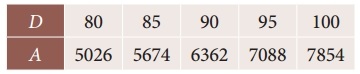
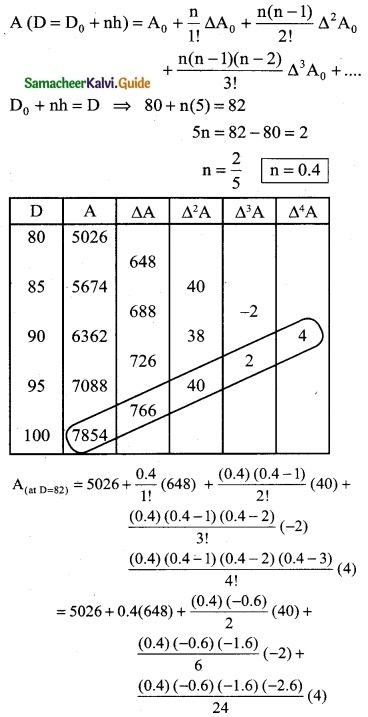
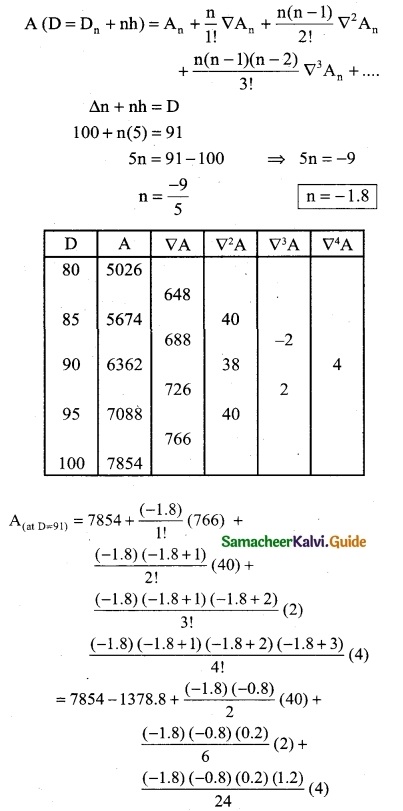
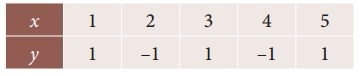
Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Guide Pdf Chapter 13 Network Cabling Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Solutions Chapter 13 Network Cabling
12th Computer Applications Guide Network Cabling Text Book Questions and Answers
Part I
Choose The Correct Answers
Question 1.
ARPANET stands for
a) American Research Project Agency Network
b) Advanced Research Project Area Network
c) Advanced Research Project Agency Network
d) American Research Programs And Network
Answer:
c) Advanced Research Project Agency Network
Question 2.
WWW was invented by
a) Tim Berners Lee
b) Charles Babbage
c) Blaise Pascal
d) John Napier
Answer:
a) Tim Berners Lee
![]()
Question 3.
Which cable is used in cable TV to connect with setup box?
a) UTP cable
b) Fibre optics
c) Coaxial cable
d) USB cable
Answer:
c) Coaxial cable
Question 4.
Expansion of UTP is
a) Uninterrupted Twisted Pair
b) Uninterrupted Twisted Protocol
c) Unshielded Twisted Pair
d) Universal Twisted Protocol
Answer:
c) Unshielded Twisted Pair
Question 5.
Which medium is used in the optical fibre cables to transmit data?
a) Microwave
b) infra red
c) light
d) sound
Answer:
c) light
![]()
Question 6.
Which of the following is a small peripheral device with a sim slot to connect the computers to Internet?
a) USB
b) Dongles
c) Memory card
d) Mobiles
Answer:
a) USB
Question 7.
Which connector is used in the Ethernet cables?
a) RJ11
b) RJ21
c) RJ61
d) RJ45
Answer:
d) RJ45
Question 8.
Which of the following connector is called as champ connector?
a) RJ11
b) RJ21
c) RJ61
d) RJ45
Answer:
b) RJ21
![]()
Question 9.
How many pins are used in RJ45 cables?
a) 8
b) 6
c) 50
d) 25
Answer:
a) 8
Question 10.
Which wiring standard is used for connecting two computers directly?
a) straight Through wiring
b) Cross Over wiring
c) Rollover wiring
d) None
Answer:
b) Cross Over wiring
Question 11.
