Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 4th English Guide Pdf Term 3 Prose Chapter 1 The Seven Seeds Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Summary, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 4th English Solutions Term 3 Prose Chapter 1 The Seven Seeds
4th English Guide The Seven Seeds Text Book Back Questions and Answers
![]()
A. Choose the correct option.
Question 1.
The kingdom was situated in the foothills of ____________
(a) Kollimalai
(b) Sirumalai
(c) Anaimalai
Answer:
(c) Anaimalai
Question 2.
The king looked for a ___________
(a) Minister .
(b) Leader
(c) Great soldier
Answer:
(b) Leader
Question 3.
The king gave __________ seeds.
(a) Five
(b) Six
(c) Seven
Ans:
(c) Seven
Question 4.
In real, the test is for ___________
(a) Testing honesty
(b) Growing wheat
(c) Growing paddy
Answer:
(a) Testing honesty
![]()
B. Read the statement and write True or False.
Question 1.
The king shouted at Ani.
Answer:
False
Question 2.
Ani grew the seed well.
Answer:
False
Question 3.
Ani valued honesty.
Answer:
True
![]()
C. Answer the questions.
Question 1.
How long did the competition take to reach the final?
Answer:
The competition took nearly six months to reach the final.
Question 2.
Why did the king want a leader who knows to grow a plant?
Answer:
The king wanted a leader who knew to grow a plant because his kingdom depended on agriculture.
Question 3.
Did the seeds given to Ani sprout? why?
Answer:
No, the seeds given to Ani did not sprout because they were boiled seeds which cannot grow.
Question 4.
What did Ani’s parents teach her?
Answer:
Ani’s parents taught her the value of honesty.
Question 5.
Do you think Ani will be a good leader? Why?
Answer:
Yes. Ani will be a good leader because of her honesty.
![]()
I. Match the word with its meaning.
Question 1.
Leader – fate
Answer:
Leader – head
Question 2.
Anxious – head
Answer:
Anxious – eager
Question 3.
Destiny – eager
Answer:
Destiny – fate
![]()
II. Link the correct opposites.
Question 1.
Open × old
Answer:
Open × close
Question 2.
end × close
Answer:
end × beginning
Question 3.
New × beginning
Answer:
New × old
![]()
III. Fill in the blanks.
Question 1.
The king was getting old and had no __________ to take his place.
Answer:
Heir
Question 2.
Our kingdom depends on __________ so the new leader must know how to grow plants.
Answer:
Agriculture
Question 3.
The king raised his hands and __________ for silence.
Answer:
Signalled
Question 4.
The days stretched into weeks but the seeds _________ to sprout.
Answer:
Failed
Question 5.
The entire _________ was excited and anxious to see who the next king would be.
Answer:
kingdom
![]()
IV. Read the statement and write True or False.
Question 1.
The king decided to adopt and raise a child as the minister.
Answer:
False
Question 2.
The other nine children had great success with their seeds.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
Ani feared that the king might throw her into the prison for wasting his precious seeds.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
The king gave boiled seeds and the boiled seeds can grow well.
Answer:
False
![]()
V. Identify the character / speaker.
Question 1.
“May be you’re not destined for the throne”.
Answer:
Ani’s parents
Question 2.
“How can anyone tell if they were the same seeds?”
Answer:
Ani’s friends
Question 3.
“I am sorry, but they failed to sprout”.
Ans: Ani
Question 4.
“How can she be the right choice?”
Answer:
The people
Question 5.
“Dear people, behold my heir. The next leader of our kingdom!”
Answer:
The king
![]()
VI. Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
What do you know about the king and his kingdom?
Answer:
The king ruled the kingdom at the foot hills of Anaimalai for 30 years. It flourished in trade and arts. The king was respected and revered by all but he had no heir.”
Question 2.
Who entered the last round of the competition? Why?
Answer:
Five boys and five girls made it to the last round of the competition because they were intelligent, strong and capable.
Question 3.
What was the last test of the competition?
