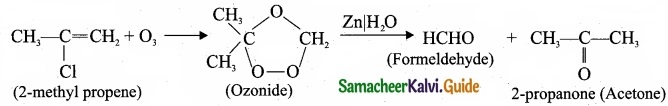
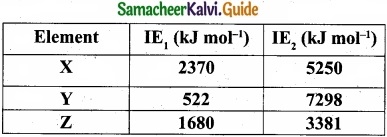
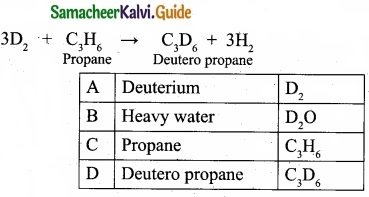
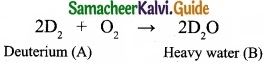Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Commerce Model Question Paper 4 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th Commerce Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
TN State Board 11th Commerce Model Question Paper 4 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 20 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each.
These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer - Question numbers 21 to 30 in Part II are two-mark questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 31 to 40 in Part III are three-mark questions. These are to be answered in above three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 41 to 47 in Part IV are five-mark questions. These are to be answered in detail Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 2:30 Hours
Maximum Marks: 90
PART – I
Choose the correct answer. Answer all the questions. [20 × 1 = 20]
Question 1.
……………………….. is a special type of bond issued in the currency other than the home currency.
(a) Government bond
(b) Foreign currency convertible bond
(c) Corporate bond
(d) Investment bond
Answer:
(b) Foreign currency convertible bond
![]()
Question 2.
……………………. acts as connective link between the producer and the consumer.
(a) Trade
(b) Industry
(c) Commerce
(d) Business
Answer:
(a) Trade
Question 3.
From the following which is not a recent trend in transportation?
(a) Metro rail
(b) Pipeline transport
(c) Bullock carts
(d) Ropeway transport
Answer:
(c) Bullock carts
Question 4.
Minimum how much amount can be transferred through RTGS?
(a) Any amount
(b) Rs 50,000
(c) Rs 2 lakhs
(d) Rs 5 Lakhs
Answer:
(c) Rs 2 lakhs
![]()
Question 5.
Goods are imported for the purpose of exporting to another country is termed as ……………………….
(a) Import trade
(b) Export trade
(c) Entrepot trade
(d) Internal trade
Answer:
(c) Entrepot trade
Question 6.
Agriculture income earned in india is ………………………..
(a) Fully taxable
(b) Fully exempted
(c) Not considered for income
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Fully exempted
![]()
Question 7.
An …………………………. is a document prepared by the importer and sent to the exporter to buy the goods.
(a) Invoice
(b) Indent
(c) Enquiry
(d) Charter party
Answer:
(b) Indent
Question 8.
Which of the parties cannot demand performance of promise?
(a) Promisee
(b) Any of the joint promisees
(c) Death of a promisee, his legal representative
(d) Stranger to the contract
Answer:
(d) Stranger to the contract
Question 9.
The income paid to the (mercantile agent), broker is ………………………..
(a) Profit
(b) Brokerage
(c) Commission
(d) Salary
Answer:
(b) Brokerage
![]()
Question 10.
Ethics is important for ……………………….
(a) Top management
(b) Middle – level management
(c) Non – managerial employees
(d) All of them
Answer:
(d) All of them
Question 11.
……………………. is the oldest form of transport found in hilly areas, forest areas in remote places.
(a) Bullock carts
(b) Road transport
(c) Motor lorries
(d) Pathways transport
Answer:
(d) Pathways transport
![]()
Question 12.
The document which invites the public to buy the shares and debentures is known as …………………………
(a) Memorandum of Association
(b) Articles of Association
(c) Prospectus
(d) Partnership articles
Answer:
(c) Prospectus
Question 13.
Which one of the following is not correctly matched?
(a) Minimum two members – Partnership firm
(b) Minimum paid up capital Rs 100000 – Private company
(c) Voluntary Membership – Co – operatives
(d) 51% of paid up capital – Foreign company
Answer:
(d) 51% of paid up capital – Foreign company
Question 14.