Pick the odd one out from the following cables
a) roll over
b) cross over
c) null modem
d) straight through
Answer:
c) null modem
![]()
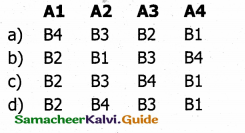
Question 12.
Match the following
1. Ethernet – Port
2. RJ45 connector – Ethernet
3. RJ45 jack – Plug
4. RJ45 cable – 802.3
a) 1, 2, 4, 3
b) 4, 1, 3, 2
c) 4, 3, 1, 2
d) 4, 2, 1, 3
Answer:
d) 4, 2, 1, 3
Part II
Short Answers
Question 1.
Write a note on twisted pair cable?
Answer:
- Twisted Pair Cables is a type of cable with two or more insulated wires twisted together.
- It started with the speed of 10 Mbps (10BASE-T cable is used).
- It started with the speed of 10 Mbps (10BA.SE-T cable is used).
- Then the cable is improved and the speed was higher and went to 100 Mbps and the cable was renamed 100BASE-TX.
Question 2.
What are the uses of USB cables?
Answer:
- The Universal Serial Bus is used to connect the keyboard, mouse, and other peripheral devices.
- Micro USB is a miniaturized version of the USB used for connecting mobile devices such as smartphones, GPS devices, and digital cameras.
![]()
Question 3.
Write a note on the types of RJ45 connectors?
Answer:
- Wiring schemes specify how the wires to be connected with the RJ45 connector.
- There are two wiring schemes available to terminate the twisted-pair cable on each end, which are
- T-568A
- T-568B.
Question 4.
What is an Ethernet port?
Answer:
- The Ethernet port is the jack where the Ethernet cable is to be connected.
- This port will be there In both the computers and the LAN port.
Question 5.
What is the use of the Crimping tool?
Answer:
A crimping tool is a physical tool which is used to connect the patch wire and the Ethernet connector. The tool will puncture the connector and makes the wire set in the connector.
![]()
Question 6.
What are the types of twisted pair cables?
Answer:
There are two types of twisted pair cables, Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and Shielded Twisted pair (STP). The UTP is used nowadays as modem cables for the Internet and they are lower in cost and installation and maintenance is easy compared to the coaxial cables.
Question 7.
What is meant by champ connector?
Answer:
The RJ-21 connector has 50 pins with 25 pins at one end and 25 pins at the other end. It is also called a champ connector or Amphenol connector. The Amphenol is a connector manufacturer. The RJ-21 interface is typically used for data communication trucking applications.
Part III
Explain In Brief Answer
Question 1.
Write a note on crossover cables.
Answer:
- If you require a cable to connect two computers or Ethernet devices directly together without a hub, then you will need to use a Crossover cable instead.
- The easiest way to make a crossover cable is to make one end to T568A colour coding and the other end to T568B.
- Another way to make the cable is to remember the colour coding used in this type. Here Green set of wires at one end are connected with the Orange set of wires at another end and vice versa.
Question 2.
Write a short note on RJ45 connector?
Answer:
RJ45 Connector:
- The RJ45 connector is a small plastic cup which will be used to connect the wire inside the connector and ready to connect to the Internet.
- The RJ45 connector looks similar to a telephone jack but it looks slightly wider. The Ethernet cables are sometimes called RJ45 cables.
- In RJ45 the “RJ” stands for the Registered Jack and the “45” simply refers to the number of interface standards in the cable.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the differences between serial and parallel ports?
Answer:
Subject | Serial Port | parallel port |
| Pins | 9 pins | 25 pins |
| Type of port | Male port | Female Port |
| Color | Usually Purple in color | Usually Green in color |
| Data Transfer Rate | Slower than Parallel Port | Faster than Serial Port |
| Moving Bits | Serial move bits inline, one at a time. | Parallel moves bits next to each other |
| Usage of Wire | Serial ports are only used 2 wires for transmitting and receiving data | Parallel Port used 8 or more wire for transmitting and receiving data. |
Question 4.
What is meant by a null modem cable?
Answer:
RS-232 cable is also used for interconnecting two computers without a modem. So it is also a null-modem cable. A cable interconnecting two devices directly are known as a null-modem cable.
![]()
Question 5.
