Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Biology Model Question Paper 3 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th Biology Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
TN State Board 11th Biology Model Question Paper 3 English Medium
General Instructions:
-
- The question paper comprises of four parts. Questions for Botany and Zoology are asked separately.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 8 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer.
- Question numbers 9 to 14 in Part II are two-marks questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 15 to 19 in Part III are three-marks questions. These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 20 and 21 in Part IV are five-marks questions. These are to be answered in detail. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3:00 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
Bio – Botany [Maximum Marks: 35]
PART – 1
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer. [8 × 1 = 8]
Question 1.
Identify the correct sequence regarding lytic cycle of viruses.
(i) Penetration
(ii) Adsorption
(iii) Assembly
(iv) Synthesis
(a) (ii), (i), (iv), (iii)
(b) (iii), (i), (ii), (iv)
(c) (ii), (iv), (i), (iii)
(d) (i), (iv), (ii), (iii)
Answer:
(a) (ii), (i), (iv), (iii)
![]()
Question 2.
Zygote meiosis is characterisitic of ………………………
(a) Marchantia
(b) Fucus
(c) Funaria
(d) Chlamydomonas
Answer:
(d) Chlamydomonas
Question 3.
Pinus roots are in symbiotic relationship with ……………………
(a) Blue green algae
(b) Mycorrhiza
(c) Euglena
(d) Rhizobium
Answer:
(b) Mycorrhiza
![]()
Question 4.
Climbers are also called as ……………………
(a) Herbs
(b) Trees
(c) Vines
(d) Shrubs
Answer:
(c) Vines
Question 5.
Arrangement of sepals and petals in flower bud is called ………………………
(a) Adhesion
(b) Aestivation
(c) Placentation
(d) Cohesion
Answer:
(b) Aestivation
![]()
Question 6.
Cell cycle was discovered by ………………………
(a) Singer & Nicholson
(b) Prevost & Dumans
(c) Schleider & Schwann
(d) Boveri
Answer:
(b) Prevost & Dumans
Question 7.
Parenchyma storing calcium carbonate crystals are called ……………………
(a) Leucoplasts
(b) Elaioplasts
(c) Idioblasts
(d) Chromoplasts
Answer:
(c) Idioblasts
![]()
Question 8.
Which of the following is a free – living bacterium?
(a) Rhizobium
(b) Clostridium
(c) Escherichia
(d) Cyanobacteria
Answer:
(b) Clostridium
PART – II
Answer any four of the following questions. [4 × 2 = 8]
Question 9.
Distinguish between deoxyviruses and riboviruses?
Answer:
|
Deoxyviruses |
Riboviruses |
| 1. Viruses having DNA are called deoxyviruses. E.g. Animal viruses except HIV | 1. Viruses having RNA are called riboviruses. E.g: Plant viruses except cauliflower mosaic virus (CMV) |
Question 10.
What is plant morphology?
Answer:
Plant morphology also known as external morphology deals with the study of shape, size and structure of plants and their parts like (roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits and seeds).
![]()
Question 11.
Differentiate Regional Flora from continental flora?
Answer:
|
Regional Flora |
Continental Flora |
| 1. Flora covering a large geographical area or a botanical region Eg: flora of Madras Presidency. | 1. Flora covering the entire continent. Eg: flora of Europaea. |
Question 12.
Define C – Value?
Answer:
C-Value is the amount in picograms of DNA contained within a haploid nucleus.
![]()
Question 13.
Expand and Define TP?
Answer:
TP stands for Turgor pressure. When a plant cell is placed in pure water (hypotonie solution) the diffusion of water into the cell takes place by endosmosis. It creates a positive hydrostatic pressure on the rigid cell wall by the cell membrane.
Hence forth the pressure exerted by the ccli membrane towards the cell wall is Turgor Pressure (TP).
![]()
Question 14.
Mention the events of Photochernical phase of light reaction?
Answer:
Photocheinical Phase:
- Photolysis of water and oxygen evolution
- Electron transport and synthesis of assimilatory power.
PART – III
Answer any three questions in which question number 19 is compulsory. [3 × 3 = 9]
Question 15.
Name few fossil sites of India?
Answer:
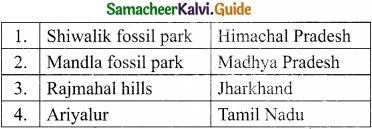
![]()
Question 16.
What is a liana? Mention its importance?
Answer:
Liana is a vine that is perennial and woody. Lianas are major components in the tree canopy layer of some tropical forests. e.g., Ventilago.
Question 17.
Enumerate the steps ino1ed in herbarium preparation?
