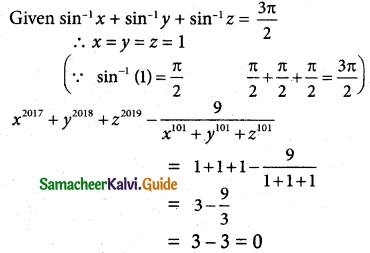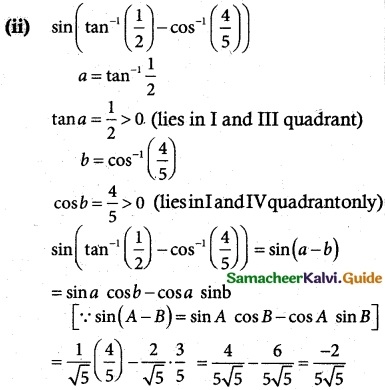Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 5 Two Dimensional Analytical Geometry – II Ex 5.2 Textbook Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 5 Two Dimensional Analytical Geometry – II Ex 5.2
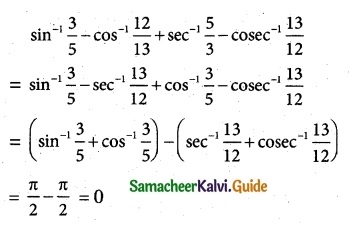
Question 1.
Find the equation of the parabola in each of the cases given below:
(i) focus (4, 0) and directrix x = -4.
(ii) passes through (2, – 3) and symmetric about y axis.
(iii) vertex (1,-2) and focus (4, – 2).
(iv) end points of latus rectum (4, -8) and (4, 8).
Solution:
(i) focus (4, 0) and directrix x = -4
Parabola is open rightwards vertex (0, 0)
a = 4
(Distance AS = 4 unit)
f² = 4(4) x
Equation of parabola
y² = 16x.
![]()
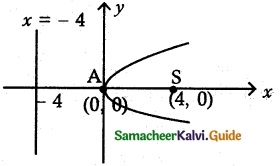
(ii) passes through (2, – 3) and symmetric about y-axis
x2 = 4ay
It passes through (2, -3)
⇒ 22 = 4a(-3)
4 = -12a ⇒ a = \(-\frac{1}{3}\) ⇒ 4a = \(-\frac{4}{3}\)
∴ Equation of parabola is x2 = \(-\frac{4}{3}\) y
3x2= – 4y.
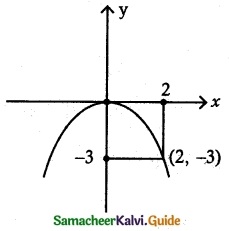
(iii) vertex (1,-2) and focus (4, – 2)
In given data the parabola is open rightwards and symmetric about the line parallel to x-axis.
Equation of parabola
(y – k)² = 4a(x – h)
Vertex (h, k) = (1, -2)
(y + 2)² = 4a(x – 1)
a = AS = 3
Equation of parabola
(y + 2)² = 4(3)(x – 1)
(y + 2)² = 12(x – 1)
(iv) end points of latus rectum (4, -8) and (4, 8)
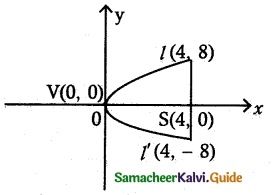
Focus = (4, 0)
Equation of the parabola will be of the form y2 = 4ax
Here a = 4
⇒ y2 = 16x
![]()
Question 2.
Find the equation of the ellipse in each of the cases given below:
(i) foci (± 3, 0), e = \(\frac {1}{2}\)
(ii) foci (0, ±4) and end points of major axis are (0, ±5).
(iii) length of latus rectum 8, eccentricity = \(\frac {3}{5}\) and major axis on x-axis.
(iv) length of latus rectum 4, distance between foci and major axis as y axis.
