Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Physics Model Question Paper 2 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th Physics Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
TN State Board 11th Physics Model Question Paper 2 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 15 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each.
These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer - Question numbers 16 to 24 in Part II are two-mark questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 25 to 33 in Part III are three-mark questions. These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 34 to 38 in Part IV are five-mark questions. These are to be answered in detail Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
PART – I
Answer all the questions: [15 × 1 = 15]
Question 1.
If the error in the measurement of radius is 2%, then the error in the determination of volume of the sphere will be ………………..
(a) 8%
(b) 2%
(c) 4%
(d) 6%
Hint:
Volume of the sphere, V = \(\frac{4}{3}\) πr3
\(\frac{∆V}{V}\) × 100 = 3 × (\(\frac{∆r}{r}\) × 100) = 3 × 2%
\(\frac{∆V}{V}\) × 100 = 6%
Answer:
(d) 6%
![]()
Question 2.
A ball is dropped from a building. It takes 4s to reach the ground. The height of the building is (use g= 10 m/s2)
(a) 20 m
(b) 40 m
(c) 80 m
(d) 75 m
Hint:
s = ut + \(\frac{1}{2}\) at2 s = h, g = a, u = 0
h = \(\frac{1}{2}\) gt2
h = \(\frac{1}{2}\) × 10 × (4)2; h = 80m
Answer:
(c) 80 m
Question 3.
For inelastic collision between two spherical rigid bodies ……………………
(a) the total kinetic energy is conserved
(b) the total mechanical energy is not conserved
(c) the linear momentum is not conserved
(d) the linear momentum is conserved
Answer:
(d) the linear momentum is conserved
![]()
Question 4.
Two rods OA and OB of equal length and mass are lying on xy plane as shown in figure. Let Ix, Iy and Iz be the moments of inertia of the the rods about x, y and z axis respectively, then …………………….
(a) Ix = Iy > Iz
(b) Ix > Iy > Iz
(c) Ix = Iy < Iz
(d) Iz > Iy > Ix
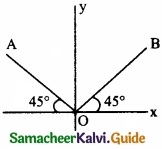
Hint:
Ix = Iy = 2\(\left[\frac{\mathrm{M} l^{2}}{3} \sin ^{2} 45^{\circ}\right]\) = \(\frac { ml^{ 2 } }{ 3 }\)
Iz = \(\left[\frac{m l^{2}}{3}\right]\) = \(\frac { 2ml^{ 2 } }{ 3 }\)
Answer:
(c) Ix = Iy < Iz
Question 5.
The motion of a rocket is based on the principle of conservation of ………………….
(a) Linear momentum
(b) Mass
(c) Angular momentum
(d) Kinetic energy
Answer:
(a) Linear momentum
![]()
Question 6.
The work done by the Sun’s gravitational force on the Earth is ………………….
(a) Always zero
(b) Always positive
(c) Can be positive or negative
(d) Always negative
Answer:
(c) Can be positive or negative
Question 7.
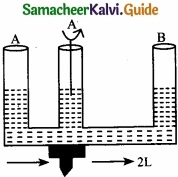
A given glass tube having uniform cross section is filled with water and is mounted on a rotatable shaft as shown. If the tube is rotated with a constant angular velocity ω, then …………………
(a) Water levels in both sections A and B go up
(b) Water level in section A goes up and that in B comes down
(c) Water level in section B goes up and that in A comes down
(d) Water level remain same in both
Answer:
(a) Water levels in both sections A and B go up
Question 8.
The efficiency of a heat engine working between the freezing point and boiling point of water is …………………..
(a) 6.25%
(b) 20%
(c) 26.8%
(d) 12.5%
Hint:
Freezing point of water TL = 0°C = 273K
Boiling point of water TH – 100°C = 373K
∴ Efficiency, η = 1 – \(\frac { T_{ L } }{ T_{ H } } \) = 1- \(\frac{273}{373}\) = 0.2861; η = 26.8%.
Answer:
(c) 26.8%
![]()
Question 9.
Two waves represented by the following equation are travelling in the same medium
y1 = 5 sin 2π (75 t – 0.25 x), y2 = 10 sin 2π (150 – 0.25 x)
The intensity ratio of the two waves is ………………….
(a) 1 : 2
(b) 1 : 4
(c) 1 : 8
(d) 1 : 16
Hint:
I ∝ A2 ⇒ \(\frac { I_{ 1 } }{ I_{ 2 } }\) = (\(\frac { A_{ 1 } }{ A_{ 2 } }\))2 = (\(\frac{5}{2}\))2 = \(\frac{1}{4}\)
Answer:
(b) 1 : 4
Question 10.
A man pushes a wall and fails to displace it. He does …………………..
(a) Negative work
(b) Positive but not maximum work
(c) No work at all
(d) Maximum work
Answer:
(c) No work at all
![]()
Question 11.
A car moving on a horizontal road may be thrown out of the road in taking a turn …………………
(а) By the gravitational force
(b) Due to lack of sufficient centripetal force
(c) Due to rolling frictional force between tyre and road
(d) Due to the reaction of the ground
Answer:
(b) Due to lack of sufficient centripetal force
Question 12.
The volume of a gas expands by 0.25 m3 at a constant pressure of 103 N/m, the workdone is equal to ……………………..
(a) 250 W
(b) 2.5 W
(c) 250 N
(d) 250 J
Hint:
Workdone = P. ∆V = 103 × 0.25 = 250 J
Answer:
(d) 250 J
![]()
Question 13.
