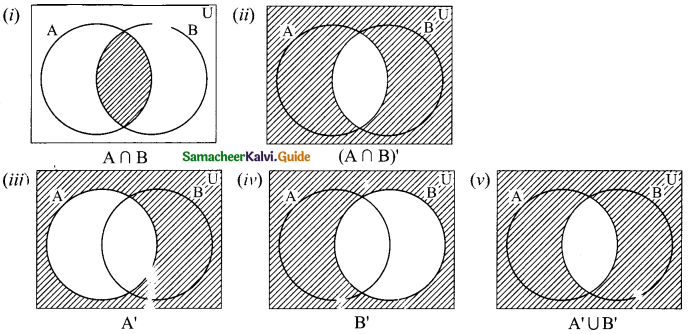
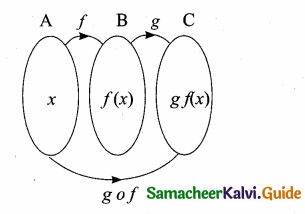
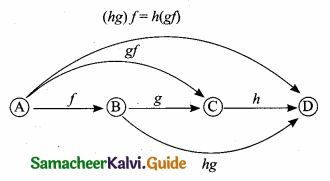
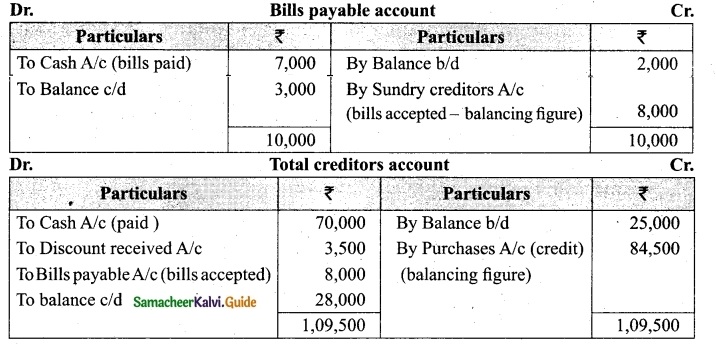
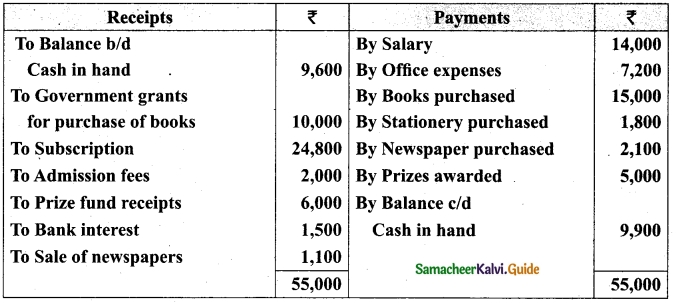
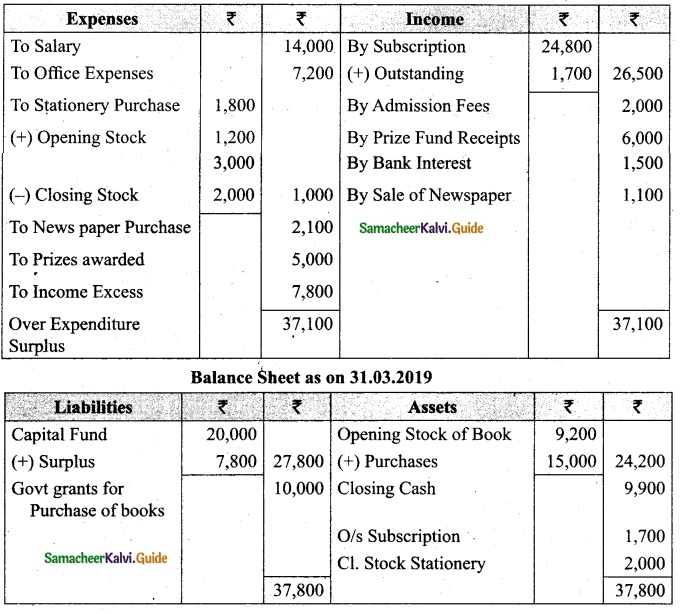
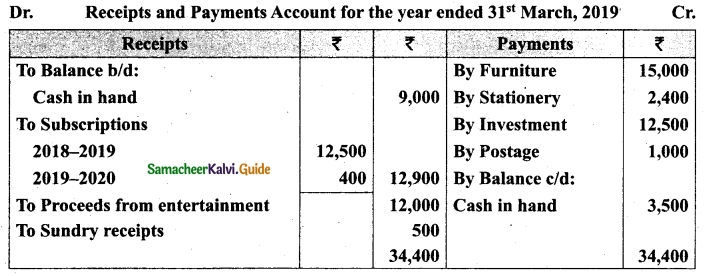
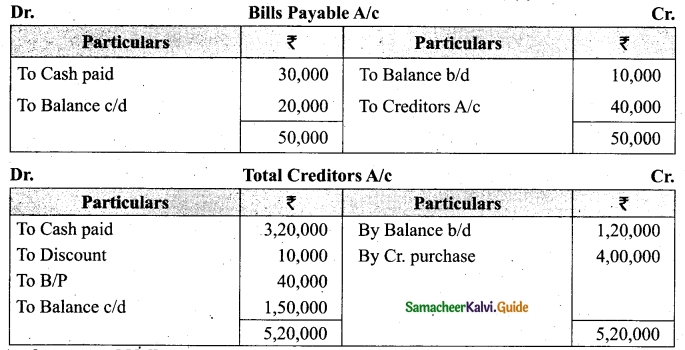
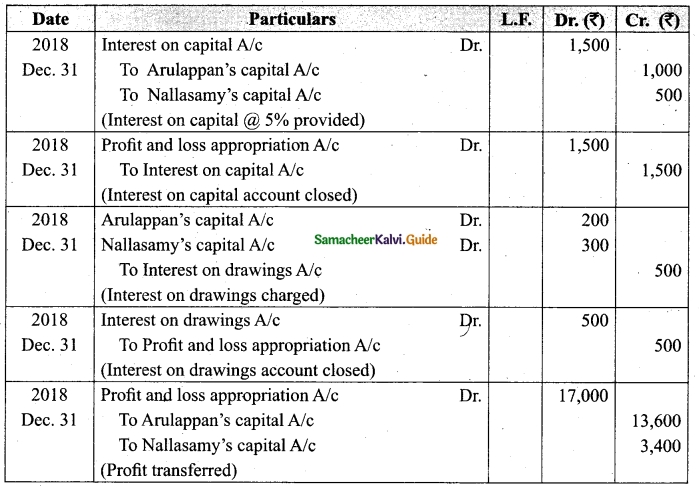
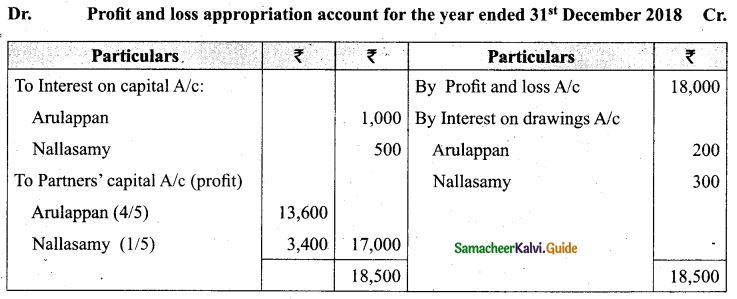
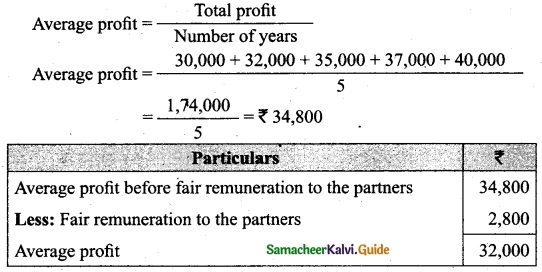
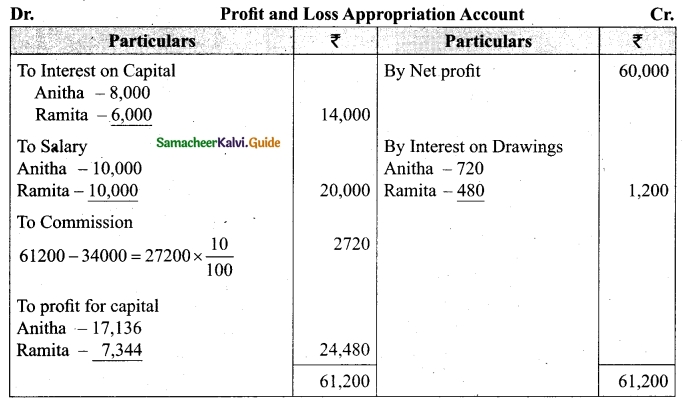
