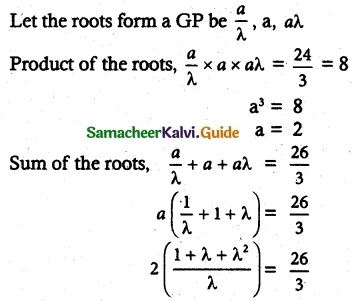
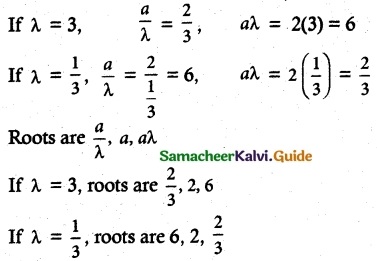
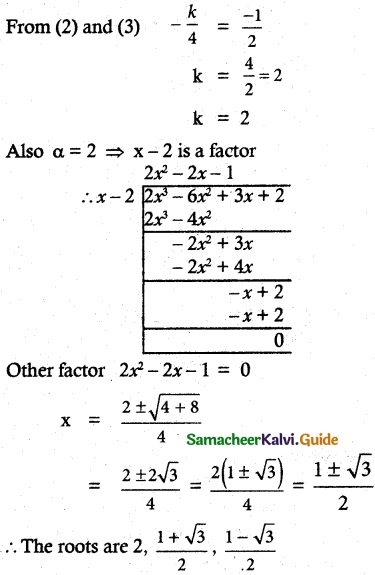
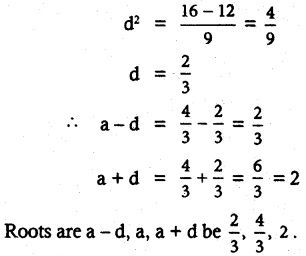Students can download 6th Science Term 3 Chapter 2 Water Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 3 Chapter 2 Water
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Water Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct Answer:
Question 1.
Around 97% of water available on earth is water.
a. fresh
b. pure
c. salty
d. polluted
Answer:
c. salty
Question 2.
Which of the following is not a part of the water cycle?
(a) evaporation
(b) condensation
(c) rain
(d) distillation
Answer:
(d) distillation
Question 3.
Which of the following processes add water vapour to the atmosphere?
i. Transpiration
ii. Precipitation
iii. Condensation
iv. Evaporation
a. ii and iii
b. ii and iv
c. i and iv
d. i and ii
Answer:
c. i and iv
Question 4.
About 30% of the freshwater is found in?
(a) glaciers
(b) groundwater
(c) other sources of water
(d) 0.3%
Answer:
(b) groundwater
![]()
Question 5.
Using R.O. plant at home eliminates lot of non-potable water. The best way to effectively use the expelled water of R.O. plant is ……….
a. make the expelled water go and seep near the bore well
b. use it for watering plants
c. to drink the expelled water after boiling and cooling
d. to use for cooking as the water is full of many nutrients
Answer:
b. use it for watering plants
II. Fill in the Blanks
- Only ……… percent of natural water is available for human consumption.
- The process of changing water into its vapour is called ………..
- ……….. is built on rivers to regulate water flow and distribute water.
- Water levels in rivers increase greatly during …………
- Water cycle is also called as ………..
Answer:
- 3%
- Evaporation
- Dam
- Rainy days
- hydrological cycle
III. True or False. If False, give the correct statement.
- Water present in rivers, lakes and ponds is unfit for use by human beings.
- Seas are formed when the water table meets the land surface.
- The evaporation of water takes place only in sunlight.
- Condensation results in the formation of dew on grass.
- Seawater can be used for irrigation as such.
Answer:
- False – Water present in rivers, lakes and ponds is fit for use by human beings.
- True
- False – The evaporation of water takes place in any source of heat.
- True
- False – Sea water can not be used for irrigation as such.
