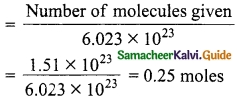
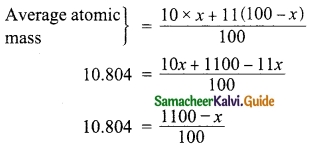
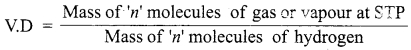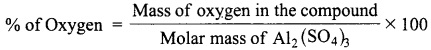Students can download 10th Science Chapter 20 Breeding and Biotechnology Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Solutions Chapter 20 Breeding and Biotechnology
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Breeding and Biotechnology Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Which method of crop improvement can be practised by a farmer if he is inexperienced?
(a) clonal selection
(b) mass selection
(c) pureline selection
(d) hybridisation
Answer:
(b) mass selection
Question 2.
Pusa Komal is a disease resistant variety of ______.
(a) sugarcane
(b) rice
(c) cow pea
(d) maize.
Answer:
(c) cow pea
![]()
Question 3.
Himgiri developed by hybridisation and selection for disease resistance against rust pathogens is a variety of:
(a) chilli
(b) maize
(c) sugarcane
(d) wheat
Answer:
(d) wheat
Question 4.
The miracle rice which saved millions of lives and celebrated its 50th birthday is ______.
(a) IR – 8
(b) IR – 24
(c) Atomita – 2
(d) Ponni.
Answer:
(a) IR – 8
Question 5.
Which of the following is used to produce products useful to humans by biotechnology techniques?
(a) enzyme from organism
(b) live organism
(c) vitamins
(d) both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(a) enzyme from organism
Question 6.
We can cut the DNA with the help of ______.
(a) scissors
(b) restriction endonucleases
(c) knife
(d) RNAase.
Answer:
(b) restriction endonucleases
Question 7.
rDNA is a:
(a) vector DNA
(b) circular DNA
(c) recombinant of vector DNA and desired DNA:
(d) satellite DNA
Answer:
(c) recombinant of vector DNA and desired DNA:
Question 8.
DNA fingerprinting is based on the principle of identifying ______ sequences of DNA.
(a) single-stranded
(b) mutated
(c) polymorphic
(d) repetitive.
Answer:
(d) repetitive
Question 9.
Organisms with modified endogenous gene or a foreign gene are also known as:
(a) transgenic organsims
(b) genetically modified
(c) mutated
(d) both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(a) transgenic organsims
Question 10.
In a hexaploid wheat (2n = 6x = 42) the haploid (n) and the basic (x) number of chromosomes respectively are ______.
(a) n = 7 and x = 21
(b) n = 21 and x = 21
(c) n = 7 and x = 7
(d) n = 21 and x = 7.
Answer:
(d) n = 21 and x = 7.
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks:
1. Economically important crop plants with superior quality are raised by ………..
2. A protein rich wheat variety is ………
3. ………. is the chemical used for doubling the chromosomes.
4. The scientific process which produces crop plants enriched with desirable nutrients are called ………
5. Rice normally grows well in alluvial soil, but ………… is a rice variety produced by mutation breeding that grows well in saline soil.
6. ……….. technique made it possible to genetically engineer living organism.
7. Restriction endonucleases cut the DNA molecule at specific positions known as …………
8. Similar DNA fingerprinting is obtained for ………..
9. ………… cells are undifferentiated mass of cells.
10. In gene cloning the DNA of interest is integrated in a …………
Answer:
