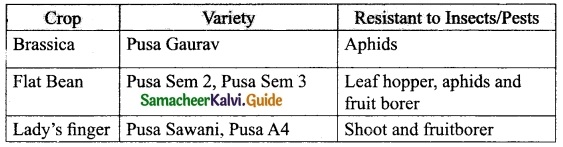
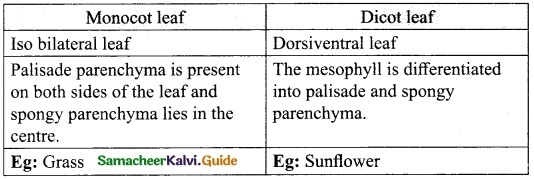
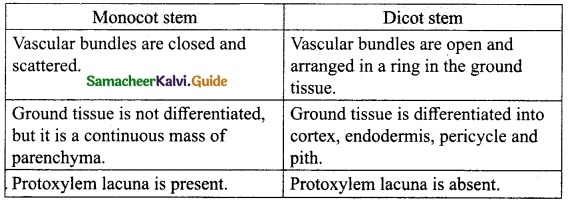
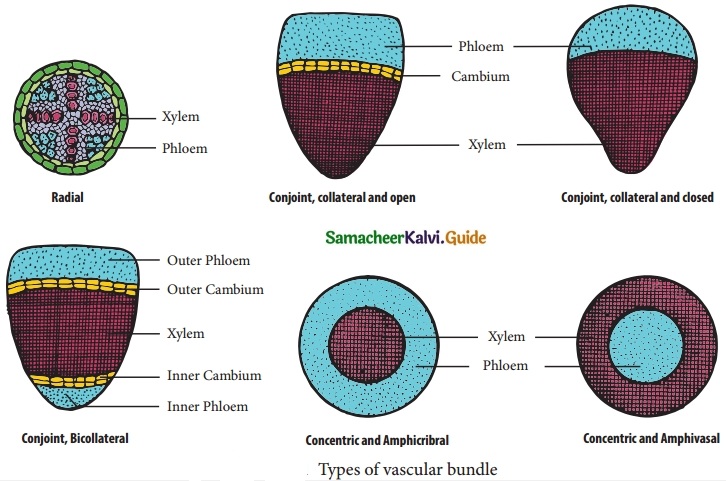
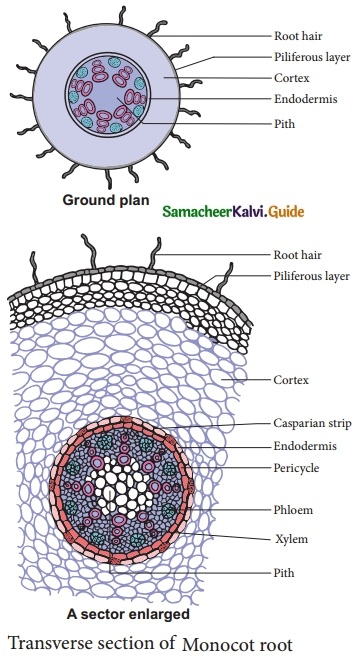
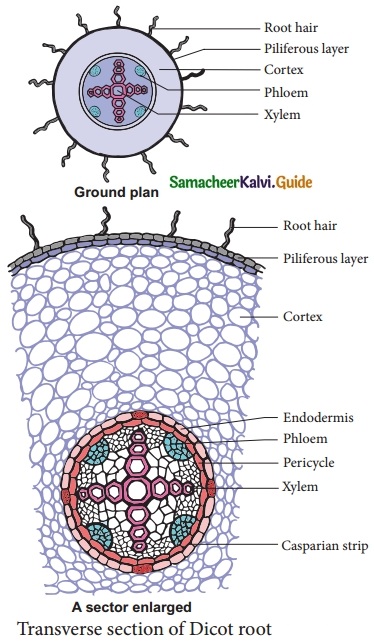
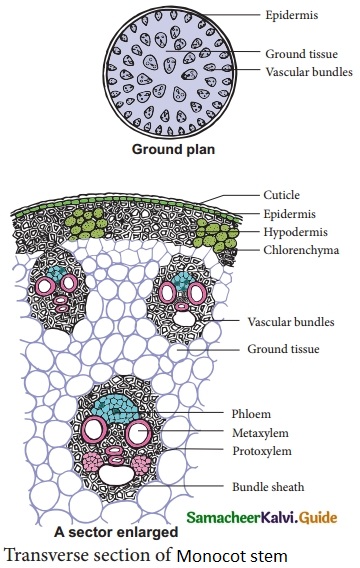
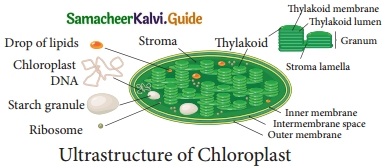
Students can download 10th Science Chapter 23 Visual Communication Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Solutions Chapter 23 Visual Communication
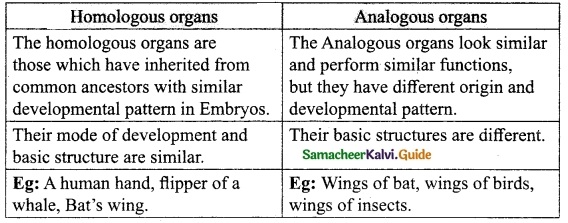
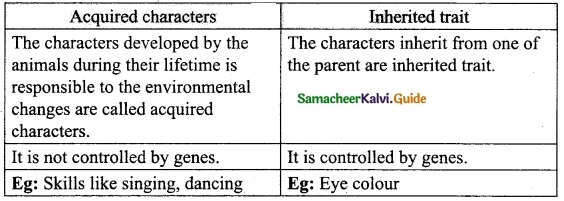
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Visual Communication Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the best answer:
