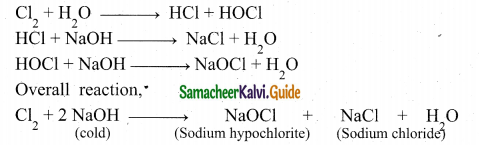
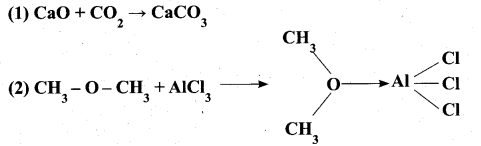
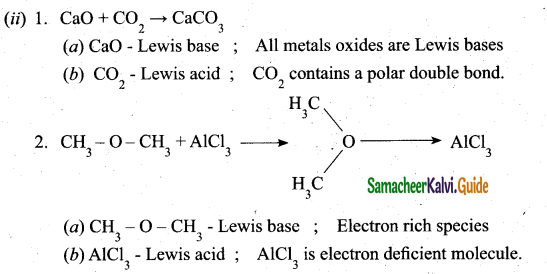
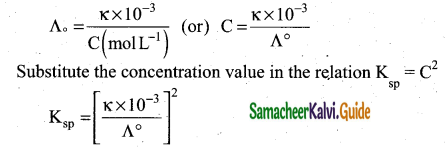
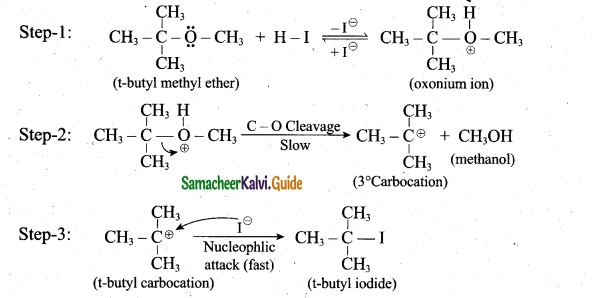
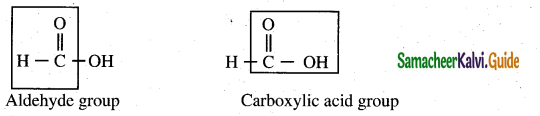Students can Download Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Model Question Paper 3 English Medium Pdf, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamil Nadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Social Science Model Question Paper 3 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts
- You are to attempt all the questions in each part. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III, and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 14 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each.
These are to be answered by writing the correct answer along with the corresponding option code and the corresponding answer - Question numbers 15 to 28 in Part II are of two marks each. Any one question should be answered compulsorily.
- Question numbers 29 to 42 in Part III are of five marks each. Any one question should be answered compulsorily.
- Question numbers 43 to 44 in Part IV are of Eight marks each. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 100
Part – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer [14 × 1 = 14]
Question 1.
What were the three major empires shattered by the end of First World War?
(a) Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottomans
(b) Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Russia
(c) Spain, Portugal and Italy
(d) Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy
Answer:
(a) Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottomans
Question 2.
Which quickened the-process of liberation in South America?
(a) Support of US
(b) Napoleonic Invasion
(c) Simon Bolivar’s involvement
(d) French Revolution
Answer:
(d) French Revolution
Question 3.
When was people’s Political consultative conference held in China?
(a) September 1959
(b) September 1948
(c) September 1954
(d) September 1949
Answer:
(d) September 1949
![]()
Question 4.
Who were driven out of their homeland during the process of creation of zamins under permanent Settlement?
(a) Santhals
(b) Titu Mir
(c) Munda
(d) Kol.
Answer:
(a) Santhals
Question 5.
Which among the following was declared as ‘Independence Day’?
(a) 26th January 1930
(b) 26th December 1929
(c) 16th June 1946
(d) 15th January 1947
Answer:
(d) 15th January 1947
Question 6.
The extent of Himalayas in the east-west is about …………………
(a) 2,500 km
(b) 2,400 km
(c) 800 km
(d) 2,200 km
Answer:
(a) 2,500 km
Question 7.
Western disturbances cause rainfall in …………………
(a) Tamil Nadu
(b) Kerala
(c) Punjab
(d) Madhya Predesh
Answer:
(c) Punjab
Question 8.
The soil formed by the river are …………………
(a) Red soils
(b) Black soils
(c) Desert soils
(d) Alluvial soils
Answer:
(d) Alluvial soils
Question 9.
Retreating monsoon wind pick up moisture from …………………
(a) Arabian sea
(b) Bay of Bengal
(c) Indian ocean
(d) Timor sea
Answer:
(b) Bay of Bengal
Question 10.
Second staple food of the people of Tamil Nadu is …………………
(a) Pulses
(b) Millets
(c) Oilseeds
(d) Rice
Answer:
(b) Millets
![]()
Question 11.
Which one of the following rights was described by Dr. B. R. Ambedkar as the heart and soul of the constitution?
(a) Right to freedom of religion
(b) Right to equality
(c) Right to constitutional remedies
(d) Right to property
Answer:
(c) Right to constitutional remedies
Question 12.
Which of the following country is not the founder member of NAM?
(a) Yugoslavia
(b) Indonesia
(c) Egypt
(d) Pakistan
Answer:
(d) Pakistan
Question 13.
………………… is the process of providing or obtaining the food necessary for health and growth.
