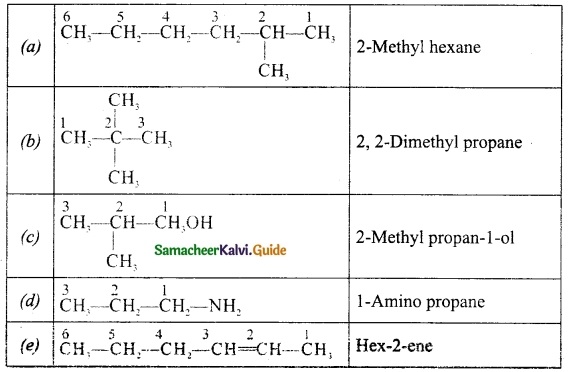
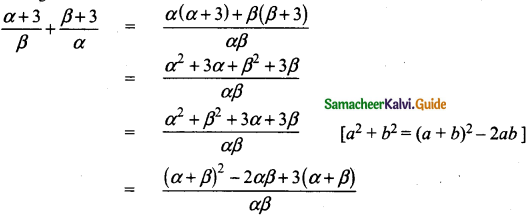
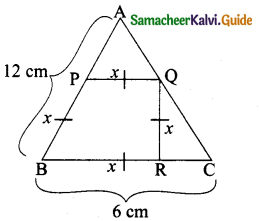
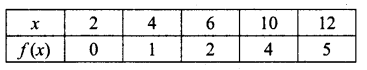
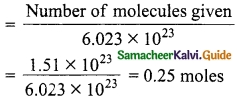
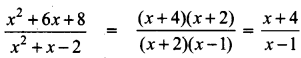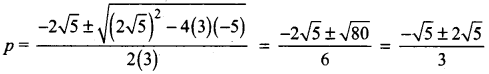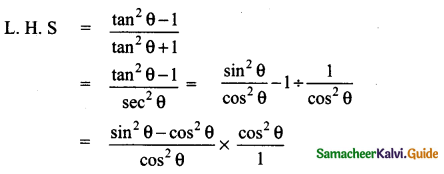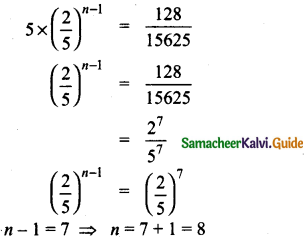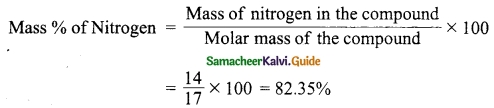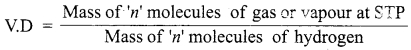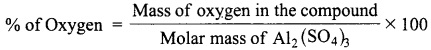Students can download 10th Social Science Geography Chapter 3 Components of Agriculture Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Solutions Geography Chapter 3 Components of Agriculture
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Components of Agriculture Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The soil which is rich in iron oxides is
(a) Alluvial
(b) Black
(c) Red
(d) Alkaline
Answer:
(c) Red
Question 2.
Which of the following organization has divided the Indian soils into 8 major groups?
(a) Indian Council of Agricultural Research
(b) Indian Meteorological Department
(c) Soil Survey of India
(d) Indian Institute of Soil Science
Answer:
(a) Indian Council of Agricultural Research
![]()
Question 3.
The soils formed by the rivers are:
(a) Red soils
(b) Black soils
(c) Desert soils
(d) Alluvial soils india.
Answer:
(d) Alluvial soils india.
Question 4.
……….. dam is the highest gravity in India.
(a) Hirakud dam
(b) Bhakra Nangal dam
(c) Mettur dam
(d) Nagaijuna Sagar dam
Answer:
(b) Bhakra Nangal dam
Question 5.
……………… is a cash crop.
(a) Cotton
(b) Wheat
(c) Rice
(d) Maize
Answer:
(a) Cotton
![]()
Question 6.
Black soils are also called as ………..
(a) Arid soils
(b) Saline soils
(c) Regur soils
(d) Mountain soils
Answer:
(c) Regur soils
Question 7.
The longest dam in the world is:
(a) Mettur dam
(b) Kosi dam
(c) Hirakud dam
(d) Bhakra Nangal dam
Answer:
(c) Hirakud dam
Question 8.
The leading producer of rice in India is ……….
(a) Punjab
(b) Maharashtra
(c) Uttar Pradesh
(d) West Bengal
Answer:
(c) Uttar Pradesh
Question 9.
Which crop is called as “Golden Fibre” in India?
(a) Cotton
(b) Wheat
(c) Jute
(d) Tobacco
Answer:
(c) Jute
Question 10.
The state which leads in the production of coffee is ……….
(a) West Bengal
(b) Karnataka
(c) Odisha
(d) Punjab
Answer:
(b) Karnataka
![]()
II. Consider the given statements and choose the right option given below
Question 1.
Assertion (A): Horticulture involves the cultivation of fruits, vegetables, and flowers.
Reason (R): India ranks first in the world in the production of mango, banana, and citrus fruits.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R)are true: (R) does not explain (A)
(c) (A) is correct (R) is false
(d) (A) is false (R) is true
Answer:
(c) (A) is correct (R) is false
Question 2.
Assertion(A): Alluvial soil is formed by the deposition of eroded and decayed materials brought by the rivers.
Reason(R): Paddy and wheat are grown well in the soil.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R)are true and (R) does not explain (A)
(c) (A) is correct (R) is false
(d) (A) is false (R) is true
Answer:
(b) Both (A) and (R)are true and (R) does not explain (A)
III. Pick the odd one out
Question 1.
(a) Wheat
(b) Rice
(c) Millets
(d) Coffee
Answer:
(d) Coffee
Question 2.
(a) Khadar
(b) Bhangar
(c) Alluvial soil
(d) Black soil
Answer:
(d) Black soil
Question 3.