Solution:
(i) foci (± 3, 0), e = \(\frac {1}{2}\)
foci (± c, 0) = (± 3, 0)
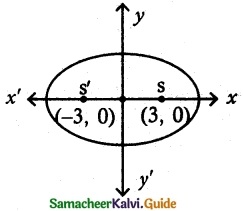
e = \(\frac {1}{2}\)
c = ae = 3
a(\(\frac {1}{2}\)) = 3
a = 6 ⇒ a² = 36
b² = a² – c²
b² = 36 – 9 = 27
b² = 27
Equation of the ellipse be \(\frac {x^2}{a^2}\) + \(\frac {y^2}{b^2}\) = 1
\(\frac {x^2}{36}\) + \(\frac {y^2}{27}\) = 1
(ii) foci (0, ±4) and end points of major axis are (0, ±5)
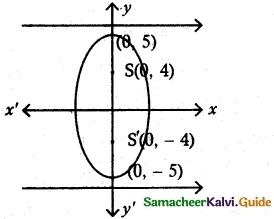
foci (0, ±c) = (0, +4)
vertex (0, ±a) = (0, ±5)
∴ c = 4, a = 5
ae = 4
5e = 4
e = \(\frac {4}{5}\)
b² = a² – c²
= 25 – 16
b² = 9
Equation of the ellipse be \(\frac {x^2}{b^2}\) + \(\frac {y^2}{a^2}\) = 1
\(\frac {x^2}{9}\) + \(\frac {y^2}{25}\) = 1
![]()
(iii) length of latus rectum 8, eccentricity = \(\frac {3}{5}\) and major axis on x-axis.
e = \(\frac {3}{5}\)
Latus rectum \(\frac {2b^2}{a}\) = 8
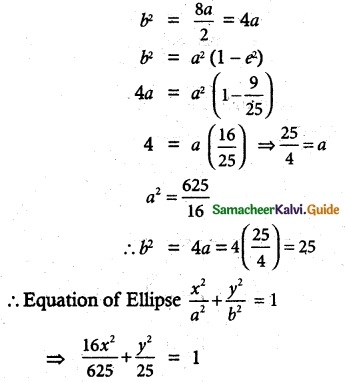
(iv) length of latus rectum 4, distance between foci 4√2 and major axis as y-axis
Given \(\frac{2 b^{2}}{a}\) = 4 and 2ae = \(4 \sqrt{2}\)
Now \(\frac{2 b^{2}}{a}\) = 4 2b2 = 4a
⇒ b2 = 2a
2ae = \(4 \sqrt{2}\) ae = \(2 \sqrt{2}\)
So a2e2 = 4(2) = 8
We know b2 = a2(1 – e2) = a2 – a2e2
⇒ 2a = a2 – 8 ⇒ a2 – 2a -8 = 0
⇒ (a – 4) (a +2) = 0 ⇒a = 4 or -2
As a cannot be negative
a = 4 So a2 = 16 and b2 = 2(4) = 8
Also major axis is along j-axis
So equation of ellipse is \(\frac{x^{2}}{8}+\frac{y^{2}}{16}\) = 1
Question 3.
Find the equation of the hyperbola in each of the cases given below:
(i) foci (± 2, 0), eccentricity = \(\frac {3}{2}\)
(ii) centre (2, 1) one of the foci (8, 1) and corresponding directrix x = 4.
(iii) passing through (5, -2) and length of the transverse axis along x axis and length 8 units.
Solution:
(i) foci (± 2, 0), eccentricity = \(\frac {3}{2}\)
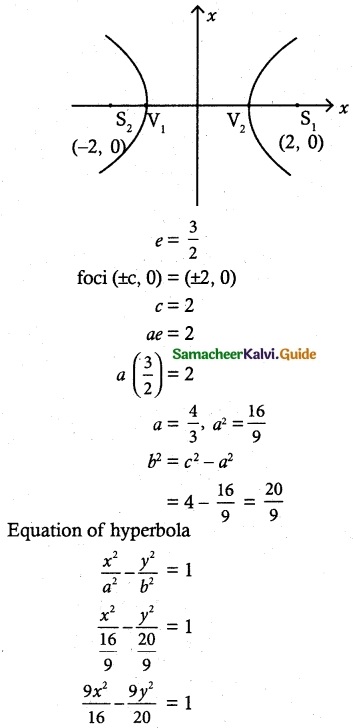
![]()
(ii) centre (2, 1) one of the foci (8, 1) and corresponding directrix x = 4.