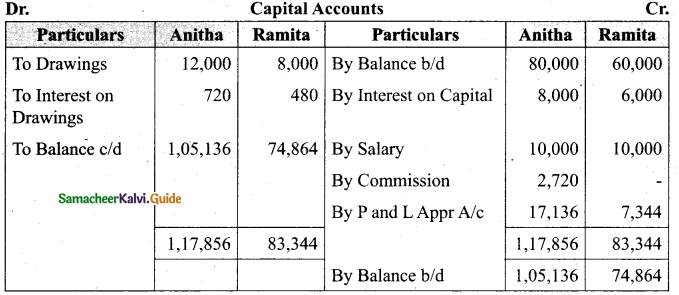
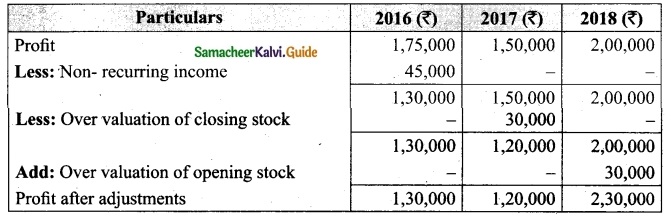
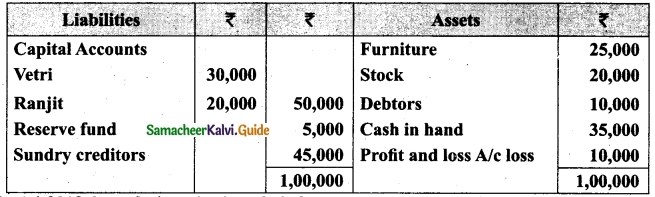
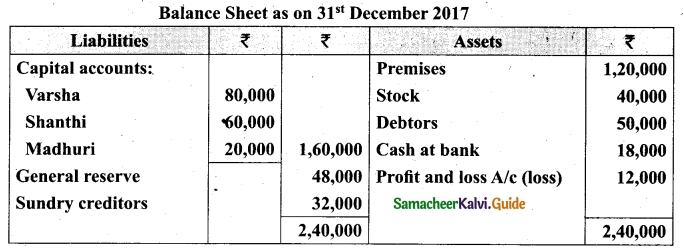
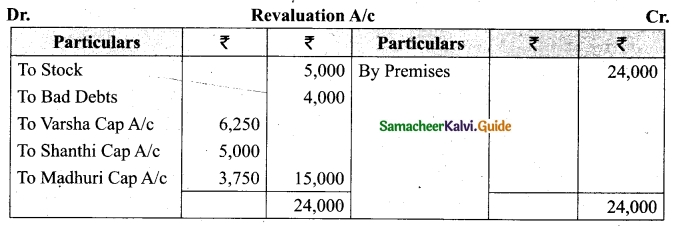
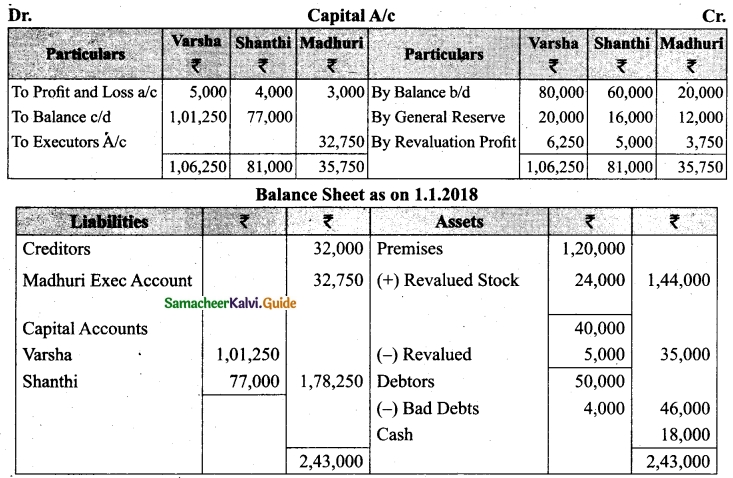
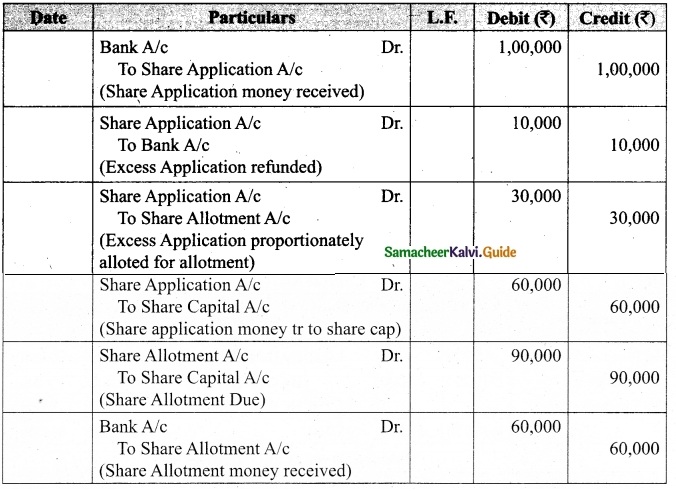
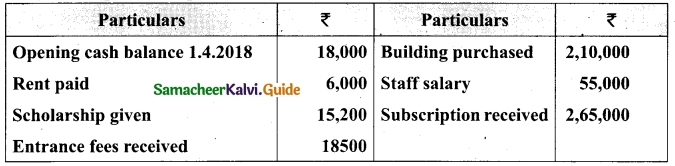
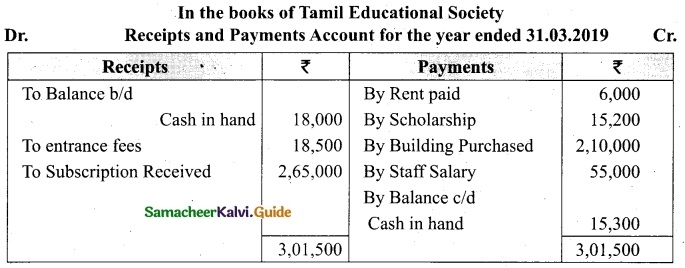
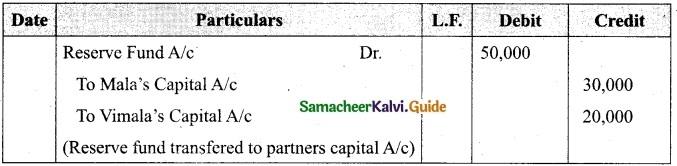
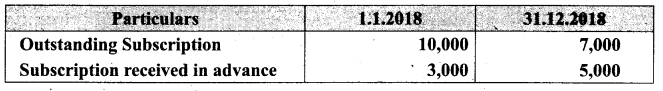