1. Hybridization
2. Altas 66
3. Colchicine
4. Bio fortification
5. Atomita 2 rice
6. Recombinant
7. Phosphodiester
8. Identical twins
9. stem cells
10. bacterial cell
III. State whether true or false. If false, write the correct statement:
1. Raphanobrassica is a tetraploid man-made genus produced by colchicine treatment.
2. The process of producing an organism with more than two sets of chromosome is called mutation.
3. A group of plants produced from a single plant through vegetative or asexual reproduction are called a pureline.
4. Iron fortified rice variety determines the protein quality of the cultivated plant.
5. Golden rice is a hybrid.
6. Bt gene from bacteria can kill insects. ,
7. In vitro fertilisation means the fertilisation done inside the body.
8. DNA fingerprinting technique was developed by Alec Jeffrey.
9. Molecular scissors refers to DNA ligases.
Answer:
1. False – Raphanobrassica is a allotetra ploid man-made genus produced by colchicine treatment.
2. False – The process of producing an organism with more than two sets of chromosome is called polyploidy.
3. True
4. False – Iron rich rice variety determines the protein quality of the cultivated plant.
5. False – Golden rice is a genetically modified plant
6. True
7. False – In vitro fertilisation means the fertilisation done outside the body.
8. True
9. False – Molecular scissors refers to Restriction enzymes
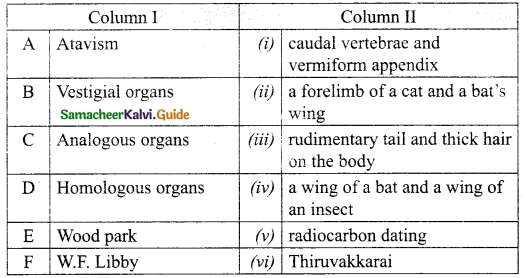
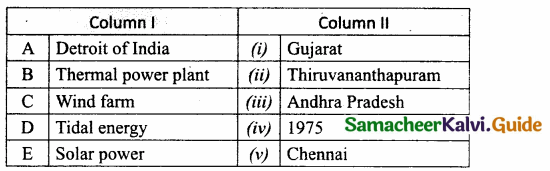
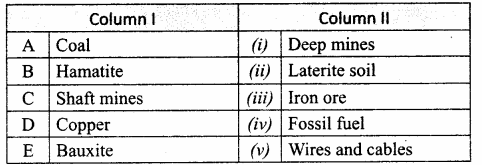
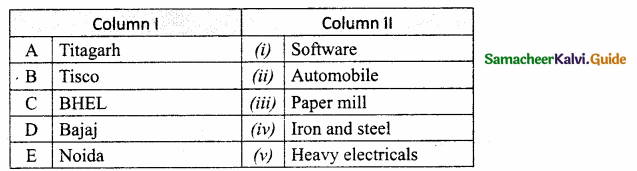
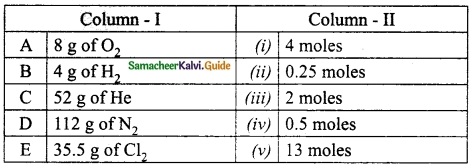
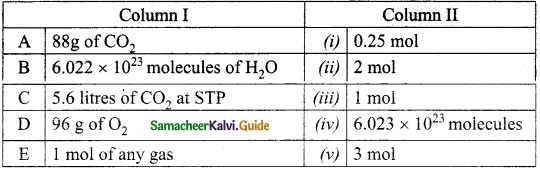
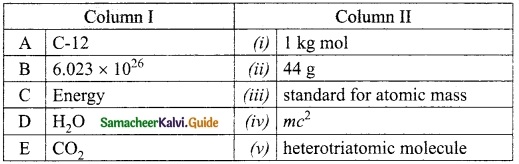
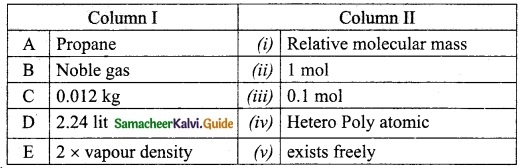
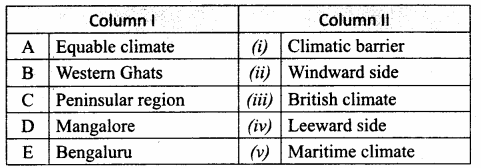
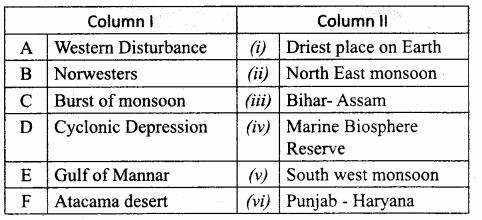
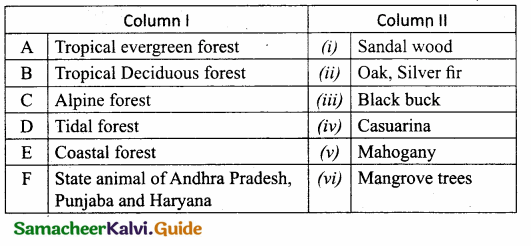
IV. Match the following:
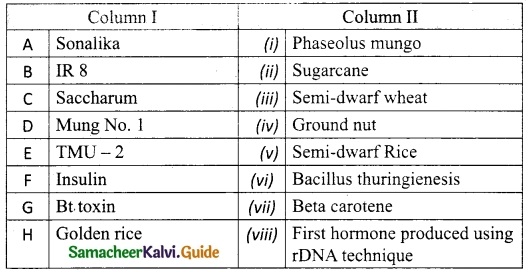
Answer:
A. (iii)
B. (v)
C. (ii)
D. (i)
E. (iv)
F. (viii)
G. (vi)
H. (vii)
![]()
V. Understand the assertion statement, justify the reason given and choose the correct choice:
(a) Assertion is correct and reason is wrong.
(b) Reason is correct and the assertion is wrong.
(c) Both assertion and reason is correct.
(d) Both assertion and reason is wrong.
1. Assertion : Hybrid is superior than either of its parents.