Distance CS = ae = 6 …….. (1)
Directrix \(\frac {a}{e}\) = 4 ……… (2)
(1) × (2) ⇒ ae × \(\frac {a}{e}\) = 24
a² = 24
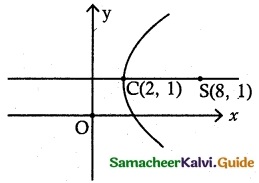
∴ c = ae = 6
b² = c² – a²
= 36 – 24 = 12
The transverse axis is parallel to x-axis
∴ \(\frac {(x-h)^2}{a^2}\) – \(\frac {(y – k)^2}{b^2}\) = 1 (h, k) = (2, 1)
\(\frac {(x-2)^2}{24}\) – \(\frac {(y – 1)^2}{12}\) = 1
(iii) passing through (5,-2) and length of the transverse axis along x axis and of length 8 units.
Transverse axis along x-axis
\(\frac {x^2}{a^2}\) – \(\frac {y^2}{b^2}\) = 1
Length of transverse axis 2a = 8
⇒ a = 4
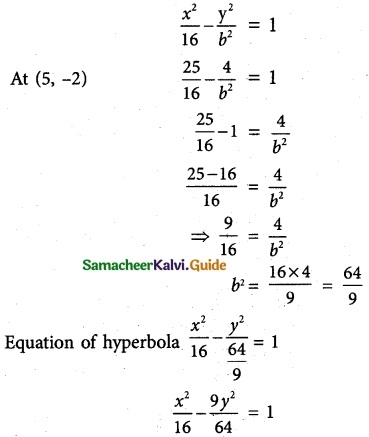
Question 4.
Find the vertex, focus, equation of directrix and length of the latus rectum of the following:
(i) y² = 16x
(ii) x² = 24y
(iii) y² = -8x
(iv) x² – 2x + 8y + 17 = 0
(v) y² – 4y – 8x + 12 = 0
Solution:
(i) y² = 16x
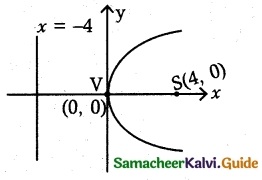
4a = 16
a = 4
(a) Vertex V (0, 0)
(b) Focus S(a, 0) = S(4, 0)
(c) Equation of the directrix x = – a
x = -4 ⇒ x + 4 = 0
(d) Length of the latus rectum = 4a = 4(4)
= 16
![]()
(ii) x² = 24y
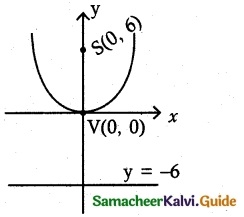
(a) Vertex V (0, 0),
(b) Focus S (0, a) = S(0, 6)
(c) Equation of the directrix y = -a = -6
⇒ y + 6 = 0
(d) Length of the latus rectum = 4a
= 4 (6) = 24
(iii) y² = -8x
4a = 8,
a = 2
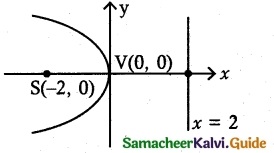
(a) Vertex V(0, 0) = ( 0, 0)
(b) Focus S(-a, 0) = (-2, 0)
(c) Equation of the directrix x = a = 2
x – 2 = 0
(d) Length of the latus rectum 4a = 8
(iv) x² – 2x + 8y + 17 = 0
x² – 2x = -8y – 17
(x – 1)² = -8y – 17 + 1
(x – 1)² = -8y – 16
(x – 1)² = -8(y + 2)
It is form of (x – h)² = -4a(y – k)
4a = 8 ⇒ a = 2
(a) Vertex be (h, k) = (1, -2)
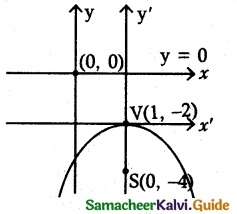