(a) Health
(b) Nutrition
(c) Sanitation
(d) Security
Answer:
(b) Nutrition
Question 14.
Gross value added at current prices for services sector is estimated at lakh crore
in 2018-19.
(a) 91.06
(b) 92.26
(c) 80.07
(d) 98.29
Answer:
(b) 92.26
Part – II
Answer any 10 questions. Question No. 28 is compulsory. [10 x 2 = 20]
Question 15.
Access the role of Ayyankali in fighting for the cause of “Untouchables”.
Answer:
(i) Ayyankali brought tremendous social changes especially in caste structure. The discrimination he faced as a child turned him into a leader of an anti-caste movement and who later fought for basic rights including access to public spaces and entry to schools.
(ii) Ayyankali challenged many caste conventions such as clothing style, he wore clothes associated with upper castes that were prohibited for lower castes.
Question 16.
How did Hitler get the support from the people of germany?
Answer:
(i) Hitler was well aware of the discontent among the Germans. He used his oratorical skills to sway the common people and promised them to return the glorious military past of Germany. He founded the National Socialist Party, generally known as “the Nazis”.
(ii) The fundamental platform on which Hitler built his support was the notion of the racial superiority of the Germans as a pure, ‘Aryan’ race and a deep-seated hatred of the Jews. Hitler came to power in 1933 and ruled Germany for twelve long years.
Question 17.
Why was Heron dismissed from service?
Answer:
- Colonel Heron was urged to deal with Puli Thevar as he continued to defy the authority of the company. Puli Thevar wielded much influence over the western Palayakkarars.
- Heron had to abandon the plan for want of cannon and of supplies and pay to soldiers. He retired to Madurai. He was then recalled and dismissed from service.
Question 18.
Why did Gandhi withdraw the Non- cooperation Movement?
Answer:
- The Non-cooperation Movement started in 1920. It soon became a nation-wide movement because it got support of the people across the country. But in February 1922, a violent incident occurred at Chauri Chaura, a village near Gorakhpur in Uttar Pradesh.
- In this incident a procession of nationalists provoked by the police turned violent. The police finding themselves outnumbered shut themselves inside the police station.
- The mob burnt the police station in which 22 policemen lost their lives. The incident hurt Gandhiji too much and he immediately withdrew the movement.
Question 19.
What are “Jet Stream”?
Answer:
In the upper layers of the atmosphere, there are strong westerly winds concentrated in a relatively narrow and shallow streams known as “Jet streams” They cause heavy rainfall in North-west India.
Question 20.
State any two characteristics of block cotton soil.
Answer:
- This soil is rich in calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash, lime and iron but deficient in phosphorous. It is clayey and impermeable which has great capacity to retain moisture for a long time.
- It becomes sticky when wet but develops cracks during dry summer season. The soil is suited for dry farming due to its high moisture retentivity.
Question 21.
Name the tributaries of river Thamirabarani.
Answer:
Karaiyar, Servalar, Manimuthar, Gadananathi, Pachaiyar, Chittar and Ramanathi are its main tributaries.
Question 22.
List out the three leads of the relations between the centre and the states.
Answer:
There are –
- Legislative relations
- Administrative relations
- Financial relations.
Question 23.
What do you know about kaladan Multi-Model Transit Transport?
Answer:
(i) India is building the Kaladan Multi-Model Transit Transport, a road-river-port cargo transport project to link Kolkata to Sittwe in Myanmar.
(ii) A project aiming to connect Kolkata with Ho Chi Minh City on the South Sea for the formation of an economic zone will have a road pass through Myanmar, Cambodia and Vietnam and work on the first phase connecting Guwahati with Mandalay is currently underway.
![]()
Question 24.
What is national emergency?
Answer:
National emergency is a situation beyond the ordinary. The President declares this emergency if he is satisfied that India’s security is threatened due to war, external aggression or armed rebellion or if there is an imminent danger or threat.
Question 25.
How the state of Jammu and Kashmir differ from the other states of India.
Answer:
- The Constitution of India grants special status to Jammu and Kashmir among Indian States, and it is the only state in India to have a separate Constitution.
- The Directive Principles of the State Policy and Fundamental Duties of the Constitution are not applicable to the State of Jammu and Kashmir.
- Rights to property, which is denied as a Fundamental Right to rest of India is still guaranteed in Jammu and Kashmir.
Question 26.
what are the factors supporting to develop the Indian economy?
Answer:
Factors supporting to develop the Indian economy :
- A fast growing population of working age.
- India has a strong legal system and many English language speakers
- Wage costs are low here.
- India’s economy has successfully developed highly advanced and attractive clusters of business in the technology space.
Question 27.
What is the main objective of WTO?
Answer:
The main objective of WTO is to set and enforce rules for international trade and to provide a forum for negotiating and monitoring further trade liberalisations.
Question 28.
Name the important multipurpose projects of Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Mettur Dam, Amaravathi Dam, Papanasam Dam, Bhavani Sagar Dam.
Part – III
Answer any 10 questions. Question No. 42 is compulsory. [10 x 5 = 50]
Question 29.
Fill in the blanks:
(i) ………………… treaty signed on February 7, 1922 created the EU.
(ii) The riverine island of Srirangam is located between …………………and ………………… branches of Cauvery.
(iii) …………………was India’s policy in the face of the bipolar order of the cold war.
(iv) In the year ………………… National Food Security Act was passed by the Indian Parliament.