When three springs of spring constants k1, k2, k3 connected in parallel, then the resultant spring constant is ……………………
(a) K = k1 + k2 + k3
(b) \(\frac{1}{K}\) = \(\frac { 1 }{ k_{ 1 } } +\frac { 1 }{ k_{ 2 } } +\frac { 1 }{ k_{ 3 } } \)
(c) K = \(\frac { 1 }{ k_{ 1 } } +\frac { 1 }{ k_{ 2 } } +\frac { 1 }{ k_{ 3 } } \)
(d) K = k1 – k2 – k3
Answer:
(a) K = k1 + k2 + k3
Question 14.
The distance of the two planets from Sun are 1013 and 1012 m respectively. The ratio of time period of the planets is …………………..
(a) 100
(b) \(\frac { 1 }{ \sqrt { 10 } } \)
(c) \(\sqrt{10}\)
(d) 10\(\sqrt{10}\)
Hint:
According to Kepler’s third law of planetary motion.
\(\frac { T_{ 1 } }{ T_{ 2 } } \) = \(\sqrt{\frac{R_{1}^{3}}{R_{2}^{3}}}\) = \(\sqrt{\frac{\left(10^{13}\right)^{3}}{\left(10^{12}\right)^{3}}}\) = \(\sqrt{\frac{10^{39}}{10^{36}}}\) = \(\sqrt{10^{3}}\) = 10\(\sqrt{10}\)
Answer:
(d) 10\(\sqrt{10}\)
![]()
Question 15.
The dimensional formula of planck’s constant is ………………..
(a) [M L2 T-1]
(b) [M L2 T-3]
(c) [M L T-1]
(d) [M L3 T-3]
Answer:
(a) [M L2 T-1]
PART – II
Answer any six questions in which Q. No 23 is compulsory. [6 × 2 = 12]
Question 16.
A particle is moving along a circular track of radius lm with uniform speed. What is the ratio of the distance covered and the displacement in half revolution?
Answer:
Distance covered by a particle = π × 1 = πm
Displacement covered by a particle = 2 × 1 = 2m
Ratio between distance and displacement
![]()
Question 17.
Give one argument in favour of the fact that frictional force is a non-conservative force?
Answer:
The direction of the frictional force is opposite to the direction of motion. When a body is moved, say from A to B and then back to A, work is required to be done both during forward and backward motion. So, the net workidone in a round trip is not zero. Hence, the frictional force is a non-conservative force.
Question Question 18.
Why does a gas not have a unique value of specific heat?
Answer:
This is because a gas can be heated under different conditions of pressure and volume. The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of unit mass through unit degree is different under different conditions of heating.
Question 19.
A boat which has a speed of 5 km/h in still water crosses a river of width 1 km along the shortest path in 15 min. Calculate the velocity of river water in km/h?
Answer:
Resultant velocity = \(\frac{1km}{(15/60)h}\) = 4 km/h
If v is velocity of river, then v2 + 42 = 52 ⇒ v = \(\sqrt{2-16}\) =3 km/h
![]()
Question 20.
In a dark room would you be able to tell whether a given note had been produced by a Piano or a Violin?
Answer:
Yes, in a dark room we can easily identify a sound produced by a Piano or a Violin by using the knowledge of timber or quality of sound. The two sources even though having the same intensity and fundamental frequency will be associated with different number of overtones of different relative intensities. These overtones combine and produce different sounds which enables us to identify them.
Question 21.
What is mean by P – V diagram?
Answer:
PV diagram is a graph between pressure P and volume V of the system. The P-V diagram is used to calculate the amount of work done by the gas during expansion or on the gas during compression.
Question 22.
Why does a parachute descend slowly?
Answer:
The surface area of a parachute is much larger as compared to the surface area of stone. So, the air resistance in the case of a parachute is much larger than in the case of a stone. This explains as to why parachute descends slowly.
![]()
Question 23.
What is Brownian motion?
Answer:
The motion of the particles in a random and zig-zag mannar in a fluid is called Brownian motion.
Question 24.
Write a note on reverberation?
Answer:
The persistence of audible sound after the source has ceased to emit sound is called reverberation.
PART – III
Answer any six questions in which Q.No. 29 is compulsory. [6 × 3 = 18]
Question 25.
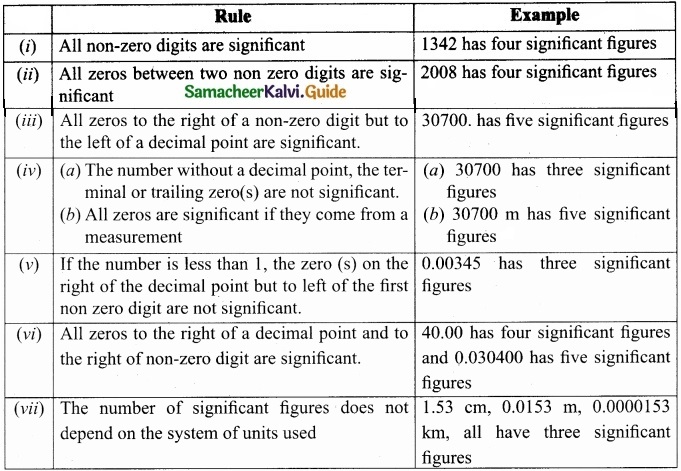
Write the rules for determining significant figure?
Answer:
Rules for counting significant figures:
Question 26.
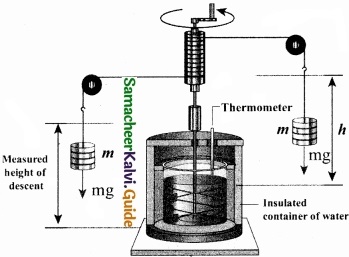
Explain Joule’s experiment of the mechanical equivalent of heat?