ABC jointly promised to pay Rs. 50000 to D. Before performance of the contract, ‘C’ dies. Here the contract ………………………
(a) Becomes void on C’s death.
(b) Should be performed by A and B along with C’s legal representative.
(c) Should be performed by A and B alone.
(d) Should be renewed between A, B and D.
Answer:
(b) Should be performed by A and B along with C’s legal representative.
Question 15.
Airport Authority of India, is a public enterprise. Identify the form of organisation.
(a) Statutory corporations
(b) Departmental undertakings
(c) Multi – national corporations
(d) State – owned company
Answer:
(b) Departmental undertakings
![]()
Question 16.
Debenture holders are entitled to a fixed rate of ………………………
(a) Dividend
(b) Profits
(c) Interest
(d) Ratio
Answer:
(c) Interest
Question 17.
The State Bank of India came into being in ………………………
(a) 1995
(b) 1945
(c) 1955
(d) 1965
Answer:
(c) 1955
![]()
Question 18.
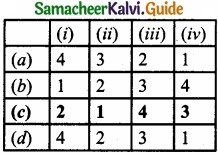
Match List – I with List – II and select the correct answer using the codes given below:
|
List – I |
List – II |
| (i) Assembling industry | 1. Sugar |
| (ii) Processing industry | 2. Computer |
| (iii) Analytical industry | 3. Fishery |
| (iv) Genetic industry | 4. Oil industry |
Answer:
Codes:
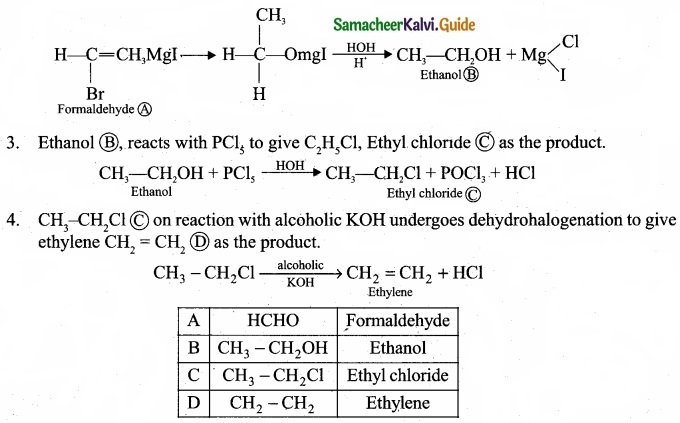
Question 19.
An ……………………… is a document prepared by the importer and sent to the exporter to buy the goods.
(a) Invoice
(b) Indent
(c) Enquiry
(d) Charter party
Answer:
(b) Indent
Question 20.
Point out the wrong statement from the following.
(a) Extractive industries extract products from natural resources.
(b) Genetic industries are engaged in breeding plants and animals for their use in further reproduction
(c) Manufacturing industries are engaged in producing goods through processing of raw material.
(d) Construction industries are involved in the successive stages for manufacturing sugar and paper, etc.
Answer:
(d) Construction industries are involved in the successive stages for manufacturing sugar and paper, etc.
PART – II
Answer any seven questions in which question No. 30 is compulsory. [7 × 2 = 14]
Question 21.
It is the oldest form of organisation in public enterprises. It is run by the particular department. What is the name of the organisation? How is it controlled?
Answer:
Departmental form of organisation of managing state enterprises is the oldest form of organisation. Under departmental form of organisation, a public enterprise is run as a separate full – fledged ministry or as a major sub-division of a department of the Government.
![]()
Question 22.
Banks which do not provide regular service, and are controlled by stock exchange, What is the name of the bank? Write a short note about the bank?
Answer:
The name of the bank is Merchant bank. A commercial bank or its subsidiary may offer services like project counselling, underwriting etc for starting a company. It is called merchant banking.
Question 23.
What is meant by chartered company?
Answer:
Chartered companies are established by the King or Queen of a country. Powers and privilege of chartered company are specified in the charter. Power to cancel the charter is vested with King/Queen.
Question 24.
Some co – operative societies are formed for providing short term finance to the members. It is useful to the farmers especially. What is the name of the society?