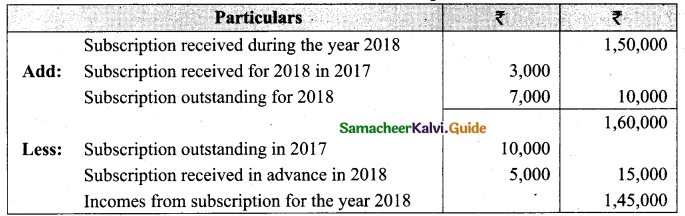
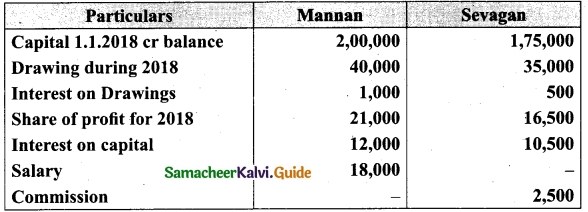
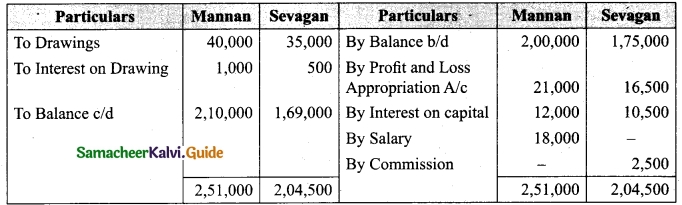
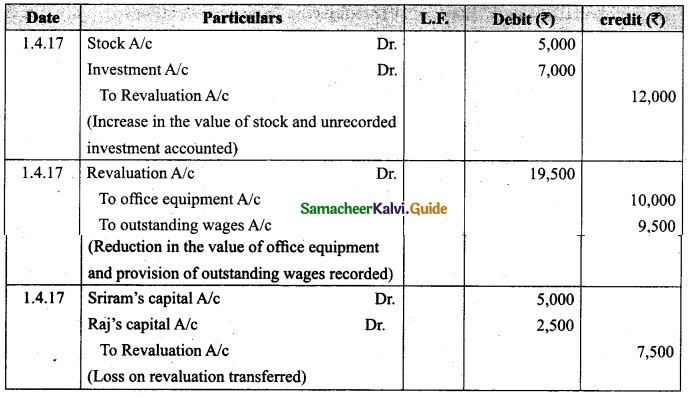
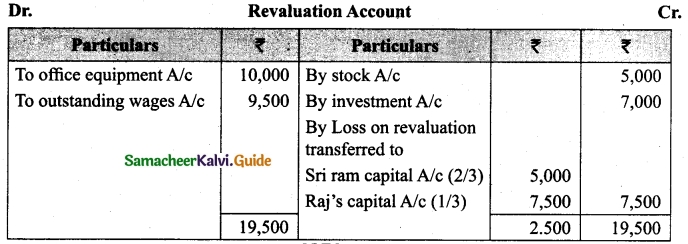
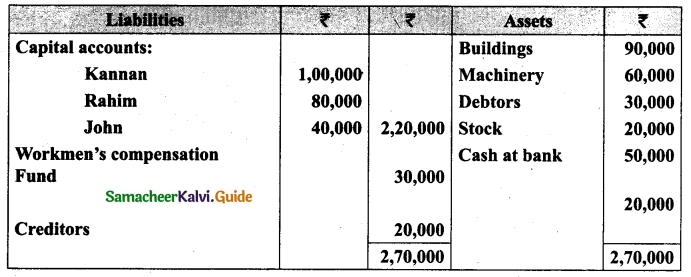
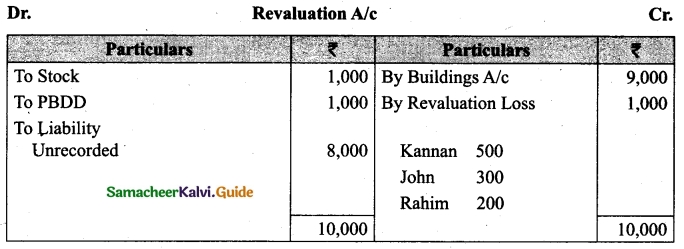
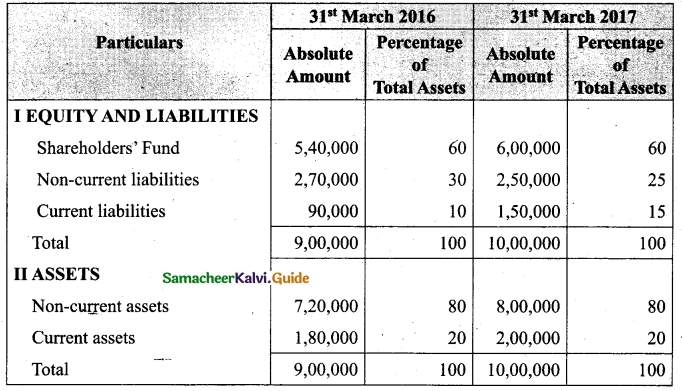
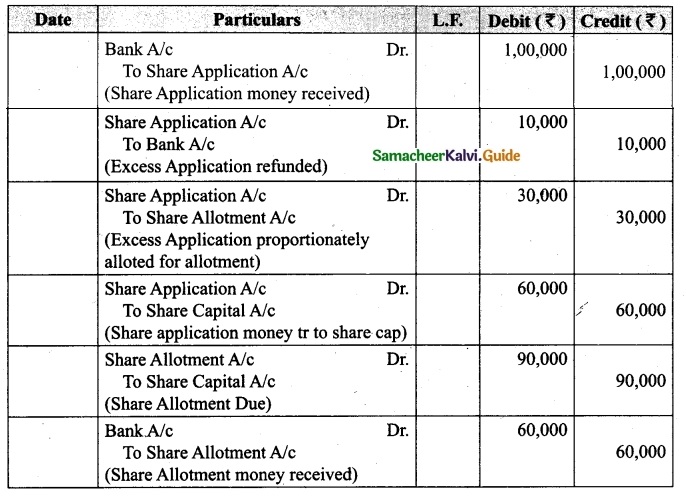
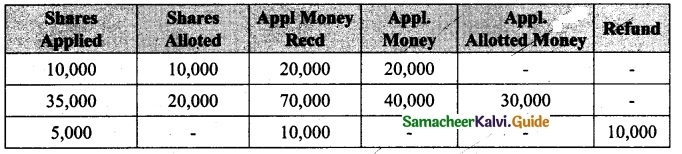
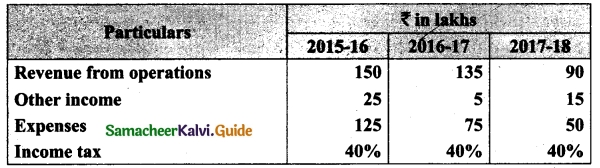
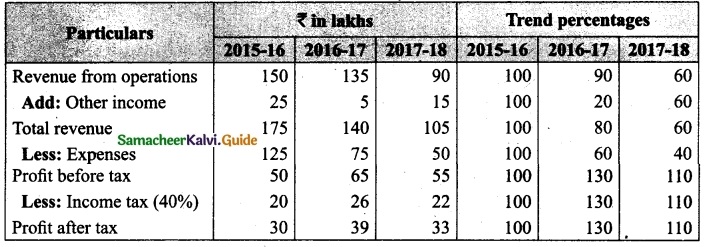
