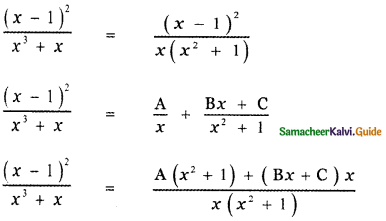
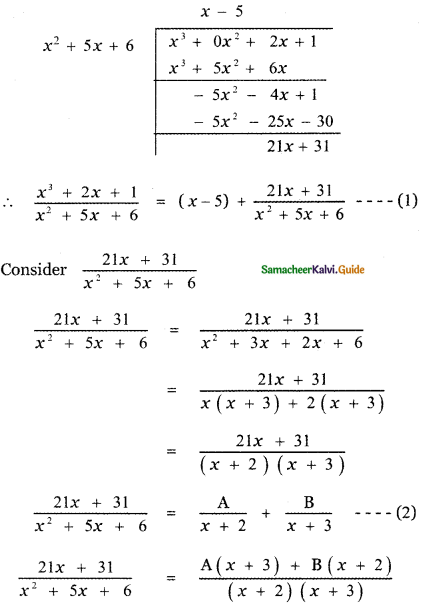
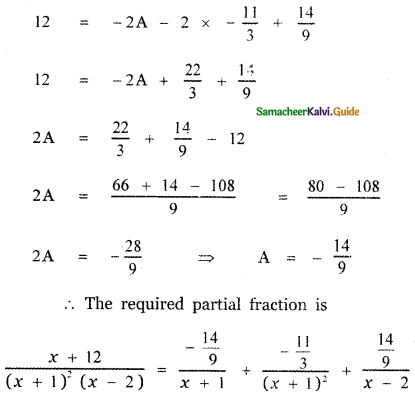
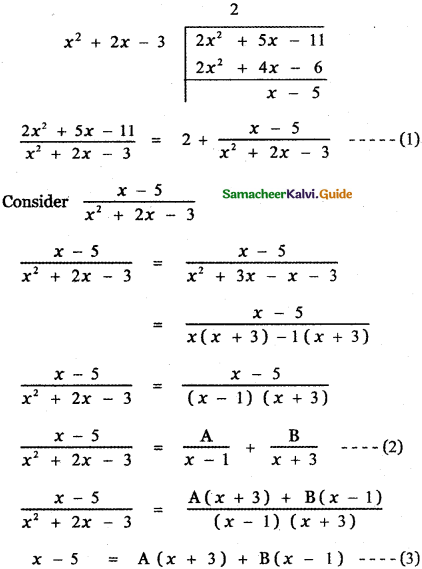
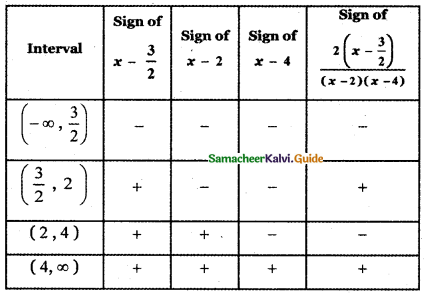
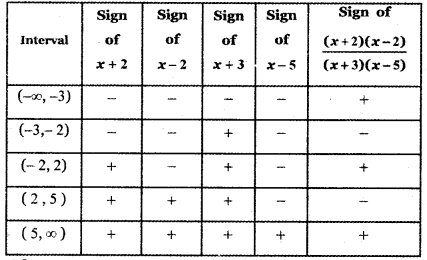
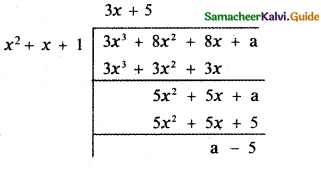
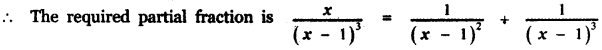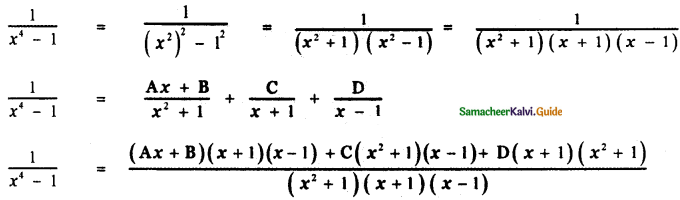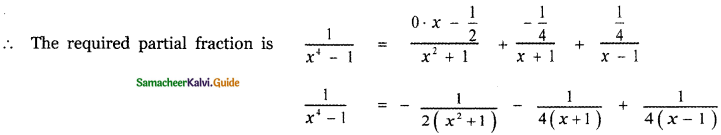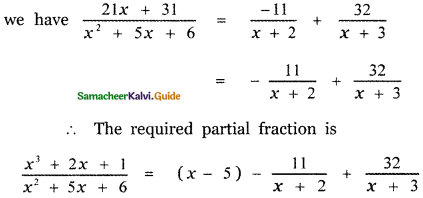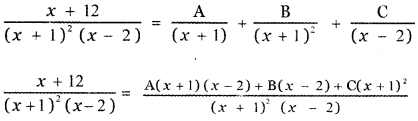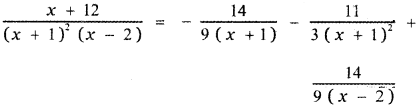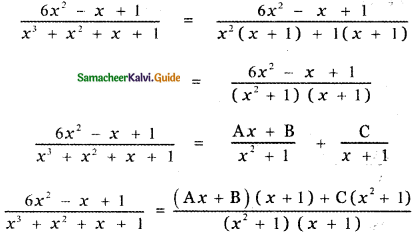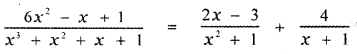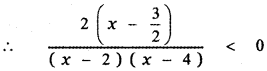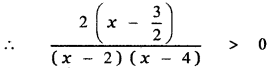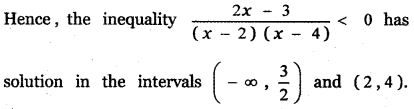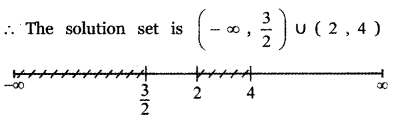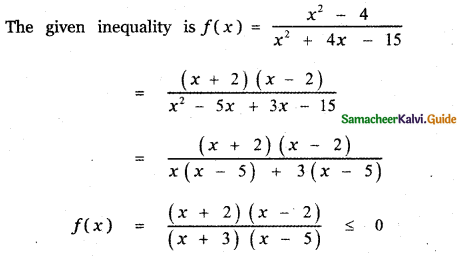Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 5th English Guide Pdf Term 3 Supplementary Chapter 1 The Witty Sparrow Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Summary, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 5th English Solutions Term 3 Supplementary Chapter 1 The Witty Sparrow
5th English Guide The Witty Sparrow Text Book Back Questions and Answers
In-Text Question:
Question 1.
Guess how would the sparrow pull the elephant and the crocodile.
Answer:
The sparrow would not pull the elephant and the crocodile by itself. It took a strong creeper and tied the elephant with one end of the creeper. Then it tied the crocodile with the other end of the creeper. When it told them to pull, the elephant and the crocodile pulled each other at the same time.
![]()
A. Choose the best answer:
Question 1.
All the animals called the sparrow _______.
a) queen
b) madam
c) princess
Answer:
b) madam
Question 2.
The brown sparrow laid _______ eggs.
a) four
b) six
c) three
Answer:
c) three
Question 3.
_______ lies stretching in the river.
a) crocodile
b) snake
c) tortoise
Answer:
a) Crocodile
Question 4.
Sparrow tied the elephant and the crocodile with a _______.
a) rope
b) cloth
c) creeper
Answer:
c) creeper
Question 5.