(b) Foeus = (0 +h, -a + k) = (0 + 1, -2 – 2) = (1, -4)
(c) Equation of the directrix is y + k + a = 0
y – 2 + 2= 0
y = 0
(d) Length of latus rectum is 4a = 4 × 2 = 8 units,
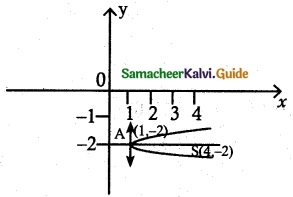
(v) y² – 4y – 8x + 12 = 0
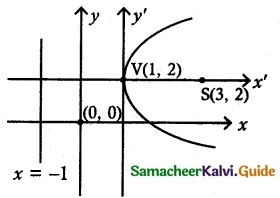
y² – 4y = 8x – 12
(y – 2)² = 8x – 12 + 4
= 8x – 8
= 8 (x – 1)
(y – 2)² = 8 (x – 1)
It is form of (y – k)² = Aa(x – h)
4a = 8 ⇒ a = 2
(a) Vertex (h, k) = (1, 2)
(b) Focus = (a+h, 0 + k) = (2 + 1, 0 + 2) = (3, 2)
(c) Equation of the directrix x = -a + h
= -2 + 1
= -1
x + 1 = 0
(d) Length of latus rectum is
4a = 4 × 2 = 8 units.
![]()
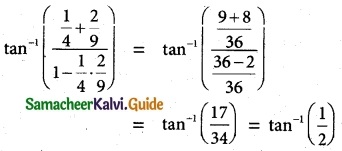
Question 5.
Identify the type of conic and find centre, foci, vertices and directrices of each of the following:
(i) \(\frac {x^2}{25}\) + \(\frac {y^2}{9}\) = 1
(ii) \(\frac {x^2}{3}\) + \(\frac {y^2}{10}\) = 1
(iii) \(\frac {x^2}{25}\) – \(\frac {y^2}{144}\) = 1
(iv) \(\frac {y^2}{16}\) – \(\frac {x^2}{9}\) = 1
Solution:
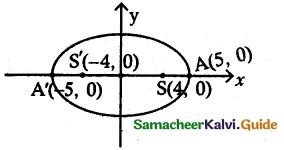
(i) \(\frac{x^{2}}{25}+\frac{y^{2}}{9}\) = 1
It is of the form \(\frac{x^{2}}{a^{2}}+\frac{y^{2}}{b^{2}}\) = 1, which is an ellipse
Here a2 = 25, b2 = 9
a = 5, b = 3
e2 = \(\frac{a^{2}-b^{2}}{a^{2}}=\frac{25-9}{25}=\frac{16}{25}\) ⇒ e = \(\frac{4}{5}\)
Now e = \(\frac{4}{5}\) and a = 5 ⇒ ae = 4 and \(\frac{a}{e}=\frac{5}{4 / 5}=\frac{25}{4}\)
Here the major axis is along x axis
∴ Centre = (0, 0)
Foci = (± ae, 0) = (± 4, 0)
Vertices = (± a, 0) = (±5, 0)
Equation of directrix x = ± \(\frac{a}{e}\) (ie.,) x = ± \(\frac{25}{4}\)
(ii) \(\frac {x^2}{3}\) + \(\frac {y^2}{10}\) = 1
It is an ellipse. The major axis is along y axis
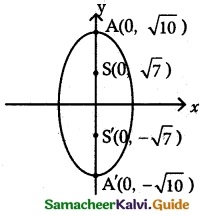
a² = 10 b² = 3
a = \(\sqrt {10}\) b = √3
c² = a² – b²
= 10 – 3 = 7
c = √7
ae = √7 .