Answer:
The last test of the competition was to know how to grow plants. Seven seeds of wheat were given to each to take home, plant and nurture them for six weeks. The person who does the best job of nurturing them will be the heir to the throne.
Question 4.
What did Ani do for her seeds to grow?
Answer:
Selected the soil with care, put the right manure and very dutifully watered it. She even prayed over it day and night.
Question 5.
When Ani’s seeds failed to grow why didn’t she buy new seeds and plant?
Answer:
Ani’s parents had taught her the value of honesty. She knew that using anything different from what the king gave, would be dishonest and it was wrong to cheat the king. So Ani did not buy new seeds and plant even when her seeds failed to grow.
Question 6.
Why didn’t the seeds given to Ani by the king, not grow?
Answer:
The seeds given by the king to Ani didn’t grow because the king had given boiled seeds which cannot grow.
Question 7.
Did the seeds given to the other children grow? What did they do?
Answer:
No, the seeds given to the other children did not grow. They had bought new seeds from the market and planted which grew into healthy seedlings. They had cheated the king by being dishonest.
Question 8.
What did the king actually test? Why?
Answer:
The king actually tested the character and honesty of the leader to be. Because people should be able to trust the leader.
![]()
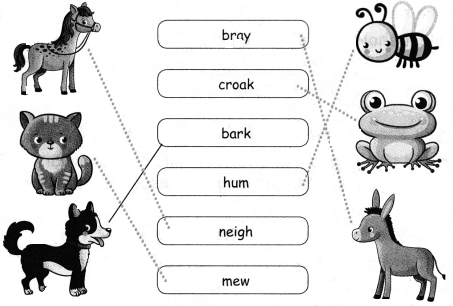
Let us build
A. Match the animals with their sounds.
Question 1.
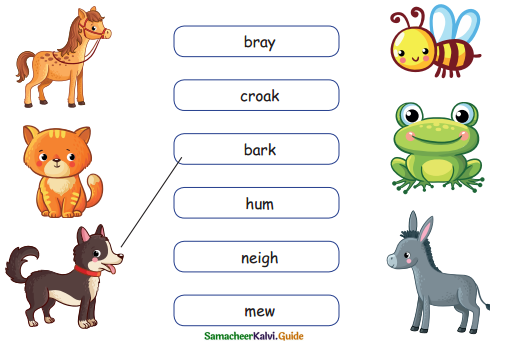
Answer:
![]()
B. What we say?
Question 1.

Answer:
I am a Duck
I quack
Question 2.

Answer:
I am a rabbit
I squeak
Question 3.

Answer:
I am a sheep
I bleat
Question 4.

Answer:
I am a pig
I grunt
Question 5.

Answer:
I am a rooster
I crow
![]()
Additional Questions and Answers.
Match the sounds of animals.
Question 1.
Crows – sing
Answer:
Crows – caw
Question 2.
Doves – caw
Answer:
Doves – соо
Question 3.
Larks – соо
Answer:
Larks – sing
Question 4.
Vulture – bell
Answer:
Vulture – scream
Question 5.
Cattle – scream
Answer:
Cattle – moo
Question 6.
Tigers – moo
Answer:
Tigers – growl
Question 7.
Deers – growl
Answer:
Deers – bell
![]()
The Seven Seeds Summary in English and Tamil
Long ago, there was a kingdom at the foothills of Anaimalai. The kingdom flourished in trade and arts under the rule of their king’s rule. He was respected and revered by all. It has been thirty years under his rule now. One day, the ageing king woke up worried. He was getting very old and had no heir to take his place. He decided to adopt and raise a child as the heir, but he knew that the adopted child must be honest.