The sparrow solves the problem with her _______.
a) cunningness
b) intelligence
c) braveness
Answer:
b) intelligence
![]()
B. Number the pictures and incorrect order of the story:
Question 1.

Answer:






![]()
C. Try your own:
Question 1.
Answer:
![]()
D. Speak and win:
Join in either group and speak using 4 to 5 sentences to win.
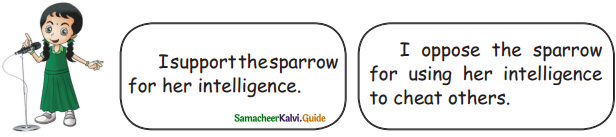
I support the sparrow for her intelligence:
- The sparrow was worried that the elephant might crack the eggs.
- The crocodile was blocking the way and asked the sparrow to drink muddy water.
- The sparrow gave a warning to the elephant and also to the crocodile.
- But both ignored the sparrow’s warnings.
- So, the sparrow tied both the animals with a strong creeper.
- So, nothing wrong in punishing both the animals, using intelligence.
I oppose the sparrow for using her intelligence to cheat others:
- Sparrow is a very small bird.
- It is not possible to tie both animals with a creeper.
- If the sparrow wanted to safeguard its eggs, it should shift its nest to a safer place.
![]()
Let us read aloud:
Read the passage 3 times and colour a camel for each time:
Once two merchants lost a camel. They met a boy who was passing by and asked him if he had seen it. The boy said he had not seen the camel. He asked, “Was your camel blind in the right eye?”. “Yes, he was”, said the merchants. “Was it lame in one left foot?”, asked the boy. It was!”, said the merchants. “Was it’s front tooth missing?” asked the boy.” yes,” they said. “Did it have honey on one side and wheat on the other?”. “yes!,” they answered. “Please take us to it.”
“But, I have not seen your camel,” said the boy “and I do not know where it is”. The merchants got angry and said, “Really! How could you tell us everything about our camel?” “That is my secret”. said the boy.
The merchants took him to the king. The boy told the king that he had not seen it. Then, the king asked him how he knew so much about it. The boy said that the camel had eaten grass only on the left side of the path. So he knew that it was blind. The marks of its one left foot were faint.
This showed that the camel was lame. While eating grass, it had not eaten the grass in the middle. So he learnt that it had lost its front teeth. There were ants carrying grains of wheat on one side of the path and flies eating honey on the other.”
![]()
Find and write the clues:
Question 1.
Clue for blind eye _______.
Answer:
The camel had eaten grass only on the left side of the path.
Question 2.
Clue for lame _______.
Answer:
The marks of its one left foot were faint.
Question 3.
Clue for lost teeth _______.
Answer:
While eating grass, the camel had not eaten the grass in the middle.
Question 4.
Clue for the load on the camel _______.
Answer:
There were ants carrying grains of wheat on one side of the path and flies eating honey on the other.
![]()
Let us write:
Dialogue Writing:
Write the dialogue and complete the story.

Rabbit: Lion King, as I was coming to give myself as lunch for you, another lion blocked me on the way.

Lion: How can another lion live in this forest, when I am here? Take me immediately to his place.

Lion: Ah! yes, he looks like me. Here I will jump into the well and kill him.

Rabbit: Oh foolish lion. It was not another lion, it was your own image reflection.
![]()
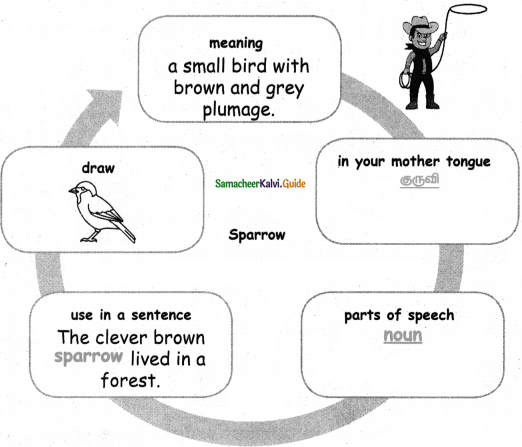
I can do:
A. Answer the following:

Question 1.