Answer:
Preparation of herbarium specimen includes the following steps.
- Plant Collection
- Documentation of field site data
- Preparation of plant specimen
- Mounting herbarium specimen
- Herbarium labels
- Protection of herbarium sheets against mold and insects
![]()
Question 18.
Draw and label the open vascular bundle?
Answer:
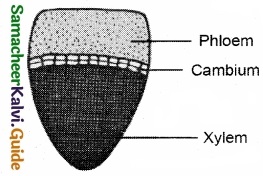
Question 19.
When does an essential mineral is considered as a “toxic”?
Answer:
Increase of mineral nutrients more than the normal concentration causes toxicity. A concentration, at which 10 % of the dry weight of tissue is reduced, is considered as toxic.
PART – IV
Answer all the questions. [2 × 5 = 10]
Question 20.
Tabulate the economic importance of algae?
Answer:
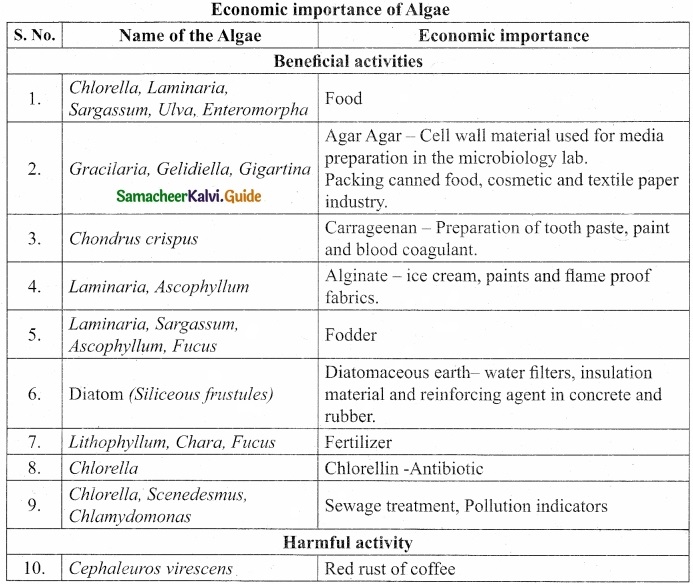
[OR]
Explain Datura metal in botanical terms. Draw floral diagram?
Answer:
1. Habit:
Large, erect and stout herb.
2. Root:
Branched tap root system.
3. Stem:
Stem is hollow, green and herbaceous with strong odour.
4. Leaf:
Simple, alternate, petiolate, entire or deeply lobed, glabrous exstipulate showing unicostate reticulate venation.
5. Inflorescence:
Solitary and axillary cyme.
6. Flower:
Flowers are large, greenish white, bracteate, ebracteolate, pedicellate, complete, heterochlamydeous, pentamerous, regular actinomorphic, bisexual and hypogyncas.
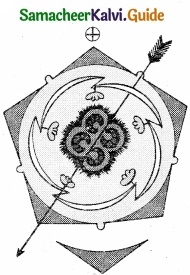
7. Calyx:
Sepals 5, green synsepalous showing valvate aestivation. Calyx is mostly persistant, odd sepal is posterior in position.
8. Corolla:
Petals 5, greenish white, sympetalous, plicate (folded like a fan) showing twisted aestivation, funnel shaped with wide mouth and 10 lobed.
9. Androecium:
Stamens 5, free from one another, epipetalous, altemipefalous and are inserted in the middle of the corolla tube. Anthers are basifixed, dithecous, with long filament, introse and longitudinally dehiscent.
10. Gynoecium:
Ovary bicarpellary, syncarpous superior ovary, basically biloculear but tetralocular due to the formation of false septum. Carpels are obliquely placed and ovules on swollen axile placentation. Style simple long and filiform, stigma two lobed.
11. Fruit:
Spinescent capsule opening by four special valves with persistent calyx.
12. Seed:
Endospermous
13. Floral Formula:
![]()
![]()
Question 21.
Describe the types of transpiration in plants?
Answer:
Types of Transpiration: Transpiration is of following three types:
1. Stomatal transpiration:
Stomata are microscopic structures present in high number on the lower epidermis of leaves. This is the most dominant form of transpiration and being responsible for most of the water loss (90 – 95%) in plants.
2. Lenticular transpiration:
In stems of woody plants and trees, the epidermis is replaced by periderm because of secondary growth. In order to provide gaseous exchange between the living cells and outer atmosphere, some pores which looks like lens – shaped raised spots are present on the surface of the stem called Lenticels. The loss of water from lenticels is very insignificant as it amounts to only 0.1% of the total.