வெகு காலத்திற்கு முன்னர், ஆனைமலையின் அடிவாரத்தில் ஒரு ராஜ்ஜியம் இருந்தது. அரசரின்ஆட்சியில் அந்த ராஜ்ஜியம் வியாபாரத்திலும் கலைகளிலும் செழித்தது. அந்த அரசர் அனைவராலும் மதிக்கப்பட்டு, மரியாதையும் செய்யப்பட்டார். அவர் அரசாள ஆரம்பித்து முப்பதுவருடங்களாகிவிட்டன. வயதான அந்த அரசர் ஒருநாள் கவலையுடன் எழுந்தார்அவருக்கு வயதாகிக் கொண்டே போவதாலும், வாரிசுகள் இல்லாததாலும் ஒரு குழந்தையை வாரிசாக தத்தெடுத்து வளர்க்க எண்ணினார். ஆனால் தத்தெடுக்கப்படும் குழந்தை நேர்மையாக இருக்க வேண்டும் என்பதும் அவருக்கு தெரியும்.
To find the child, he held a competition in his kingdom that was open to all. The competition had many levels and spanned for nearly six months. At the end of it, five boys and five girls made it to the very last round. There seemed little to separate them; each one of them was intelligent, strong and capable.
சரியான குழந்தையை கண்டுபிடிப்பதற்காக, எல்லாரும் பங்கேற்கக்கூடிய ஒரு போட்டியை அவர் நடத்தினார்.அந்த போட்டி, பல நிலைகளை கொண்டதாகவும், ஆறு மாதங்களுக்கு நீண்டதாகவும் இருந்தது. அதன் முடிவில், ஐந்து சிறுமிகளும், ஐந்து சிறுவர்களும் கடைசி சுற்றுக்கு தேர்வு பெற்றனர். ஒவ்வொருவரும் புத்திசாலியாகவும், வலிமையானவராகவும், தகுதிபெற்றவராகவும் இருந்ததால், தேர்ந்தெடுப்பது மிகவும் சிரமமாக இருந்தது.
The kina said, “I have one last test for you all. The one who passes this test will be the winner. As you all know the winner will be the heir to my throne.” He continued, “Our kingdom depends on agriculture, so the new leader must know how to grow plants. Here are seven seeds of wheat for each of you. Take them home. Plant and nurture them for six weeks. At the end of the sixth week, we shall see who has done the best job of nurturing them. That person will be the heir to the throne.”
“உங்கள் அனைவருக்கும் ஒரு கடைசி பரீட்சை உள்ளது, இதில் வெல்பவரே வெற்றியாளர் ஆவார்” எனக் கூறிய அரசர், “அவரே என் அரியணைக்குவாரிசு” என்றும் கூறினார். மேலும் “நம் ராஜ்ஜியம் விவசாயத்தை நம்பியுள்ளது, எனவே புதிய தலைவர்பயிர்களை பற்றியும்) வளர்ப்பது பற்றியும் தெரிந்திருக்க வேண்டும்” என்றார். “உங்கள் அனைவருக்கும் ஏழு கோதுமை விதைகளை அளிக்கிறேன். அவற்றை வீட்டிற்கு எடுத்துச் சென்று, நட்டு ஆறு வாரங்கள்பராமரிக்க வேண்டும். ஆறு வாரங்களின் முடிவில், யார்சரியாக அவற்றை வளர்த்து பராமரிக்கிறாரோ அவரே அரியணைக்கு வாரிசாவார்” என்றார்.
![]()
The children took their seeds and hurried home. They all got a pot, prepared some soil and sowed their seeds. The entire kingdom was excited. They were all anxious to see who the next king would be.
குழந்தைகள் விதைகளை எடுத்துக் கொண்டு வீட்டிற்குவிரைந்தனர். அனைவரும் ஒரு தொட்டியை எடுத்து,சிறிது மண்ணை இட்டு, விதைகளை விதைத்தனர். தமது அடுத்த அரசர் யார் என அறிய மொத்த ராஜ்ஜியமும் ஆவலாக இருந்தது.
One of the finalists was Ani. The days stretched into weeks. but the seeds failed to sprout. Ani didn’t know what had gone wrong. Ani and her parents were heartbroken. She had selected the soil with care, put the right manure, and very dutifully watered it. She had even prayed over it, day and night, and yet her seeds hadn’t grown at all.