(a) Inundation canals
(b) Perennial canals
(c) Tanks
(d) Canals
Answer:
(c) Tanks
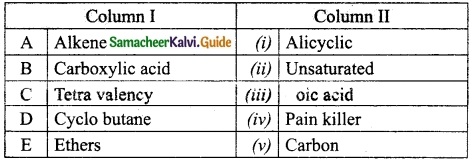
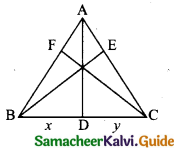
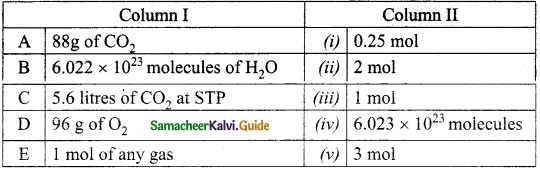
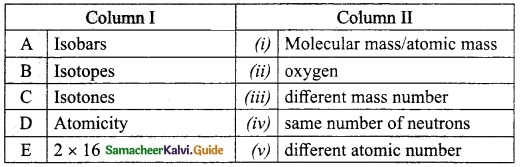
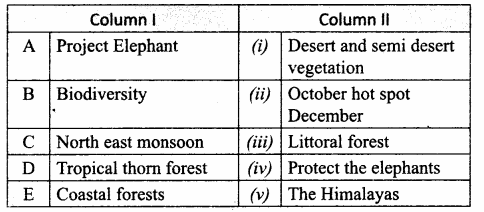
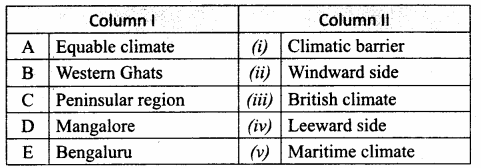
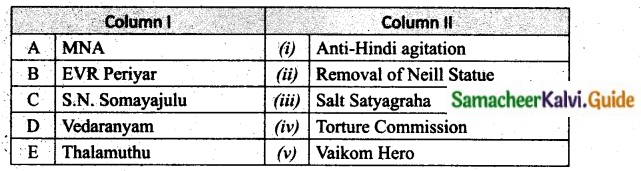
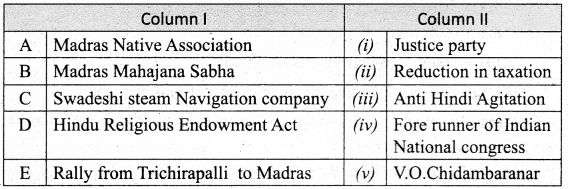
IV. Match the following
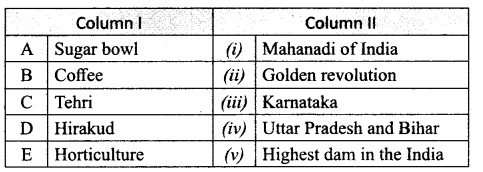
Answer:
A. (iv)
B. (iii)
C. (v)
D. (i)
E. (ii)
![]()
V. Answer in brief
Question 1.
Define soil.
Answer:
Soil is the uppermost layer of the land surface, usually composed of minerals, organic matter, living organisms, air and water. Its formation is mainly related to the parent rock material, surface relief, climate and natural vegetation.
Question 2.
Name the types of soil found in India.
Answer:
There are 8 major groups of soil found in India classified by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research. They are
- Alluvial soil
- Black soil
- Red soil
- Forest and Mountain soil
- Arid and Desert soil
- Laterite soil
- Saline and Alkaline soil
- Peaty and Marshy soil
Question 3.
State any two characteristics of black cotton soil.
Answer:
- This soil is rich in calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash, lime and iron but deficient in phosphorous. It is clayey and impermeable which has great capacity to retain moisture for a long time.
- It becomes sticky when wet but develops cracks during dry summer season. The soil is suited for dry farming due to its high moisture retentivity.
Question 4.
What is Multipurpose project?
Answer:
- Multipurpose projects are the River valley projects.
- Dams are constructed across rivers aims to serve many purposes such as irrigation, power generation, water supply, controlling floods, navigation, development of fisheries etc.
Question 5.
Define Agriculture.
Answer:
Agriculture is the process of producing food for people, fodder for cattle, fiber and many other desired products by the cultivation of certain plants and the raising of domesticated animals
Question 6.
State the types of agriculture practices in India?
Answer:
- Owing to physical environment and culture the following cultivation systems prevail in India.
- Subsistence farming
- Intensive farming
- Dry farming
- Mixed farming agriculture
- Terrace cultivation
![]()
Question 7.
Name the seasons of agriculture in India.
Answer:
- Kharif Season
- Rabi Season
- Zaid Season
Question 8.
Mention the plantation crops of India.
Answer:
- Plantation crops are mainly cultivated for the purpose of exports.
- These crops are cultivated in large estates on hilly slopes.
- Tea, coffee, rubber and spices are the main plantation crops of India.
Question 9.
What do you mean by livestock?
Answer:
Livestocks is defined as farm animals who are raised to generate a profile. It is an integral component of the farming system in India.
Question 10.
Write a brief note on the categories of fisheries in India?
Answer:
In India fisheries are categorised into two.They are marine or sea fisheries and inland or fresh water fisheries.
Marine or Sea fisheries:
- It includes coastal off-shore and deep sea fishing mainly on continental shelf upto a depth of 200 mts.
- Kerala leads in Marine fish production.
Inland or Fresh water fisheries:
- Rivers, lakes, canals, reservoirs, ponds tanks etc are the sources of fresh water fisheries,
- Andhra Pradesh is leading in the fresh water fisheries.
- About 50% of the country’s total fish production comes from inland fisheries.
![]()
VI. Give reasons
Question 1.
Agriculture is the backbone of India.
Answer:
Agriculture provide food for the entire population. It supplies raw materials to the agro-based industries. It contributes to export trade. So, agriculture is the backbone of India.
Question 2.
Rain water harvesting is necessary.
Answer:
India experiences Tropical monsoon climate. Rainfall in India is seasonal, irregular and uneven and highly eractic. Hence it is necessary’ to save rain water when it is available and use in times of need. In order to prevent surface . run off Rainwater harvesting is needed.
Question 3.
Small farms are predominant in India.
Answer:
The predominant type of Indian agriculture is subsistence farming. In this agriculture land holding is small and half of the production is used for family consumption and the rest is sold in the nearby markets. The farmers concentrate on stage food crops like rice and wheat. As the farmers are poor, they can’t apply the modem inputs which cost more.
VII. Distinguish between the following
Question 1.
Rabi and Kharif crop seasons.
Answer:
Rabi crop season:
- Rabi crop season is from October – March.
- Seeds are sown in winter and harvested before summer.
- Major crops of this season are mainly Wheat, Mustard, Maize etc.
Kharif crop season:
- Kharif crop season is from June – September.
- Seeds are sown after the summer monsoon and harvested before winter.
- Major crops are Rice, Cotton, Groundnut, Turmeric etc.
Question 2.
Inundation canal and perennial canal.
Answer:
Inundation canal:
- Undependable source of irrigation.
- Operational only during flood in rivers and not have weir system to regulate water.
Perennial canal:
- Dependable source of irrigation.
- Have weir system through barrage to regulate water from perennial rivers or dams.
Question 3.
Marine fishing and Inland fishing.
Answer:
Marine fishing:
- Marine fishing includes coastal, off¬shore and deep sea fishing mainly on the continental shelf upto a depth of 200m.
- Kerala is the leading producer in marine fishing.
Inland fishing:
- Inland fishing is done in rivers, lakes, canals, ponds, tanks, reservoirs etc.
- Andhra Pradesh, West Bengal, Gujarat, Kerala and TamilNadu are the leading states.
![]()
Question 4.
Alluvial soils and Black soils.
Answer:
Alluvial soil:
- Formed by the sediments deposited by the rivers and streams.
- Silt clay, sandy and loamy in nature.
- Found in the river valleys and plains.