Answer:
Cooperative credit societies are societies formed for providing short-term financial help to their members. Agriculturists, artisans, industrial workers, salaried employees, etc., form these credit societies.
![]()
Question 25.
Give any two functions of warehouses?
Answer:
- Storage
- Price stabilization
- Equalization of demand and supply
Question 26.
Define the term‘factoring’?
Answer:
The term ‘factoring’ is derived from a Latin term ‘facere’ which means ‘to make or do’. Factoring is an arrangement wherein the trade debts of a company are sold to a financial institution at a discount.
Question 27.
State the meaning of Mail order business?
Answer:
Mail order business means that the buying and selling is through mail. There is no personal contact between the buyers and sellers in this type of trading.
![]()
Question 28.
Explain the term – Credit card?
Answer:
Banks issue credit cards to customers and other eligible persons. With this card, the holder can purchase goods and services on credit at any shop in India.
Question 29.
What is meant by consumer co-operatives?
Answer:
Consumer co – operatives are organised by consumers. The aim of the consumers co-operative is to supply the quality goods at fair prices. They also supply essential commodities through Public Distribution System (PDS).
![]()
Question 30.
What is mutual funds?
Answer:
An individual investor who wants to invest in equities and bond with a balance of risk and return generally can invest in mutual funds. Nowadays people invest in stock markets through a mutual fund.
PART – III
Answer any seven questions in which question No. 40 is compulsory. [7 × 3 = 21]
Question 31.
What are the advantages of company? Explain any three?
Answer:
1. Large Capital:
A company can secure large capital compared to a sole trader or partnership. Large amount of capital is necessary for conducting business on a large scale.
2. Limited Liability:
The liability of a shareholder is limited. The risk of loss is limited to the unpaid amount on the face value of shares held. In the case of a company limited by shares, the liability of a shareholder is restricted to the unpaid amount on the shares held by him.
3. Transferability of Shares:
Transaction of Shares between two individuals is easy. So there is liquidity of investment. Any shareholder can easily convert his shares into money by selling his shares.
![]()
Question 32.
What is the necessity for Entrepot trade?
Answer:
Entrepot is necessary because of the following reasons:
- The country may not have any accessible trade routes connecting the importing country.
- The goods imported may require further processing or finishing before exporting, and these facilities may be lacking in the exporting or importing country.
- There may not have any bilateral trade agreement between both the countries.
Question 33.
This is a loan taken by depositing document of title to the property with the banker. What is the name of the loan? Also how the banker grants the loan to the customers?
Answer:
The name of the loan is ‘hypothecation’. In this type of loan, the customer has to deposit the document of title to the property with the banker. But the physical possession of the property is with the borrower. If the loan is not paid, the lender will sell the property and can receive the loan amount.
![]()
Question 34.
What are the objectives of GST?
Answer:
- To create a common market with uniform tax rate in India. (One Nation, One Tax, One Market)
- To eliminate the cascading effect of taxes, GST allows set – off of prior taxes for the same transactions as input tax credit.
- To boost Indian exports, the GST already collected on the inputs will be refunded and thus there will be no tax on all exports.
- To increase the tax base by bringing more number of tax payers and increase tax revenue.
- To simplify tax return procedures through common forms and avoidance of visiting tax departments.
- To provide online facilities for payment of taxes and submission of forms.
Question 35.
Cargo vessels which do not follow set routes and timetable?
What is the kind and name of the transport?
Answer:
The name of the transport is Tramps. They are a kind of ocean going ships. They are essentially cargo vessels. They have no set routes. They do not follow any timetable. They sail only when they get sufficient load.
Question 36.
What is Gross Total Income?
Answer:
Income from the five heads, namely – Salaries, House Property, Profits and Gains of Business or Profession, Capital Gains, and Other Sources – is computed separately according to the provisions given in the Act. Income computed under these heads shall be aggregated after adjusting past and present losses and the total so arrived at is known as ‘Gross Total Income’.
![]()
Question 37.
The retailers having permanent establishment and deal in large scale are called fixed shop large scale retailers. There are various types of large scale retailers. What is telemarketing? Explain the types?