Reason: Hybrid vigour is lost upon inbreeding.
Answer:
(c) Both assertion and reason is correct.
2. Assertion: Colchicine reduces the chromosome number.
Reason: It promotes the movement of sister chromatids to the opposite poles.
Answer:
(d) Both assertion and reason is wrong.
3. Assertion: rDNA is superior over hybridisation techniques.
Reason: Desired genes are inserted without introducing the undesirable genes in target organisms.
Answer:
(a) Assertion is correct and reason is wrong.
VI. Answer in a sentence:
Question 1.
Give the name of the wheat variety having higher dietary fibre and protein.
Answer:
Triticale a hybrid of wheat having dietary fibre and protein.
Question 2.
Semi-dwarf varieties were introduced in rice. This was made possible by the presence of the dwarfing gene in rice. Name this dwarfing gene.
Answer:
The dwarfing gene is Sd.I.
Question 3.
Define genetic engineering.
Answer:
Genetic engineering is the manipulation and transfer of genes from one, organism to another organism to create a new DNA called as recombinant DNA(rDNA).
Question 4.
Name the types of stem cells?
Answer:
Embryonic stem cell and Adult stem cell or somatic stem cell, are the two types of stem cells.
Question 5.
What are transgenic organisms?
Answer:
Plants or animals expressing a modified endogenous gene or a foreign gene is known as transgenic organism.
![]()
Question 6.
State the importance of bio-fertiliser.
Answer:
Increasing the harvest yields, improving soil structure, better water relation, economical, eco – friendly and more efficient farms are due importance of biofertilizer.
VII. Short Answers Questions:
Question 1.
Discuss the method of breeding for disease resistance.
Answer:

Question 2.
Name three improved characteristics of wheat that helped India to achieve high productivity.
Answer:
- High yielding
- Semi – dwarf
- Fertilizer responsive.
These are the three improved characteristics of wheat that helped India to achieve high productivity. Sonalika and Kalyan Sona are the high yielding varieties of wheat.
Question 3.
Name two maize hybrids rich in amino acid lysine.
Answer:
Protina, shakthi are the maize hybrids rich in amino acid lysin.
Question 4.
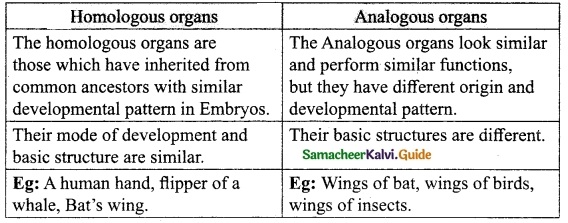
Distinguish between
(a) somatic gene therapy and germ line gene therapy.