ஓர் இல்லத்தில், அனி என்ற சிறுமியும் அவளுடைய பெற்றோரும் மனமுடைந்து இருந்தனர்.நாட்கள், வாரங்களாக நீண்டன. ஆயினும், விதைகள் முளைக்கவில்லை. தவறு எங்கே நேர்ந்ததென, அனி; க்கும் புரியவில்லை . ஏனெனில், சரியானபடி மண்ணை தேர்ந்தெடுத்து, சரியான உரத்தையும் இட்டு, கடமை தவறாது நீரை ஊற்றியும் வந்தாள். அவள் இரவும், பகலுமாக பிரார்த்தனை செய்து வந்தும்அவளுடைய விதைகள் வளரவே இல்லை .
Some of her friends advised her to go and buy new seeds from the market and plant. After all, they said, “How can anyone tell if they were the same seeds?”Ani’s parents had always taught her the value of honesty. They reminded her that if the king wanted them to plant just any wheat, he would have asked them to get their seed.
அவளுடைய சில நண்பர்கள் கடைவீதிக்கு சென்று புதிய விதைகளை வாங்கி பயிரிடும்படி கூறினர். ஏனெனில் யாராலும் விதைகளை குறிப்பாக அது, இது எனகண்டுபிடிக்க இயலாது. அனியின் பெற்றோர் அவளிடம் நேர்மையின் மதிப்பை பற்றி அவளுக்கு போதித்து இருந்தனர்.
![]()
“If you use anything different from what the king gave, that would be dishonest. I Maybe you’re not destined for the throne. If so, let it be, but it would be wrong to cheat the king,” they told her. Ani agreed.
அவர்கள் அனியிடம் “குழந்தைகள் ஏதாவது ஒரு கோதுமையைபயிரிடட்டும் என அரசர் நினைத்திருந்தால், அவர், விதைகளை நீங்களே ஏற்பாடு செய்து கொள்ளுங்கள் என்று கூறியிருப்பாரே” என்பதையும் அவளுக்கு நினைவுபடுத்தினர். “அவர் அளித்த விதைகளுக்கு மாறாக, வேறு ஒன்றை உபயோகப்படுத்தினால் அது நேர்மையற்ற செயலாகிவிடும். அரியணைக்கு நீ தேர்வாகாவிட்டாலும் பரவாயில்லை, ஆனால் அரசரை ஏமாற்றுவது தவறாகும்” என அவர்கள் கூற, அனியும்அதை ஏற்றுக்கொண்டாள்.
It had been six weeks now. The muchawaited day had come. The children returned to the palace, each of them proudly carrying a pot of healthy seedlings. It was obvious that the other nine had great success with their seeds.
ஆறு வாரங்களும் முடிந்துவிட்டன. எதிர்பார்க்கப்பட்ட நாளும் வந்தது. குழந்தைகள் அனைவரும்அரண்மனைக்கு திரும்பினர். ஒவ்வொருவரும் கையில் ஆரோக்கியமான பயிர்களை, தொட்டியில் வைத்திருந்தனர். இதன் மூலம் (அனியைத் தவிர மற்ற ஒன்பது பேரும் தங்கள் விதைகளை நடவு செய்வதில் வெற்றியடைந்திருந்தனர்.
The king arrived. He was beaming looking at the children and their pot of healthy seedlings. He began walking along the line of pots the children had kept. He asked each of them, “Is this what grew from the seeds I gave you?” And each of them responded, “Yes, your majesty.” And the king would nod and move down the line.
அவைக்கு வந்த அரசர், குழந்தைகளின் தொட்டிகளில் ஆரோக்கியமான பயிர்கள் இருப்பதை கண்டு புன்னகைசெய்தார்! குழந்தைகள் வரிசையாக வைத்திருந்த தொட்டிகளை பார்வையிட்டவர், ஒவ்வொருவரிடமும் “நான் கொடுத்த விதைகளிலிருந்தா இவை வளர்ந்தன?” என்று கேட்டார். ஒவ்வொருவரும் “ஆம், மாட்சிமை பொருந்திய அரசே” என கூறவும், அரசர் தலையசைத்து சென்றார்.