Answer:
Joule’s mechanical equivalent of heat:
The temperature of an object can be increased by heating it or by doing some work on it. In the eighteenth century, James Prescott Joule showed that mechanical energy can be converted into internal energy and vice versa. In his experiment, two masses were attached with a rope and a paddle wheel as shown in Figure. When these masses fall through a distance h due to gravity, both the masses lose potential energy equal to 2 mgh.
When the masses fall, the paddle wheel turns. Due to the turning of wheel inside water, frictional force comes in between the water and the paddle wheel. This causes a rise in temperature of the water. This implies that gravitational potential energy is converted to internal energy of water.
The temperature of water increases due to the work done by the masses. In fact, Joule was able to show that the mechanical work has the same effect as giving heat. He found that to raise 1 g of an object by 1°C , 4.186 J of energy is required. In earlier days the heat was measured in calorie. 1 cal = 4.186 J This is called Joule’s mechanical equivalent of heat.
Question 27.
How do you classify the physical quantities on the basis of dimension?
Answer:
(I) Dimensional variables:
Physical quantities, which possess dimensions and have variable values are called dimensional variables. Examples are length, velocity, and acceleration etc.
(II) Dimensionless variables:
Physical quantities which have no dimensions, but have variable values are called dimensionless variables. Examples are specific gravity, strain, refractive index etc.
(III) Dimensional Constant:
Physical quantities which possess dimensions and have constant values are called dimensional constants. Examples are Gravitational constant, Planck’s constant etc.
(IV) Dimensionless Constant:
Quantities which have constant values and also have no dimensions are called dimensionless constants. Examples are n, e, numbers etc.
![]()
Question 28.
State laws of simple pendulum?
Answer:
Law of length:
For a given value of acceleration due to gravity, the time period of a simple pendulum is directly proportional to the square root of length of the pendulum.
T ∝ \(\sqrt{l}\)
Law of acceleration:
For a fixed length, the time period of a simple pendulum is inversely proportional to square root of acceleration due to gravity.
T ∝ \(\frac { 1 }{ \sqrt { g } } \)
Question 29.
Explain super position principle for gravitational field?
Answer:
The total gravitational field at a point due to all the masses is given by the vector sum of the gravitational field due to the individual masses. This principle is known as superposition of
\(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}_{\text {total }}=\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}_{1}+\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}_{2}+\ldots \overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}_{n}=-\frac{\mathrm{G} m_{1}}{r_{1}^{2}} \hat{r}_{1}-\frac{\mathrm{G} m_{2}}{r_{2}^{2}} \hat{r}_{2}-\ldots \cdot \frac{\mathrm{G} m_{n}}{r_{n}^{2}} \hat{r}_{n}\)
\(\overrightarrow{\mathrm{E}}_{\mathrm{total}}=-\sum_{i=1}^{n} \frac{\mathrm{G} m_{n}}{r_{n}^{2}} \hat{r}_{n}\)
![]()
Question 30.
Write a note on static friction?
Answer:
Static Friction:
Static friction is the force which opposes the initiation of motion of an object on the surface. The magnitude of static frictional force fs lies between
0 ≤ fs ≤ µsN
where, µs – coefficient of static friction
N – Normal force then, equation shows that fs can take any value from 0 & µsN. If object is at rest, when no external force acts on it then fs = 0. If object is at rest, also external force acts on it, then fs = Fext
But still the static friction fs is less than µsN when object begins to slide, the static friction (fs) acting on the object attains maximum.
Question 31.
A small metal ball falls in liquid with a terminal velocity of V. If a ball of radius twice of first ball but same mass falls through a same medium, calculate the terminal velocity with which it falls?
Answer:
Given v = \(\frac{2 r^{2} \rho g}{9 \eta}\)
mass = \(\frac{4}{3}\) πr3 ρ = \(\frac{4}{3}\)π(2r)3 ρ1 or ρ1 = \(\frac{ρ}{8}\)
Terminal velocity of second ball is
v1 = \(\frac{2(2 r)^{2}\left(\frac{\rho}{8}\right) g}{9 \eta}\) = \(\frac{v}{2}\)
v1 = \(\frac{v}{2}\)
![]()
Question 32.
Derive an expression for co-efficient of performance of refrigerator?
Answer:
Coefficient of performance (COP) (β):
COP is a measure of the efficiency of a refrigerator. It is defined as the ratio of heat extracted from the cold body (sink) to the external work done by the compressor W.
COP = β = \(\frac { Q_{ L } }{ W } \) …………………… (1)
From the equation QL + W = QH
β = \(\frac{Q_{L}}{Q_{H}-Q_{L}}\)
β = \(\frac{1}{\frac{\mathrm{Q}_{\mathrm{H}}}{\mathrm{Q}_{\mathrm{L}}}-1}\) ………………. (2)
But we know that \(\frac { Q_{ H } }{ Q_{ L } } \) = \(\frac { T_{ H } }{ T_{ L } } \)
Substituting this equation (1) we get β = \(\frac{1}{\frac{T_{H}}{T_{L}}-1}\) = \(\frac{\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{L}}}{\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{H}}-\mathrm{T}_{\mathrm{L}}}\)
![]()
Question 33.
Derive an expression for Laplace’s correction?
Answer:
Laplace’s correction:
In 1816, Laplace satisfactorily corrected this discrepancy by assuming that when the sound propagates through a medium, the particles oscillate very rapidly such that the compression and rarefaction occur very fast. Hence the exchange of heat produced due to compression and cooling effect due to rarefaction do not take place, because, air (medium) is a bad conductor of heat.
Since, temperature is no longer considered as a constant here, sound propagation is an adiabatic process. By adiabatic considerations, the gas obeys Poisson’s law (not Boyle’s law as Newton assumed), which is
PVγ = Constant …………… (4)
where, γ = \(\frac { C_{ p } }{ C_{ v } } \) which is the ratio between specific heat at constant pressure and specific heat at constant volume.