\(\sqrt {10}\) = √7
e = \(\sqrt {\frac{7}{10}}\)
(a) Centre (0, 0)
(b) Vertex (0, ±a) = (0, ±\(\sqrt {10}\))
(c) Foci (0, ±c) – (0, ±√7)
(d) Equation of the directrix a
y = ±\(\frac{a}{e}\)
= ±\(\frac{\sqrt {10}}{√7}\).\(\sqrt {10}\) = ±\(\frac {10}{√7}\)
y = ±\(\frac {10}{√7}\)
![]()
(iii) \(\frac {x^2}{25}\) – \(\frac {y^2}{144}\) = 1
It is Hyperbola. The transverse axis the x axis.
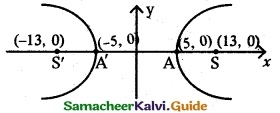
a² = 25; b² = 144
a = 5; b = 12
c² = a² + b²
= 25 + 144 = 169
c = 13
ae = 13
5e = 13
e = \(\frac {13}{5}\)
(a) Centre (0, 0)
(b) Vertex (± a, 0) = (± 5, 0)
(c) Foci (± c, 0) = (± 13, 0)
(d) Equation of the directrix
x = ±\(\frac {a}{e}\) = ±\(\frac {5}{\frac{13}{5}}\) = ±\(\frac {25}{13}\)
x = ±\(\frac {25}{13}\)
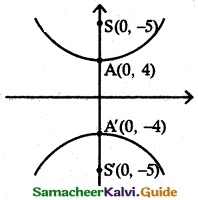
(iv) \(\frac {y^2}{16}\) – \(\frac {x^2}{9}\) = 1
It is Hyperbola. The transverse axis the y axis.
a² = 16; b² = 9
a = 4; b = 3
c² = a² + b²
= 16 + 6 = 25
c = 5
ae = 5
4e = 5
e = \(\frac {5}{4}\)
(a) Centre (0, 0)
(b) Vertex (0, ±a) = (0, ±4)
(c) Foci (0, ±ae) = (0, ±5)
(d) Equation of the directrix
y = ±\(\frac {a}{e}\) = ±\(\frac {4}{\frac{5}{4}}\) = ±\(\frac {16}{5}\)
y = ±\(\frac {16}{5}\)
![]()
Question 6.
Prove that the length of the latns rectum of the hyperbola \(\frac {x^2}{a^2}\) – \(\frac {y^2}{b^2}\) = 1 is \(\frac {2b^2}{a}\)
Solution:
The latus rectum LL’ of an hyperbola \(\frac {x^2}{a^2}\) – \(\frac {y^2}{b^2}\) = 1 passes through S(ae, 0)
Hence L is (ae, y1)
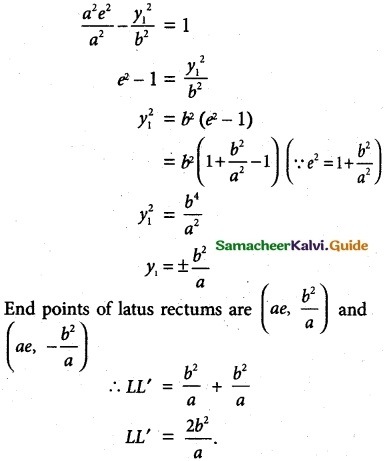
Hence proved
Question 7.
Show that the absolute value of the difference of the focal distances of any point P on the hyperbola is the length of its transverse axis.
Solution:
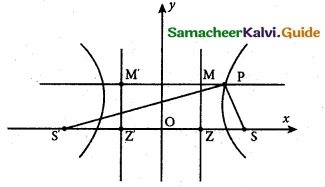
Let P be a point on the hyperbola.