Question 1.
Which software is used to create animation?
(a) Paint
(b) PDF
(c) MS Word
(d) Scratch
Answer:
(d) Scratch
Question 2.
All files are stored in the _______.
(a) folder
(b) box
(c) pai
(d) scanner.
Answer:
(a) folder
![]()
Question 3.
Which is used to build scripts?
(a) Script area
(b) Block palette
(c) Stage
(d) Sprite
Answer:
(a) Script area
Question 4.
Which is used to edit programs?
(a) Inkscape
(b) Script editor
(c) Stage
(d) Sprite.
Answer:
(b) Script editor
Question 5.
Where you will create category of blocks?
(a) Block palette
(b) Block menu
(c) Script area
(d) sprite
Answer:
(b) Block menu
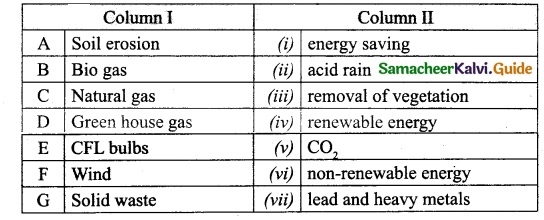
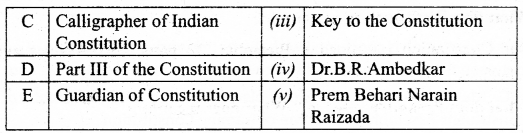