What are the components involved in Ethernet cabling?
Answer:
The three main components are used in the Ethernet cabling components are
- Patch Cable (Twisted pair)
- RJ45 Connector
- Ethernet Ports
- Crimping Tool
Question 6.
What are the types of Fibre optic cables?
Answer:
There are two types of fiber optic cables available.
- One is single-mode (100BaseBx)
- Multimode (lOOBaseSX).
- Single-mode cables are used for long-distance transmission and at a high cost
- Multimode cables are used for short-distance transmission at a very low cost.
![]()
Part IV
Explain In Detail
Question 1.
What is meant by Registered Jack? Explain briefly the types of Jacks.
Answer:
Registered Jacks:
- A Registered Jack commonly known as RJ is a network interface used for network cabling, wiring, and jack construction.
- The primary function of the registered jack is to connect different data equipment and telecommunication devices.
- The commonly known registered jacks are RJ-11, RJ-45, RJ-21, and RJ-28.
- The registered jack refers to the male physical connector (Plug), a female physical connector (Jack) and it’s the wiring.
RJ-11:
- It is the most popular modern form of the registered jack.
- It is found in the home and office.
- This registered jack is mainly used in telephone and landlines.
- There are 6 pins where
- The two pins give the transmission configuration,
- The two pins give the receiver configuration and
- The other two pins will be kept for reserved.
- The two pin will have the positive terminal and the negative terminal.
RJ-14 and RJ-61:
- The RJ-14 is the same as RJ-11 which will be used for telephone lines where same it as 6 pins whereas the RJ-61 will have 8 pins.
- This RJ-61 will use the twisted pair cable with a modular connection.
RJ-21:
- The RJ-21 connector has 50 pins with 25 pins at one end and 25 pins at the other end.
- It is also called as champ connector or Amphenol connector.
- The Amphenol is a connector manufacturer.
- The RJ-21 interface is typically used for data communication trucking applications.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain wiring techniques used in Ethernet cabling.
Answer:
- There are three types of wiring techniques to construct the Ethernet cable.
- It is also known as color coding techniques. They are
- Straight-Through Wiring
- Cross-over Wiring
- Roll-over Wiring
Straight-Through Wiring
- In general, the Ethernet cables used for Ethernet connections are “straight through cables”.
- These cable wires are in the same sequence at both ends of the cable, which means that pin 1 of the plug on one end is connected to pin 1 of the plug on the other end (for both standard – T568A & T568B).
- The straight through wiring cables are mostly used for connecting PC / NIC card to a hub.
- This is a simple physical connection used in printers, computers and other network interfaces.
Cross-over Wiring
- Crossover cable is used to to connect two com¬puters or Ethernet devices directly together without a hub.
- The pairs(Tx and Rx lines) will be crossed which means pin 1 & 2 of the plug on one end are connected with pin 3 & 6 of the plug on other end, and vice versa (3 & 6 to pin 1 & 2).
- The Null modem Cables are the example of the crossover cables.
Roll-over Wiring
- Rollover cable is a type of null-modem cable that is often used to connect a device console port to make programming changes to the device.
- The rollover wiring have opposite pin arrangements, all the cables are rolled over to different arrangements.
- In the rollover cable, the colored wires are reversed on other end i.e. the pins on one end are connected with other end in reverse order.
- Rollover cable is also known as Yost cable or Console cable. It is typically flat (and light blue color) to distinguish it from other types of network cabling.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain about RJ45 connector.
Answer:
- The RJ45 connector is a small plastic cup which will be used to connect the wire inside the connector and ready to connect the Internet.
- The RJ45 connector looks similar like a telephone jack but it looks a slightly wider.
- The Ethernet cables are sometime called as RJ45 cables.
- In RJ45 the “RJ” stands for the Registered Jack and the “45” simply refers to the number of interface standard in the cable.
- Each RJ45 connector has eight pins and connected to each end of the Ethernet cable, since it has 8-position, 8-contact (8P8C) modular plug,
- It is also known as 8P8C connector. These plugs (connector) are then inserted into Ethernet port of the network card.
Wiring schemes and color codes of the connector
- The RJ45 connector has eight small jack inside to connect eight small wires of the patch cable.