Answer:
Purchasing and selling of goods through telephones are called Telemarketing. It is divided into two types.
1. Telephonic marketing:
Potential customers are contacted through mobile to provide information about the products. Willing customers visit the office and place orders.
2. Television marketing:
In this method, customers are attracted by providing all information of product or service through TV demonstrations. Customers can contact through phone or website to place order.
![]()
Question 38.
Distinguish between hire purchase system and installment system of selling?
Answer:
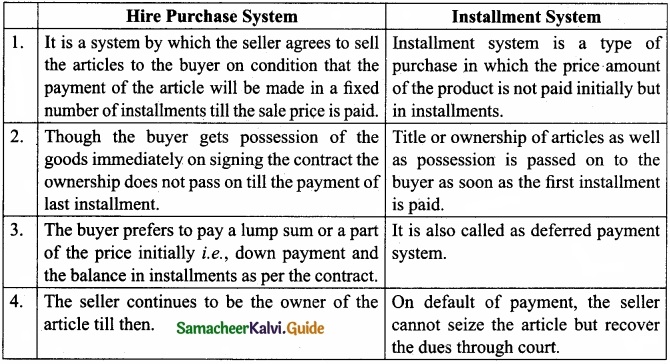
Question 39.
Explain any three features of Self Help Groups?
Answer:
Self Help Group is a small informal voluntary association created for the purpose of enabling members to reap economic benefit out of mutual help, solidarity, and joint responsibility. Features of Self Help Groups:
- The motto of every group members should be “saving first – credit latter”.
- Self Help Group is homogeneous in terms of economic status.
- The groups need not be registered.
![]()
Question 40.
What are the objectives of GST?
Answer:
- To create a common market with uniform tax rate in India. (One Nation, One Tax, One Market)
- To eliminate the cascading effect of taxes, GST allows set-off of prior taxes for the same transactions as input tax credit.
- To boost Indian exports, the GST already collected on the inputs will be refunded and thus there will be no tax on all exports.
- To increase the tax base by bringing more number of tax payers and increase tax revenue.
- To simplify tax return procedures through common forms and avoidance of visiting tax departments.
- To provide online facilities for payment of taxes and submission of forms.
PART – IV
Answer all the questions. [7 × 5 = 35]
Question 41 (a).
Write short notes on:
- Owner’s funds
- Borrowed funds
Answer:
1. Owner’s Funds:
Owner’s funds mean funds which are provided by the owner of the enterprises who may be an individual, or partners or shareholders of a company.
The profits reinvested in the business (ploughing back of profit or retained earnings) come under owner’s funds. These funds are not required to be refunded during the life time of business enterprise. It provides the owner the right to control the management of the enterprise.
2. Borrowed Funds:
The term ‘borrowed funds’ denotes the funds raised through loans or borrowings. For example debentures, loans from banks and financial institutions, public deposits, trade credit, lease financing, commercial papers, factoring, etc., represent borrowed funds.
- These borrowed sources of funds provide specific period before which the fund is to be returned.
- Borrower is under legal obligation to pay interest at given rate at regular intervals to the lender.
- Generally borrowed funds are obtained on the security of certain assets like bonds, land, building, stock, vehicles, machinery, documents of title to the goods, and the like.
[OR]
(b) What are the advantages of sole trading?
Answer:
- Easy Formation: No legal formalities are required to initiate a sole trading concern. Any person capable of entering into a contract can start it, provided he has the necessary resources for it.
- Incentive to Work hard: There is a direct relationship between effort and reward. The fact that the entire profit can be taken by himself without sharing with anybody else induces him to work ceaselessly.
- Small Capital: Small capital is an important as well as specific advantage of sole proprietorship. Sole proprietor can start business with small capital.
- Credit Standing: Since his private properties are held liable for satisfying business debts, he can get more financial assistance from others.
- Personal Contact with the Customers: Since sole proprietor knows each and every customer individually he can supply goods according to their taste and preferences. Thus he can cultivate personal relationship with the customers.
- Flexibility: The sole trader can easily adjust himself to the changing requirements of his business.