- Rice, wheat, sugarcane grow well in this soil.
Black soil:
- Formed by the disintegration of basalt rocks.
- Sticky when wet develops cracks when dry.
- Found in plateau region especially in Deccan trap.
- Cotton, sugarcane and tobacco grow well in this soil.
![]()
VIII. Answer in a paragraph
Question 1.
State the types of soil in India and explain the characteristics and distribution of soil.
Answer:
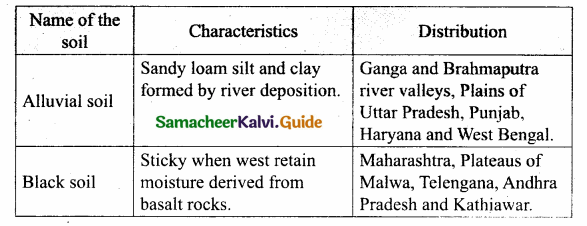
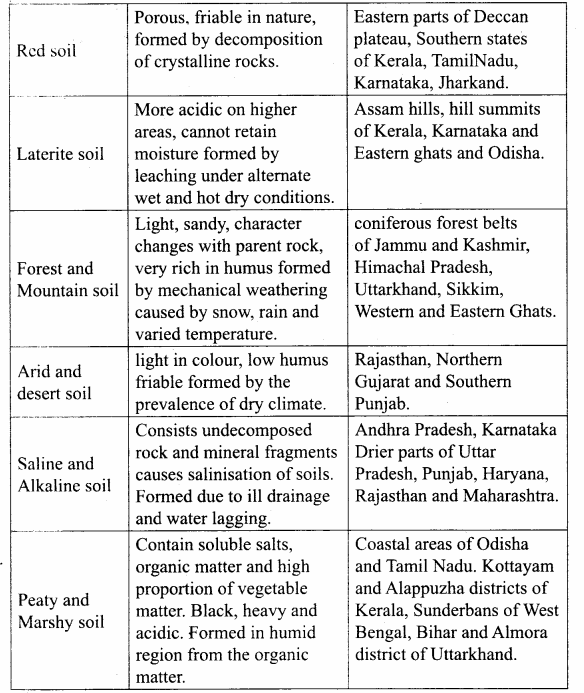
Question 2.
Write about any two multipurpose projects of India.
Answer:
A comprehensive river valley project which serves a number of purposes simultaneously is called a “Multi purposes project”.
1. The Bhakra Nangal Project: India’s biggest multipurpose river valley project is ‘Bhakra Nangal Project’. It has been built at a strategic point where two hills on either side of the Sutlej are very close to each other. It is the highest gravity dam in the world. Its length is 226 metres from the river bed. The canals taken out are 1100 kilometres long. The ‘Nangal Power Plant’ on the Sutlej produces electricity, and serves the states of Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and New Delhi. The distributaries are 8400 km in length. It irrigates an area of 1.4 million hectares.
2. Indira Gandhi Project: This project is an ambitious scheme to bring new areas under irrigation so that more areas could be cultivated. The waters of the River Beas and the Ravi are diverted to the River Sutlej. The ‘Pong’ Dam on the River Beas has been constructed to divert the Beas water into the Sutlej in a regulated manner. So that ‘Rajasthan canal’, the longest irrigation canal in the world can irrigate Gandhi Nagar, Bikaner and Jaisalmer districts of North West Rajasthan, (i.e) a part of Thar desert. The main canal now called ‘Indira Gandhi Canal’ is 468 km long runs entirely in Rajasthan, Western of Sutlej, Beas and Ravi are now being fully utilised for irrigating thirsty lands of South Western parts of our country.
![]()
Question 3.
Bring out the characteristics of intensive and Plantation farming.
Answer:
Characteristics of Intensive farming:
- Farming is done with intensification and mechanisation system to maximize yields from available land.
- In this farming heavy use of pesticides and chemical fertilizers have been applied.
- It has also been applied to the raising of live stock being held indoor as factory farms.
- Plantation fanning.
- Single crop raised on a large area testates).
- Crops are grown mainly for export purpose,
- The plantations are mostly owned by companies.
Question 4.
Examine the geographical conditions favourable for the cultivation of rice and wheat.
Answer:
Rice:
Rice is an indigenous crop. India is the second-largest producer of rice in the world. It is a tropical crop which is grown well in alluvial plains and river deltas. It requires a mean monthly temperature of 24°C and an average rainfall of 150 cm and deep fertile alluvial soil for its growth. It also needs an abundant supply of cheap labour. In areas of less rainfall particularly in Punjab and Haryana, it is grown with the help of irrigation.
Rice in India is sown in three ways:
- Broadcasting,
- Ploughing or drilling, and
- Transplanting.
Due to increased use of High Yielding Variety (HYV) seeds (CR Dhan 205, AR Dhan 306, CRR 451 etc.), many of the indigenous varieties were disappeared. In 2016, the first 10 leading rice-producing states are West Bengal (First in India) Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Assam, and Haryana.
Wheat:
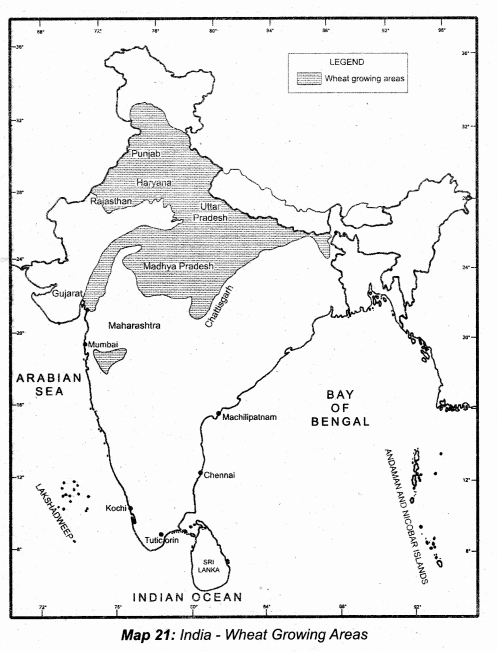
Wheat is a temperate crop. Its cultivation is mainly confined to the northwestern part of India. India produces both winter wheat and spring wheat. It is the second most important food crop of the country, after rice.
It requires 10-15°C at the time of sowing and 20-25°C at the time of ripening of grains. Over 85% of India’s wheat production comes from 5 states namely Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh. Apart from these regions, the black soil tract of the Deccan covering parts of Maharashtra and Gujarat also contribute a major wheat production.
IX. HOTS Questions
Question 1.
Can you imagine a world without agriculture?
Answer:
Agriculture is the art and science of cultivating the soil, growing crops and raising livestock. It includes the preparation of plant and animal products for people to use and their distribution to markets.
Agriculture provides most of the world’s food and fabrics. Cotton, wool and leather are all agricultural products. It also provides wood for construction and paper products.