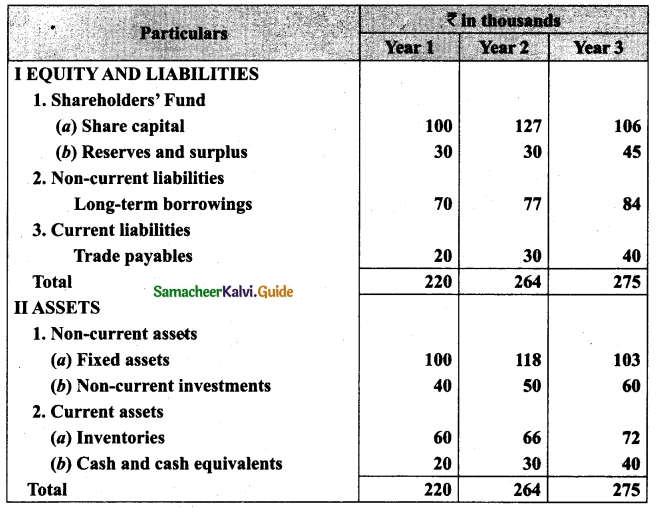
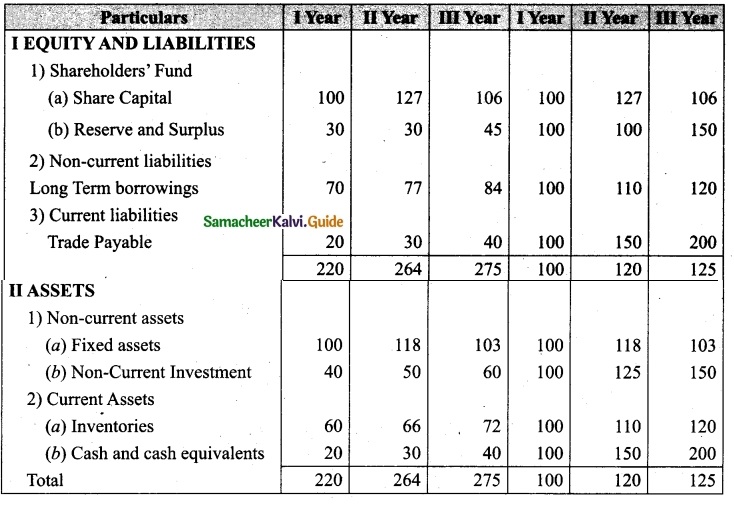
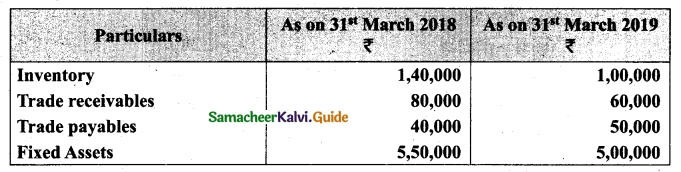
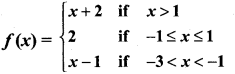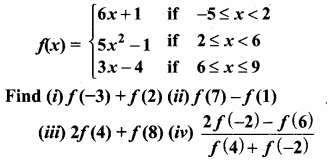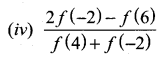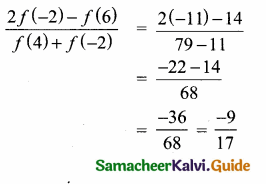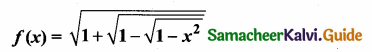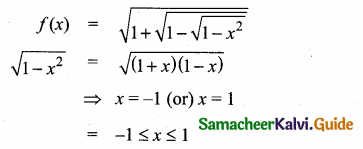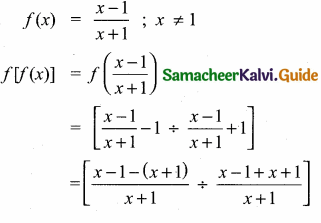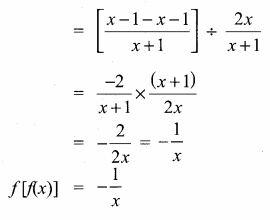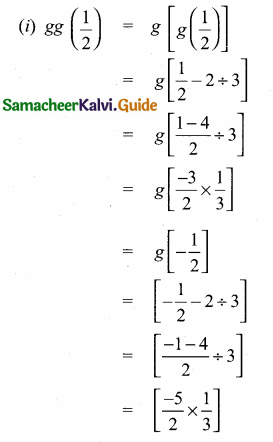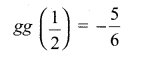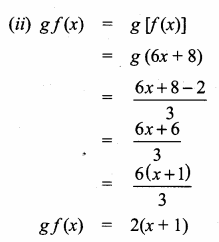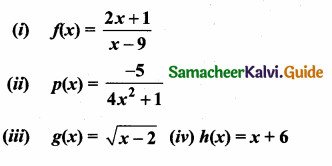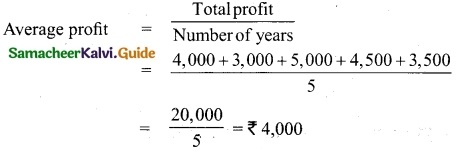Students can download Maths Chapter 1 Set Language Additional Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Set Language Additional Questions
Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
A = {set of odd natural numbers}, B = {set of even natural numbers}, then A and B are……….