Answer:
Somatic gene therapy :
It is the replacement of defective gene in somatic cells.
Germ line gene therapy :
It is replacement of defective gene in germ cell (egg and sperm).
(b) undifferentiated cells and differentiated cells.
Answer:
Undifferentiated cells :
The cells which have not become specialized are called undifferentiated cells.
Eg: Cells in early embryos
Differentiated cells :
The cells which have become specialized for doing certain job.
Eg: Muscle cell, nerve cell.
![]()
Question 5.
State the applications of DNA fingerprinting technique.
Answer:
DNA fingerprinting technique is widely used in forensic applications such as identifying the – culprit. It is also used for paternity testing in case of disputes. It also helps in the study of genetic diversity of population, evolution and speciation.
Question 6.
How are stem cells useful in regenerative process?
Answer:
If cells, tissues and organs in the body get permanently damaged or lost due to genetic condition or disease or injury, it can be cured by regeneration process of stem cell. In stem cell therapy, stem cells are used to replace the damage of lost cells.
Question 7.
Differentiate between outbreeding and inbreeding.
Answer:
Outbreeding Inbreeding
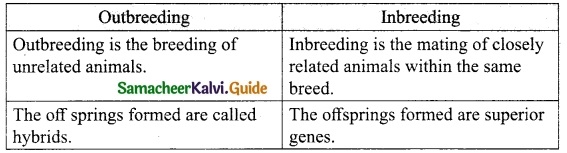
VIII. Long Answers Questions:
Question 1.
What are the effects of hybrid vigour in animals?
Answer:
The superiority of the hybrid, obtained by cross-breeding is called heterosis or hybrid vigour.
Effects of hybrid vigour in animal breeding:
- Increased production of milk by cattle.
- Increased production of an egg by poultry.
- High quality of meat is produced.
- The increased growth rate in domesticated animals.
Question 2.
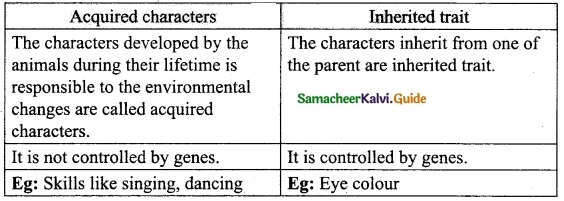
Describe mutation breeding with an example.
Answer:
Mutation is defined as the sudden heritable change in the nucleotide sequence of DNA in an organism. It is a process by which genetic variations are created which in turn brings about changes in the organism. The organism which undergoes mutation is called a mutant.
The factors which induce mutations are known as mutagens or mutagenic agents. Mutagens are of two types namely physical mutagens and chemical mutagens.
(i) Physical mutagens : Radiations like X-rays, a, (3 and y-rays, UV rays, temperature etc. which induce mutations are called physical mutagens
(ii) Chemical mutagens : Chemical substances that induce mutations are called chemical mutagens. Eg: Mustard gas and nitrous acid. The utilisation of induced mutation in crop improvement is called mutation breeding.
Achievements of mutation breeding: Some achievements of mutation breeding are-
(a) Sharbati Sonora wheat produced from Sonora-64 by using gamma rays.
(b) Atomita 2 rice with saline tolerance and pest resistance
(c) Groundnuts with thick shells
![]()
Question 3.
Biofortification may help in removing hidden hunger. How?
Answer:
Biofortification is the scientific process of helping crop plants, enriched with high levels of desirable nutrients like vitamins, proteins and minerals. Micronutrient malnutrition is called hidden hunger, the lack of micronutrients such as vitamin A, zinc and iron in the diet.
Biofortification is effective in removing hidden hunger and improving the nutritional value of food. Scientists breed crops whose edible parts (seed, tuber and roots) have improved nutritional value. Biofortified foods can contribute to body stores of micronutrients throughout the life cycle.
Some example of crop varieties developed as a result of biofortification are:
- Protina, Shakti and Rathna are lysine-rich maize hybrids.