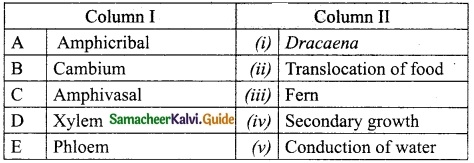
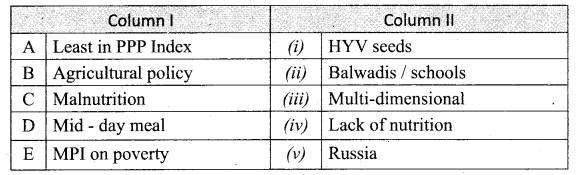
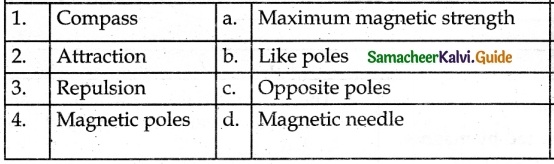
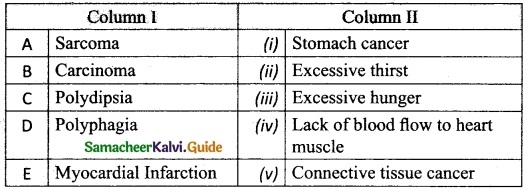
IV. Match the following
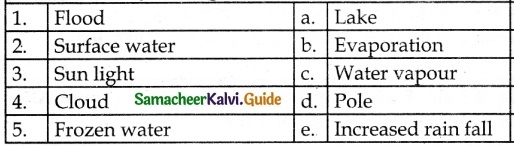
Answer:
1. – e
2. – a
3. – b
4. – c
5. – d
![]()
V. Arrange the following statements in the correct sequence
- These vapours condense to form tiny droplets of water.
- The water droplets come together to form large water droplets.
- The heat of the sun causes evaporation of water from the surface of the earth, oceans, lakes, rivers and other water bodies.
- The large water droplets become heavy and the air cannot hold them, therefore, they fall as rains.
- Water vapour is also continuously added to the atmosphere through transpiration from the surface of the leaves of trees.
- Warm air carrying clouds rises up.
- Higher up in the atmosphere, the air is cool.
- These droplets floating in the air along with the dust particles form clouds.
Answer:
- The heat of the sun causes evaporation of water from the surface of the earth, oceans, lakes, rivers and other water bodies.
- Water vapour is also continuously added to the atmosphere through transpiration from the surface of the leaves of trees.
- These droplets floating in the air along with the dust particles form clouds.
- Warm air carrying clouds rises up.
- Higher up in the atmosphere, the air is cool.
- These vapours condense to form tiny droplets of water.
- The water droplets come together to form large water droplets.
- The large water droplets become heavy and the air cannot hold them, therefore, they fall as rains.
VI. Analogy:
Question 1.
Population explosion : Water scarcity : : Recycle : ………..
Answer:
Water management
Question 2.
Groundwater : ……….. : : Surface-water : Lakes
Answer:
Wells
![]()
VII. Give Very Short Answer
Question 1.
Name four different sources of water.
Answer:
Rivers, wells, lakes, glaciers, ponds, etc.
Question 2.
How do people in cities and rural areas get water for various purposes?
Answer:
People get water from wells, canals, tanks, ponds, rivers, water tanks, hand pipes for various purposes.
Question 3.
Take out of cooled bottle of water from refrigerator and keep it on a table. After some time you notice a puddle of water around it. Why?
Answer:
The cooled surface of the bottle cools the air around it and the water vapour of the air condenses. So after some time, a puddle of water can be noticed around the bottle.
Question 4.
We could see clouds almost every day. Why doesn’t it rain daily?
Answer:
When the air around the clouds is cool the clouds then only rain comes. That is the reason why we can’t get rain daily.
Question 5.
Name the places where water is found as ice.
Answer:
Polar ice-caps, Ice sheets, and glaciers in Artie region arid Antarctica.
Question 6.
How do aquatic animals manage to live in Arctic and Antarctic Circle?
Answer:
Floating layer of ice acts as a protective coat and does not permit heat to escape from water. So aquatic animals manage to live in Arctic and Antarctic circle.
Question 7.
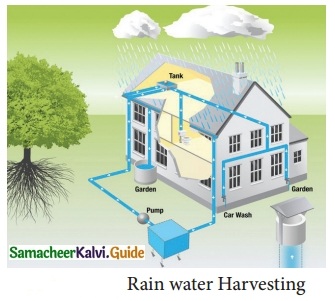
What are the types of rainwater harvesting?
Answer:
There are two types of rainwater harvesting.
- Collecting water from where it falls.
- Collecting rainwater by constructing bunds.