(v) Tamil Nadu ranks …………………in India with a share of over 20% in total road projects under
operation in the Public Private Partnership (PPP).
Answers
(i) The Maastricht
(ii) Northern, Southern
(iii) Non-Alignment
(iv) 2013
(v) Second
Question 30.
Match the following:

Answers:

Question 31.
Match the following:

Answers:

![]()
Question 32.
(a) Distinguish between
(i) North East Monsoon and South West Monsoon
(ii) Rabi and Kharif Crop Season
Answer:
(a) (i) North East Monsoon and South East Monsoon:
North East Monsoon :
- North east monsoon occurs between October and December.
- It is Winter Monsoon.
- The coromandal coast of Tamil Nadu gets, heavy rainfall from north east monsoon.
South West Monsoon :
- Southwest Monsoon occurs between June to September.
- It is Summer Monsoon.
- The districts of Nilgiris, Kanyakumari, Salem, Coimbatore and Erode get rainfall.
(ii) Rabi and Kharif crop season:
Rabi Crop Season :
- Rabi crops are sown in the beginning of the winter (i.e.) in November.
- The crops are harvested in the beginning of summer (i.e) in March. days of November.
- Major crops are wheat, tobacco, mustard, pulses, linseed and grains.
Kharif Crop Season :
- Kharif crops are sown in the beginning of monsoon (i.e.) in June.
- The crops are harvested in the early
- Major crops are paddy, maize, cotton, millets, jute and sugarcane.
(b) Give reason: Alluvial soil is fertile
Answer:
Alluvial soil are formed by the deposition of silt by the rivers. Alluvial soils are generally fertile as they are rich in minerals such as lime, potassium, magnesium, nitrogen and phosphoric acid. It is deficient in nitrogen and humus. It is porous and loamy.
Question 33.
Discuss the main causes of the First World War.
Answer:
The causes of the First World War are given below:
- Formation of European alliances and counter alliances
- Emergence of violent forms of nationalism in countries like England, France and Germany
- Aggressive attitude of the German Emperor Kaiser Wilhelm II
- Hostility of France towards Germany
- Opportunity for imperial power politics in the Balkans
- The Balkans wars
- Immediate cause which included the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand,nephew and heir to Franz Joseph, Emperor of Austria-Hungary, by Princip, a Bosnian Serb, on 28 June 1914.
Question 34.
Discuss the causes and consequences of the Revolt of 1857?
Answer:
The Great Rebellion of 1857 is a unique example of resistance to the British authorities, in India. There were several reasons that triggered the Revolt:
(i) The annexation policy of British India created dissatisfaction among the native rulers. The British claimed themselves as paramount, exercising supreme authority. New territories were annexed on the grounds that the native rulers were corrupt, and inept.
(ii) The British annexed several territories such as Satara, Sambalpur, parts of Punjab, Jhansi and Nagpur through the Doctrine of Lapse. This also angered many Indian rulers.
(iii) Indian sepoys were upset with discrimination in salary and promotion. They were paid much less than their European counterparts. They felt humiliated and racially abused by their seniors.
Consequences:
- India was pronounced as one of the many crown colonies to be directly governed by the Parliament. This resulted in the transfer of power from the East India company to the British crown.
- Queen Victoria proclaimed to the Indian people that the British government would not interfere in traditional institutions and religious matters. It was promised that Indians would be absorbed in government services.
- There came significant changes in the Indian army. The number of Indians was reduced. Indians were restrained from holding important ranks and position.
- It was also decided that instead of recruiting soldiers from Rajputs, Brahmins and North Indian Muslims, more soldiers would be recruited from the Gorkhas, Sikhs and Pathans.
Question 35.
Bring out the characteristics of Intensive and Plantation farming.
Answer:
Intensive farming:
- It involves various types of agriculture with higher levels of input, such as capital and labour, per unit of agricultural land area.
- It aims to maximize yields from available land through various means, such as heavy use of pesticides and chemical fertilizers. ,
- Intensive farming is practiced in Punjab, parts of Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh in India.
Plantation farming:
- It is a single crop farming, practised on a large area.
- Crops are mainly grown for the market.
- It is both labour intensive and capital intensive.
- It has an interface of agriculture and industry.
- Developed network of transport and communication connecting the plantation processing industries and markets play an important role in the development of plants. Example- tea, coffee, rubber, sugarcane, etc.
![]()
Question 36.
Write an account on river Cauvery.
Answer:
- The main river of Tamil Nadu is Cauvery which originates at Talacauvery in the Brahmragiri hills of Kodagu (Coorg) district of Karnataka in the Western Ghats.
- About 416 km of its course falls in Tamil Nadu. It serves as the boundary between Karnataka
and Tamil Nadu for a distance of 64 km. A tributary called Bhavani joins Cauvery on the right bank about 45 km from the Mettur Reservoir. - Thereafter, it takes easterly course to enter into the plains of Tamil Nadu. Cauvery and its distributaries in its lower course drain the districts of Nagapattinam, Thanjavur, Thivarur and Thiruchirapalli.
- The Cauvery, Kollidam and the vellar jointly drain central part of the Tamil Nadu. The head of the Cauvery delta is near the islands of Srirangam. Kollidam branches off from cauvery at Grand Anaicut, also called as Kallanai was built across the river Cauvery.