- Atlas 66, a protein-rich wheat variety.
- Iron-rich fortified rice variety.
- Vitamin A enriched carrots, pumpkin and spinach.
Question 4.
With a neat labelled diagram explain the techniques involved in gene cloning.
Answer:
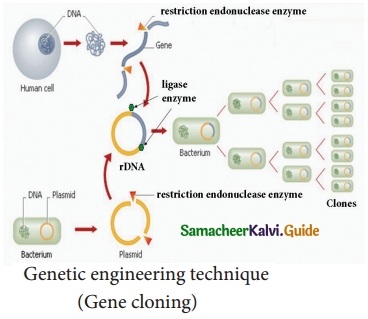
In gene cloning, a gene or a piece of DNA fragment is inserted into a bacterial cell where DNA will be multiplied (copied) as the cell divides. A brief outline of the basic steps involved in gene cloning are:
- Isolation of desired DNA fragment by using restriction enzymes.
- Insertion of the DNA fragment into a suitable vector (Plasmid) to make rDNA.
- Transfer of rDNA into bacterial host cell (Transformation)
- Selection and multiplication of recombinant host cell to get a clone.
- Expression of cloned gene in host cell.
Using this strategy several enzymes, hormones and vaccines can be produced.
Question 5.
Discuss the importance of biotechnology in the field of medicine.
Answer:
Using genetic engineering techniques, medicinally important valuable proteins or polypeptides, which form the potential pharmaceutical products for the treatment of various diseases have been developed on a commercial scale.
Pharmaceutical products developed by rDNA technique:
- Insulin used in the treatment of diabetes.
- Human growth hormone used for treating children with growth deficiencies.
- Blood clotting factors are developed to treat haemophilia.
- Tissue plasminogen activator is used to dissolve blood clots and to prevent heart attack.
- Development of vaccines against various diseases like hepatitis B and rabies.
IX. Higher Order Thinking Skills: (HOTS)
Question 1.
A breeder wishes to incorporate desirable characters into the crop plants. Prepare a list of characters he will incorporate.
Answer:
Tallness and profuse branching are desirable characters for fodder crop.
![]()
Question 2.
Organic farming is better than Green Revolution. Give reasons.
Answer:
Green revolution is the process of increasing food production through high yielding crop varieties and modem agricultural techniques. Organic farming is a method of crop production in an ecofriendly and pollution free environment to release nutrients to crop. As organic farming is an ecofriendly and pollution free, it is better than green revolution.
Question 3.
Polyploids are characterised by gigantism. Justify your answer.
Answer:
An organism having more than 2 sets of chromosomes is called polyploid. It can be induced by physical events such as heat or cold treatment, X – rays and chemical agents like colchicine. Polyploid cell or organism has three or more times the haploid chromosomal number.
Polyploid has a major role in the evolution of both wild and cultivated plants. Polyploid has a key role in plant breeding. There are increase and increased woodiness which has been observed in some insular plants. So polyploids are characterized by gigantism.
Question 4.
‘P’ is a gene required for the synthesis of vitamin A. It is integrated with genome of ‘Q’ to produce genetically modified plant ‘R’
(i) What is P, Q and R?
(ii) State the importance of ‘R’ in India.
Answer:
(i) P is Beta carotene gene
Q Bio fortification
R Golden rice
(ii) Golden rice is genetically modified rice can produce beta carotene,that prevent vitamin A deficiency.
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Breeding and Biotechnology Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Modem biotechnology consist:
(a) Genetic engineering
(b) Tissue culture
(c) Gene cloning
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 2.
The disease-resistant cauliflower variety is ______.
(a) Himgiri
(b) Pusa Shubhra
(c) Pusa Komal
(d) IR – 8.
Answer:
(b) Pusa Shubhra
Question 3.
Transgenic animals has:
(a) Foreign DNA in all its cell
(b) Foreign RNA in all its cells
(c) Foreign DNA in some of the cells
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(a) Foreign DNA in all its cell
![]()
Question 4.