![]()
The king finally got to the last one, Ani. The girl was shaking. She feared that the king might have thrown her into prison for wasting his precious seeds. “What did you do with the seeds I gave you?” the king asked. “Your majesty, I planted them and cared for them every day. I am sorry but, they failed to sprout,” Ani said. She hung her head in shame. “Boo!” jeered the crowd.
கடைசியாக இருந்த அனியிடம் அரசர் சென்றார். அந்த சிறுமி நடுங்கிக் கொண்டிருந்தாள். அரசர்கொடுத்தமதிப்புமிக்க விதைகளை வீணாக்கிவிட்டதற்காக, ” தன்னை அரசர் சிறையில் போட்டுவிடுவாரோ என அவள் பயந்தாள். “நான் கொடுத்த விதைகளை நீ என்ன செய்தாய்?” என அரசர் அவளிடம் கேட்டார். “மாட்சிமை பொருந்திய அரசரே, நானும் விதைகளை பயிரிட்டு தினமும் பராமரித்தேன். ஆனாலும் அவை முளைக்கவில்லை என்பதற்காக வருந்துகிறேன்” என்று அனி கூறிவிட்டு தலையை கவிழ்த்துக் கொண்டாள்.கூடியிருந்த கூட்டமும் அதற்கு தன் அதிருப்தியைக் காட்டியது.
But the king raisedhis hands and signalled for silence. Then he said “Dear people behold my heir. The next leader of our kingdom!” The people were confused, “Why that girl? How can she be the right choice?”
தன் கைகளை உயர்த்தி கூட்டத்தினரை அமைதியாக இருக்கும்படி சைகை காட்டிய அரசர், அன்பு மக்களே,இதோ நம் இராஜ்ஜியத்தின் அடுத்த தலைவர்” எனக் கூற மக்கள் குழப்பமடைந்தனர். “யார் இவளா? எப்படி இவள் சரியான தேர்வாக ஆனாள்?” எனக் குழம்பினர்.
The king took his place on his throne with Ani by his side and said, ‘I aave each of them, seven seeds. This test was not for growing wheat. It was a test of character, a test of honesty. If a leader must have one quality, it must be that he or she should be honest. People should be able to trust the leader. Only this girl passed the test. I gave boiled seeds and boiled seeds cannot grow.”
தன் ஆசனத்தில் அமர்ந்த அரசர், அனியை தன் அருகில் அமர்த்திக்கொண்டு இவ்வாறு கூறினார். “நான்ஒவ்வொருவருக்கும் ஏழு விதைகளை கொடுத்தேன். இது கோதுமை விளைவிப்பதற்கான போட்டியல்ல. இது குணத்திற்கும், நேர்மைக்குமான பரீட்லைகுணத்திற்கும், நேர்மைக்குமான பரீட்சையாகும். ஒரு தலைவர் யாராக இருப்பினும் அவருக்கு வேண்டிய தகுதி, அவர் நேர்மையானவராக இருக்க வேண்டும்என்பதே. மக்கள் நம்பும்படியாக தலைவர் இருக்க வேண்டும். அந்த தேர்வில் இந்த சிறுமியே தேறினாள். நான் (அவர்கள் அனைவருக்கும்) கொடுத்தது, வேகவைத்த விதைகள். அவை எவ்வாறு வளரும்?”.
![]()
The Seven Seeds Glossary
Adopt – legally take and bring up
Ageing – getting old
Anxious – eager
Awaited – expected
Behold – see
Beaming – smiling broadly
Competition – contest
Destiny – fate
Dulifully – obediently doing the duty
Destined – to have an outcome
Excited – eager and enthusiastic
Flourished – developed in a healthy way
Heir – a person legally entiled to the property or rank of another person on his death
Hurried – move with haste
Kingdom – a region ruled by a king
Leader – head
Manure – animal dung used for furtilizing the land
Nurture – care, protect and grow
Nod – to move the head in acceptance
Revered – respected
Responded – say something in reply
Signalled – pass information by action or sign
Spanned – spread
Sprout – to put out shoots
Trade – buying and selling goods
Watered – to regularly pour water to grow