- The eight cables are in eight different colors. Let’s discuss that eight colors and where does that eight colors connect to the RJ45 connector.
- Wiring schemes specifies how the wires to be connected with RJ45 connector. There are two wiring schemes available to terminate the twisted-pair cable on each end, which are T-568A and T-568B.
- Although four pairs of wires are available in the cable, Ethernet uses only two pairs: Orange and Green. The other two colors (blue and brown) can be used ISDN or phone connections.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the components used in Ethernet cabling.
Answer:
The main components are used in the Ethernet cabling are
- Patch Cable (Twisted pair)
- RJ45 Connector
- Ethernet Ports
- Crimping Tool
1. Patch Cable (Twisted Pair):
1. These Cables are generally made up of 8 wires in different colors.
2. Four of them are solid colours, and the others are striped.
3. The eight colors are white green, green, white orange, blue, white blue, orange, white brown and brown. The following figure 13.8 shows the patch cable.
Ethernet cables are normally manufactured in several industrial standards such as Cat 3, Cat 5, Cat 6, Cat 6e and cat 7. “Cat” simply stands for “Category,”. Increasing the size of the cable also lead to slower transmission speed.
4. The cables together with male connectors (RJ45) on each end are commonly referred as Ethernet cables. It is also called as RJ45 cables, since Ethernet cable uses RJ45 connectors.
2. RJ45 Connector:
- The RJ45 connector is a small plastic cup which will be used to connect the wire inside the connector and ready to connect the Internet.
- The RJ45 connector looks similar like a telephone jack but it looks a slightly wider.
- The Ethernet cables are sometime called as RJ45 cables.
- In RJ45 the “RJ” stands for the Registered Jack and the “45” simply refers to the number of interface standard in the cable.
- Each RJ45 connector has eight pins and connected to each end of the Ethernet cable.
- Since it has 8-position, 8-contact (8P8C) modular plug, It is also known as 8P8C connector. Th£se plugs (connector) are then inserted into Ethernet port of the network card.
3. Ethernet card and Port:
- Ethernet card is a Network Interface Card (NIC) that allows computers to connect and transmit data to the devices on the network. It may be an expansion card or built-in type.
- Expansion card is a separate circuit board also called as PCI Ethernet card which is inserted into PCI slot on motherboard of a computer.
- Now a days most of the computers come with built-in Ethernet cards which resides on motherboard.
- Wireless Ethernet cards are also available, which uses radio waves to transmit data.
- Ethernet port is an opening which is a part of an Ethernet card. It accepts RJ45 connector with Ethernet cable. It is also called as RJ45 jack. It is found on personal computers, laptops, routers, switches, hubs and modems.
- In these days, most of the computers and laptops have a built-in Ethernet port for connecting the device to a wired network.
4. Crimping Tool:
- Crimping is the process of joining two or more pieces of metal or wire by deforming one or both of them to hold each other.
- A crimping tool is a physical tool which is used to connect the patch wire and the Ethernet connector.
- The tool will puncture the connector and makes the wire set in the connector.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the type of Network cables?
Answer:
There are many types of cables available in networking. Here we discuss six different cables.
1. Coaxial Cables:
- This cable is used to connect the television sets to home antennas and transfer the information in 10 Mbps,
- It is divided into thinnet and thicknet cables.
- These cables have a copper wire inside and insulation Is covered on the top of the copper wire to provide protection to the cable.
- These cables are very difficult to install and maintain because they are too big to carry and replace.
- The coaxial cable got its name by the word “coax”. Nowadays coaxial cables are also used for dish TV where the setup box and the television is connected using the coaxial cable only.
- Some of the cable names are Media Bridge 50-feet Coaxial cable, Amazon basics CL2- Rated Coaxial cables, etc.
Twisted Pair Cables:
- It is type of cable with two or more insulated wires twisted together.
- It started with the speed of 10 Mbps (10BASE-T cable is used).
- Then the cable is improved and the speed was higher and went to 100 Mbps and the cable was renamed 100BASE-TX.
- Then finally the cable improved more made to 10 Gbps and named as 10GBASE-T.
- This twisted cable has 8 wires which are twisted to ignore electromagnetic interference.
- Also, the eight wires cannot be placed in a single unit there could be a difficulty in spacious, so it is twisted to make as one wire.