Differentiating equation (4) on both the sides, we get
\(\mathrm{V}^{\gamma} d \mathrm{P}+\mathrm{P}\left(\gamma \mathrm{V}^{\gamma-1} d \mathrm{V}\right)=0\)
or
\(\gamma \mathrm{P}=-\mathrm{V} \frac{d p}{d \mathrm{V}}=\mathrm{B}_{\mathrm{A}}\) ………………… (5)
where, BA is the adiabatic bulk modulus of air. Now, substituting equation (5) in equation
V = \(\sqrt{\frac{B}{\rho}}\), the speed of sound in air is
va = \(\sqrt{\frac{B_{A}}{\rho}}=\sqrt{\frac{\gamma P}{\rho}}=\sqrt{\gamma v_{T}}\)
Since air contains mainly, nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen etc, (diatomic gas), we take γ = 1.47. Hence, speed of sound in air is va = (\(\sqrt{1.4}\)) (280m s-1) = 331.30 m s-1, which is very much closer to experimental data.
PART – IV
Answer all the questions. [5 × 5 = 25]
Question 34 (a).
Explain different types of error?
Answer:
The uncertainty in a measurement is called an error. Random error, systematic error and gross error are the three possible errors.
(I) Systematic errors:
Systematic errors are reproducible inaccuracies that are consistently in the same direction. These occur often due to a problem that persists throughout the experiment. Systematic errors can be classified as follows
(i) Instrumental errors:
When an instrument is not calibrated properly at the time of manufacture, instrumental errors may arise. If a measurement is made with a meter scale whose end is worn out, the result obtained will have errors. These errors can be corrected by choosing the instrument carefully.
(ii) Imperfections in experimental technique or procedure:
These errors arise due to the limitations in the experimental arrangement. As an example, while performing experiments with a calorimeter, if there is no proper insulation, there will be radiation losses. This results in errors and to overcome these, necessary correction has to be applied
(iii) Personal errors:
These errors are due to individuals performing the experiment, may be due to incorrect initial setting up of the experiment or carelessness of the individual making the observation due to improper precautions.
(iv) Errors due to external causes:
The change in the external conditions during an experiment can cause error in measurement. For example, changes in temperature, humidity, or pressure during measurements may affect the result of the measurement.
(v) Least count error:
Least count is the smallest value that can be measured by the measuring instrument, and the error due to this measurement is least count error. The instrument’s resolution hence is the cause of this error. Least count error can be reduced by using a high precision instrument for the measurement.
(II) Random errors:
Random errors may arise due to random and unpredictable variations in experimental conditions like pressure, temperature, voltage supply etc. Errors may also be due to personal errors by the observer. Who performs the experiment. Random errors are sometimes called “chance error”. When different readings are obtained by a person every time he repeats the experiment, personal error occurs.
For example, consider the case of the thickness of a wire measured using a screw gauge. The readings taken may be different for different trials. In this case, a large number of measurements are made and then the arithmetic mean is taken.
If n number of trial readings are taken in an experiment, and the readings are
a1, a2, a3, ………………. an. The arthematic mean is
\(a_{m}=\frac{a_{1}+a_{2}+a_{3}+\ldots \ldots \ldots a_{n}}{n}\) (or) \(a_{m}=\frac{1}{n} \sum_{i=1}^{i=n} a_{i}\)
[OR]
(b) By using equations of motion, derive an expression for range and maximum height reached by the object thrown at an oblique angle θ with respect to the horizontal direction?
Answer:
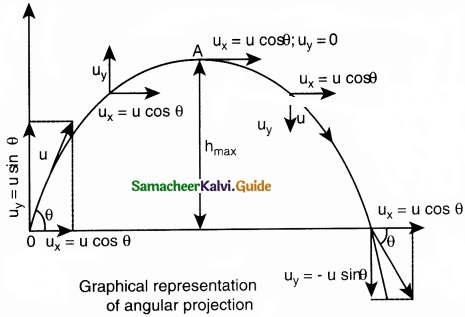
This projectile motion takes place when the initial velocity is not horizontal, but at some angle with the vertical, as shown in Figure.
(Oblique projectile):
Examples:
- Water ejected out of a hose pipe held obliquely.
- Cannot fired in a battle ground.
Consider an object thrown with initial velocity at an angle 0 with the horizontal.
Then,
\(\vec { u } \) = ux\(\hat { i } \) + uy\(\hat { j } \)
where ux = u cos θ is the horizontal component and uy = u sin θ the vertical component of velocity.
Since the acceleration due to gravity is in the direction opposite to the direction of vertical component uy, this component will gradually reduce to zero at the maximum height of the projectile.
At this maximum height, the same gravitational force will push the projectile to move downward and fall to the ground. There is no acceleration along the x direction throughout the motion. So, the horizontal component of the velocity (ux = u cos θ) remains the same till the object reaches the ground.
Hence after the time f, the velocity along horizontal motion vx = ux + axt = ux = u cos θ.
The horizontal distance travelled by projectile in time t is sx = uxt + \(\frac{1}{2}\)axt2
Here, sx = x, ux = u cos θ, ax = 0.
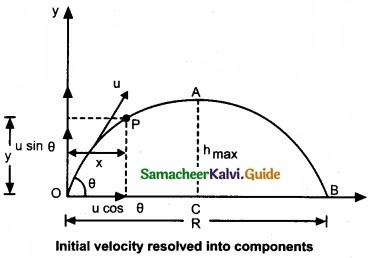
Thus, x = u cos θ.t or t = \(\frac{x}{u cosθ}\) …………….. (1)
Next, for the vertical motion vy= uy + ayt
Here uy = u sin θ, ay = – g (acceleration due to gravity acts opposite to the motion).