3. Cuticular transpiration:
The cuticle is a waxy or resinous layer of cutin, a fatty substance covering the epidermis of leaves and other plant parts. Loss of water through cuticle is relatively small and it is only about 5 to 10 % of the total transpiration. The thickness of cuticle increases in xerophytes and transpiration is very much reduced or totally absent.
[OR]
Describe the concept of Phytochrome?
Answer:
Phytochrome is a bluish biliprotein pigment responsible for the perception of light in photo physiological process. But at (1959) named this pigment and it exists in two interconvertible forms:
(I) Red light absorbing pigment which is designated as Pr and
(II) Far red light absorbing pigment which is designated as Pfr. The Pfr form absorbs red light in 660 nm and changes to Pfr. The Pfr form absorbs far red light in 730 nm and changes to Pr.
The Pr form is biologically inactive and it is stable whereas Pfr form is biologically active and it is very unstable. In short day plants, Pr promotes flowering and Pfr inhibits the flowering whereas in long day plants flowering is promoted by Pfr and inhibited by Pr form.
Pfr is always associated with hydrophobic area of membrane systems while Pr is found in diffused state in the cytoplasm. The interconversion of the two forms of phytochrome is mainly involved in flower induction and also additionally plays a role in seed germination and changes in membrane conformation.
Bio – Zoology [Maximum Marks: 35]
PART – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer. [8 × 1 = 8]
Question 1.
Entomology is concerned with the study of ……………………..
(a) Formation and properties of soil
(b) Agricultural practices
(c) Various aspects of human life
(d) Various aspects of insect
Answer:
(d) Various aspects of insect
![]()
Question 2.
Which is the site of production of blood cells?
(a) Cartilage
(b) Bone marrow
(c) Blood
(d) Plasma
Answer:
(b) Bone marrow
![]()
Question 3.
Match the List – I and List – II.
|
List – I |
List – II |
| 1. Lipase | (i) Protein |
| 2. Pepsin | (ii) Lipid |
| 3. Renin | (iii) Starch |
| 4. Ptyalin | (iv) Cassein |
(a) 1 – (ii), 2 – (i), 3 – (iv), 4 – (iii)
(b) 1 – (i), 2 – (ii), 3 – (iii), 4 – (iv)
(c) 1 – (iv), 2 – (iii), 3 – (i), 4 – (ii)
(d) 1 – (iii), 2 – (i), 3 – (iv), 4 – (ii)
Answer:
(a) 1 – (ii), 2 – (i), 3 – (iv), 4 – (iii)
Question 4.
ESV stands for ……………………..
(a) Endocard Systolic Volume
(b) End Systolic Volume
(c) Endocard Sound Volume
(d) Endocard Sinoatrial Volume
Answer:
(b) End Systolic Volume
![]()
Question 5.
Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) The descending limb of loop of Henle is impermeable to water
(b) The ascending limb of loop of Henle is permeable to water
(c) The ascending limb of loop of Henle is impermeable to water
(d) The descending limb of loop of Henle is permeable to electrolytes
Answer:
(c) The ascending limb of loop of Henle is impermeable to water
Question 6.
Which of the following statements are incorrect?
(a) Basal epithelial cells are sensitive portions of the taste
(b) Basal epithelial cells are stem cells which divide and differentiate into new gustatory cells
(c) Gustatory hairs project form the tip of the gustatory cells
(d) Gustatory cells are sensory portion of the taste
Answer:
(a) Basal epithelial cells are sensitive portions of the taste
Question 7.
Serum Calcium level is regulated by …………………….
(a) Thyroxine
(b) FSH
(c) Pancreas Assertion is true, but reason is false
(d) Thyroid and Parathyroid
Answer:
(d) Thyroid and Parathyroid
![]()
Question 8.
Ca+ metabolism is regulated by …………………..
(a) ACTH
(b) Thyroxin
(c) Parathormone
(d) Epinephrine
Answer:
(a) ACTH
PART – II
Answer any four of the following questions. [4 × 2 = 8]
Question 9.
What is Phylogenetic tree?
Answer:
A phylogenetic tree or evolutionary tree is a branching diagram or “tree”, showing the inferred evolutionary relationships upon similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics.
![]()
Question 10.
Write about Marbled cone snail?
Answer:
Marbled Cone Snail (Conus marmoreus):
This cone – shaped snail can deliver dangerous venom which may result in vision loss, respiratory failure, muscle paralysis and eventually death. There is no anti – venom available.
Question 11.
Differences between male and female cockroach?