- After Kallanai, the river breaks into a large number of distributaries and forms a network all over the delta. The network of tributaries within the delta of cauvery in the coast is called as the ‘Garden of Southern India’.
- It merges into Bay of Bengal to the south of Cuddalore. Cauvery along with its tributaries Bhavani, Noyyal, Mayar and Amaravathi is the most important source of canal irrigation.
Question 37.
Write briefly on the Right to Constitutional Remedies.
Answer:
(i) Our Constitution guarantees six Fundamental Rights to its citizens. It safeguards all these rights by granting us the Right to Constitutional Remedies. It is possible that the Government or private bodies may violate one of our Fundamental Rights.
(ii) Right to Constitutional Remedies protects us from such violations. It allows us to file a case against the Government or private bodies in the High Courts of the States and the Supreme Court of the India.
(iii) Both the Supreme Court and High Courts are empowered to issue five kinds of writs of habeas corpus, mandamus, prohibition two warrants and certiorari to protect the Fundamental Rights of the citizens. That is why the Supreme Court is called the “Guardian of the Constitutions”.
Question 38.
Briefly discuss the Functions of the State Legislature.
Answer:
The powers and functions of the State Legislature are almost the same as that of the Parliament.
- The State Legislature can pass laws on all subjects mentioned in the State List as per the constitutions. It can also pass laws on concurrent subjects.
- The Legislature controls the finances of the State. The Lower House enjoys greater power than the Upper House in money matters. Money Bills can be introduced only in the Lower House of the Assembly.
- The Legislature controls the Executive. The council of Ministers is responsible to the Assembly. The ministers have to answer questions asked by the members of the Legislature.
- The Council cannot vote for grants.
- No new tax can be levied without the sanction and permission of the Assembly.
Question 39.
Briefly explain the evolution of M[NC and its advantages and disadvantages.
Answer:
Multinational companies first started their activities in the extractive industries and controlled raw materials in the host countries during 1920s and then entered the manufacturing and service sectors after 1950s. Most of the MNCs at present belong to the four major exporting countries i.e., USA, UK, France and Germany. However, the largest is America. In 1971, the American Corporations held 52% of the total world stock of foreign direct inverstment.
Great Britain held 14.5% followed by France 5% and Federal Republic of Germany 4.4% and Japan 2.7%.
Advantages of MNCs:
- MNCs produce the same quality of goods at lower cost and without transaction cost.
- They reduce prices and increase the purchasing power of consumers world wide.
- They are able to take advantage of tax variation.
- They spur job growth in the local economy.
Disdvantages of MNCs:
(i) They have led to the downfall of smaller, local business.
(ii) With more companies transferring offices and centering operations in other countries, jobs for the people living in developed countries are threatened.
(iii) MNCs often invest in developing countries where they can take advantage of cheaper labour. Some MNCs prefer to put up branches in these parts of the world where there are no stringent policies in labour and where people need jobs because these MNCs can demand for cheaper labour and lesser healthcare benefits.
Question 40.
Write a note on history of industrialisation in Tamil Nadu.
Answer:
Industrialisation in the Colonial Period:
- The introduction of cotton cultivation in western and southern Tamil Nadu by the colonial government led to the emergence of a large-scale textile sector in these parts, which involved ginning, pressing, spinning and weaving operations.
- Introduction of railways also expanded the market for cotton yam and helped develop the sector.
- There was increase in trade during this period which led to industrial development. The two active ports in the region were Chennai and Tuticorin.
- In Western Tamil Nadu, the emergence of textiles industries also led to demand and starting of textile machinery industry in the region.
Post-Independence to early 1990s:
- After independence, several large enterprises were set up by both the central and state governments.
- The Integral Coach Factory in Chennai made railway coaches and the Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) in Tiruchirapalli manufactured boilers and turbines.
- Ashok Motors and Standard Motors together helped form an automobile cluster in the Chennai region.
- The 1970s and 1980s saw the setting up of emergence of powerloom weaving clusters in the Coimbatore region as well as expansion of cotton knitwear cluster in Tiruppur and home furnishings cluster in Karur.
- The Hosur industrial cluster is a successful case of how such policy efforts to promote industrial estates helped develop industries in a backward region.
Industrialisation in Tamil Nadu – Liberalization Phase:
- The final phase of industrialisation is the post-reforms period since the early 1990s.
- Because of trade liberalisation measures, exports of textiles, home furnishings and leather products began to grow rapidly.
- Efforts to attract investments led to entry of leading multinational firms (MNCs) into the state, especially in the automobile sector.
- Chennai region also emerged as a hub for electronics industry with MNCs such as Nokia, Foxconn, Samsung and Flextronics opening plants on the city’s outskirts.
- A significant share of these investments has come up in special economic zones in the districts bordering Chennai.
- The major industries are automobiles, autocomponents, light and heavy engineering, machinery, cotton, etc.
- This diffused process of industrialisation and corresponding urbanisation has paved the way for better rural-urban linkages in Tamil Nadu than in most other states.
![]()
Question 41.
Draw a time line for the following:
Write any five important events between 1905-1920
Answer:

Question 42.