Name of the object
Answer:
Toffee
Question 2.
In your mother tongue.
Answer:
மிட்டாய்
Question 3.
Use in a sentence
Answer:
I like to eat a toffee.
![]()
B. Fill in the blanks with to, too and two:
Question 1.
I need _______ write _______ pages on this topic.
Answer:
I need to write two pages on this topic.
Question 2.
These clothes are _______ expensive.
Answer:
These clothes are too expensive.
Question 3.
Donald ran _______ kilometers.
Answer:
Donald ran two kilometers.
![]()
C. Tick the correct word:
Question 1.
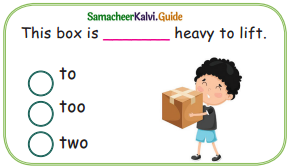
Answer:
too
Question 2.

Answer:
two
![]()
D. Recite any four lines of the poem with correct intonation:
Activity to be done by students.
E. Match the rhyming words:
| 1. soft | a. week |
| 2. blow | b. know |
| 3. grow | c. hot |
| 4. seek | d. flow |
Answer:
| 1. soft | a. hot |
| 2. blow | b. flow |
| 3. grow | c. know |
| 4. seek | d. week |
![]()
F. Circle and write the adverbs from the sentences:
Question 1.
The boy speaks loudly.
Answer:
loudly
Question 2.
She speaks English fluently.
Answer:
fluently
Question 3.
Our mum spoke to us angrily.
Answer:
angrily
Question 4.
The painter paints wonderfully.
Answer:
wonderfully
![]()
5th English Guide The Witty Sparrow Additional Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The sparrow’s nest was in a _______.
(a) hut
(b) tower
(c) bush
Answer:
(c) bush
Question 2.
Gullu is the name of the _______.
(a) crocodile
(b) elephant
(c) Sparrow
Answer:
(b) elephant
Question 3.
The crocodile told the sparrow to drink the _______ water.
(a) clean
(b) well
(c) muddy
Answer:
(c) muddy
Question 4.
At last, the elephant ran into the _______.
(a) village
(b) forest
(c) town
Answer:
(b) forest
Question 5.
The sparrow went to the _______ of the creeper.
(a) center
(b) left end
(c) right end
Answer:
(a) center
![]()
II. Identify the Speaker:
Question 1.
“Today, I will let you be.”
Answer:
The sparrow
Question 2.
“Move on, did you say?”
Answer:
The crocodile
Question 3.
“Let us see if you can move an inch.”
Answer:
The sparrow
Question 4.
“Please let me go..”
Answer:
The elephant
Question 5.
“Don’t you dare to move.”
Answer:
The sparrow
Question 6.
“I won’t stand in your way.”
Answer:
The crocodile
Question 7.
“I won’t disturb you again…”
Answer:
The elephant
Question 8.
“I warned you yesterday.”
Answer:
The sparrow
![]()
III. Say True or False:
Question 1.
Once, a very foolish sparrow lived in a forest.
Answer:
False
Question 2.
All the animals respected the sparrow except the elephant.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
The sparrow had two eggs in her nest.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
The elephant came thumping towards the bush.
Answer:
True
Question 5.
That morning, the sparrow went to the river bank to drink water.
Answer:
False
![]()
IV. Answer the following:
Question 1.
How did the elephant walk?
Answer:
The elephant walked past the bush purposefully, making a “thud, thud” sound.
Question 2.
Why was the sparrow worried?
Answer:
The sparrow was worried because the elephant might crack the eggs.
Question 3.
Why did the sparrow warn the crocodile?
Answer:
The sparrow warned the crocodile because the crocodile was stretching in the spot, where the sparrow used to drink water.
Question 4.
Why were the elephant and the crocodile exhausted?