Definition of conic
\(\frac {SP}{PM}\) = e; \(\frac {S’P}{PM’}\) = e
SP = e(PM) ……..(1)
S’P = e (PM’) ……….(2)
(2) – (1) ⇒ S’P – SP = e PM’- e PM
= e(PM’ – PM)
= e MM’
= e ZZ’
[∵ MM’ = ZZ’ = \(\frac {2a}{e}\) ]
= e(\(\frac {2a}{e}\))
S’P – SP = 2a (constant)
= length of the transverse axis.
![]()
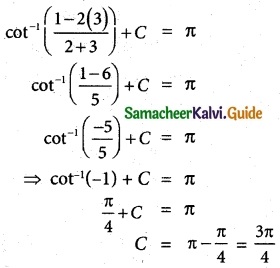
Question 8.
Identify the type of conic and find centre, foci, vertices and directrices of each of the following:
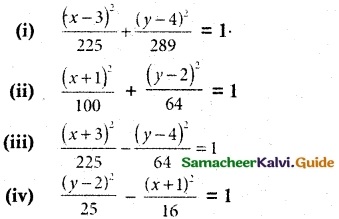
(v) 18x² + 12y² – 144x + 48y + 120 = 0
(vi) 9x² – y² – 36x – 6y + 18 = 0
Solution:
(i) \(\frac {(x-3)^2}{225}\) + \(\frac {(y-4)^2}{289}\) = 1
It is an ellipse. The major axis is parallel to y axis
a² = 289, b² = 225
a = 17, b = 15
c² = a² – b²
= 289 – 225 = 64
c = 8
ae = 8
17e = 8
e = \(\frac {8}{17}\)
Centre (h, k) = (3, 4)
Vertices (h, ±a + k) = (3, 17 + 4) & (3, -17 + 4)!
= (3, 21) and (3, -13)
Foci (h + 0, ± c + k) = (3, 8 + 4) & (3, -8 + 4)
= (3, 12) and (3, -4)

![]()
(ii) \(\frac {(x+1)^2}{100}\) + \(\frac {(y-2)^2}{64}\) = 1
It is an ellipse. The major axis is parallel to the x-axis.
a² = 100, b² = 64
a = 10, b = 8
c² = a² – b²
= 100 – 64 = 36
c = 6
ae = 6
10 e = 6
e = \(\frac {6}{10}\) = \(\frac {3}{5}\)
centre (h, k) = (-1, 2)
vertices (h±a, k) = (-1±10, 2)
= (-1+10, 2) & (-1-10, 2)
= (9, 2) & (-11, 2)
foci (h±c, k) = (-1±6, 2)
= (-1+6, 2) & (-1-6, 2)
= (5, 2) & (-7, 2)
directrix x = ±\(\frac {a}{e}\) + h
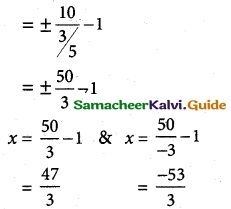
(iii) \(\frac {(x+3)^2}{225}\) + \(\frac {(y-4)^2}{64}\) = 1
It is an hyperbola. The transverse axis is parallell to x axis.
a² = 225, b² = 64
a = 15, b = 8
c² = a² – b²
= 225 + 64
c² = 289
c = 17
ae = 17
5e = 17
e = \(\frac {17}{15}\)
centre (h, k) = (-3, 4)
vertices (h±a, k) = (-3±15, 4)
= (-3+15, 4) & (-3-15, 4)
= (12, 4) & (-18, 4)
foci (h±c, k) = (-3±17, 4)
= (-3+17, 4) & (-3-17, 4)
= (14, 4) & (-20, 4)
directrix x = ±\(\frac {a}{e}\) + h
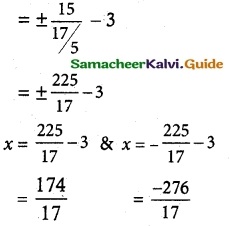
![]()
(iv) \(\frac {(y-2)^2}{25}\) + \(\frac {(x+1)^2}{16}\) = 1
It is an hyperbola. The transverse axis is parallell to y axis.