- There are two types of twisted pair cables, Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and Shielded Twisted pair (STP).
- The UTP is used nowadays as modern cables for the Internet and they are lower in cost and installation and maintenance is easy compared to the coaxial cables.
- STP is similar to UTP, but it is covered by an additional jacket to protect the wires from External interference.
Fiber Optics:
- This cable is different from the other two cables.
- The other two cables had an insulating material on the outside and the conducting material like copper inside.
- But in this cable it is of strands of glass and pulse of light is used to send the information.
- They are mainly used in Wide Area Network (WAN)/The WAN Is a network that extends to the very large distance to connect the computers,
Ethernet Cables:
- Ethernet cable is the most common type of network cable mainly used for connecting the computers or devices at home or office.
- This cable connects wired devices within the local area network (LAN) for sharing the resources and accessing the Internet.
![]()
12th Computer Applications Guide Network Cabling Additional Important Questions and Answers
Part A
Choose The Correct Answers:
Question 1.
Which year were the co-axial cables invented?
(a) 1880
(b) 1890
(c) 1990
(d) 2000
Answer:
(a) 1880
Question 2.
The latest version of USB is ………………
a) 2.0
b) 4.0
c) 5.0
d) 3.0
Answer:
d) 3.0
Question 3.
Co-axial cables transfer the information in …………………………
(a) 10 kbps
(b) 10 Mbps
(c) 10 GBPS
(d) 10 TBPS
Answer:
(b) 10 Mbps
![]()
Question 4.
……………….. cable connects wired devices within the local area network for sharing the resources and accessing the Internet.
a) wireless Cable
b) Ethernet cable
c) Coaxial Cable
d) Twisted Wire
Answer:
d) Twisted Wire
Question 5.
Co-axial cables are made up of ……………………..
(a) Steel
(b) Iron
(c) Copper
(d) Aluminium
Answer:
(c) Copper
Question 6.
………….. are used for connecting the television with the setup box.
a) UTP
b) STP
c) Twisted Cable
d) Coaxial cables
Answer:
d) Coaxial cables
![]()
Question 7.
…………………….. is a type of cable with two or more insulated wires twisted together.
Answer:
Twisted pair cables
Question 8.
The ……………. uses light to transmit the information from one place to another.
a) Fibre cable
b) Network cable
c) optic cable
d) None of these
Answer:
c) optic cable
Question 9.
Assertion (A): 8 wires of the twisted cable are twisted
Reason (R): To ignore electromagnetic interference.
(a) A is true R is the reason
(b) A, R both false
(c) A is false R is true
(d) A is true, R is not the reason
Answer:
(a) A is true R is the reason
![]()
Question 10.
…………….. are used for long-distance transmission and at a high cost.
a) optic cable
b) Network cable
c) Multimode cable
d) Single-mode cables
Answer:
b) Network cable
Question 11.
STP stands for ………………………
(a) Shielded Turn paper
(b) Shielded Twisted pair
(c) Soft Turn Photo
(d) Short Time processing
Answer:
(b) Shielded Twisted pair
Question 12.
The serial port will send ………….. at one time.
a) 2 bit
b) Null
c) 1 bit
d) 5 bit
Answer:
c) 1 bit
![]()
Question 13.
Find the wrongly matched pair.
(a) coaxial cables – TV
(b) Twisted pair cables – ATP, UTP
(c) Fiber optic cables – Single-mode, Multimode
Answer:
(b) Twisted pair cables – ATP, UTP
Question 14.
The Null modem Cables are an example of the crossover cables.
a) coaxial
b) crossover cables
c) parallel cables
d) Serial cable
Answer:
b) crossover cables
Question 15.
The ……………. is the basic component of the Local Area Network(LAN)
a) parallel cables
b) Serial cable
c) coaxial
d) Ethernet cable
Answer:
d) Ethernet cable
![]()
Question 16.
The two types of fiber optic cables are ……………………… and ………………………..
Answer:
Single-mode, Multi-mode
Fill In The Blanks
1. The …………… is a small plastic cup which will be used to connect the wire inside the connector and ready to use to connect the Internet.
Answer:
RJ45 Ethernet connector
2. The ………….. has eight small pins inside to connect eight small wires in the patch cable. The eight cables have eight different colours.