![]()
Question 42 (a).
Explain the contents of Articles of Association?
Answer:
Contents of Articles of Association (AOA):
- Amount of shares, capital, value and type of shares.
- Rights of each class of shareholders regarding voting, dividend, return of capital
- Rules regarding issue of shares and debentures
- Procedures as well as regulations in respect of making calls on shares
- Manner of transfer of shares
- Declaration of dividends
- Borrowing powers of the company
- Rules regarding the appointment, remuneration, removal of directors
- Procedure for conducting proxy, quorum, meetings, etc.
- Procedures concerning keeping of books and audits
- Seal of the company
- Procedures regarding the winding up of the company.
[OR]
(b) What are the primary functions of commercial banks?
Answer:
The primary functions of a commercial bank are of three types. They are:
1. Accepting Deposits:
The basic deposit accounts offered by commercial banks are listed below:
A. Demand Deposits:
These deposits are repayable on demand on any day. These consist of –
- Savings Deposits: General public deposit their savings into this account. This account can be opened in one individual’s name or more than one name.
- Current Deposits: This account is suitable for business institutions. Individuals too can open this account. A higher minimum balance should be kept in this account.
B. Time Deposits:
These are repayable after a period. These include –
- Fixed Deposits (FD): Certain amount is deposited for a fixed period for a fixed rate of interest.
- Recurring Deposits (RD): Certain sum is deposited into the account every month for one year or five years or the agreed period. Interest rate is more than savings deposits and almost equal to fixed deposits.
2. Granting Loans and Advances:
Commercial banks lend money in order to earn interest.
A. Advances:
- Overdraft: It is a credit facility extended mostly to current account holding business community customers.
- Cash Credit: It is a secured credit facility given mostly to business institutions. Stock in hand, raw materials, other tangible assets, etc. are provided as collateral.
- Discounting of Bills: Business customers approach banks to discount the commercial bills of exchanges and provide money
B. Loans- Short term and medium term loans are provided by commercial banks against eligible collaterals to business concerns. Examples- housing loan, consumer loan, vehicle loan, educational Loan, jewel loan, etc.
3. Creation of Credit- Apart from the currency money issued by the RBI, the credit money in circulation created by commercial banks influence economic activities of a country to a large extent. Credit money of commercial banks is far greater in volume than the currency money.
![]()
Question 43 (a).
What are the disadvantages of MNC?
Answer:
- Danger for Domestic Industries: MNCs, because of their vast economic power, pose a danger to domestic industries; which are still in the process of development. Domestic industries cannot face challenges posed by MNCs.
- Transfer of Outdated Technology: Where MNCs transfer outdated technology to host nation, it serves no purpose.
- No Benefit to Poor People: MNCs produce only those things, which are used by the rich. Therefore, poor people of host countries do not get, generally, any benefit, out of MNCs.
- Danger to Independence: Initially MNCs help the Government of the host country, in a number of ways; and then gradually start interfering in the political affairs of the host country.
- Deprivation of Job Opportunity of Local People: MNCs may not generate job opportunities to the people of home country.
[OR]
(b) Explain the organisational structure of RBI?
Answer:
The head office of the RBI is situated in Mumbai. This central office has 33 departments in 2017. It has four zonal offices in Mumbai, Delhi, Calcutta and Chennai functioning under local boards with deputy governors as their heads. It also has 19 regional offices and 11 sub-offices (2017).
The RBI is governed by a central board of directors. The 21 member board is appointed by the Government of India. It consists of:
- One Governor and four deputy governors appointed for a period of four years,
- Ten Directors from various fields
- Two Government officials
- Four Directors – one each from local boards.
![]()
Question 44 (a).
Distinguish between internal and international trade?
