root, show
that it must be equal to \(\frac{pq’-p’q}{q-q’}\) and \(\frac{q-q’}{p’-p}\)
Solution:
Let it be α common roots of x² + px + q = 0
x² + p’x + q’ = 0
(i,e.,) α² + pα + q = 0 …… (1) and
α² + p’α + q’ = 0 ………. (2)
Solving 1 and 2 by cross multiplication method, we have
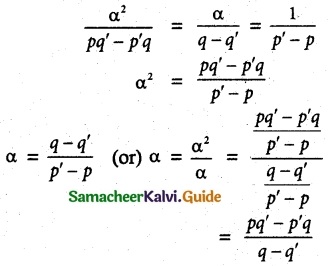
Hence proved.
![]()
Question 11.
A 12-meter tall tree was broken into two parts. It was found that the height of the part which was left standing was the cube root of the length of the part that was cut away. Formulate this into a mathematical problem to find the height of the part which was cut away.
Solution:
Let the height of the tree = 12
length of the cut part = x³
Length of left out part = \(\sqrt[3]{x^{3}}\)
= x
Given x + x³ = 12
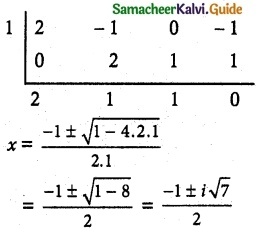
x³ + x – 12 = 0
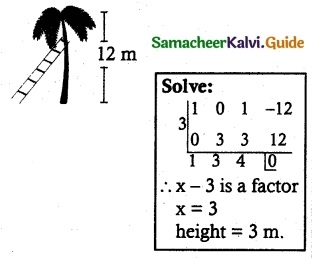
Which is required mathematical problem
![]()

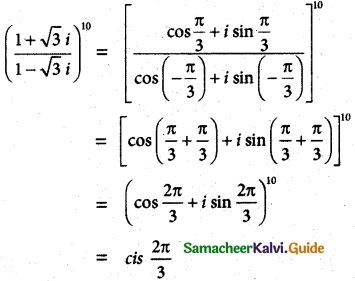
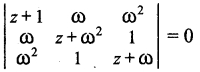
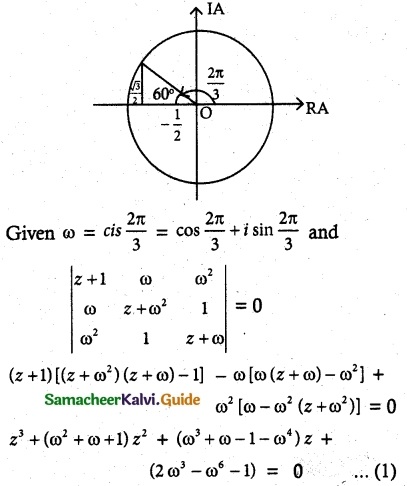
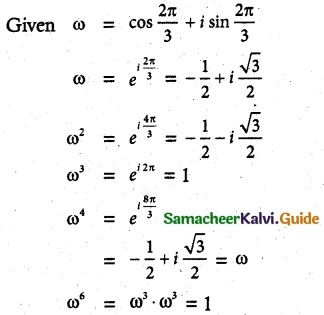
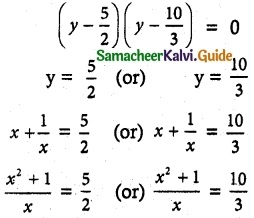































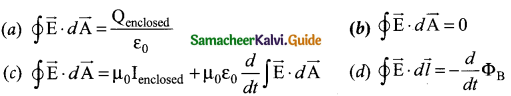
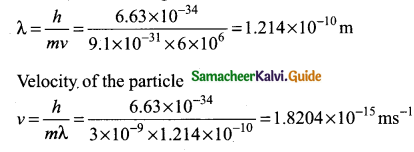

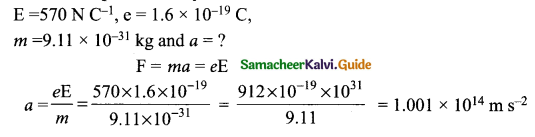

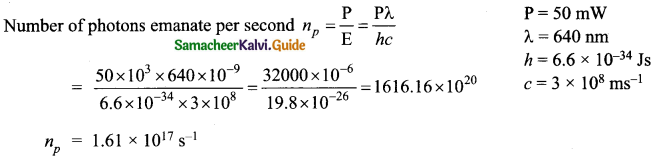
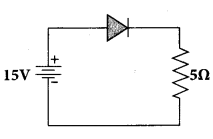
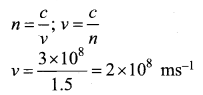
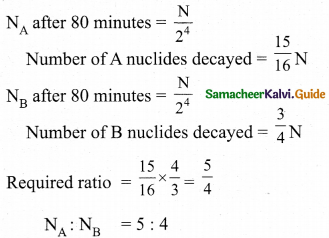
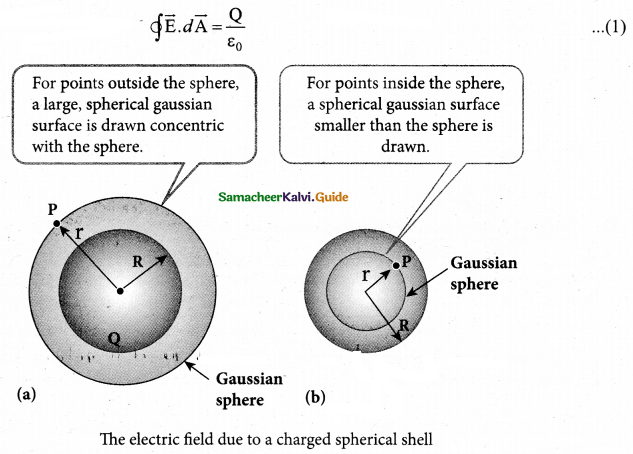
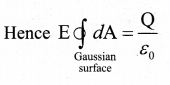
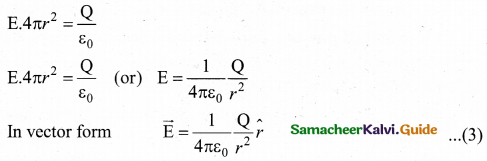
 = total area of Gaussian surface = 4πr2 Substituting this value in equation (2)
= total area of Gaussian surface = 4πr2 Substituting this value in equation (2)