Answer:
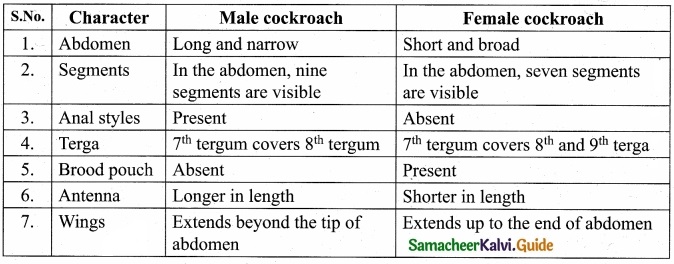
Question 12.
Define Floating ribs?
Answer:
The last 11th and 12th pairs of ribs are not connected ventrally. Therefore, they are called as ‘floating ribs’ or vertebral ribs.
![]()
Question 13.
Write a note on Tetany?
Answer:
Tetany is caused due to the hyposecretion of parathyroid hormone (PTH). Due to hyposecretion of PTH serum calcium level decreases (Hypocalcemia), as a result serum phosphate level increases.
Calcium and phosphate excretion level decreses. Generalized convulsion, locking of jaws increased heart beat rate, increases body temperature, muscular spasm are the major symptoms of tetany.
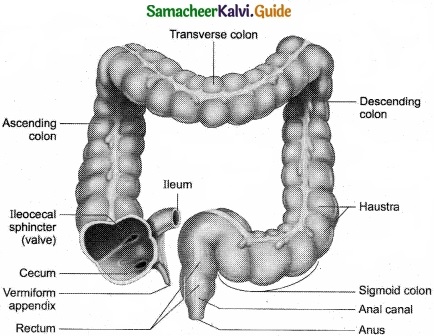
Question 14.
Draw the diagram of large intestine?
Answer:
PART – III
Answer any three questions in which question number 19 is compulsory. [3 × 3 = 9]
Question 15.
What is the need for classification?
Answer:
The basic need for classification are:
- To identify and differentiate closely related species.
- To know the variation among the species.
- To understand the evolution of the species.
- To create a phylogenetic tree among the different groups.
![]()
Question 16.
Distinguish between Diploblastic and Triploblastic animals?
Answer:
|
S.No |
Diploblastic animals |
Triploblastic animals |
| 1. | The animals in which the cells are arranged in two embryonic layers, the ectoderm and endoderm are called diploblastic animals. | The animals in which the cells are arranged in three embryonic layers, the ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm are called triploblastic animals. |
| 2. | These are lower organisms, eg. Cnidaria, Ctenophora | These are higher organisms, eg. Platyhelminthes to mammalia. |
Question 17.
Write a short note on connective tissue?
Answer:
- Connective tissue develops from the mesoderm.
- Connective tissue proper, Cartilage, bones and blood are the four main classes of connective tissues.
- Binding, support, protection, insulation and transportation of substances are the major functions of connective tissue.
![]()
Question 18.
Draw the diagram of Lamnito mauritii?
Answer:
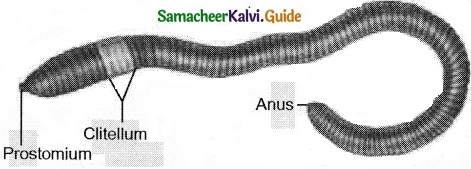
Question 19.
Define cross breedin?
Answer:
Breeding between a superior male of one breed with a superior female of another breed is known as cross breeding.
PART – IV
Answer all the questions. [2 × 5 = 10]
Question 20.
Who proposed the five kingdom classification? Represent the Five kingdom Classification in a tabular format?
Answer:
R.H. Whittaker (1969) proposed the Five kingdom Classification, the Kingdoms defined by him were Monera, Prgtista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia based on the cell structure, mode of nutrition, mode of reproduction and phylogenetic relationships. The table below gives a, comparative account of different characteristics of the five kingdoms.
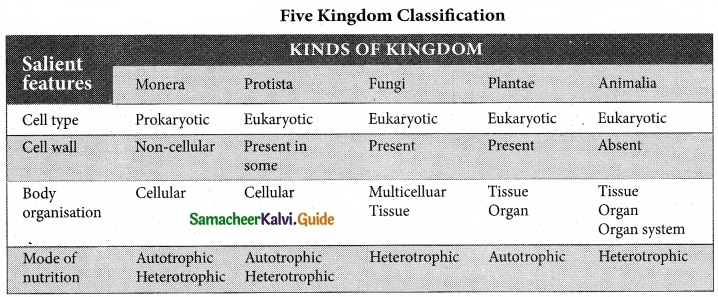
[OR]
Explain the mechanism of breathing?