Answer:
The elephant and the crocodile were tied with a strong creeper by the sparrow. They pulled each other at the same time. That process of pulling went on all day. So, both the animals were exhausted.
![]()
The Witty Sparrow Summary in English and Tamil
Once, a very clever brown sparrow lived in a forest had three eggs in her nest. The nest was in a bush. All the animals greeted her ‘Madam’ with respect. Gullu, the young elephant never did so. THUD! THUD! Gullu walked past the bush purposefully. It rattled the nest. Madam was worried that Gullu might crack the eggs.
ஒரு காலத்தில் ஒரு புத்திசாலியான பழுப்புநிறக் குருவி காட்டில் வாழ்ந்து வந்தது. புதரில் இருந்த அதன் கூட்டில் மூன்று முட்டைகள் இருந்தன. எல்லா விலங்குகளும் மரியாதையாக அந்தக்குருவியை ‘மேடம்’ என்று அழைத்தனர். ஆனால் குல்லு என்ற இளம் யானை ஒருபோதும் அப்படி செய்யவில்லை. வேண்டுமென்றே குல்லு தட தட வென்று புதரைக் கடந்து செல்லும். அதனால் கூடு அதிரும். இதனால் முட்டைகள் கீறல் விழுந்துவிடுமோ என குருவி கவலைப்பட்டது.
Sparrow to Elephant: If you do this tomorrow. I will tie you up with a strong rope and then, You can’t move at all. I warn you.
குருவி யானையிடம்: நாளை இதேமாதிரி நீ தடதடவென நடந்தால், நான் உன்னை பலமான கயிற்றைக் கொண்டு கட்டிவைத்து ”விடுவேன். உன்னால் அசையவே முடியாது. நான் உன்னை எச்சரிக்கிறேன்.
Elephant (யானை):
Tie me up!
Ha…ha…ha…
We will see.
ஹா! ஹா! என்னை கட்டி வைப்பாயா? பார்ப்போம்.
![]()
That afternoon, she went to the river bank to drink water. A crocodile was stretching in the spot she was drinking water.
Sparrow to Crocodile: Blocking me again? You have done it twice this week. Move on, I don’t want to drink muddy water.
Crocodile to Sparrow: Move on, did you say? I will stay put, you better go elsewhere to drink water.
மத்தியானம் குருவி ஆற்றங்கரைக்கு நீர் குடிக்க சென்றது. அது நீர் அருந்தும் இடத்தில் ஒரு முதலை படுத்து இருந்தது.
குருவி: மறுபடி என்னை வழிமறிக்கிறாயா? இந்த வாரத்தில் இரண்டு முறை இப்படி செய்துவிட்டாய். விலகு, நான் சேற்று நீரை குடிக்க விரும்பவில்லை.
முதலை: விலகு என்றா சொன்னாய்? நான் இங்கு தான் இருப்பேன். நீ வேறு இடத்திற்கு சென்று தண்ணீ ர் குடி.
Sparrow to Crocodile: Today, I will let you be. But if I find you in the same place tomorrow. I will tie you up with a strong rope.
Crocodile to Sparrow: The sparrow went to her nest and started thinking furiously.
குருவி முதலையிடம்: இன்று உன்னை விட்டுவிடுகிறேன். ஆனால் நாளை உன்னை இதே இடத்தில் நான் பார்த்தால், பலமான கயிற்றால் உன்னை கட்டிவிடுவேன்.
முதலை: சிறு ஜீவனான நீ என்னைக் கட்டுவாயா? ஹா… ஹா….
குருவி தன் கூட்டிற்கு சென்றது. அதற்கு புத்திசாலித்தனமான ஒரு யோசனை கிடைத்தது.
The next morning, Gullu came thumping towards the bush.
Elephant to Sparrow: HEY! Are you not tying me up?
Sparrow to Elephant: How dare you! Aren’t you afraid of me? Just wait.
மறுநாள் காலை, யானை தடதடவென்று புதரை நோக்கி வந்தது.