Thus, vy = u sin θ – gt
The vertical distance travelled by the projectile in the same time t is
Here, sy = y, uy = u sin θ, ax = – g Then,
y = u sin θ t – \(\frac{1}{2}\)gt2 ……………….. (2)
Subsitute the value of t from equation (i) and equation (ii), we have
y = \(u \sin \theta \frac{x}{u \cos \theta}-\frac{1}{2} g \frac{x^{2}}{u^{2} \cos ^{2} \theta}\)
y = \(x \tan \theta-\frac{1}{2} g \frac{x^{2}}{u^{2} \cos ^{2} \theta}\) ………………… (3)
Thus the path followed by the projectile is an inverted parabola.
Maximum height (hmax):
The maximum vertical distance travelled by the projectile during the journey is called maximum height. This is determined as follows:
For the vertical part of the motion
\(v_{y}^{2}=u_{y}^{2}+2 a_{y} s\)
Here, uy = u sin θ, a = -g, s = hmax, and at the maximum height vy = 0
Hence, (0)2 = u2 sin2 θ = 2ghmax
or
hmax = \(\frac{u^{2} \sin ^{2} \theta}{2 g}\) …………….. (4)
Time of flight (Tf):
The total time taken by the projectile from the point of projection till it hits the horizontal plane is called time of flight.
This time of flight is the time taken by the projectile to go from point O to B via point A as shown in figure.
We know that sy = uyt + \(\frac{1}{2}\) ayt2
Here, sy = y = 0 (net displacement in y-direction is zero), uy = u sin θ, ay = -g, t = Tf.
Then 0 = u sinθ Tf – \(\frac{1}{2}\)gT2f
Tf = 2u \(\frac{sin θ}{g}\) …………………. (5)
Horizontal range (R):
The maximum horizontal distance between the point of projection and the point on the horizontal plane where the projectile hits the ground is called horizontal range (R). This is found easily since the horizontal component of initial velocity remains the same. We can write
Range R = Horizontal component of velocity x time of flight = u cos θ × Tf = \(\vec{r}_{1} \times \vec{r}_{2}\)
The horizontal range directly depends on the initial speed (u) and the sine of angle of projection (θ). It inversely depends on acceleration due to gravity ‘g’.
For a given initial speed u, the maximum possible range is reached when sin 2θ is maximum,
sin 2θ = 1. This implies 2θ = π/2
or θ = \(\frac{π}{4}\)
This means that if the particle is projected at 45 degrees with respect to horizontal, it attains maximum range is given by.
Rmax = \(\frac { u^{ 2 } }{ g }\) ……………….. (6)
![]()
Question 35 (a).
Explain in detail the triangle law of vector addition?
Answer:
Let us consider two vectors \(\vec { A } \) and \(\vec { B } \) as shown in figure.
To find the resultant of the two vectors we apply the triangular law of addition as follows: Represent the vectors \(\vec { A } \) and \(\vec { B } \) by the two adjacent sides of a triangle taken in the same order. Then the resultant is given by the third side of the triangle as shown in figure.
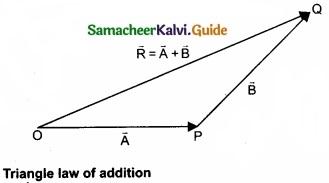
To explain further, the head of the first vector \(\vec { A } \) is connected to the tail of the second vector \(\vec { B } \). Let 0 be the angle between A and B. Then R is the resultant vector connecting the tail of the first vector \(\vec { A } \) to the head of the second vector \(\vec { B } \).
The magnitude of R (resultant) is given geometrically by the length of \(\vec { R } \)(OQ) and the direction of the resultant vector is the angle between R and A. Thus we write \(\vec { R } \) = \(\vec { A } \) + \(\vec { B } \).
\(\overline { OQ } \) = \(\overline { OP } \) + \(\overline { PQ } \)
(I) Magnitude of resultant vector:
The magnitude and angle of the resultant vector are determined by using triangle law of vectors as follows.
From figure, consider the triangle ABN, which is obtained by extending the side OA to ON. ABN is a right angled triangle.
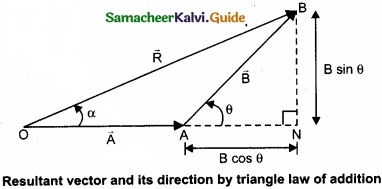
From figure, let R is the magnitude of the resultant of \(\vec { A } \) and \(\vec { B } \).
cos θ = \(\frac{AN}{B}\) ∴ AN = B cos θ and sin θ = \(\frac{BN}{B}\) ∴BN = B sin θ
For ∆OBN, we have OB2 = ON2 + BN2
⇒ R2 = (A + B cos θ)2 + (B sin θ)2
⇒ R2 = A2 + B2 cos2 θ + 2AB cos θ + B2 sin2 θ
⇒ R2 = A2 + B 2 (cos2 θ + sin2 θ) + 2AB cos θ
⇒ R2 = \(\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}+2 A B \cos \theta}\)
(II) Direction of resultant vectors:
If θ is the angle between \(\vec { A } \) and \(\vec { B } \), then
|\(\vec { A } \) + \(\vec { B } \)| = \(\sqrt{A^{2}+B^{2}+2 A B \cos \theta}\)
IF \(\vec { R } \) makes an angle α with \(\vec { A } \), then in ∆OBN,
tan α = \(\frac{BN}{ON}\) = \(\frac{BN}{OA + AN}\)
tan α = \(\frac{B \sin \theta}{A+B \cos \theta}\) ⇒ α = tan-1(\(\frac{B \sin \theta}{A+B \cos \theta}\))
[OR]
(b) Arrive at an expression for velocity of objects in one dimensional elastic collision?