(a) equal set
(b) equivalent sets
(c) overlapping sets
(d) disjoint sets
Solution:
(d) disjoint sets
Question 2.
Number of subsets in set A = {1, 2, 3} is
(a) 3
(b) 6
(c) 8
(d) 9
Solution:
(c) 8
![]()
Question 3.
The set does not have a proper subset is
(a) Finite set
(b) Infinite set
(c) Null set
(d) Singleton set
Solution:
(c) Null set
Question 4.
Sets having the same number of elements are called
(a) overlapping sets
(b) disjoints sets
(c) equivalent sets
(d) equal sets
Solution:
(c) equivalent sets
Question 5.
The set (A – B) ∪ (B – A) is
(a) AΔB
(b) A∪B
(c) A∩B
(d) A’∪B’
Solution:
(a) AΔB
![]()
Question 6.
The set of (A∪B) – (A∩B) is
(a) (A∪B)’
(b) AΔB
(c) (A∩B)’
(d) A’∪B’
Solution:
(b) AΔB
Question 7.
The set {x : x ∈ A, x ∈ B, x ∉ A∩B} is
(a) A∩B
(b) A∪B
(c) A – B
(d) AΔB
Solution:
(d) AΔB
Question 8.
The number of elements of the set {x : x ∈ Z , x² = 1} is
(a) 0
(b) 1
(c) 2
(d) 3
Solution:
(c) 2
![]()
Question 9.
If A is a proper subset of B, then A∩B =…………..
(a) A
(b) B
(c) 0
(d)A∪B
Solution:
(a) A
Question 10.
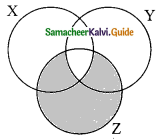
The shade region with adjoint diagram represents ……….
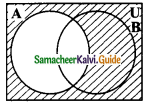
(a) A – B
(b) B – A
(c) A’
(d) B’
Solution:
(c) A’
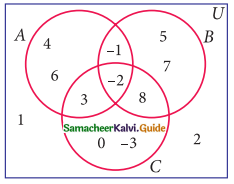
Question 11.
From the given venn diagram (A∪B)’ is ………..
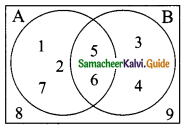
(a) {5, 6}
(b) {1, 2, 3, 4, 7}
(c) {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
(d) {8, 9}
Solution:
(d) {8, 9}
![]()
Question 12.
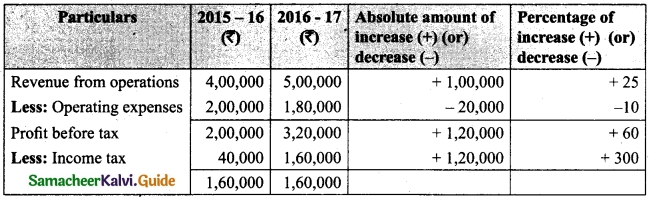
If n(A∪B∪C) = 73, n(A) = 2x, n(B) = 3x, n(C) = 5x, n(A∩B) = 10, n(B∩C) = 15, n(A∩C) = 5 and n(A∩B∩C) = 3, then the value of x is ………
(a) 9
(b) 10
(c) 5
(d) 18
Solution:
(b) 10
Question 13.
For any three sets, n(A∪B∪C) = 60, n(A) = 25, n(B) = 20, n(C) = 15, n(A∩B) = 10, n(B∩C) = 7, n(A∩C) = 3, then n(A∩B∩C) is……….
(a) 10
(b) 15
(c) 20
(d) 25
Solution:
(c) 20
Question 14.
If n(U) = 70, n(A) = 25, n(B) = 30, n(A∩B) = 5, then n(A∪B)’ is……….
(a) 5
(b) 10
(c) 15
(d) 20
Solution:
(d) 20
![]()
Question 15.
Which of the following is not correct?