என்னிடம் உனக்கு பயம் இல்லையா? இங்கே சிறிது
யானை குருவியிடம்: “ஏய் நீ என்னை கட்டவில்லையா?”
குருவி யானையிடம்: “என்ன தைரியம் உனக்கு? காத்திரு”.
![]()
The sparrow took a strong creeper and tied the elephant on one end. USHHHHH! Don’t you dare to move? Stay here, until I fly and reach the other end of the rope to pull you. When I say ‘pull’, pull with all your strength. Let us see if you can move an inch.
குருவி ஒரு பலமான தாவரக் கொடியை எடுத்து வந்து அதன் ஒரு முனையில் யானையை கட்டியது.
குருவி யானையிடம்: “உஷ்! உன்னை இழுக்க கயிற்றின் மறுமுனைக்கு நான் பறந்து செல்லும் வரை, நீ அசையாமல் இங்கேயே இரு. நான் இழு என்று சொல்லும் போது உன் முழு பலத்துடன் இழு. உன்னால் ஓர் அங்குலமாவது நகர முடிகிறதா என்று பார்ப்போம்.
It went to the river, saw the crocodile blocking its way.
Crocodile to Sparrow: I will not move! Just like yesterday, drink the muddy water.
குருவி ஆற்றுக்கு சென்றது. முதலை மறுபடியும் அதன் வழியில் குறுக்கிடுவதைக் கண்டது.
முதலை குருவியிடம்: “நான் நேற்றுப் போலவே சிறிது கூட அசைய மாட்டேன். நீ சேற்று நீரை குடி.”
Sparrow took the other end of the creeper and tied the crocodile.
Sparrow to Crocodile: I warned you yesterday. Now stay still, until I grab the other end. When I say ‘Pull’, let’s see if you are able to pull or not.
குருவி, தாவரக் கொடியின் மறுமுனையை எடுத்து வந்து முதலையை கட்டியது.
குருவி முதலையிடம்: “நான் நேற்றே உன்னை எச்சரித்தேன். இப்பொழுது நான் மறு முனையை பற்றி, இழுக்கும்வரை அசையாமல் இரு. நான் ‘இழு’ என்று சொல்லும்போது உன்னால் இழுக்க முடிகிறதா இல்லையா என பார்க்கலாம்.”
Sparrow went to the center of the creeper. Pull The elephant and the crocodile pulled each other at the same time.
![]()
குருவி, கொடியின் மையப் பகுதிக்கு சென்றது. ‘இழு’ என்று சத்தமிட்டது. யானையும், முதலையும் ஒரே சமயத்தில் ஒன்றையொன்று இழுத்தன.
This went on all day. Both the animals were exhausted.
Elephant to Sparrow: Please let me go. I won’t disturb you again…
Crocodile to Sparrow: Untie me! I won’t stand in your way.
Sparrow : Good, I will remove the rope. Gullu ran into the forest and the crocodile dived into the river. Soon the eggs hatched. Madam Sparrow lived happily with her three little babies.
நாள் முழுவதும் இப்படியே இழுத்துக் கொண்டு இருந்தன. முடிவில் இரண்டு விலங்குகளும் களைப்படைந்தன.
யானை குருவியிடம்: “தயவு செய்து என்னை விட்டுவிடு. நான் மறுபடியும் உன்னை தொந்தரவு செய்யமாட்டேன்,
முதலை குருவியிடம்: “என்னை கட்டவிழ்த்து விடு நான் மறுபடியும் உன் வழியில் குறுக்கிடமாட்டேன்”.
குருவி: இப்பொழுது நான் கொடி கயிற்றை எடுத்து விடுகிறேன். யானை குல்லு காட்டிற்குள் ஓடிவிட்டது. முதலையும் ஆற்றில் நீந்திச் சென்றுவிட்டது. விரைவில் குருவியின் முட்டைகள் பொறிந்தன. குருவி தன் மூன்று குருவிக்குஞ்சுகளுடன் மகிழ்ச்சியாக வாழ்ந்தது.