Answer:
RJ45 connector
3. The …………….. is the jack where the Ethernet cable is to be connected.
Answer:
Ethernet port
![]()
4. …………….. port will be there in both the computers and the LAN port.
Answer:
Ethernet port
5. The …………… is a physical tool which is used to connect the patch wire and the Ethernet connector(RJ45).
Answer:
crimping tool
6. A ……………. is a network interface used for connecting different data equipment and telecommunication devices.
Answer:
Registered Jack (RJ)
7. ……………… jack is mainly used in telephone and landlines.
Answer:
RJ11
8. ……………… cable is used to transfer the information in 10 Mbps.
Answer:
Coaxial
![]()
Very Short Answers
Question 1.
What is the purpose of network cables?
Answer:
The Network cables are used to transfer the data and information to another computer.
Question 2.
What is the use of coaxial cable?
Answer:
Coaxial cables are used for connecting the television with the setup box.
Question 3.
How many wires are there in the twisted cable? Why?
Answer:
Twisted cable has 13 wires which are twisted to ignore electromagnetic interference
Question 4.
What are the two types of twisted pair cables?
Answer:
Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and Shielded Twisted pair (STP).
![]()
Question 5.
Expand ARPANET.
Answer:
Advanced Research Project Agency Network
Question 6.
What is ARPANET?
Answer:
It is the predecessor of the modern Internet.
Question 7.
What is the use of USB cables?
Answer:
USB cables are used to connect keyboard, mouse, and other peripheral devices
Question 8.
What is the use of parallel cables?
Answer:
The parallel cables are used to connect to the printer and other disk drivers.
Question 9.
What are the two types of fiber-optic cable?
Answer:
Single-mode ((100 Base Bx)) and Multimode ((100 Base SX))
![]()
Question 10.
How serial port and parallel port differ?
Answer:
It will send 1 bit at one time whereas the parallel port will send 13 bit at one time.
Question 11.
What is the use of serial and parallel interface?
Answer:
The Serial and Parallel interface cables are used to connect the Internet to the system.
Question 12.
What is the purpose of cross-over cable?
Answer:
Cross over cable is used to join two network devices of the same type
![]()
Question 13.
What is RJ Network?
Answer:
A Registered Jack (RJ) is a network interface
Question 14.
Where is the RJ11 cable used?
Answer:
RJ11 jack is mainly used in telephone and landlines
Question 15.
What is the use of a crimping tool?
Answer:
The crimping tool is used to connect the patch wire and the Ethernet connector.
Question 16.
What is an Ethernet port?
Answer:
The Ethernet port is the jack where the Ethernet cable is to be connected.
![]()
Question 17.
What is an Ethernet cable?
Answer:
The Ethernet cable is the basic component of the Local Area Network
Question 18.
What is the purpose of using Fiber optic cable?
Answer:
Fiber optic cables are used in Wide Area Network (WAN).
Question 19.
What is a dongle?
Answer:
The dongle is a small peripheral device which has compatible with mobile broadband.
Question 20.
How the internet is connected through a dongle?
Answer:
A sim slot in it and connects the Internet and acts as a modem to the computer.