Answer:
The movement of air between the atmosphere and the lungs is known as ventilation or breathing. Inspiration and expiration are the two phases of breathing. Inspiration is the movement of atmospheric air into the lungs and expiration is the movement of alveolar air that diffuse out of the lungs.
Lungs do not contain muscle fibres but expands and contracts by the movement of the ribs and diaphragm. The diaphragm is a sheet of tissue which separates the thorax from the abdomen. In a relaxed state, the diaphragm is domed shaped.
Ribs are moved by the intercostal muscles. External and internal intercostal muscles found between the ribs and the diaphragm helps in creating pressure gradients.
Inspiration occurs if the pressure inside the lungs (intrapulmonary pressure) is less than the atmospheric pressure likewise expiration takes place when the pressure within the lungs is higher than the atmospheric pressure.
Inspiraton is initiated by the contraction of the diaphragm muscles and external intercostal muscles, which pulls the ribs and sternum upwards and outwards and increases the volume of the thoracic chamber in the dorso – ventral axis, forcing the lungs to expand the pulmonary volume.
The increase in pulmonary volume and decrease in the intrapulmonary pressure forces the fresh air from outside to enter the air passages into the lungs to equalize the pressure. This process is called inspiration.
Relaxation of the diaphragm allows the diaphragm and sternum to return to its dome shape and the internal intercostal muscles contract, pulling the ribs downward reducing the thoracic volume and pulmonary volume.
This results in an increase in the intrapulmonary pressure slightly above the atmospheric pressure causing the expulsion of air from the lungs. This process is called expiration.
![]()
Question 21.
What are the benefits of regular exercise?
Answer:
Regular exercises can produce the following beneficial physiological changes:
- The muscles used in exercise grow larger and strongcr
- More enzymes are synthesized in the muscle fibre
- Ligaments and tendons become stronger
- Influences hormonal &tivity
- Prcvcnts Obesity
- Aesthetically bettcr with good physique
- Over all well-bcing with good quality of life
- Prevents depression, stress and anxiety
- The resting heart rate goes down
- Joints become more flexible
- Protection from hcart attack
- Improves cognitive functions
- Promotes confidence, esteem
During muscular exercise, there is an increase in metabolism. The O2 need of the muscles is increased. This requirement is met with more oxygen rich RBCs available to the active sites. There is an increase in heart rate and cardiac output. Along with balanced diet, physical activity plays a significant role in strengthening the muscles and bones.
[OR]
What are the types of chicken breeds in Poultry Farming?
Answer:
There are more than 100 breeds. The commonly farmed chicken breeds are categorized into five based on the purpose for which it is farmed. They are egg layers, broiler type, dual type, games and ornamental types.
1. Egg layers: These are farmed mainly for the production of egg.
Leghorn:
This is the most popular commercial breed in India and originated from Italy. They are small, compact with a single comb and wattles with white, brown or black colour.
They mature early and begin to lay eggs at the age of 5 or 6 months. Hence these are preferred in commercial farms. They can also thrive well in dry areas.
Chittagong:
It is the breed chiefly found in West Bengal. They are golden or light yellow coloured. The beak is long and yellow in colour. Ear lobes and wattles are small and red in colour. They are good egg layers and are delicious.
2. Broiler type: These are well known for fast growth and soft quality meat.
White Plymouth rock:
They have white plumage throughout the body. It is commonly used in broiler production. This is an American breed. It is a fast growing breed and well suitable for growing intensively in confined farms.
3. Dual purpose breeds: These are for both meat and egg production purpose.
Brahma:
It is a breed popularly known for its massive body having heavy bones, well feathered and proportionate body. Pea comb is one of the important breed characters. It has two common varieties namely, Light Brahma and Dark Brahma.
4. Game breeds: Since ancient times, special breed of roosters have been used for the sport of cockfighting.
Aseel:
This breed is white or black in colour. The hens are not good egg layers but are good in incubation of eggs. It is found in all states of India. Aseel is noted for its pugnacity, high stamina, and majestic gait and dogged fighting qualities. Although poor in productivity, this breed is well-known for their meat qualities.
5. Ornamental breeds: Ornamental chicken are reared as pets in addition to their use for egg production and meat.
Silkie:
It is a breed of chicken has a typical fluffy plumage, which is said to feel like silk and satin. The breed has numerous additional special characters, such as black skin and bones, blue earlobes, and five toes on each foot, while the majority chickens only have four.
They are exhibited in poultry shows, and come out in various colours. Silkies are well recognized for their calm, friendly temperament. Silkie chicken is especially simple to maintain as pets.