![]()
VIII. Give Short Answer
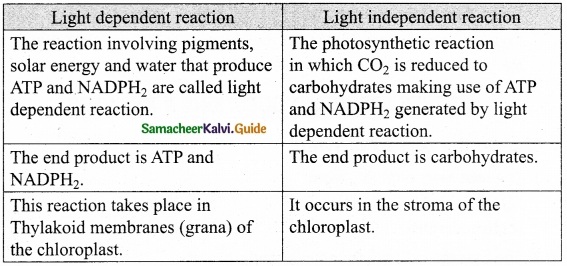
Question 1.
Differentiate between surface water and groundwater.
Answer:
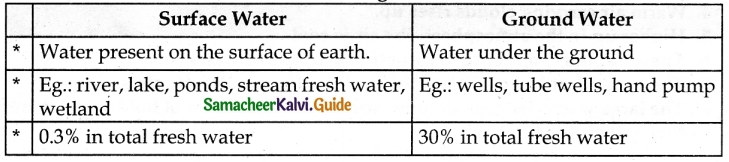
Question 2.
Write a few slogans of your own on the topic “Save Water”.
Answer:
- “To a thirsty man, a drop of water is worth more than a sack of gold”.
- “Water covers 2/3 of the surface of the earth. But only 0.002% is drinkable. Save water”
- “Save water to secure your future”
- “Don’t make nature cry, keep your water clean”
- “Store water for dry days”.
Question 3.
About 71% of earth’s surface is covered with water, then why do we face scarcity of water?
Answer:
71% of the earth’s surface is covered with water. The freshwater will be only 3%. It remains the same. But the water useful for plants, animals, and men is increasing day by day. So we face water scarcity.
Question 4.
Give reason for the following statement – Sewage should not be disposed of in rivers or oceans before treatment.
Answer:
Sewage contains harmful and toxic chemicals. They can disturb the ecosystem of the living animals, in the rivers or oceans. So it should be treated effectually before disposing into rivers or oceans.
Question 5.
The freshwater available on earth is only 3%. We cannot increase the amount of water. In that case, how can sustain the water level?
Answer:
- The sewage water treatment is to be adopted.
- Decrease the usage of pesticides, insecticides, and fertilizers in agriculture.
- Protect forest and trees.
- Adopt drip irrigation and sprinkler irrigation in agriculture.
- Rainwater harvesting should be implemented in every building.
- Create awareness about the impact of throwing wastes into the water bodies.
![]()
IX. Answer in detail
Question 1.
What is potable water? List down its characteristics.
Answer:
The water which is fit for drinking by human beings is called potable water, characteristics
- It is transparent.
- It is odourless and colourless.
- It is harmless or free from disease-causing bacteria.
Question 2.
Who is known as waterman of India? Browse the net and find the details about the award, the waterman received for water management. State the findings by drafting a report.
Answer:
The ‘Waterman of India’ is Dr. Rajendra Singh. He is a well-known water conservationist and environmentalist from Alwar district, Rajasthan.
Awards:
- He gets the Ramon Magsaysay award for community leadership in 2001.
- In 2005, he got the Jamnalal Bajaj Award for Science and Technology for rural development.
- In 2008, The Guardian named him amongst its list of 50 people who could save the planet.
- In 2015, he won the Stockholm Water Prize. He runs an NGO called ‘Tarun Bharat Sangh’ (TBS), which was founded in 1975.
- In 2016, he was bestowed with Ahimsa Award by the Institute of Jainology based in UK.
Question 3.
What is rainwater harvesting? Explain in a few sentences how it can be used in houses.
Answer:
Rainwater harvesting:
Direct collection and use of rainwater are called rainwater harvesting.
There are two types of rainwater harvesting.
(a) Collecting water from where it falls.
Example: Collecting water from the rooftops of the houses or buildings (Roof water harvesting).
(b) Collecting flowing rainwater.
Example: Collecting rainwater by constructing ponds with bund.
![]()
X. Questions Based on Higher Order Thinking Skills.
Question 1.
When there is no pond or lake in an area, will there be the formation of clouds possible in that area?
Answer:
When there is no pond or lake in an area formation of clouds will be possible. Transpiration from the aerial parts of all plants and trees will evaporate water and it will form clouds.
Question 2.
To clean the spectacles, people often breathe out on glasses to make them wet. Explain why do the glasses become wet.
Answer:
When we breathe out, the hot air comes out from our mouth which gets condensed and changed into tiny water droplets, and glasses become wet.