![]()
Abbreviation:
- ARPANET – Advanced Research Project Agency Network
- WWW – World Wide Web
- W3C – World Wide Web Consortium
- LAN – Local Area Network
- WAN – Wide Area Network
- UTP – Unshielded Twisted Pair
- STP – Shielded Twisted pair
- NIC – Network Interface Card
- USB – Universal Serial Bus
- RJ – Registered Jack
- 8P8C – 8-position, 8-contact
Find The Odd One On The Following
l. (a) Media Bridge
(b) 50feet coaxial cable
(c) 10BASE-T
(d) CL2
Answer:
(c) 10BASE-T
2. (a) 100BaseBX
(b) 100BaseSX
(c) WAN
(d) 10 Base T
Answer:
(d) 10 Base T
![]()
3. (a) Keyboard
(b) Monitor
(c) Mouse
(d) peripheral devices
Answer:
(b) Monitor
4. (a) Smartphones
(b) GPS devices
(c) Digital cameras
(d) Mouse
Answer:
(d) Mouse
5. (a) Speakers
(b) Infra Red
(c) Blue tooth
(d) WiFi
Answer:
(a) Speakers
![]()
6. (a) RJ45Connector
(b) UTP Cable
(c) coaxial cable
(d) plastic covering
Answer:
(c) coaxial cable
7. (a) USB cable
(b) RJ45 Connector
(c) Ethernet Ports
(d) Crimping Tools
Answer:
(a) USB cable
8. (a) White Green
(b) White Red
(c) White Orange
(d) White brown
Answer:
(b) White Red
9. (a) Cat 5
(b) Cat 6e
(c) Cat 7
(d) Cat 5e
Answer:
(d) Cat 5e
![]()
10. (a) RJ-11
(b) RJ-21
(c) RJ-08
(d) RJ-45
Answer:
(c) RJ-08
11. (a) Registered Jack
(b) Mobile
(c) 6pin
(d) Landlines
Answer:
(b) Mobile
12. (a) ChampConnector
(b) Amphenol Connector
(c) Wireless Connector
(d) RJ21
Answer:
(c) Wireless Connector
![]()
13. (a) Champ over
(b) Cross Over
(c) Straight Through
(d) Roll Over
Answer:
(a) Champ over
14. (a) T568A
(b) T568B
(c) Tx, Rx lines
(d) RJ-28
Answer:
(d) RJ-28
15. (a) Twisted pair
(b) UTP
(c) FTP
(d) STP
Answer:
(c) FTP
![]()
Choose The Incorrect Pair:
1. a) Media Bridge 50-feet Coaxial cable, Amazon basicsCL2-Rated Coaxial cables.
b) Unshielded Twisted Pair and Shielded Twisted pair.
c) USB cables and Parallel cables
d) Single-Mode and Multimode
Answer:
c) USB cables and Parallel cables
2. a) Serial and Parallel cables
b) Patch Cable, RJ45 Connector
c) Ethernet Ports, Crimping Tool
d) Coaxial cable, Serial Port
Answer:
d) Coaxial cable, Serial Port
3. a) Ethernet cable and serial cable
b) RJ45 plug, Ethernet connector.
c) Rj45 jack, Ethernet Port
d) RJ45, 802.3
Answer:
a) Ethernet cable and serial cable
![]()
4. a) RJ-11, RJ-45
b) RJ-45 and RJ47
c) RJ-14 and RJ-61
d) RJ-21, RJ-28
Answer:
b) RJ-45 and RJ47
5. a) USB cables, Peripheral devices
b) Coaxial cables, 10 Mbps
c) Ethernet port, LAN port
d) Parallel port, 100BaseSX
Answer:
d) Parallel port, 100BaseSX
![]()
Match The Following:
Question 1.
A) Tim Berners Lee -1) WAN
B) Coaxial cables – 2) WWW
C) Twisted pair – 3) CL2 Related coaxial
D) Fiber optics cable – 4) STP
a) 1 2 3 4
b) 2 31 4
c) 4 3 2 1
d) 2 3 4 1
Answer:
d) 2 3 4 1
Question 2.
A) Coaxial cables – 10gbps
B) Twisted pair – 100 BASE-BX
C) Fiber optics cable – 100 GBASE-T
D) Ethernet Cable -10 Mbps
a) 1 2 3 4
b) 2 31 4
c) 4 3 2 1
d) 2 3 4 1
Answer:
c) 4 3 2 1
![]()
Question 3.
A) RJ45 connector -1) Crimping Tool
B) Ethernet -2) Small 8 jack inside
C) Expansion card -3) NIC
D) RJ45 Cable -4) Ethernet cable
a) 1234
b) 2 31 4
c) 4 3 2 1
d) 2 3 4 1
Answer:
d) 2 3 4 1
Question 4.
A) Ethernet Technology – RJ45, 802.3
B) RJ45 Connector(male) – RJ45 plug, Ethernet connector, 8P8C connector
C) RJ45 socket (female) – Rj45 jack, Ethernet Port
D) RJ45 Cable – Ethernet cable
a) 1 2 3 4
b) 2 31 4
c) 4 3 2 1
d) 2 3 4 1
Answer:
a) 1 2 3 4
Question 5.
A) RJ11 Jack – Peripheral devices
B) RJ45 Connector – Telephones and landlines
C) USB Cables – Crimping Tool
D) Cross over cable – Null modem Cables
a) 1 2 3 4
b) 2 31 4
c) 4 3 2 1
d) 2 3 4 1
Answer:
b) 2 31 4
![]()
Part B
Short Answers
Question 1.