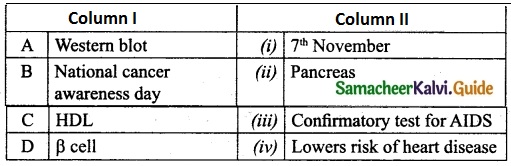
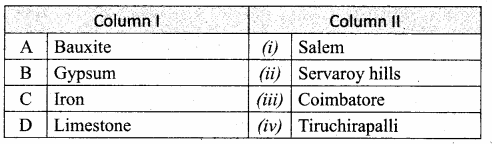
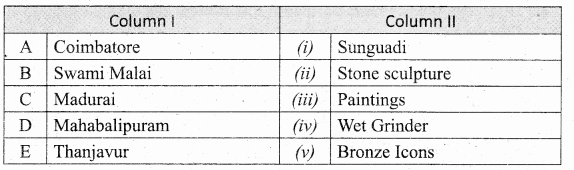
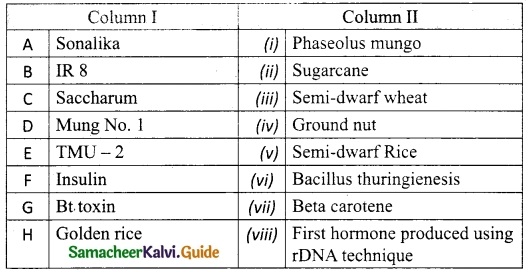
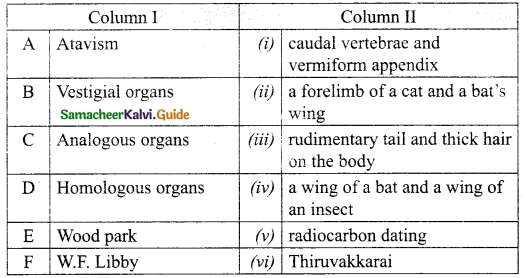
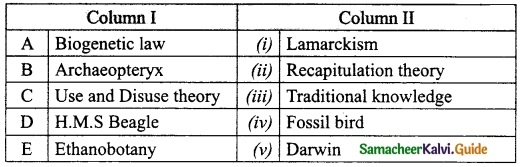
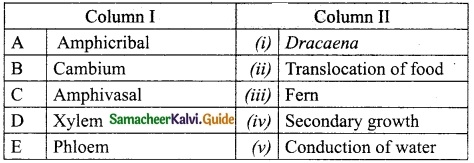
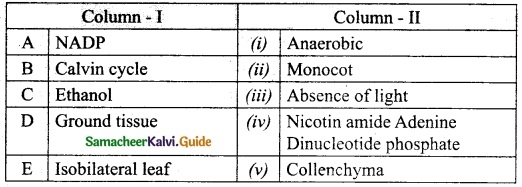
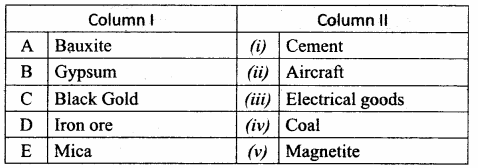
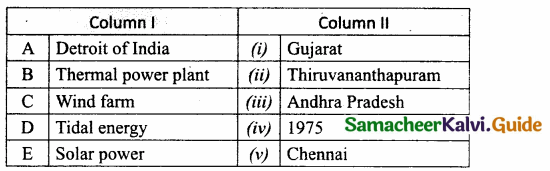
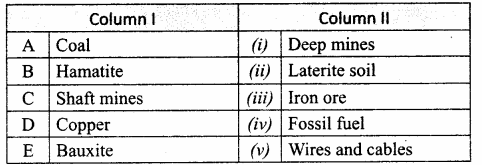
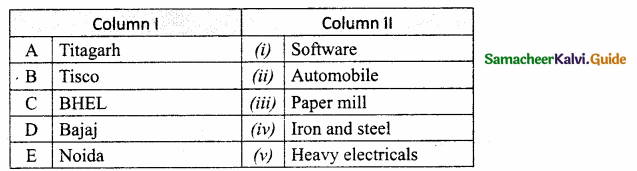
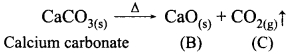
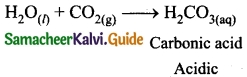
II. Match the following:
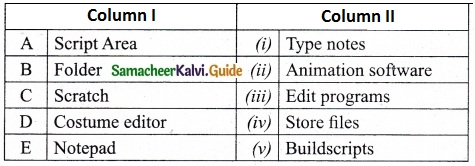
Answer:
A. (v)
B. (iv)
C. (ii)
D. (iii)
E. (i)
III. Answer the following:
Question 1.