Answer:
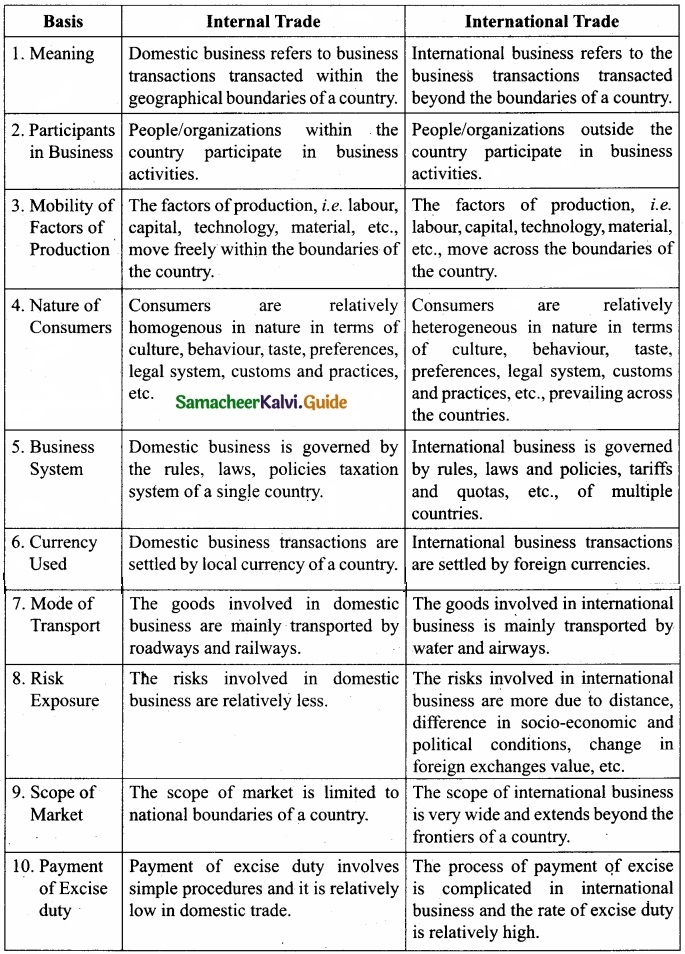
[OR]
(b) State the features of departmental stores?
Answer:
- Large Size: A department is a large scale retail showroom requiring a large capital investment by forming a joint stock company managed by a board of directors.
- Wide Choice: It acts as a universal provider of a wide range of products from low priced to very expensive goods (Pin to Car) to satisfy all the expected human needs under one roof.
- Departmentally organized: Goods offered for sale are classified into various departments.
- Facilities provided: It provides a number of facilities and services to the customers such as restaurant, rest rooms, recreation, packing, free home delivery, parking, etc.
- Centralised purchasing: All the purchases are made centrally and directly from the manufacturers and operate separate warehouses whereas sales are decentralised in different departments.
![]()
Question 45 (a).
What are the different types of transportation? Explain?
Answer:
Types of transportation:
(A) Land Transport:
Transport of people and goods by land vehicles is known as Land transport. It is also called as‘Surface Transport’.
- Pack Animals: Animals like horse, mule, donkey, camel, elephant etc., are used for carrying small loads in backward areas, hilly tracks, forest regions and deserts.
- Bullock Carts: It constitutes the predominant form of rural road transport in India for goods traffic and to some extent for passengers’ traffic.
- Road Transport: It is one of the most promising and potent means suitable for short and medium distances.
- Motor lorries and Buses: From the dawn of civilization, people have been endeavoring to form roads and use wheeled vehicles to facilitate transport of men and materials.
- Tramways: Tramways were initially horse drawn, later stearmpowered and now they are electrically operated.
- Railway Transport: The invention of steam engine by James Watt, revolutionized the mode of transport all over the world.
- Recent Trends in Transport: Metro Rail, Monorail, Bullet train, Pipeline Transport, Conveyor Transport, Ropeway transport and Hyper loop transport.
(B) Water Transport:
- Inland Waterways: Inland Waterways comprise of rivers, canals and lakes. It is also known as internal water transport.
- Ocean or Sea Transport: Ocean transport has been playing a significant role in development of economic, social and cultural relations among countries of the world.
- Coastal shipping
- Overseas shipping:
- Liner
- Tramps
(C) Air Transport:
Air transport is the fastest and the costliest mode of transport. Commercial air transport is now one of the most prominent modes of overseas transport. Domestic and International flights are the air travels.