A world without agriculture would be very different compared to the world we live in today. It is easy for us as humans to take for granted things when we don’t really know how they are grown or produced. Without agriculture, we may not get food and clothing. Without timber, we may not be able to build houses and furniture. We may also be deprived of some everyday-products like soap, paper and ethanol, which are made up of some sort of agricultural by-product. Modern medicine also depends on agriculture. Without agriculture, we wouldn’t be here. We must always be thankful for this industry and for those involved in the various activities related to it.
Question 2.
Can you give solutions for the prevailing water disputes in South India (construction of dams / raising of dams / cleaning of tanks}?
Answer:
- Construction of check dams: In order to prevent surface run off water • during heavy rains. Check dams has to be constructed to regulate the flow of water.
- Raising of dams: Improves the storage capacity, Strengthening the dams is a must.
- Cleaning of tanks: Preventing encroachment by strict legal action, desilting the tanks and deepening it in the local areas will provide water supply to the locality, as well as to maintain the areas of ground water level cleaning of tanks is a must
![]()
X. Map exercise
![]()
Question 1.
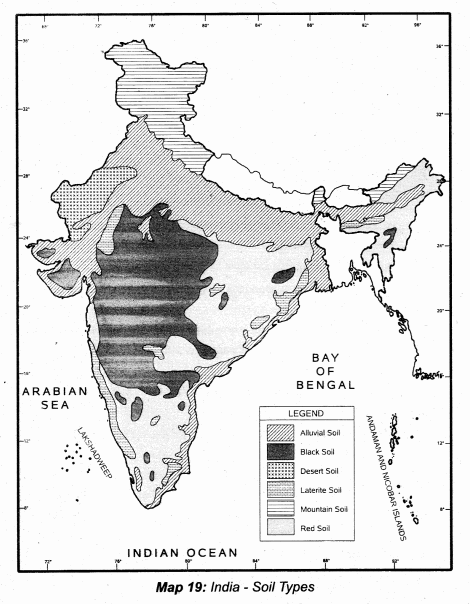
Demarcate the major tracts of alluvial soils.
Answer:

Question 2.
Delineate the main regions of black soil.
Answer:

Question 3.
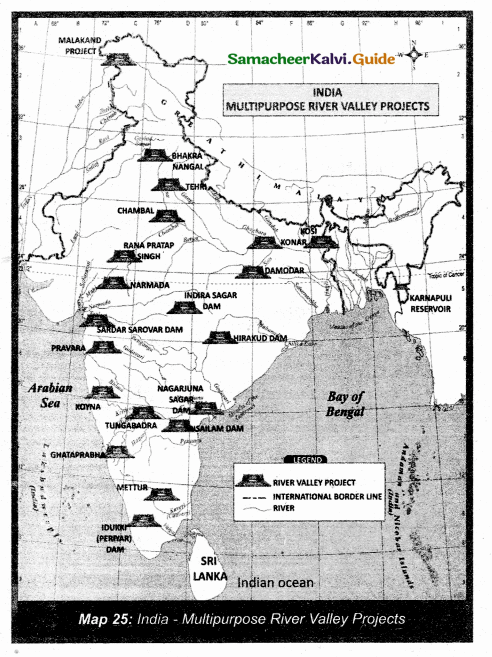
Locate the Hirakud dam, Mettur dam and Damodar dam.
Answer:

![]()
Question 4.
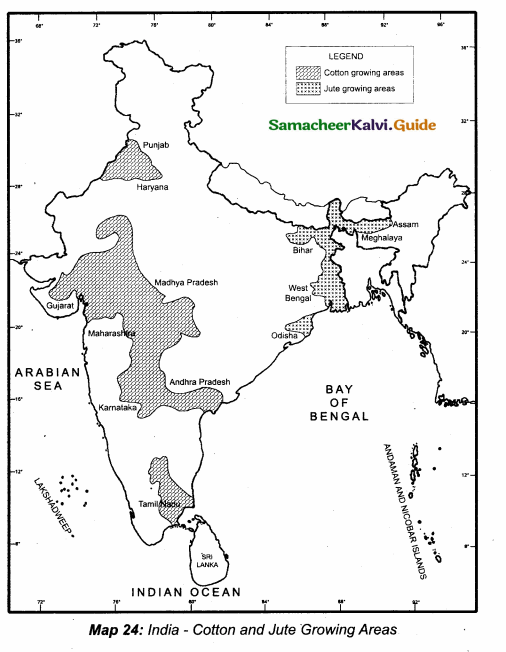
Shade the regions of jute cultivation.
Answer:

Question 5.
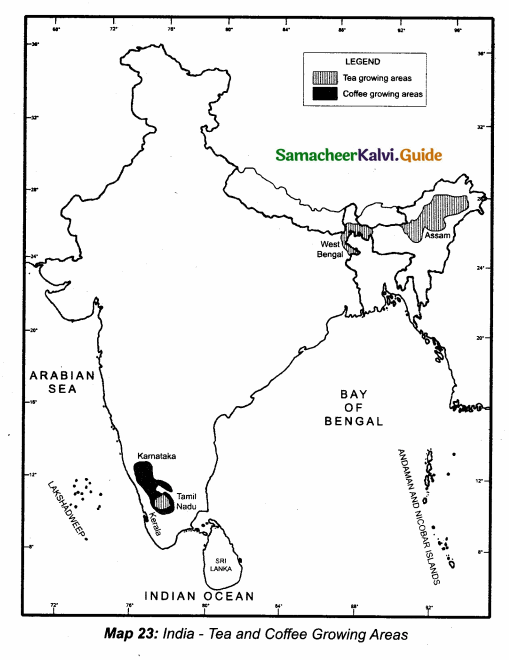
Mark any three tea and coffee growing areas.
Answer:

Question 6.
Demarcate the regions of desert soil.
Answer:

Question 7.
Locate the fishing hubs: Tuticorin, Chennai,Cochin, Mumbai, Machiiipatnam
Answer:

Question 8.
Demarcate: Cauvery delta, Godavari delta.
Answer:

![]()
TB. PNo: 115
Activity 1:
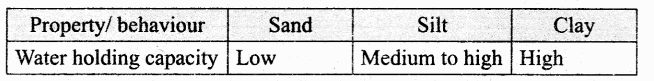
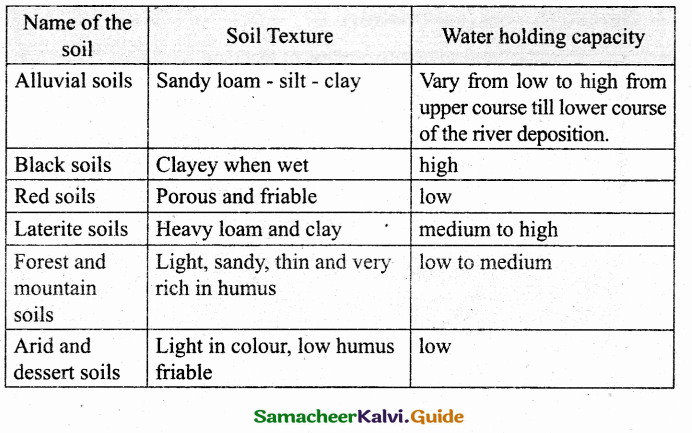
Question 1.