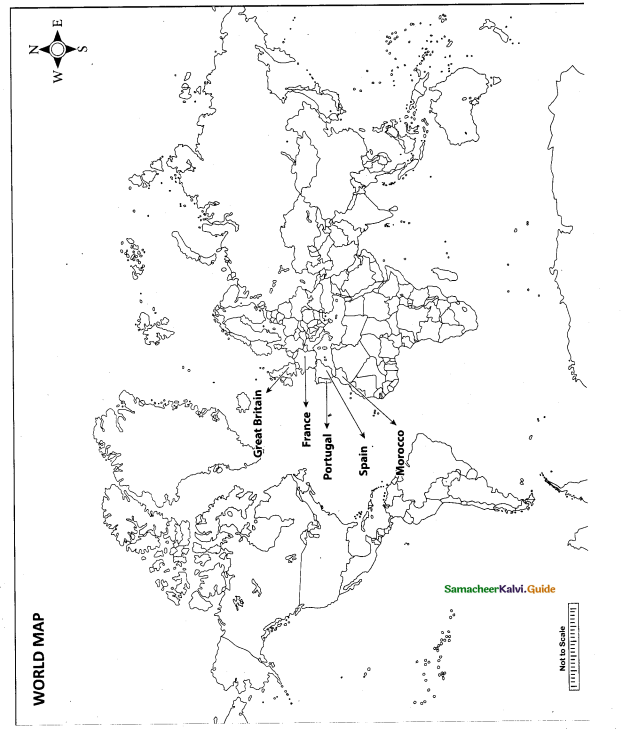
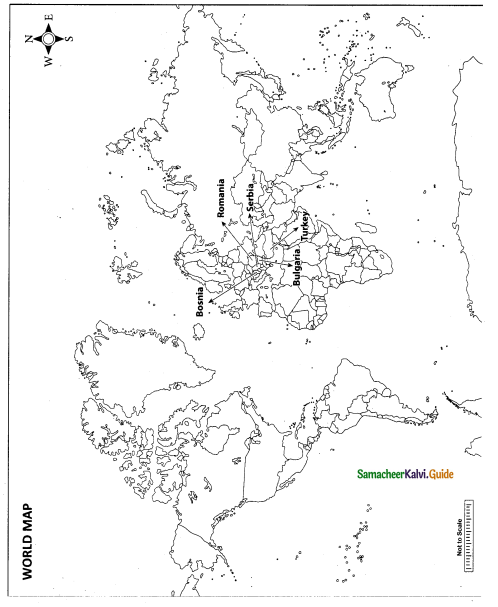
Mark the following places on the world map.
(i) Portugal
(ii) Spain
(iii) Morocco
(iv) France
(v) Great Britian
Answer:
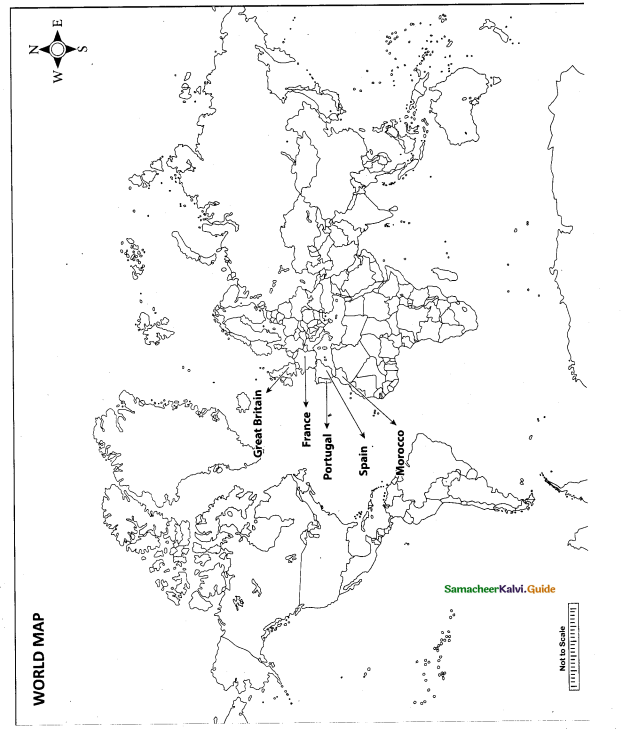
![]()
Part – IV
Answer both questions. [2 x 8 = 16]
Question 43.
(a) Battle of Stalingrad
(i) When did Germany attack Stalingrad?
(ii) What were the main manufactures of Stalingrad?
(iii) What was the name of the plan formulated by Hitler to attack Stalingrad?
(iv) What is the significance of the Battle of Stalingrad?
Answer:
(a) Battle of Stalingrad:
(i) In August 1942, Germany attacked Stalingrad.
(ii) The main manufactures of Stalingrad were armaments and tractors.
(iii) Fall Blau or Operation Blue
(iv) The people of Russia were grateful for Stalin’s conduct of the war. They regarded him as ‘a prodigy of patience, tenacity and vigilance, almost omnipresent, almost omniscient.’
(b) Political developments in South America.
(i) By which year did the whole of South America become free from European domination?
(ii) How many republics came into being from the Central America?
(iii) In which year was Cuba occupied by the USA?
(iv) What made oligarchic regimes unpopular in South America?
Answer:
(b) Political developments in South America:
(i) By 1830 the whole of South America was free from European domination.
(ii) Five republics came into being from the Central America.
(iii) The USA occupied Cuba in the year 1898.
(iv) Economic growth, urbanisation and industrial growth in countries like Argentina, Chile, Brazil, and Mexico helped consolidate the hold of middle class and the emergence of militant working class oganisations. At the same time American power and wealth came to dominate Central and South America. These factors made olgarchic regimes unpopular in South America.