[OR]
(b) Explain the principles of insurance?
Answer:
1. Utmost Good Faith:
According to this principle, both insurer and insured should enter into contract in good faith. Insured should provide all the information that impacts the subject matter. Insurer should provide all the details regarding insurance contract.
2. Insurable Interest:
The insured must have an insurable interest in the subject matter of insurance. Insurable interest means some pecuniary interest in the subject matter of the insurance contract.
3. Indemnity:
Indemnity means security or compensation against loss or damages. In insurance, the insured would be compensated with the amount equivalent to the actual loss and not the amount exceeding the loss.
This principle ensures that the insured does not make any profit out of the insurance. This principle of indemnity is applicable to property insurance alone.
4. Causa Proxima:
The word ‘Causa proxima’ means ‘nearest cause’. According to this principle, when the loss is the result of two or more cause, the proximate cause, i.e. the direct. The direct, the most dominant and most effective cause of loss should be taken into consideration. The insurance company is not liable for the remote cause.
5. Contribution:
The same subject matter may be insured with more than one insurer then it is known as ‘Double Insurance’. In such a case, the insurance claim to be paid to the insured must be shared on contributed by all insurers in proportion to the sum assured by each one of them.
6. Subrogation:
Subrogation means ‘stepping the shoes on others’. According to this principle, once the claim of the insured has been settled, the ownership right of the subject matter of insurance passes on to the insurer.
7. Mitigation: In case of a mishap, the insured must take off all possible steps to reduce or mitigate the loss or damage to the subject matter of insurance.
![]()
Question 46 (a).
Elucidate any five features of Income Tax?
Answer:
Features of Income Tax in India:
1. Levied as Per the Constitution Income tax is levied in India by virtue of entry No. 82 of list I (Union List) of Seventh Schedule to the Article 246 of the Constitution of India.
2. Levied by Central Government Income tax is charged by the Central Government on all incomes other than agricultural income. However, the power to charge income tax on agricultural income has been vested with the State Government as per entry 46 of list II, i.e., State List.
3. Direct Tax Income tax is direct tax. It is because the liability to deposit and ultimate burden are on same person. The person earning income is liable to pay income tax out of his own pocket and cannot pass on the burden of tax to another person.
4. Annual Tax Income tax is an annual tax because it is the income of a particular year which is chargeable to tax.
5. Tax on Person It is a tax on income earned by a person. The term ‘person’ has been defined under the Income tax Act. It includes individual, Hindu Undivided Family, Firm, Company, local authority, Association of person or body of Individual or any other artificial juridical persons. The persons who are covered under Income tax Act are called ‘assessees’.
[OR]
(b) Write down the functions of IMF?
Answer:
- It acts as short term credit institution at the international level.
- It provides machinery for ordinary adjustments of exchange rates.
- It has a reservoir of currencies of the member countries from which a borrower can borrow currencies of other nations.
- It promotes economic stability and global growth by encouraging countries adopt sound economic and financial policies.
- It offers technical assistance and training to help member countries strengthen and implement effective policies. Technical assistance is offered in formulating banking, fiscal, monetary and exchange policies.
- It helps member countries correct their imbalance in balance of payment.
![]()
Question 47 (a).
Describe the importance of international finance?
Answer:
- International finance helps in calculating exchange rates of various currencies of nations and the relative worth of each and every nation in terms thereof.
- It helps in comparing the inflation rates and getting an idea about investing in international debt securities.
- It helps in ascertaining the economic status of the various countries and in judging the foreign market.
- International Financial Reporting System (IFRS) facilitates comparison of financial statements made by various countries.
- It helps in understanding the basics of international organisations and maintaining the balance among them.
[OR]
(b) What are the advantages of Railway transport?
Answer:
- Railways are well suited for carrying heavy and bulky goods over long distances.
- It provides long distance travel throughout the day and night service.
- It can provide better production and safety to the goods than motor transport.
- Though initial investment is large, in the long run the operating expenses will be very low in railways and it will prove a cheaper mode of transport.
- It has regular schedule of timing and is available throughout the year.
- It provides unaffected services whether rainy or sunny weather conditions.