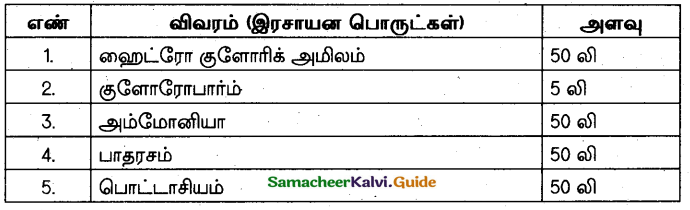
Soil Texture (sand, silt, clay) influence on some properties of soils including water holding capacity. Find out water holding capacity of soils which given above based on following table.
Answer:

TB. PNo: 131
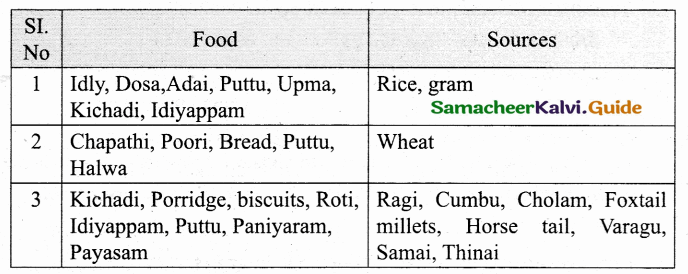
Activity 2:
Question 1.
Complete the following table by your day to day life experience.
Answer:
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Components of Agriculture Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
……………… soil is formed by the process of leaching.
(a) Alluvial
(b) Black
(c) Laterite
(d) Arid
Answer:
(c) Laterite
Question 2.
Cotton is a ………
(a) food crop
(b) cash crop
(c) dry crop
Answer:
(b) cash crop
Question 3.
……………… is one of the method of soil conservation.
(a) Deforestation
(b) Irrigation
(c) Water logging
(d) Afforestation
Answer:
(d) Afforestation
Question 4.
The “rice bowl of Tamil nadu” is ………..
(a) Madurai
(b) Chennai
(c) Thanjavur
Answer:
(c) Thanjavur
Question 5
……………… are useful for the diversion of flood water from the rivers during rainy season.
(a) Perennial canals
(b) Inundation canals
(c) Open wells
(d) Tube wells
Answer:
(b) Inundation canals
Question 6
The type of fanning which is practised in Punjab and Haryana is ………
(a) subsistence farming
(b) commercial farming
(c) wet farming
Answer:
(b) commercial farming
Question 7.
……………… project is constructed on the river Kaveri in TamilNadu.
(a) Tehri Dam
(b) Kosi Dam
(c) Mettur Dam
(d) Horakud Dam
Answer:
(c) Mettur Dam
Question 8.
In the regions with abundant rainfall ……. is grown.
(a) millet
(b) wheat
(c) rice
Answer:
(c) rice
Question 9.
The traditional farming method that results in low productivity is:
(a) mixed farming
(b) shifting agriculture
(c) intensive farming
(d) subsistence farming
Answer:
(d) subsistence farming
Question 10.
One of the important zaid crops is ………….
(a) rice
(b) wheat
(c) watermelon
Answer:
(c) watermelon
Question 11.
First Live-stock census was conducted in India in the year:
(a) 1819
(b) 1919
(c) 1618
(d) 1981
Answer:
(b) 1919
Question 12.
The National Research Center on Plant Biotechnology was established in ………
(a) 1985
(b) 1980
(c) 1990
Answer:
(a) 1985
![]()
II. Consider the given statements and choose the right option given below
Question 1.
Assertion (A): Indian agriculture is largely dominated by food crops. Reason (R): India has a large population.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R)are true: (R) does not explain (A)
(c) (A) is correct (R) is false
(d) (A) is false (R) is true
Answer:
(c) (A) is correct (R) is false
Question 2.
Assertion (A): Forest and mountain soils differ from region to region. Reason (R): Due to the absence of vegetative cover.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R)are true: (R) does not explain (A)
(c) (A) is correct (R) is false
(d) (A) is false (R) is true
Answer:
(c) (A) is correct (R) is false
Hint: Reason is due to mechanical weathering caused by snow, rain, temperature variation depending on climate.
Question 3.
Assertion (A): Terrace farming method is practiced on hill and mountain slopes. Reason (R): The availability of land is limited and it checks soil erosion.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R)are true: (R) does not explain (A)
(c) (A) is correct (R) is false
(d) (A) is false (R) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
Question 4.
Assertion (A): Pulses are usually rotated with other crops.
Reason (R): They are used as human food and feeding cattle.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) does not explain (A)
(c) (A) is correct (R) is false
(d) (A) is false (R) is true
Answer:
(c) (A) is correct (R) is false
Hint: They are mostly leguminous in nature and fixes atmospheric nitrogen helps soil to regain its fertility.
![]()
III. Pick the odd one out
- (a) Tea, (b) Sugarcane, (c) Cotton, (d) Ragi
- (a) Khandsari, (b) Herrings, (c) Mackerels, (d) Eels
- (a) Damodhar, (b) Mahanadi, (c) Kaveri, (d) Raingun
- (a) Water wheel, (b) Sprinkler, (c) Open well, (d) poly house
- (a) Blue Revolution, (b) soil erosion, (c) Green Revolution, (d) Soil erosion
- (a) Fishing, (b) Kharif, (c) Rabi, (d) Zaid
Answer:
- (d) Ragi
- (a) Khandsari
- (d) Raingun
- (c) Open well
- (d) Soil erosion
- (a) Fishing
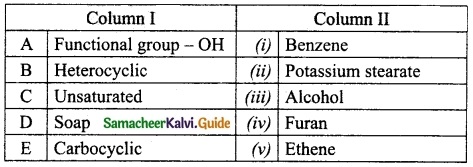
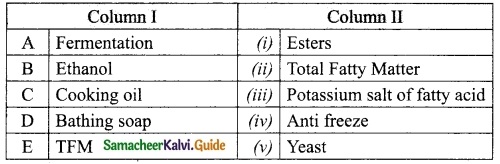
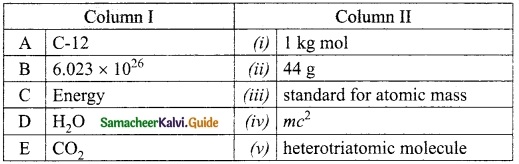
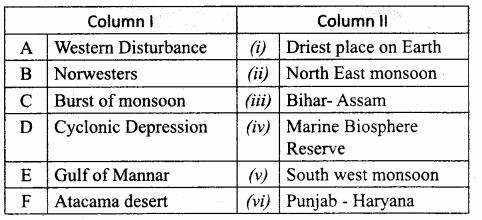
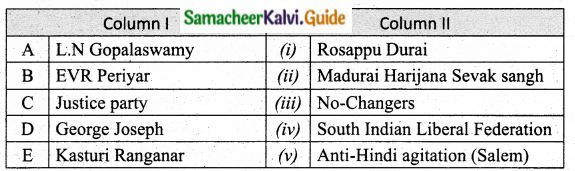
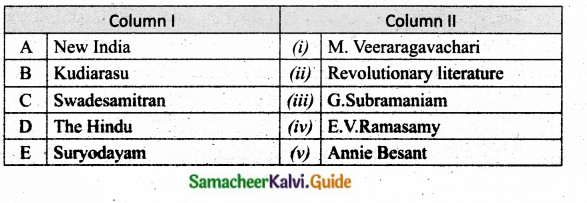
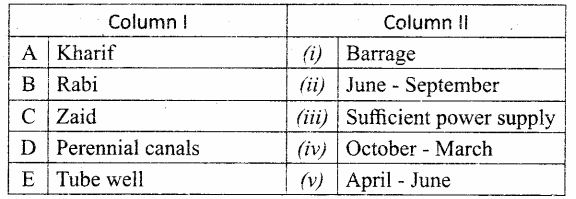
IV. Match the following
Question 1.