[OR]
(c) Gandhi and Mass nationalism.
(i) Which incident is considered a turning point in the life of Gandhi?
(ii) Name the works that influenced Gandhi?
(iii) How did Gandhi use satyagraha as a strategy in South Africa?
(iv) What do you know about the Champaran Satyagraha?
Answer:
(c) Gandhi and Mass nationalism:
(i) On his journey from Durban to Pretoria, at the Pietermaritzburg railway station, he was physically thrown out of the first class compartment in which he was travelling despite having a first class ticket. This incident is considered a turning point in the life of Gandhi.
(ii) Tolstoy’s The Kingdom of God is Within You, Ruskin’s Unto This Last and Thoreau’s Civil Disobedience.
(iii) Gandhi developed satyagraha (truth-force) as a strategy, in which campaigners went on peaceful marches and presented themselves for arrest in protest against unjust laws.
(iv) The Champaran Satyagraha of 1916 was the first satyagraha movement inspired by Gandhi. It was a farmer’s uprising that took place in Champaran district of Bihar, India during the British colonial period.
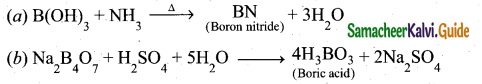
(d) Periyar E. V. R.
(i) When did Periyar found Dravidar Kazhagam?
(ii) What were the Newspapers and Journals run by Periyar?
(iii) Why was Periyar known as Vaikom hero?
(iv) Which was the most important work of Periyar?
Answer:
(d) Periyar E. V. R.
(i) Periyar found Dravidar Kazhagam in 1944.
(ii) The newspapers and journals started by Periyar were – Kudi Arasu, Revolt, Puratchi, Paguththarivu and Viduthalai.
(iii) In Vaikom, people protested against the practice of no access to the temples by the lower caste people. After the local leaders were arrested Periyar led the Temple Entry Movement and was imprisoned. So, people hailed him as Vaikom Virar or hero of Vaikom.
(iv) Right from 1929, when the Self-respect Conferences began to voice its concern over the plight of women, Periyar had been emphasising women’s right to divorce and property. Periyar’s most important work on this subject is Why the Woman is Enslaved.
![]()
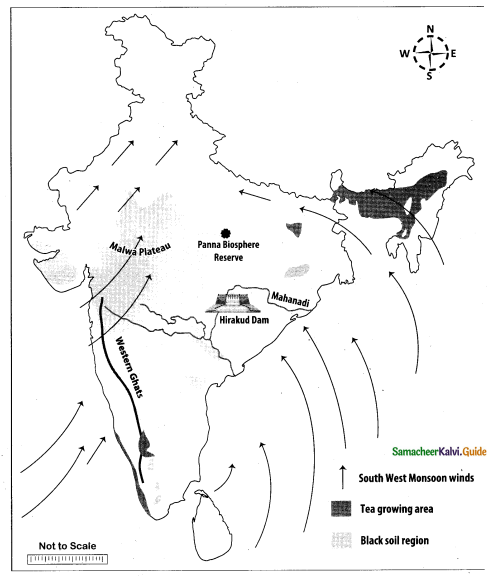
Question 44.
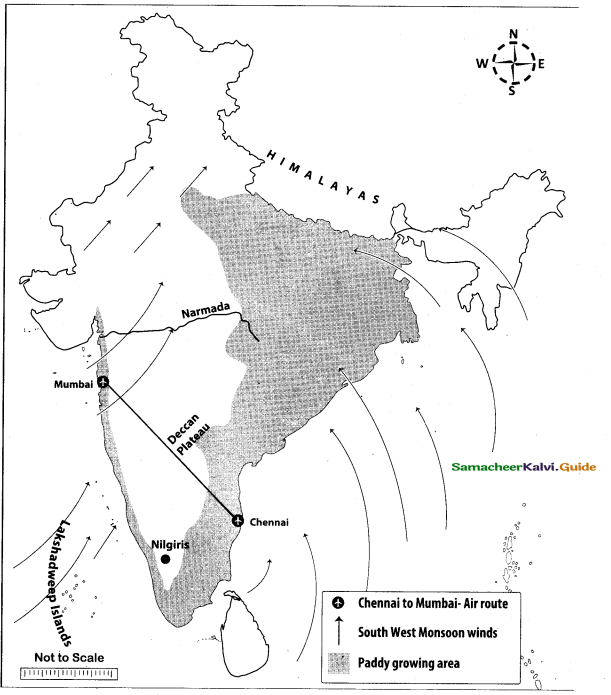
Mark the following places on the given outline map of India.