What is Scratch?
Answer:
Scratch is a software used to create animations, cartoons and games easily. Scratch, on the other hand, is a visual programming language.
![]()
Question 2.
Write a short note on the editor and its types.
Answer:
Editors or text Editors are software programs that enable the user to create and edit text files Editors are generally classified into 5 types as,
- Line Editor [Ex: teco]
- Stream Editor [Ex: Sed]
- Screen Editor [Ex: Notepad]
- Word processors [Ex: MS – word]
- Structure Editor [Ex: Netbeans IDE].
Question 3.
What is stage?
Answer:
Stage is the background appearing when we open the scratch window. The background will most often be white. You can change the background colour as you like.
Question 4.
What is Sprite?
Answer:
The characters on the background of a Scratch window are known as Sprite. Usually, a cat appears as a sprite when the Scratch window is opened. The software provides facilities to make alternations in the sprite.
Samacheer Kalvi 10th Science Visual Communication Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the best answer:
Question 1.
The output we get from any application is commonly referred as
(a) file
(b) data
(c) record
(d) folder
Answer:
(a) file
Question 2.
_______ is used to choose the block to use.
(a) Script area
(b) Block palette
(c) Block menu
(d) Sprite.
Answer:
(b) Block palette
![]()
Question 3.
Which app is used, we can draw and edit pictures?
(a) My computer
(b) Notepad
(c) Paint
(d) Games
Answer:
(c) Paint
Question 4.
Choose the odd one from the following _______.
(a) File
(b) Folder
(c) Memory space
(d) Mouse.
Answer:
(d) Mouse.
Question 5.
Write a good example for visual communication.
(a) Picture
(b) Cinema
(c) Radio
(d) FM
Answer:
(b) Cinema
Question 6.
Choose the wrong statement from the following statements _______.
(a) The scripts tab contains additional tabs of costumes and sounds.
(b) Block palette is used to choose the block to use.
(c) The right contains additional tabs of costumes and sounds.
(d) Scratch is software.
Answer:
(a) The scripts tab contains additional tabs of costumes and sounds.
Question 7.
Choose the incorrect pair:
(a) Windows – operating system
(b) Visual – Cinema
(c) Costume – editor
(d) Stage – a input device
Answer:
(d) Stage – a input device
![]()
Question 8.
Identify which is not a file format _______.
(a) CSS
(b) PSO
(c) PNG
(d) EPS.
Answer:
(b) PSO
Question 9.
Choose the incorrect statement:
(a) More people are using windows operating system.
(b) We can collect our notes in Notepad application.
(c) We can draw pictures in paint application.
(d) A folder is a file name.
Answer:
(d) A folder is a file name.
Question 10.
The start button is present in the ______ corner of the computer.
(a) Center
(b) top
(c) left
(d) right.
Answer:
(c) left
Question 11.
Assertion (A) : Pictures and audio-visuals gives us more understanding than teaching and writing on the black board.
Reason (R) : The device which helps in explaining the concepts easily through pictures is known as visual communication device.
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation assertion.
(b) Both assertion and reason are true, but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion and reason are true, and reason is the correct explanation assertion.
Question 12.