Match the Column I with Column II.
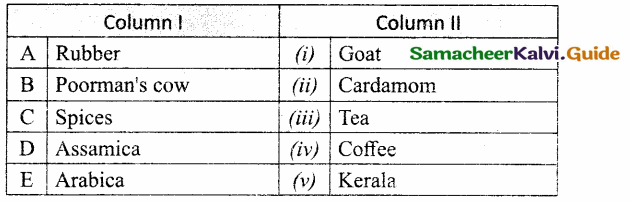
Answer:
A. (v)
B. (i)
C. (ii)
D. (iii)
E. (iv)
![]()
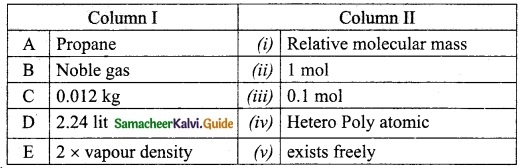
Question 2.
Match the Column I with Column II.
Answer:
A. (ii)
B. (iv)
C. (v)
D. (i)
E. (iii)
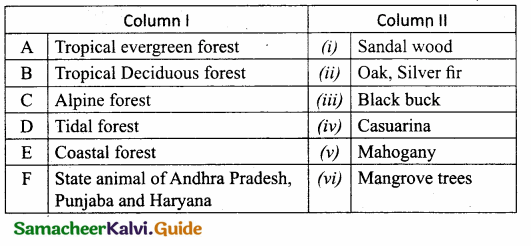
Question 3.
Match the Column I with Column II.
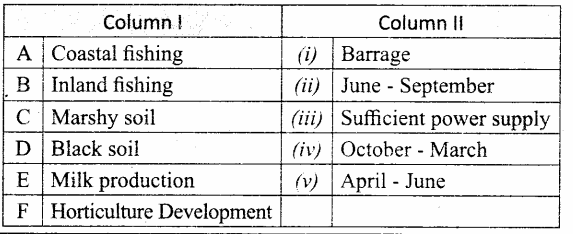
Answer:
A. (vi)
B. (iii)
C. (ii)
D. (i)
E. (iv)
F. (v)
![]()
V. Answer in brief
Question 1.
Why is tank irrigation more prevalent in South India than North India?
Answer:
The undulated topography of peninsular region forms large depressions to collect water which become tanks. So the tank irrigation is more prevalent in South India than North India.
Question 2.
How laterite soils are formed?
Answer:
Laterite soils are formed in the regions where alternate wet and dry conditions prevail.
It is formed by the process of leaching.
Question 3.
Which is an acute problem in India? How?
Answer:
Soil degradation is an acute problem in India. According to a 2015 report of the Indian institute of remote sensing (IIRS). The estimated the amount of soil .erosion that occurred in India was 147 million hectares.
The main problems of the Indian soils are
- Soil erosion
- Degradation of Soil
- Water-logging
- Saline and Alkaline and
- Salt Flats.
Question 4.
Draw a flow chart showing the sources of irrigation and their classification.
Answer:
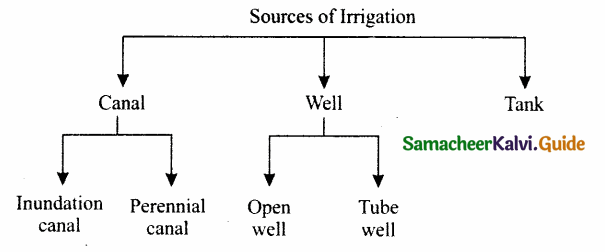
Question 5.
Write few lines about Rain Gun.
Answer:
It is used to spread water like rain and used to serve for crops which used to grow up to 4 feet or high also but we have to adjust sprinklers height as per crop size, typical usage of Rain guns are in sugarcane, maize crops.
Question 6.
Name the food crops grown in India.
Answer:
Food crops that are grown in India include cereals and pulses amongst which rice, wheat, jowar, bajra, maize, barely, ragi, gram and tur are important.
Question 7.
Give short notes about Terrace cultivation.
Answer:
This is practised especially in hilly areas, where lands are of sloping nature. The hill and mountains slopes are cut to form terraces and the land is used in the same way as in permanent agriculture.
![]()
Question 8.
Name the five leading states that contribute 85% of India’s wheat production.
Answer:
Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh are the leading states in wheat production in India.
Question 9.
What are the products of Sugarcane?
Answer:
Sugarcane provides raw material for the sugar industry. Besides providing sugar, gur and Khandsari it supplies molasses for alcohol industry and bagasse for paper industry.
Question 10.
How jute is useful for trade?
Answer:
- Jute fibre provides raw material for Jute industry.
- It is used for manufactruing of gunny bags, carpets, hessian, ropes and strings, rugs, clothes, tarpaulins, upholstery etc.
Question 11.
What is the other name of ‘Shifting Agriculture1? Who practice shifting agriculture? and how it is called in different regions?
Answer:
‘Shifting Agriculture’ is also called as ‘Slash and bum’ Agriculture. The tribal people follow this type of agriculture. It is called by different names in different regions in India as follows.
| Name | Place |
| Jhum | Assam |
| Poonam | Kerala |
| Podu | Andhra Pradesh, Odisha |
| Beewar, Mashan, Penda, Beera | Various parts of Madhya Pradesh |
Question 12.
What is dry farming?
Answer:
Dry farming is the type of farming practiced in arid areas where there is lack of irrigation facilities. Crops grown in these areas can withstand dry conditions.
![]()
Question 13.
What are called cash crops? Give examples.
Answer:
Crops which are cultivated for commercial purpose are called cash crops, eg: Sugarcane, tobacco, fibre crops and oil seeds.