(i) Himalayas
(ii) Nilgiris
(iii) Narmada
(iv) Lakshadweep
(v) Deccan Plateau
(vi) Southwest Monsoon
(vii) Paddy growing area
(viii) Chennai to Mumbai air route
Answer:
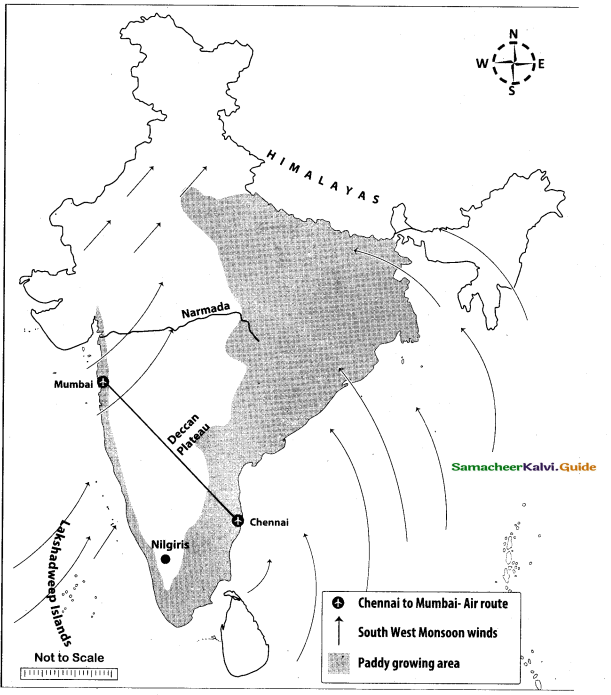
[OR]
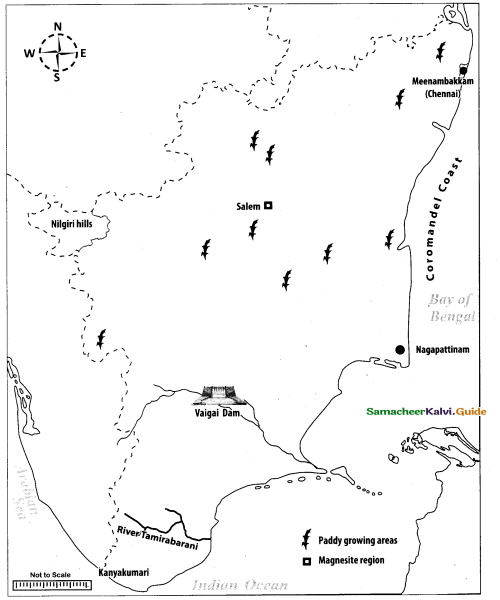
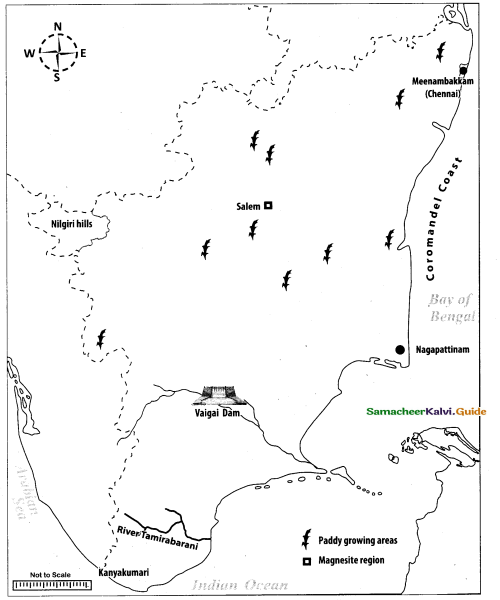
Mark the following places are given outline map of Tamil Nadu:
(i) Coromandel coast
(ii) Paddy growing area
(iii) Nilgiri Hills
(iv) Nagapattinam
(v) Meenambakkam
(vi) Thamirabarani
(vii) Magnesite region (any one place)
(viii) Vaigai Dam
Answer:
Map for Q. 42
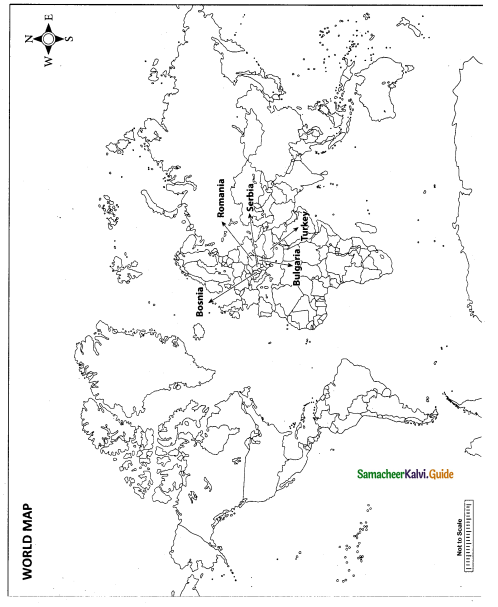
(i) Portugal
(ii) Spain
(iii) Morocco
(iv) France
(v) Great Britain
Answer:
Map for Q. 44
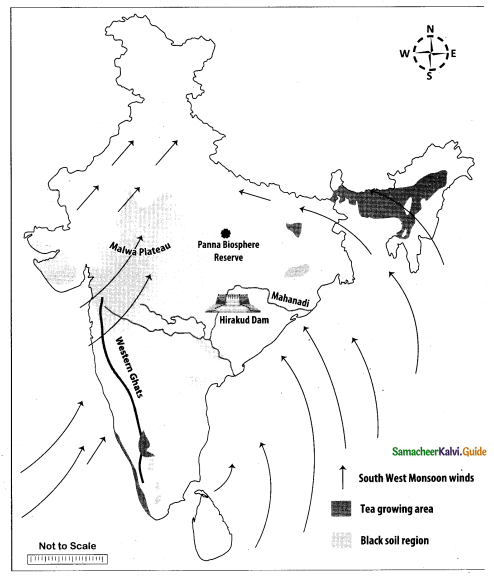
(i) Himalayas
(ii) Nilgiris
(if) Narmada
(iv) Lakshadwccp
(v) Deccan Plateau