The gamete cells, which have only one set of chromosomes is called ______.
(a) diploid
(b) polyploid
(c) triploid
(d) haploid.
Answer:
(d) haploid.
Question 5.
A kind of Biotechnology involving manipulation of DNA is:
(a) DNA replication
(b) Denaturation
(c) Genetic Engineering
(d) Renaturation
Answer:
(c) Genetic Engineering
Question 6.
A foreign DNA and plasmid cut by the same restriction endonuclease can be joined to form a recombinant plasmid using:
(a) ECORI
(b) Taq polymerase
(c) Polymerase III
(d) Ligase
Answer:
(d) Ligase
Question 7.
Consumption of which one of the following foods can prevent the kind of blindness associated with Vitamin ‘A’ deficiency?
(a) Golden Rice
(b) Bt-Brinjal
(c) Flaver savr tomato
(d) Canolla
Answer:
(a) Golden Rice
Question 8.
Restriction endonucleses are enzymes which:
(a) Remove nucleotides from the ends of the DNA molecule.
(b) Make cuts at specific positions within the DNA molecule.
(c) Recognise a specific nucleotide sequence for binding of DNA ligase.
(d) Restrict the action of the enzyme DNA polymerase.
Answer:
(b) Make cuts at specific positions within the DNA molecule.
Question 9.
……….. is the Father of Indian Green Revolution.
(a) Nammalvar
(b) Dr Borloug
(c) Dr M.S.Swaminathan
(d) Dr Sultan Ismail
Answer:
(c) Dr M.S.Swaminathan
Question 10.
New lined of sheep developed in Punjab is:
(a) Sahiwal
(b) Hisardale
(c) Triticale
(d) Sharbati sonara
Answer:
(b) Hisardale
II. Fill in the blanks:
1. ………. is a cross between Male Donkey and Female Horse.
2. ……….. is a DNA molecule found in the cytoplasm of bacterial cell.
3. ………. was the first cloned female sheep.
4. Human insulin can be synthesized by using ……….
5. In genetic engineering, a DNA segment is transfered to the host cell through ………..
6. Genetically identical individuals are ………..
7. Ligase is used for joining two ………..
8. Enzyme that cleaves nucleic acids within the polynucleotide chain is known as …………
9. The bacterium used as biopesticide is …………
10. A strain of golden rice contains high content of …………..
Answer:
1. Mule
2. Plasmid
3. Dolly
4. rDNA technology
5. Vector
6. Clones
7. DNA fragments
8. Endonuclease
9. Bacillus thuringiensis.
10. Vitamin A
![]()
III. State whether true or false. If false, write the correct statement:
- The structure used to transfer the piece of DNA attached to it into a host ceil is vector.
- Restriction endonucleases are used to join the DNA fragments having sticky ends.
- The progeny of a single individual obtained by self breeding is clonal selection.
- The aim of crop improvement is to develop improved crop varieties.
- International Rice Research institute (IRRI) is in Indonesia.
Answer:
- True
- False – Restriction endonucleases are used to join the DNA fragments having ligase ends.
- False – The progeny of a single individual obtained by self breeding is pureline selection.
- True
- False – International Rice Research institute (IRRI) is in Philippines.
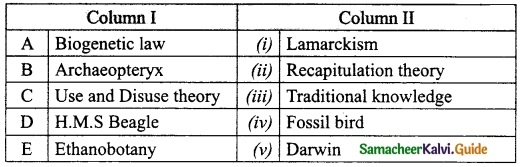
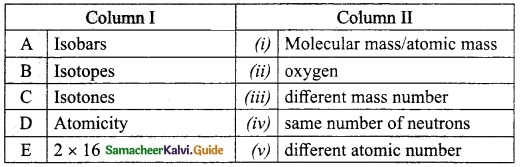
IV. M.atch the following:
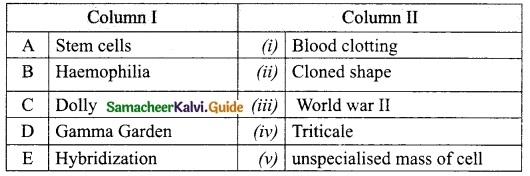
Answer:
A. (v)
B. (i)
C. (ii)
D. (iii)
E. (iv)
V. Understand the assertion statement, justify the reason given and choose the correct choice:
(a) Assertion is correct and reason is wrong
(b) Reason is correct and the assertion is wrong
(c) Both assertion and reason is correct
(d) Both assertion and reason is wrong
1. Assertion: Bacillus thuringiensis is toxic to many insects.
Reason: It inhibits ion transport in the mid gut.