Question 14.
Which is the largest oil seeds producing state? What is the position of India in oil seeds production in the world?
Answer:
Gujarat is India’s largest oil seeds producing state. India is the second largest producer of oil seeds in the world next to China.
Question 15.
Define Green Revolution.
Answer:
The process of improving and increasing the production of food crops using modem techniques is referred as Green Revolution.
Question 16.
Mention the different breeds of cattle population in India.
Answer:
Cattle population in India belongs to different breeds. They are
- Milch breed
- Draught breed
- Mixed or General breed
VI. Give Reasons
Question 1.
Tank irrigation is popular in peninsular India.
Answer:
The undulating relief, absence of perennial rivers, Impermeable rock structure and natural depression are the reasons for having tank irrigation most popular in Peninsular India.
Question 2.
Why tea is grown on the hill slopes?
Answer:
Tea plants require high rainfall but its roots cannot tolerate water logging. Frost condition is a must for tea plants. So it is grown on the hill slopes.
![]()
Question 3.
Inundation canals are not dependable source of irrigation.
Answer:
Inundation canals are operational only during rainy season for the diversion of flood water directly from the rivers. Hence these canals are not dependable source of irrigation.
Question 4.
Shifting agriculture is also called as slash and burn agriculture.
Answer:
Once the forest land piece is cleared by tribal people they grow crops for two to three years and bum the stumps after harvest and abandoning the lands to regain its fertility and then move to new areas. Thus, shifting agriculture is also called ‘slash and bum’ agriculture.
Question 5.
Only little surplus is left in subsistence farming.
Answer:
Mainly in subsistence farming crops are grown for family consumption leaving little surplus to sell in the market. Preference will be given to food crops as per their needs.
Question 6.
Indian agriculture is mainly dominated by the food crops.
Answer:
As the population increases the need for food also increase. Due to the need and to supply to the large population Indian agriculture is mainly dominated by the food crops.
![]()
VII. Distinguish between the following
Question 1.
Laterite and Red soil.
Solution:
Laterite soil:
- Femed by the process of leaching under wet and hot dry conditions.
- Mainly composed of hydrated oxides of iron and aluminium.
- Found mostly on hilly areas.
- Suitable for tea, coffee, rubber and cashewnut.
Red soil:
- Formed by the decomposition of ancient crystalline rocks.
- Rich in minerals like iron and magnesium.
- Found in plateau regions.
- Suitable for pulses and sugarcane.
Question 2.
Arid and desert soil and Peaty and marshy soil.
Answer:
Arid and Desert soil:
- Formed due to dry climate and high temperature.
- Poor in organic matter and nitrogen rich in salt content.
- Found in Rajasthan Northern Gujarat and Southern Punjab.
- Millets, barley and pulses grow with irrigation.
Peaty and Marshy soil:
- Formed in humid regions from organic matter.
- Poor in potash and phosphate rich in vegetable organic matter.
- Found in coastal areas and Sunderban Deltaic region, Kerala, Odisha, West Bengal.
- Ideal for paddy and Jute cultivation.
Question 3.
Open well and Tube well irrigation.
Answer:
Open well irrigation:
- Need sufficient ground water availability.
- Practiced in areas of Ganga plains and river Deltaic regions.
Tube well irrigation:
- Can be found in areas of low water table and soft geological subsurface.
- Need sufficient water supply. Predominant in the states of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh and TamilNadu.
![]()
Question 4.
Bhakra Nangal and Hirakud project.
Answer:
Bhakra Nangal Project:
- Constructed on the river Sutlej.
- Highest gravity dam in the world.
- Punjab, Haryana and Rajasthan states are benefitted.
Hirakud Project:
- Constructed on the river Mahanadhi.
- Longest dam in the world.
- State of Odhisha is benefitted by this project.
Question 5.
Subsistence and Mixed farming.
Answer:
Subsistence farming:
- Crops is mainly cultivated for family consumption.
- Traditional farming methods are used due to small land holdings.
- Mainly concentrated on food crops.
Mixed farming:
- Integrated farming to satisfy many needs of the farmers.
- Modem techniques is used for crop cultivation done in a vast area.
- System include crop production along with raising live stock, poultry, fisheries, bee keeping etc.
Question 6.
Food and Cash crops.
Answer:
Food crops:
- Mainly grown for consumption purpose.
- Food crops include rice, wheat, pulses etc.
- Apart from consumption used as raw materials for agro based industries.
Cash crops:
- Crops are cultivated for commercial purpose.
- Sugarcane, cotton, jute, oil seeds are the main cash crops. .
- Mainly produced for raw materials for industries and earn valuable foreign exchange.
Question 7.
Rice and Wheat.
Answer:
Rice:
- Mainly Tropical crop.
- Need abundant supply of water till harvest.
- West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, TamilNadu, Andhra Pradesh are some of the leading states in Rice production.
Wheat:
- Sub tropical or Temperate crop.
- Need moderate water supply.
- Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh are the leading states in wheat production.
![]()
VIII. Answer in a paragraph
Question 1.
What is a multipurpose project and explain its purpose?
Answer:
A comprehensive river valley project which serves a number of purposes simultaneously is called a “Multipurpose project”. Multipurpose projects serve the following purposes.
- They help to store water, that can be utilised, when water, is in great demand both for agricultural and domestic purpose.
- They check floods and famines.
- Afforestation is undertaken in the catchment areas of river, which helps conservation of water, soil and wildlife. Thus it keeps ecosystem intact.
- Production of hydro electricity is also another purpose of these projects. It is a pollution free of energy and is renewable energy.
- They attract tourists and develops tourism industry.
- Soil conservation and land relamation are other purpose of these projects.
Question 2.
What do you mean by Irrigation? Why it is necessary in India?
Answer:
- Watering to agricultural lands by artificial means for cultivation is called Irrigation.
- India is a tropical monsoon country.
- 75% of rainfall is received within a span of four months.
- Indian rainfall from monsoons are seasonal, uneven, irregular and erratic in nature.
- So always there is a need for irrigation to carry out agricultural activities during dry period.
- Besides erratic rainfall prevalence of high temperature, cultivation of annual crops and hydrophytes.
- Commercial farming and porous soil make irrigation an essential one for agriculture in India.
Question 3.
What are the different sources of irrigation used in different parts of India?
Answer:
The main sources of irrigations are
1. Canal irrigation
2. Well irrigation
3. Tank irrigation
1. Canal irrigation:
It is the second most important sources of irrigation in India. The Canals are of two types.
i. Inundation canals
ii. Perennial canals
i. Inundation canals:
In this, water is taken directly from the rivers without making any kind of barrage or dam. Such canals are useful for the diversion of flood water from the rivers and remains operational during rainy season.
ii. Perennial canals:
These are developed from perennial work by constructing barrage to regulate the flow of water. These canals are useful for irrigation.