Write a note on coaxial cables?
Answer:
Coaxial Cables:
This cable was invented in the late 1880s, which is used to connect television sets to home antennas. This cable is used to transfer the information in 10 Mbps.
Question 2.
What is mean by Expansion card?
Answer:
- The expansion card is a separate circuit board also called PCI.
- Ethernet card is inserted into a PCI slot on the motherboard of a computer.
Question 3.
Mention the different types of cables used to connect the computer on Network?
Answer:
Computers can be connected on the network with the help of wired media (Unshielded Twisted pair, shielded Twisted pair, Co-axial cables, and Optical fiber) or wireless media (Infra Red, Bluetooth, WiFi)
![]()
Question 4.
List the type of Network cables
Answer:
- Coaxial Cables
- Twisted Pair Cables
- Fiber Optics
- USB Cables
- Serial and Parallel cables
- Ethernet Cables
Question 5.
Give the Pin details of RJ-11?
Answer:
Pin details of the RJ-11, there is 6 pin where the two pins give the transmission configuration, the two pins give the receiver configuration and the other two pins will be kept for reserved. The two-pin will have the positive terminal and the negative terminal.
Question 6.
What are the two types of twisted-pair cables?
Answer:
There are two types of twisted pair cables,
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and
- Shielded Twisted pair (STP).
![]()
Question 7.
What is the use of UTP?
Answer:
- The UTP is used nowadays as modern cables for the Internet and they are lower in cost and installation and maintenance is easy compared to the coaxial cables.
- STP is similar to UTP, but it is covered by an additional jacket to protect the wires from External interference.
Question 8.
Write about Fiber Optics
Answer:
- Fiber Optics cable is different from the other two cables.
- The other two cables had an insulating material at the outside and the conducting material like copper inside.
- But in this cable it is of strands of glass and pulse of light is used to send the information.
Question 9.
What are the two types of fiber optic cables available,
Answer:
There are two types of fiber optic cables available
- Single-mode (100BaseBx) another
- Multimode (100BaseSX).
![]()
Question 10.
What is the use of a Single-mode Cable?
Answer:
Single-mode cables are used for long-distance transmission and at a high cost.
Question 11.
What is the use of Multi-Mode Cable?
Answer:
- Multimode cables are used for short-distance transmission at a very low cost.
- The optic cables are easy to maintain and install.
Question 12.
What is the use of Micro USB?
Answer:
Micro USB is a miniaturized version of the USB used for connecting mobile devices such as smartphones, GPS devices, and digital cameras.
Question 13.
What is the use of cross-over Cable?
Answer:
Cross over cable is used to join two network devices of the same type for example two PCs or two network devices.
![]()
Part C
Explain In Brief Answer
Question 1.
Compare UTP and STP?
Answer:
UTP: The UTP is used nowadays as modem cables for the Internet and they are lower in cost and installation and maintenance is easy compared to the coaxial cables.
STP: STP is similar to UTP, but it is covered by an additional jacket to protect the wires from External interference.
Question 2.
How to determine the type of Ethernet Cable?
Answer:
- Straight-through: The coloured wires are in the same sequence at both ends of the cable.
- Cross-over: The first coloured wire at one end of the cable is the third coloured wire at the other end of the cable.
- Poll-over: The coloured wires are in the opposite sequence at either end of the cable.
![]()
Part D
Explain In Detail
Question 1.
Explain the Crimping process to make Ethernet cables?
Answer:
Crimping process for making Ethernet cables
- Cut the cable with the desired length
- Strip the insulation sheath about 1 inch from both ends of the cable and expose the Twisted pair of wires
- After stripping the wire, untwist the smaller wires and arrange them into the proper wiring scheme, T568B preferred generally.
- Bring the wires tighter together and cut them down so that they all have the same length ( Vi inch).
- Insert all 8 coloured wires into the eight grooves in the connector. The wires should be, inserted until the plastic sheath is also inside the connector.
- Use the crimping tool to lock the RJ45 connector on the cable. It should be strong enough to handle manual traction. Now it is ready for data transmission.
- Use a cable tester to verify the proper connectivity of the cable, if need.