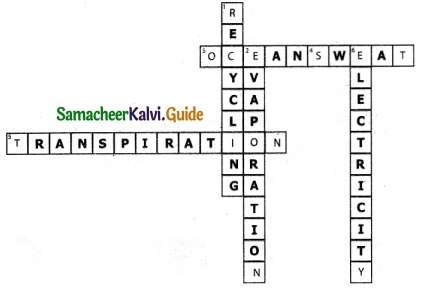
XI. Crossword
Down:
1. A method of water conservation.
2. Process of getting water vapour from seawater.
6. Water stored in dams is used for the generation of ………..
Across:
3. ………. is a large body of non -potable water found in nature.
4. In summer, the body loses water as ……..
5. Plants undergo ………….. and contribute to the water cycle.
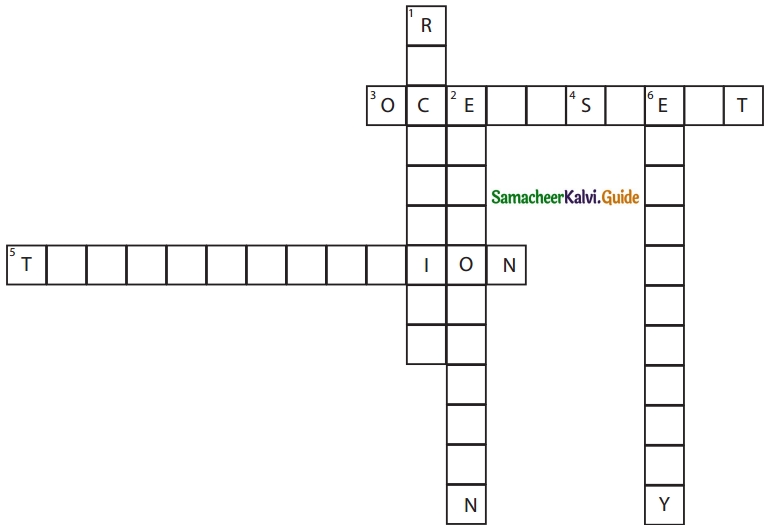
Answer:
XII. Observe the given graph carefully and answer the questions.
Question 1.
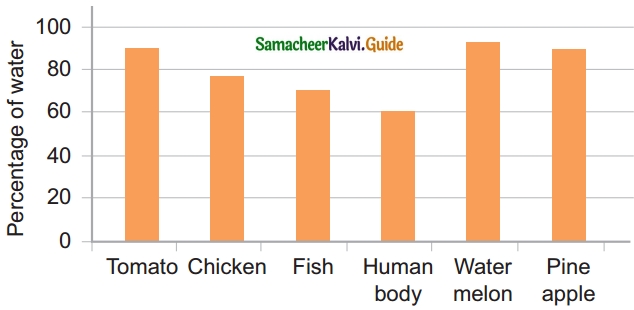
- What percentage of water is seen in fish?
- Name the food item that has the maximum amount of water in its content.
- Name the food item that has a minimum amount of water in its content.
- The human body consists of about ………. percentage of water.
- Specify the food item that can be consumed by a person when he / she is suffering from dehydration.
Answer:
- Fish – 70%
- Watermelon
- Fish
- 60%
- watermelon, pineapple
Question 2.
Look at the map of Tamilnadu showing annual rainfall and answer the questions given below
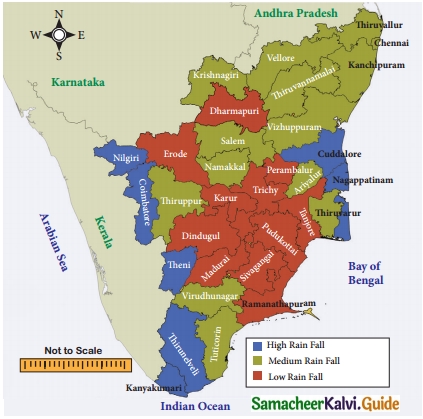
a. Identify the districts that get only low annual rainfall in Tamilnadu.
Answer:
northwest zone (Coimbatore, Erode, Namakkal, Karur)
b. Identify the districts that get a medium annual rainfall in Tamilnadu.
Answer:
Pudhukottai, Virthunagar, Sivagangai, Salem, Dindigul, Theni, Vellore.
c. State the districts that enjoy high annual rainfall in Tamilnadu.
Answer:
Tirunelveli, Kanyakumari, Chennai, Vizhupuram, Thiruvallur, Kadalur, Nagapattinam
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Water Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the best Answer:
Question 1.