Answer:
(a) Assertion is correct and reason is wrong
2. Assertion.: Recombinant DNA technology has become successful due to restriction endonucleases present in Eukaryotic cells.
Reason: Restriction endonucleases cut the DNA molecule to form blunt ends.
Answer:
(d) Both assertion and reason is wrong
VI. Answer in a word or sentence:
Question 1.
Name two neurodegenerative disorders.
Answer:
Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer disease.
Question 2.
Name two chemical mutagens.
Answer:
Mustard gas and nitrous acid.
Question 3.
What is plant breeding?
Answer:
Plant breeding is the art of developing economically important plants with superior quality.
![]()
Question 4.
What is the aim of Animal husbandry?
Answer:
The aim of Animal husbandry is to improve the genotypes of animals to make them more useful to the welfare of mankind.
Question 5.
What are exotic species?
Answer:
The process of introducing high yield varieties of plants from one place to another are called as exotic species.
Question 6.
List the two main aspects of hybridization.
Answer:
Combining the characters of two plants in one plant and to utilize hybrid vigour are the two main aspects of hybridization.
Question 7.
What is heterosis?
Answer:
The superiority of the hybrid obtained by cross breeding is called heterosis.
Question 8.
What are plasmids?
Answer:
Circular, self-replicating, extra chromosomal DNA in bacteria.
Question 9.
What is transgene?
Answer:
A gene which is transferred from one organism into another organism by genetic engineering.
![]()
Question 10.
Name the Research institute found by Nammalvar.
Answer:
Nammalvar ecological foundation for farm research and global food security trust.
VII. Short Answers Questions:
Question 1.
List out the pest-resistant crop varieties.
Answer:
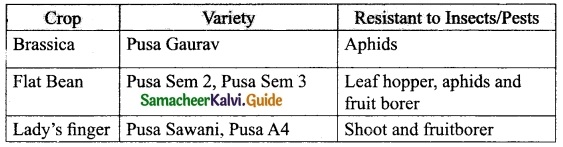
Question 2.
What does the nutritional quality of crop depend on?
Answer:
The nutritional quality of crops depends on the quality and quantity of nutrients.
The nutritional quality may be improved with respect to its:
- Protein content and quality of proteins.
- Oil content.
- Mineral content.
Question 3.
Write a note on Gamma Garden.
Answer:
Gamma garden or Atomic garden is a concept popularised after World War -II for the peaceful use of atomic energy for crop improvement. This is a type of induced mutation breeding where radioactive sources particularly gamma rays from Cobalt-60 or Caesium-137 are used to induce desirable mutations in crop plants.
![]()
Question 4.
An organism having more than two sets of chromosomes is called polyploid. It can be induced by physical agents such as heat or cold treatment, X-rays and chemical agents like colchicine.
Answer:
Achievements of polyploidy breeding:
- Seedless watermelons (3n) and bananas (3n).
- TV – 29 (triploid variety of tea) with larger shoots and drought tolerance.
- Triticale (6n) is a hybrid of wheat and rye: It has higher dietary fibre and protein.
- Rapuano brassica is an allotetraploid by colchicine treatment.
Question 5.
Mention the two important properties of stem cells.
Answer:
- Its ability to divide and give rise to more stem cells by self-renewal.
- Its ability to give rise to specialised cells with specific functions by the process of differentiation.
Question 6.
Illustrate hybridization with example.