Answer:
Consider two elastic bodies of masses m1 and m2 moving in a straight line (along positive x direction) on a frictionless horizontal surface as shown in figure.
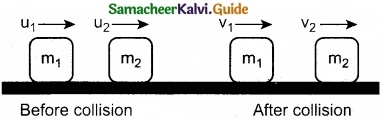
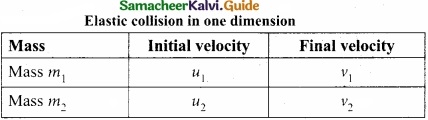
In order to have collision, we assume that the mass m1 moves faster than mass m2 i.e., u1 > u2. For elastic collision, the total linear momentum and kinetic energies of the two bodies before and after collision must remain the same.
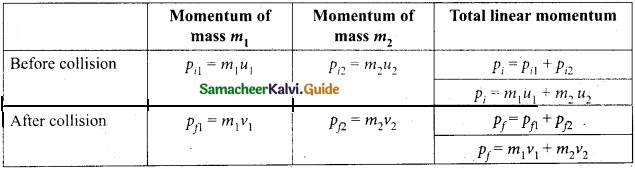
From the law of conservation of linear momentum,
Total momentum before collision (ρi) = Total momentum after collision (ρf)
m1u1 + m2u2 = m1u1 + m2v1 ………………. (1)
or m1 (u1 – v1) = m2(v2 – u2) ………………. (2)
Further,
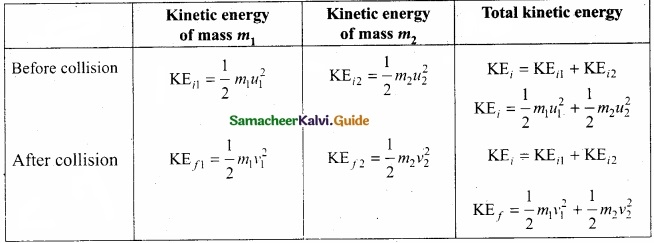
Total kinetic energy before collision KEi = Total kinetic energy after collision KEf
\(\frac{1}{2} m_{1} u_{1}^{2}+\frac{1}{2} m_{2} u_{2}^{2}=\frac{1}{2} m_{1} v_{1}^{2}+\frac{1}{2} m_{2} v_{2}^{2}\) ……………….. (3)
After simplifying and rearranging terms,
\(m_{1}\left(u_{1}^{2}-v_{1}^{2}\right)=m_{2}\left(v_{2}^{2}-u_{2}^{2}\right)\)
Using the formula a2 – b2 = (a + b) (a – b), we can rewrite the above equation as
m1(u1 + v1) = m2(v2 + u2) (v2 – u2) …………………. (4)
Dividing equation (4) by (2) gives,
\(\frac{m_{1}\left(u_{1}+v_{1}\right)\left(u_{1}-v_{1}\right)}{m_{1}\left(u_{1}-v_{1}\right)}=\frac{m_{2}\left(v_{2}+u_{2}\right)\left(v_{2}-u_{2}\right)}{m_{2}\left(v_{2}-u_{2}\right)}\)
u1 + v1 = v2 + u1
Rearranging, u1 – u2 = v2 – v1 ………………… (5)
Equation (5) can be written as
u1 – u2 = -(v1 – v2)
This means that for any elastic head on collision, the relative speed of the two elastic bodies after the collision has the same magnitude as before collision but in opposite direction. Further note that this result is independent of mass.
Rewriting the above equation for v1 and v2,
v1 = v2 + u2 – u1 …………………. (6)
or v2 = u1 + v1 – u1 ………………. (7)
To find the final velocities v1 and v2:
Substituting equation (7) in equation (2) gives the velocity of m1 as
m1 (u1 – v1) = m2 (u1 + v1 – u2 – u2)
m1 (u1 – v1) = m2 (u1 + v1 – 2a2)
m1u1 – m1v1 = m2u1 + m2v1 + 2m2u2
m1u1 = m2u1 + 2m2u2 = m1v1 + m2v1
(m1 – m2) u1 + 2m2u2 = (m1 + m2)v1
or v1 = \(\left(\frac{m_{1}-m_{2}}{m_{1}+m_{2}}\right)\) u1 + \(\left(\frac{2 m_{2}}{m_{1}+m_{2}}\right)\) u2 ……………. (8)
Similarly, by substituting (6) in equation (2) or substituting equation (8) in equation (7), we get the final velocity of m2 as
v2 = \(\left(\frac{2 m_{1}}{m_{1}+m_{2}}\right)\) u1 + \(\left(\frac{m_{2}-m_{1}}{m_{1}+m_{2}}\right)\) u2 ………………. (9)
![]()
Question 36 (a).
Discuss the variation of g with change in altitude and depth?
Answer:
When an object is on the surface fo the Earth, it experiences a centrifugal force that depends on the latitude of the object on Earth. If the Earth were not spinning, the force on the objecf would have been mg. Elowever, the object experiences an additional centrifugal force due to spinning of the Earth.
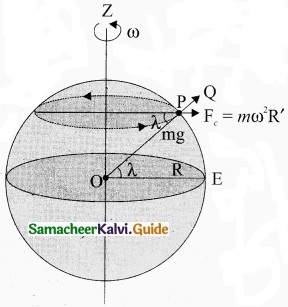
This centrifugal force is given by mω2R’.