a² = 25, b² = 16
a = ±5, b = 4
c² = a² + b²
= 25 + 16
= 41
c = \(\sqrt {41}\)
ae = \(\sqrt {41}\)
5 e = \(\sqrt {41}\)
e = \(\frac {\sqrt {41}}{5}\)
centre (h, k) = (-1, 2)
vertices (h, ±a + k) = (-1, ±5 + 2)
= (-1, 5 + 2) & (-1, -5 + 2)
= (-1, 7) & (-1, -3)
foci (h, ±c + k) = (-1, ±\(\sqrt {41}\) + 2)
= (-1, \(\sqrt {41}\) + 2) & (-1, –\(\sqrt {41}\) + 2)
directrix x = ±\(\frac {a}{e}\) + k
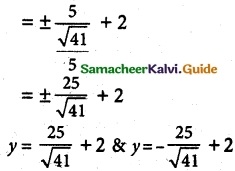
(v) 18x² + 12y² – 144x + 48y + 120 = 0
18x² – 144x + 12y² + 48y = -120
18 (x² – 8x) + 12 (y² + 4y) = -120
18 (x – 4)² + 12 (y + 2)² = -120 + 288 + 48
18(x – 4)² + 12 (y + 2)² = 216
\(\frac {18(x-4)^2}{216}\) + \(\frac {12(y+2)^2}{216}\) = 1
\(\frac {(x-4)^2}{12}\) + \(\frac {(y+2)^2}{18}\) = 1
It is an ellipse. The major axis is parallell to y axis.
a² = 18, b² = 12
a = \(\sqrt {18}\), b = 2√3
= 3 √2
c² = a² + b²
= 18 – 12
= 6
c = √6
ae = √6
3√2 e = √6
e = \(\frac {√6}{3√2}\) = \(\frac {√3}{3}\) = \(\frac {1}{√3}\)
centre (h, k) = (4, -2)
vertices (h, ±a + k) = (4, ±3√2 – 2)
= (4, 3√2 – 2) & (4, -3√2 – 2)
foci (h, ±c + k) = (4, ±√6 – 2)
= (4, ±√6 – 2) & (4, -√6 – 2)
directrix y = ±\(\frac {a}{e}\) + k
= ±\(\frac {3√2}{1}\) – 2
= ±3√6 – 2
y = 3√6 – 2 & y = -3√6 – 2
![]()
(vi) 9x² – y² – 36x – 6y + 18 = 0
9x² – 36x – y² – 6y = – 18
9(x² – 4x) – (y² + 6y) = -18
9(x – 2)² – (y + 3)² = -18 + 36 – 9
9(x – 2)² – (y + 3)² = 9
\(\frac {(x-2)^2}{1}\) – \(\frac {(y+3)^2}{9}\) = 1
It is hyperbola. The transverse axis is parallel to x axis.
a² = 1; b² = 9
a = 1; b = 3
c² = a² + b²
= 1 + 9
= 10
c = \(\sqrt {10}\)
ae = \(\sqrt {10}\)
e = \(\sqrt {10}\)
centre (h, k) = (2, -3)
vertices (h ± a, k) = (2 ± 1, -3)
= (2 + 1, -3) & (2 – 1, -3)
= (3, -3) & (1, -3)
foci (h ± c, k) = (2 ±\(\sqrt {10}\), -3)
= (2 + \(\sqrt {10}\), -3) & (2 –\(\sqrt {10}\), -3)
directrix x = ±\(\frac {a}{e}\) + h
= ±\(\frac {1}{\sqrt {10}}\) + 2 & x = –\(\frac {1}{\sqrt {10}}\) + 2
![]()