Pick the odd one out:
(a) LINUX
(b) Paint
(c) Spread sheet
(d) PPTs
Answer:
(a) LINUX
![]()
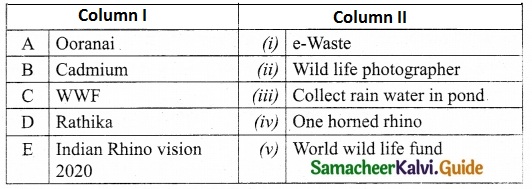
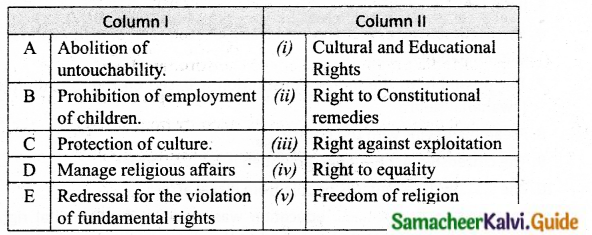
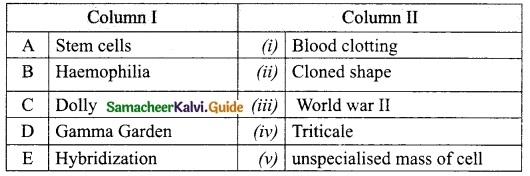
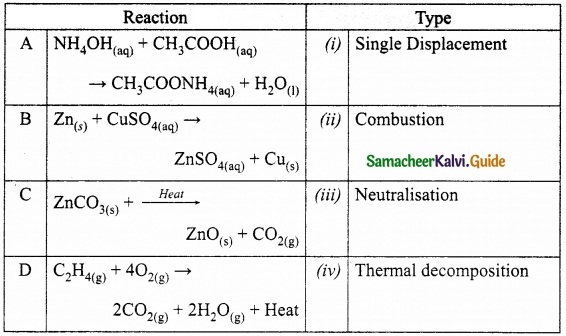
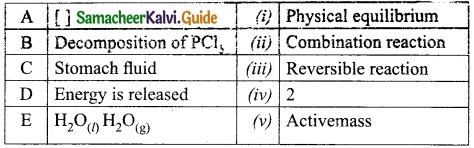
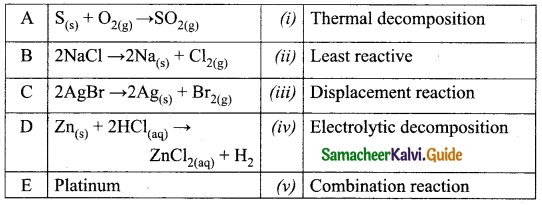
II. Match the following:
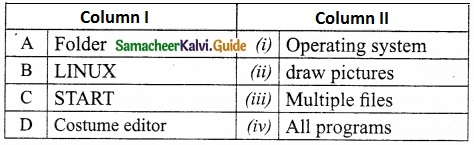
Answer:
A – (iii)
B – (i)
C – (iv)
D – (ii)
III. Answer the following:
Question 1.
What is the reason, we prefer computer?
Answer:
The reason, we prefer computer is its speed and the ability to store data.
Question 2.
What is a folder?
Answer:
A folder is a storage space that contains multiple files. We can create files as per the user’s need.
Question 3.
What is a file?
Answer:
The output we get from any application is commonly referred as file.
Therefore, the application for the specific purposes determines the nature of the file.
Question 4.
Name the different parts of Scratch Editor?
Answer:
- Stage
- Sprite
- Script Editor / Costume Editor.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the using script editor?
Answer:
Script editor / costume editor: Where you edit your programs or your sprite’s pictures.
You should see a single window with at least the following three panes: the stage (top left), the Sprite List (bottom left), and the Scripts tab (right), which contains the Blocks tab and the Scripts Area. The right pane also contains two additional tabs, Costumes and Sounds.
The script editor has three main parts:
- Script area: Where you build scripts.
- Block menu: Where you choose the category of blocks (programming statements) to use.
- Block palette: Where your choose the block to use.
Question 6.
Write a note on Script editor.
Answer:
Script editor/costume editor: Where you edit your programs or your sprite’s pictures. You should see a single window with at least the following three panes: the Stage (top left), the Sprite List (bottom left), and the Scripts tab (right), which contains the Blocks tab and the Scripts Area. The right pane also contains two additional tabs, Costumes and Sounds.