\(\mathrm{OP}_{z}, \cos \lambda=\frac{\mathrm{PZ}}{\mathrm{OP}}=\frac{\mathrm{R}^{\prime}}{\mathrm{R}}\)
R’ = R cos λ
where λ is the latitude. The component of centrifugal acceleration experienced by the object in the direction opposite to g is
\(a_{\mathrm{PQ}}=\omega^{2} \mathrm{R} \cos \lambda=\omega^{2} \mathrm{R} \cos ^{2} \lambda\)
Since R’ = R cos λ
Therefore, g’ = g – ω22 R cos2 λ
From the above expression, we can infer that at equator, λ = 0, g’ = g – ω2R. The acceleration due to gravity is minimum. At poles λ = 90; g’ = g, it is maximum. At the equator, g’ is minimum.
Variation of g with depth:
Consider a particle of mass m which is in a deep mine on the Earth. (Example: coal mines in Neyveli). Assume the depth of the mine as d. To calculate g’ at a depth d, consider the following points. The part of the Earth which is above the radius (Re – d) do not contribute to the acceleration. The result is proved earlier and is given as
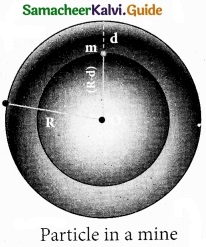
g’ = \(\frac{\mathrm{GM}^{\prime}}{\left(\mathrm{R}_{\mathrm{e}}-d\right)^{2}}\) ………………. (1)
Here M’ is the mass of the Earth of radius (Re – d) Assuming the density of the earth ρ be constant,
ρ = \(\frac{M}{V}\) …………………. (2)
where M is the mass of the Earth and V its volume, Thus,
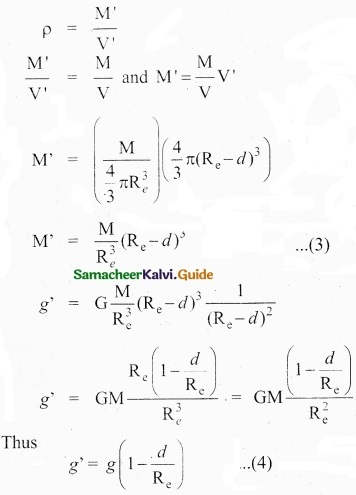
Here also g’ < g. As depth increases, g’ decreases. It is very interesting to know that acceleration due to gravity is maximum on the surface of the Earth but decreases when we go either upward or downward.
[OR]
(b) Explain in detail the maxwell Boltzmann distribution function?
Answer:
Maxwell-Boltzmann: In speed distribution function:-
Consider an atmosphere, the air molecules-are moving in random directions. The speed of each molecule is not the same even though macroscopic parameters like temperature and pressure are fixed. Each molecule collides with every other molecule and they exchange their speed.
In the previously we calculated the rms speed of each molecule and not the speed of each molecule which is rather difficult. In this scenario we can find the number of gas molecules that move with the speed of 5 ms-1 to 10 ms-1 or 10 ms-1
to 15 ms-1 etc. In general our interest is to find how many gas molecules have the range of speed from v to v + dv. This is given by Maxwell’s speed distribution function.
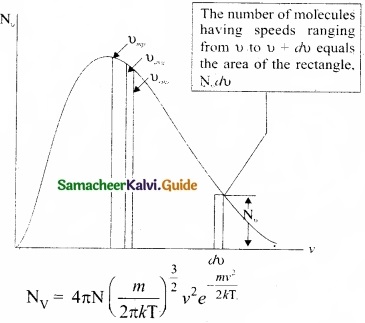
The above expression is graphically shown as follows:
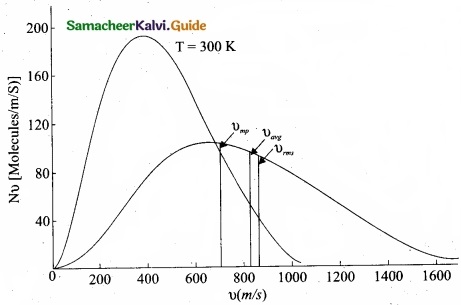
From the figure (1), it is clear that, for a given temperature the number of molecules having lower speed increases parabolically but decreases exponentially after reaching most probable speed. The rms speed, average speed and most probable speed are indicated in the figure (1). It can be seen that the rms speed is greatest among the three.
- The area under the graph will give the total number of gas molecules in the system.
- Figure 2 shows the speed distribution graph for two different temperatures.
As temperature increases, the peak of the curve is shifted to the right. It implies that the average speed of each molecule will increase. But the area under each graph is same since it represents the total number of gas molecules.
![]()
Question 37 (a).
What is meant by simple harmonic motion?
Answer:
A particle is said to execute simple harmonic motion if it moves to and fro about a mean position under the action of a restoring force which is directly proportional to its displacement from the mean position and is always directed towards the mean position.
(b) The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon is 1.7 ms-2. What is the time period of simple pendulum on the moon if its time period on the Earth is 3.5 s? Given g on Earth = 9.8 ms-2?
Answer:

(c) A man with wrist watch on his hand falls from the top of the tower. Does the watch , give correct time during the free fall?
Answer:
Yes. Because the working of a wrist watch does pot depend on gravity at that place but depends on spring action.
[OR]
(d) State Wien’s law?
Answer:
When the animals feed cold, they curl their bodies into the ball so as to decrease the surface area of their bodies. As total energy radiated by a body varies directly as the surface area of the body, the loss of heat due to radiation would be reduced.
(e) Normal human body of the temperature is 98.6°F. During high fever if the temperature increases to 104°F. What is the change in peak wavelength that emitted by our body (Assume human body is a black body)?
Answer:
Normal human body temperature (T) = 98.6°F.