Answer:
Triticale is the first man made cereal hybrid. It is obtained by crossing wheat Triticum durum (2n = 28) and rye (secale cereal, 2n = 14)
Parent Tritium durum × Secale cereal
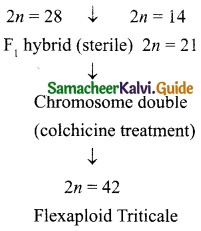
VIII. Long Answer Questions:
Question 1.
Explain the following methods of plant breeding for crop improvement.
Answer:
(a) Introduction of new varieties in plants:
The process of introducing high yielding varieties of plants from one place to another is called exotic species. These imported plants may carry pathogens and pests. It should be thoroughly checked before introducing to the fields, eg. Phaseolus mungo was introduced from China.
(b) Selection:
Selection is a type of plant breeding, in which individual plants or group of plants are sorted out from a mixed population based on the morphological characters.
Methods of selection:
(i) Mass selection:
Seeds of plants with desired characters are collected from a mixed population. The collected seeds are allowed to raise the second generation. This process is carried out for seven or eight generations. In the end, they are distributed to the farmers for cultivation, eg. TMV – 2 and AK – 10 (groundnut varieties).
(ii) Pure line selection:
Pureline is the “progeny of a single individual obtained by self breeding”. This is also called as individual plant selection. In pure line selection, large numbers of plants are selected from a self – pollinated crop and harvested individually. Progeny is similar, both genotypically and phenotypically.
(iii) Clonal selection:
A group of plants produced from a single plant through vegetative or asexual reproduction are called clones. All the plants of a clone are similar both in genotype and phenotype. Selection of desirable clones from the mixed population of the vegetatively propagated crop is called clonal selection.
Question 2.
In what way trans organism are better?
Answer:
Plants or animals expressing a modified endogenous gene or a foreign gene are also known as transgenic organisms.
The transgenic plants are much stable, with improved nutritional quality, resistant to diseases and tolerant to various environment conditions. Similarly transgenic animals are used to produce proteins of medicinal importance at low cost and improve livestock quality.
![]()
Question 3.
Describe the tools of recombinant DNA technology.
Answer:
Techniques of Genetic Engineering – Basic Requirements:
Important discoveries that led to the stepping stone of rDNA technology were
- Presence ofplasmid in bacteria that can undergo replication independently along with chromosomal DNA.
- Restriction enzymes cuts or break DNA at specific sites and are also called as molecular scissors.
- DNA ligases are the enzymes which help in ligating (joining) the broken DNA fragments.
Question 4.
Give the Schematic representation of Mass selection.
Answer:
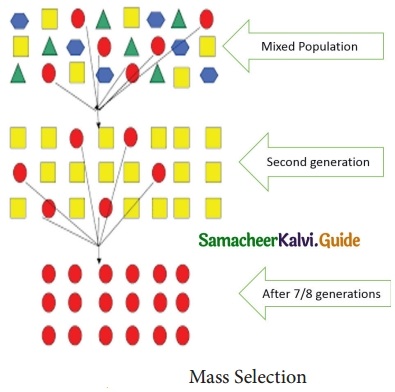
Mass selection : Seeds of best plants showing desired characters are collected from a mixed population. The collected seeds are allowed to raise the second generation. This process is carried out for seven or eight generations. At the end, they will be multiplied and distributed to the farmers for cultivation. Some common examples for mass selection are groundnut varieties like TMV-2 and AK-10. Its schematic representation is given below.
IX. Higher Order Thinking Skills: (HOTS)
Question 1.
Although ‘green revolution’ increases the food production, it is not enough to feed growing population. This probelm is overcomed by ‘X’ crops.
(a) What is ‘X’?
(b) Explain it with examples.
Answer:
(a) ‘X’ is Genetically modified crops.
(b) Genetic modification refers to the manipulation of genes in the organism using rDNA techniques to produce desired character.
![]()
Question 2.
What is Gamma garden?
Answer:
In gamma garden or atomic garden, a type of induced mutation breeding, where radioactive sources, particularly gamma rays from Cobalt – 60 or Caesium – 137 are used to induce desirable mutations in crop plants.