(vi) Southwest Monsoon
(vii) Paddy growing area
(viii) Chennai to Mumbai air route
Answer:
Map for Q. 44
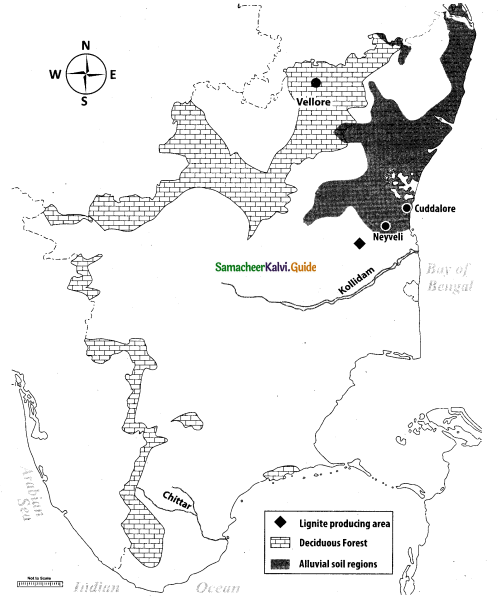
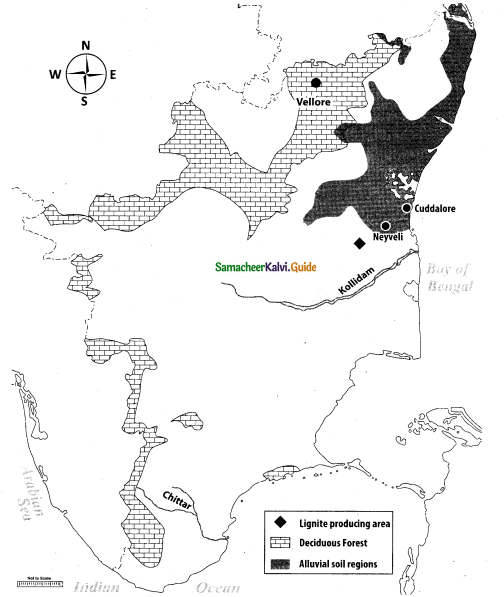
(i) Coromandel coast
(ii) Paddy growing area
(iii) Nilgiri Hills
(iv) Nagapattinam
(v) Meenambakkam
(vi) Thamirabarani
(vii) Magnesite region (any one place)
(viii) Vaigai Dam
Answer:






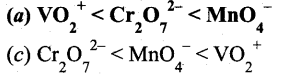
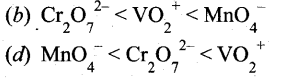


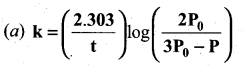
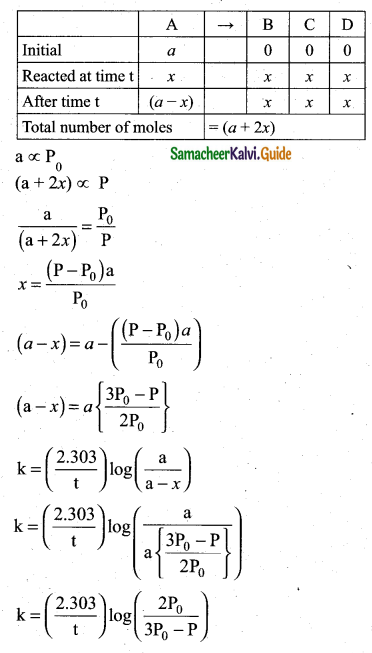


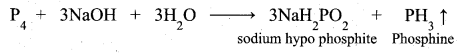
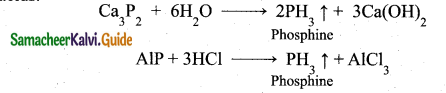
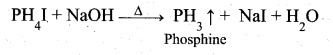
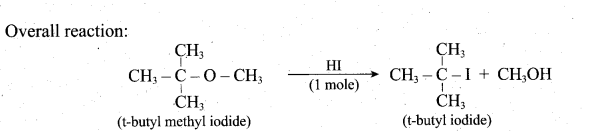
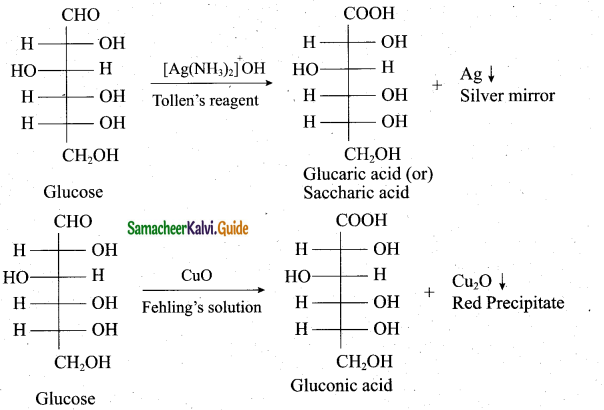
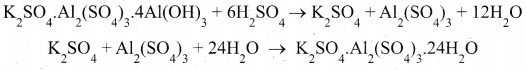 (2)
(2)