If the total water on earth be 100% the percentage of freshwater is ………..
(a) 97%
(b) 93%
(c) 3%
(d) 0.3%
Answer:
(c) 3%
Question 2.
_______ is a transparent, tasteless, odourless, chemical substance.
(a) Petrol
(b) Wax
(c) Water
(d) Kerosene
Ans:
(c) Water
Question 3.
Which one is not an example of groundwater?
(a) hand pump
(b) borewell
(c) wetland water
(d) well
Answer:
(c) wetland water
Question 4.
Water from oceans, lakes, ponds, and rivers evaporates due to the heat of _______
(a) Sun
(b) Pressure
(c) Atmosphere
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Sun
Question 5.
………. are wetlands where water bodies meet the sea.
(a) lake
(b) well
(c) estuary
(d) glacier
Answer:
(c) estuary
![]()
II. True or False.
- Maximum surface water is stored in lakes.
- The oceanic volcanoes add salts to the sea.
- Water is a non-transparent chemical.
- Transpiration takes place in rivers and lakes.
- Nitrogen is used for the treatment of drinking water.
Answer:
- True
- True
- False
- False
- False
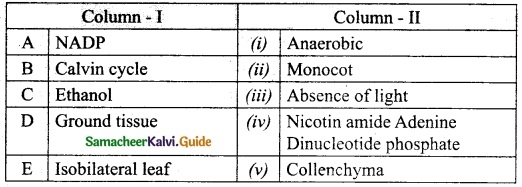
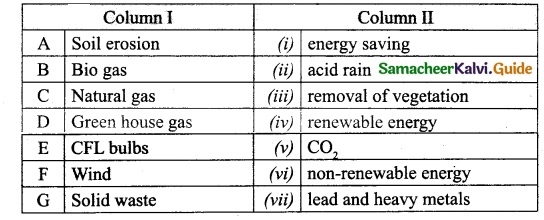
III. Match the Following:
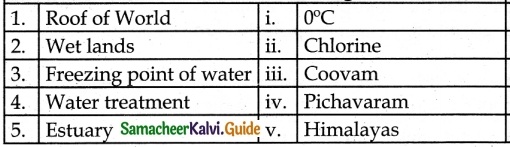
Answer:
1. – v.
2. – iv.
3. – i.
4. – ii.
5. – iii.
IV. Analogy:
- Low rainfall: Water scarcity : : Recycling Water : ………..
- Frozen Water : Glaciers : : Surface Water : ………..
- Evaporation : Sea : : …………. : Trees
- Filtering : Sand : : ………….. : Ammonia
- Solid State : ………… : : Gaseous State : Vapour
Answer:
- Water Management
- River
- Transpiration
- Disinfection
- Ice
V. Very Short Answer
Question 1.
What is the composition of water?
Answer:
- Water is composed of two atoms of hydrogen combining with one atom of oxygen gas.
- The molecular formula of water is H2O.
Question 2.
What is water?
Answer:
Water is a transparent, tasteless, odourless and nearly colourless chemical substance.
![]()
Question 3.
What is saltwater?
Answer:
Water which has more than 3% salt is called saltwater. We can not drink and use this water.
Question 4.
What are the three stages in the water cycle?
Answer:
Evaporation, condensation and precipitation.
Question 5.
What is transpiration?
Answer:
It is the process of loss of water from the aerial parts of a plant in vapour form is called transpiration.
VI. Long Answer Questions:
Question 1.
Explain the three stages of the water cycle.
Answer:
- Water cycle is a continuous process.
- It is also called the hydrological cycle.
- The stages are
1. Evaporation :
Water from oceans, lakes, ponds and rivers evaporates due to the heat of the Sun.
2. Condensation:
Water vapour which enters into the atmosphere by evaporation moves upward with air, gets cooled and changes into tiny water droplets that form clouds in the sky.
3. Precipitation:
Millions of tiny droplets collide with each other to form large droplets. The air around the clouds is cool these drops of a waterfall in the form of snow or rain.
![]()
Question 2.
How water is conserved by water management method?
Answer:
Water management consists of the following factors:
- Bringing awareness about the bad effects of throwing wastes into the water bodies.
- Recycling of water by separating pollutants.
- Minimizing the use of chemical fertilizers in agriculture. It reduces the pollution of underground water.
- Controlling deforestation.
- Adopting drip irrigation and sprinkler irrigation in agriculture. In this way, a lesser amount of water can be used for irrigation.