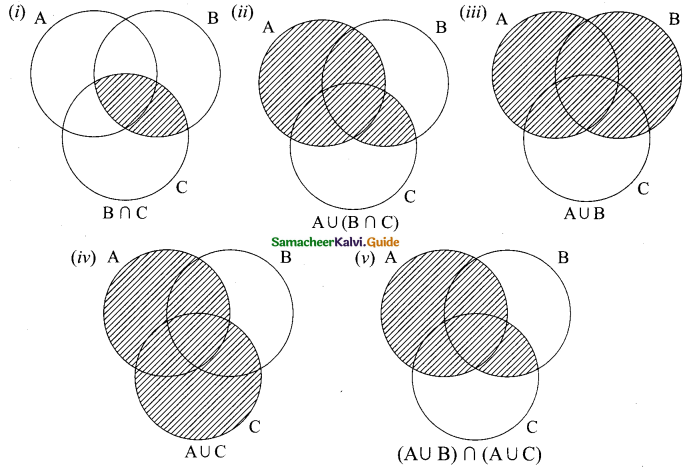
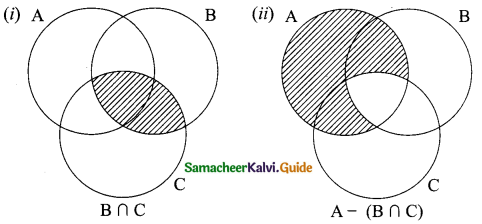
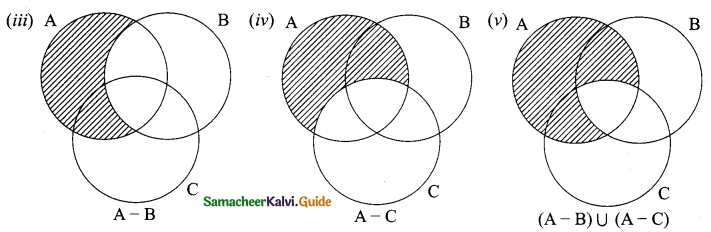
(a) A – (B∪C) = (A – B) ∩ (A – C)
(b) A – (B∩C) = (A – B) ∪ (A – C)
(c) (A∪B)’ = A’∩B’
(d) A’∪B’ = (A – B)’
Solution:
(d) A’∪B’ = (A – B)’
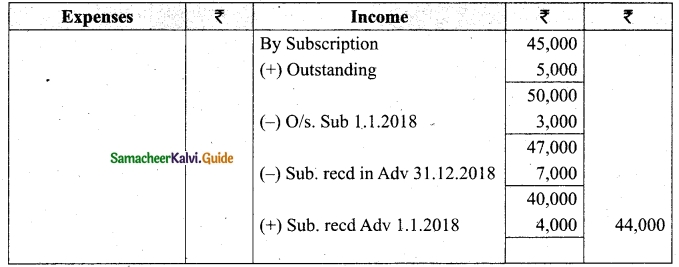
Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
Write the following in “Roster” form?
(a) A = set of the months having 31 days.
(b) B = {x : x is a natural number of 2 digits divisible by 13}
(c) C = {set of vowels in the word “father”}
(d) D = {x : 5 < x ≤ 10; x ∈ N}
(e) E = {x : x is a square natural number less than 16}
Solution:
(a) A = {Jan, March, May, July, Aug, Oct, Dec}
(b) B = {13, 26, 39, 52, 65, 78, 91}
(c) C = {a, e}
(d) D = {6, 7, 8, 9, 10}
(e) E = {1, 4, 9}
![]()
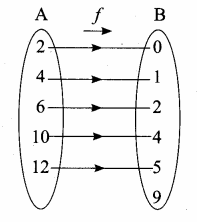
Question 2.
Given that A = {1, 3, 5, 7} B = {1, 2, 4, 6, 8}. Find
(i) AΔB and
(ii) BΔA
Solution:
(i) A = {1, 3, 5, 7}; B = {1, 2, 4, 6, 8}
A – B = {1, 3, 5, 7} – {1, 2, 4, 6, 8}
= {3, 5, 7}
B – A = {1, 2, 4, 6, 8} – {1, 3, 5, 7}
= {2, 4, 6, 8}
AΔB = (A – B) ∪ (B – A)
= {3, 5, 7} ∪ {2, 4, 6, 8}
= {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
(ii) BΔA = (B – A) ∪ (A – B)
= {2, 4, 6, 8} ∪ {3, 5, 7}
= {2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8}
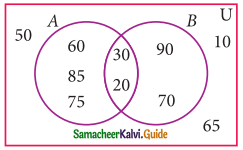
Question 3.
From the venn-diagram, list the following:
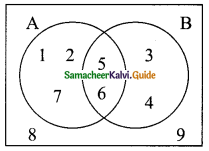
(i) A
(ii) B
(iii) A∩B
(iv)A∪B
(v) A – B
(vi) B – A
(vii) (A – B) ∩ (B – A)
Solution:
(i) A = {1, 2, 5, 6, 7}
(ii) B = {3, 4, 5, 6}
(iii) A∩B = {5, 6}
(iv) A∪B = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
(v) A – B = {1, 2, 7}
(vi) B – A = {3, 4}
(vii) (A – B) ∩ (B – A) = { }
![]()
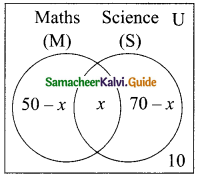
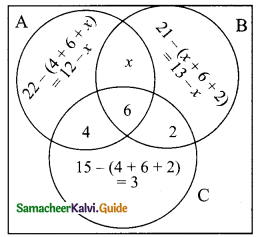
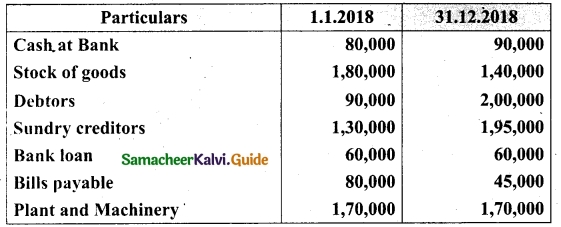
Question 4.
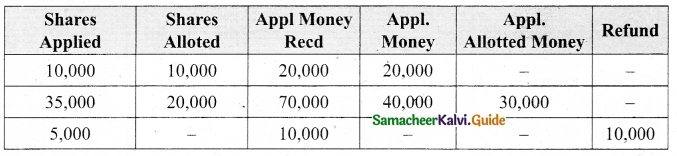
In a class there are 40 students. 26 have opted for Mathematics and 24 have opted for Science. How many student have opted for Mathematics and Science.
Solution:
Let M be the set of students opting for Mathematics.
Let S be the set of students opting for Science.
n (M∪S) = 40, n (M) = 26, n(S) = 24
n(M∪S) = n (M) + n (S)- n(M∩S)
40 = 26 + 24 – n(M∩S)
n (M∩S) = 26 + 24 – 40 = 50 – 40 = 10
∴ Number of students opted for Mathematics and Science = 10.
Another Method:
Let “x” be the number of students opted for Mathematics and Science.
Let M and S represent students opting Mathematics and Science.
n(M∪S) = 40, n(M) = 26, n(S) = 24
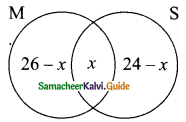
By venn-diagram, number of students in a class = 26 – x + x + 24 – x
40 = 50 – x
x = 50 – 40 = 10
x = 10
∴ Number of students opted for Mathematics and Science = 10.
![]()
Question 5.
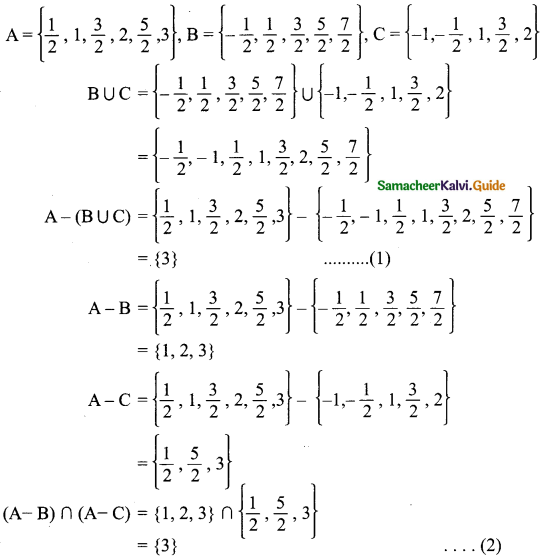
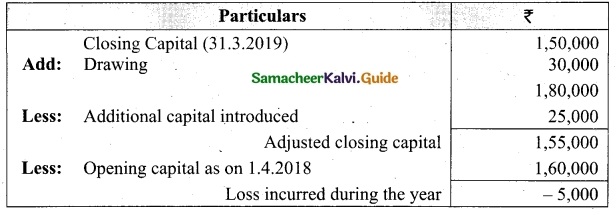
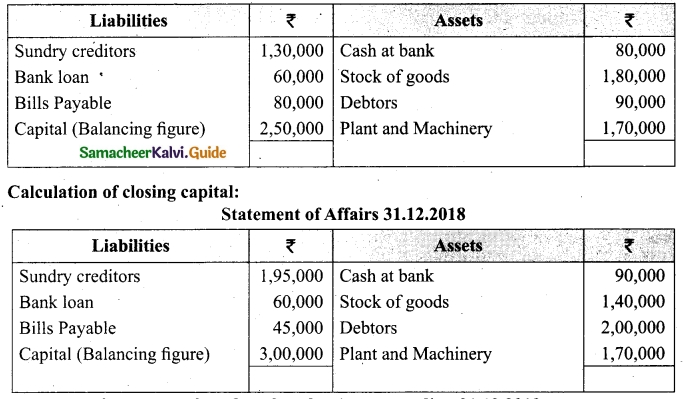
If U = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}, A = {4, 5, 7, 9}, B = {1, 3, 5, 7, 8}, Verify De Morgan’s Laws for complementation.
De Morgan’s Laws (i) (A∪B)’ = A’∩B’ (ii) (A∩B)’ = A’∪B’
Solution:
(i) A∪B = {4, 5, 7, 9} ∪ {1, 3, 5, 7, 8}
= {1, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9}
(A∪B)’ = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9} – {1, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9}
= {2, 6}……….(1)
A’= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9} – {4, 5, 7, 9}
= {1, 2, 3, 6, 8}
B’ = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9} – {1, 3, 5, 7, 8}
= {2, 4, 6, 9}
A’∩B’ = {1, 2, 3, 6, 8} ∩ {2, 4, 6, 9}
= {2, 6}………(2)
From (1) and (2) we get (A∪B)’ = A’∩B’.
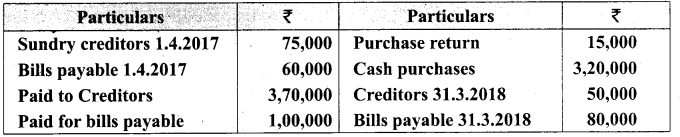
(ii) A∩B = {4, 5, 7, 9} ∩ {1, 3, 5, 7, 8}
= {5, 7}
(A∩B)’= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9} – {5, 7}
= {1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9}………(1)
A’ = {1, 2, 3, 6, 8}
B’ = {2, 4, 6, 9}
A’∪B’ = {1, 2, 3, 6, 8} ∪ {2, 4, 6, 9}
= {1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9}………(2)
From (1) and (2) we get (A∩B)’ = A’∪B’.