Convert Fahrenheit into Kelvin, \(\frac{F-32}{180}\) = \(\frac{K-273}{100}\)
So, T = 98.6°F = 310K
From Wien’s displacement law
Maximum wavelength λmax = \(\frac{b}{T}\) = \(\frac { 2.898\times 10^{ -3 } }{ 313 } \)
λmax = 9348 × 10-9 m
λmax = 9348 nm (at 98.6°F)
During high fever, human body temperature
T = 104°F = 313K
Peak wavelength λmax = \(\frac{b}{T}\) = \(\frac { 2.898\times 10^{ -3 } }{ 313 } \)
λmax = 9259 × 10-9 m
λmax = 9259 (at 104°F)
(f) Animals curl into a ball, when they feel very cold. Why?
Answer:
When animals feel cold, they curl their bodies into the ball so as to decrease the surface area of their bodies. As total energy radiated by a body varies directly as the surface area of the body, the loss of heat due to radiation would be reduced.
![]()
Question 38 (a).
Explain the horizontal oscillations of spring?
Answer:
Horizontal oscillations of a spring-mass system: Consider a system containing a block of mass m attached to a massless spring with stiffness constant or force constant or spring constant k placed on a smooth horizontal surface (frictionless surface) as shown in figure.
Let x0 be the equilibrium position or mean position of mass m when it is left undisturbed. Suppose the mass is displaced through a small displacement x towards right from its equilibrium position and then released, it will oscillate back and forth about its mean position x0. Let F be the restoring force (due to stretching of the spring) which is proportional to the amount of displacement of block. For one dimensional motion, . mathematically, we have.
F ∝ x
F = -kx ……………… (1)
where negative sign implies that the restoring force will always act opposite to the direction of the displacement. This equation is called Hooke’s law. Notice that, the restoring force is linear with the displacement (i.e., the exponent of force and displacement are unity).
This is not always true; in case if we apply a very large stretching force, then the amplitude of oscillations becomes very large (which means, force is proportional to displacement containing higher powers of x) and therefore, the oscillation of the system is not linear and hence, it is called non-linear oscillation.
We restrict ourselves only to linear oscillations throughout our discussions, which means Hooke’s law is valid (force and displacement have a linear relationship). From Newton’s second law, we can write the equation for the particle executing simple harmonic motion.
\(m \frac{d^{2} x}{d t^{2}}=-k x\) ……………….. (1)
\(\frac{d^{2} x}{d t^{2}}=-\frac{k}{m} x\) ……………….. (2)
Comparing the equation with simple harmonic motion equation, we get
ω2 = \(\frac{k}{m}\) ………………….. (3)
which means the angular frequency or natural frequency of the oscillator is
ω = \(\sqrt{\frac{k}{m}} \mathrm{rad} s^{-1}\) ……………….. (4)
The frequency of the oscillation is
f = \(\frac{\omega}{2 \pi}=\frac{1}{2 \pi} \sqrt{\frac{k}{m}} \mathrm{Hertz}\) …………………… (5)
and the time period of the oscillation is
T = \(\frac{1}{f}\) = 2π \(\sqrt{m/k}\) seconds …………………. (6)
[OR]
(b) What is capillarity? Obtain an expression for the surface tension of a liquid by capillary rise method?
Answer:
In a liquid whose angle of contact with solid is less than 90° suffers capillar rise. On the other hand, in a liquid whose angle of contact is greater than 90°, suffers capillary fall. The rise or fall of a liquid in a narrow tube is called capillarity or capillary action.
Practical application of capillarity:
- Due to capillary action, oil rises in the cotton within an earthen lamp. Likewise, sap raises from the roots of a plant to its leaves and branches.
- Absorption of ink by a blotting paper.
- Capillary action is also essential for the tear fluid from the eye to drain constantly.
- Cotton dresses are preferred in summer because cotton dresses have fine pores which act as capillaries for sweat.
Surface Tension by capillary rise method:
The pressure difference across a curved liquid air interface is the basic factor behind the rising up of water in a narrow tube (influence of gravity is ignored). The capillary rise is more dominant in the case of very fine tubes.
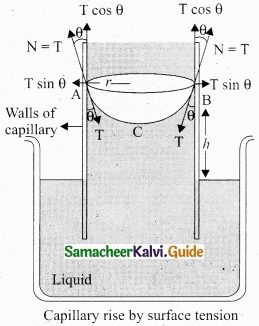
But this phenomenon is the outcome of the force of surface tension. In order to arrive a relation between the capillary rise (h) and surface tension (T), consider a capillary tube which is held vertically in a beaker containing water, the water rises in the capillary tube to a height h due to surface tension.
The surface tension force FT acts along the tangent at the point of contact downwards and its reaction force upwards. Surface tension T, it resolved into two components
- Horizontal component T sin θ and
- Vertical component T cos θ acting upwards, all along the whole circumference of the meniscus.
Total upward force = (T cos θ) (2nr) = 2nrT cos θ)
where θ is the angle of contact, r is the radius of the tube. Let ρ be the density of water and h be the height to which the liquid rises inside the tube. Then,

The upward force supports the weight of the liquid column above the free surface, therefore,
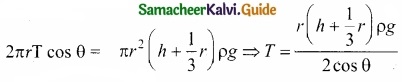
If the capillary is a very fine tube of radius (i.e., radius is very small) then \(\frac{r}{3}\) can be neglected when it is compared to the height h. Therefore,
T = \(\frac{r \rho g h}{2 \cos \theta}\)
Liquid rises through a height h
h = \(\frac{2 \mathrm{T} \cos \theta}{r \rho g} \Rightarrow h \alpha \frac{1}{r}\)
This implies that the capillary rise (h) is inversely proportional to the radius (r) of the tube, i.e., the smaller the radius of thd tube greater will be the capillarity.