2. Well irrigation:
A Well is a hole or trough usually vertical excavated in the earth for brining groundwater to the surface. It contributes about 62% of net irrigated area in India. Wells are of two types.
i. Open well
ii. Tube well
i. Open well:
This type of irrigation is widely practiced in the areas where groundwater is sufficiently available. The areas are in Ganga plains, the deltaic region of Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, Cauvery and parts of Narmada and Tapti valleys.
ii. Tube well:
Tube wells are developed in the areas of low water table, sufficient power supply and soft subsurface geological units. Tube wells are predominant in the states of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Punjab, MP, and Tamil Nadu.
3. Tank irrigation:
A tank is a natural or man-made hollow on the surface developed by constructing a small bund around it across a stream It is used to collect and store water for irrigation and other purpose. It also includes irrigation from taken and ponds.
![]()
Question 4.
How is Live-stock census conducted in TamilNadu?
Answer:
State Government is conducting Live stock census with the help of:
- Department of Animal Husbandary at State level and
- Regional Joint Director at District level under the guidelines of Government of India ministry of Agriculture and farmers welfare,
- Department of Animal husbandary, Dairying and Fisheries conducted once in 5 years.
Question 5.
Explain about the major issues faced by the Indian farmers?
Answer:
We can divide the problems faced by the Indian agriculture and by the farmers into two Natural and Man made.
Natural problems:
- Soil erosion: Large tracts of land suffer from soil erosion by wind and water.
- Infertile soil: Growing crops for many years without replenishing led to the exhaution of soil and its depletion.
- Lack of Irrigation: Only some areas of the cropped falls under irrigation.
Man made problems:
- Small land holdings and fragmented land: Poor status made the farmers to have small land and also some farmers possesses share from their ancestral property cannot afford to apply mechanism.
- High costs of Inputs: Good quality of seeds are out of reach for many small and marginal farmers due to their high price.
- Agricultural marketing: Absence of sound marketing, facility, interference of local traders and middlemen for the disposal of their produce, fluctuations in the price.
- In adequate transport: Lakhs of villages are not w7ell connected with main roads or with market centres. Lack of cheap and efficient means of transportation is not available.
- Scarcity of capital: Huge capital is needed to purchase advanced farm machineries and equipments which the poor farmers cannot afford to buy.
Question 6.
List out some of the Agricultural Revolutions in India.
Answer:
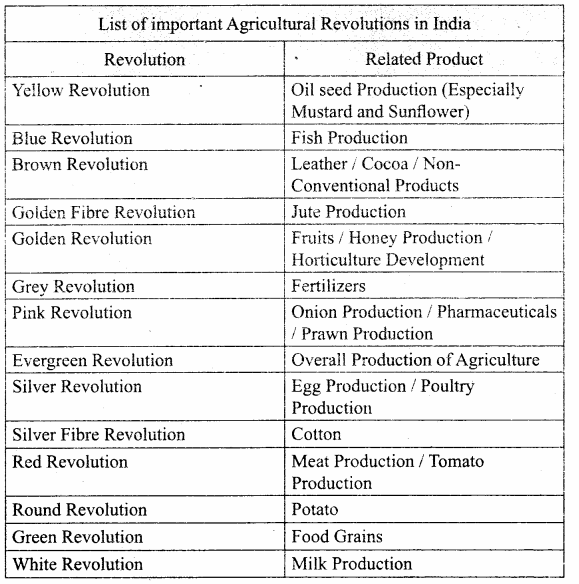
![]()
Question 7.
“Per Drop more Crop”. Explain this statement.
Answer:
- It is the scheme introduced by the Government of India with the objective to enhance water use efficiency.
- This micro irrigation scheme comes under “Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) and centrally sponsored scheme on micro irrigation.
- It promotes appropriate technological interventions like drop and sprinkler irrigation technologies in agriculture and encourage farmers to use water saving and conservation technique.
- Following five states progressed 78% under micro irrigation scheme
- Andhra Pradesh
- Karnataka
- Gujarat
- Maharashtra
- TamilNadu
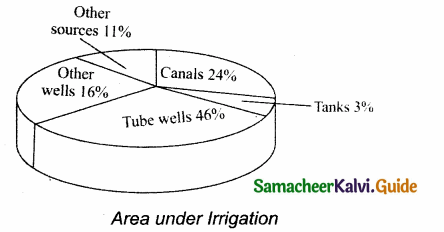
IX. Map Questions
Mark the following on the outline map of India.
Question 1.
Areas of Red soil and Mountain soil.
Answer:

![]()
Question 2.
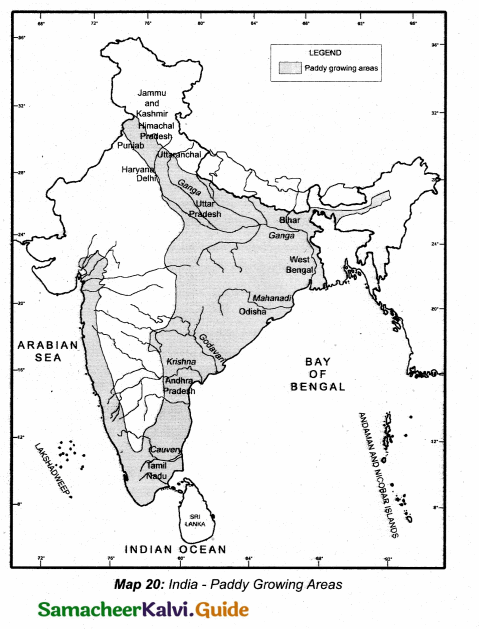
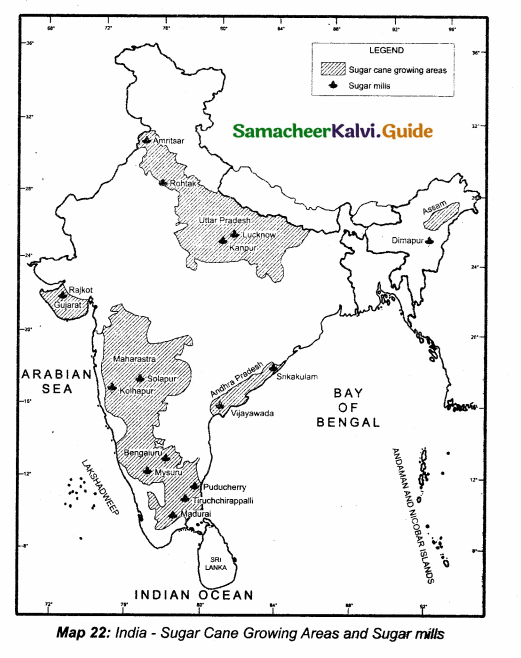
Demarcate the states producing the highest for the following crops.
Answer:
(i) Paddy

(ii) Sugarcane

(iii) Cotton

(iv) Wheat

![]()
Question 3.
Kosi project, Tungabadra, Periyar Dam, Nagarjuna Sagar.
Answer: