Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Physics Model Question Paper 3 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th Physics Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
TN State Board 11th Physics Model Question Paper 3 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 15 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each.
These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer - Question numbers 16 to 24 in Part II are two-mark questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 25 to 33 in Part III are three-mark questions. These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 34 to 38 in Part IV are five-mark questions. These are to be answered in detail Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
PART – I
Answer all the questions: [15 × 1 = 15]
Question 1.
A new unit of length is chosen such that the speed of light in vacuum is unity. The distance between the Sun and the Earth in terms of the new unit, if light takes 8 minute and 20 sec to cover the distance is …………………..
(a) 100 new unit
(b) 300 new unit
(c) 500 new unit
(d) 700 new unit
Hint:
Speed is unity = 1 unit/sec
Time = 8 min and 20 sec = 500 sec
Distance b/w sun and earth = Speed × Time
= 1 × 500 = 500 unit
Answer:
(c) 500 new unit
![]()
Question 2.
For a satellite moving in an orbit around the Earth, the ratio of kinetic energy to potential energy is ………………….
(a) 2
(b) 1 : 2
(c) 1 : \(\sqrt{2}\)
(d) \(\sqrt{2}\)
Hint:
\(\frac { GMm }{ R^{ 2 } } \) = mω2R
K.E = \(\frac{1}{2}\)Iω2 = \(\frac{1}{2}\)mR2ω2 = \(\frac{GMm}{2R}\)
P.E = – \(\frac{GMm}{R}\) ⇒ So \(\frac{K.E}{|P.E|}\) = \(\frac{1}{2}\)
Answer:
(b) 1 : 2
Question 3.
In the equilibrium position a body has ……………….
(a) Maximum potential energy
(b) Minimum potential energy
(c) Minimum kinetic energy
(d) Neither maximum nor minimum potential energy
Answer:
(c) Minimum kinetic energy
![]()
Question 4.
The centrifugal force appears to exist ………………….
(a) Only in inertial frames
(b) Only in rotating frames
(c) In any accelerated frame
(d) Both in inertial and non-inertial frames
Answer:
(b) Only in rotating frames
Question 5.
A particle is moving with a constant velocity along a line parallel to positive x-axis. The magnitude of its angular momentum with respect to the origin is …………………..
(a) Zero
(b) Increasing with x
(c) Decreasing with x
(d) Remaining constant
Answer:
(d) Remaining constant
Question 6.
When 8 droplets of water of radius 0.5 mm combine to form a single droplet. The radius of it is …………………
(a) 4 mm
(b) 2 mm
(c) 1 mm
(d) 8 mm
Hint:
Volume of 8 droplets of water = 8 × \(\frac{4}{3}\) π(0.5)3
When each droplet combine to form one volume remains conserved
R3 = 8 × (0.5)3
R3 = (8 × (0.5)3)
R3 = 2 × 0.5 = 1 mm
Answer:
(c) 1 mm
![]()
Question 7.
Pressure head in Bernoulli’s equation is …………………
(a) \(\frac { P_{ \rho } }{ g } \)
(b) \(\frac { P }{ \rho g } \)
(c) ρg
(d) Pρg
Answer:
(b) \(\frac { P }{ \rho g } \)
Question 8.
The angle between particle velocity and wave velocity in a transverse wave is ……………………
(a) Zero
(b) π/4
(c) π/2
(d) π
Answer:
(c) π/2
Question 9.
If the masses of the Earth and Sun suddenly double, the gravitational force between them will …………………….
(a) Remains the same
(b) Increase two times
(c) Increase four times
(d) Decrease two times
Answer:
(c) Increase four times
Question 10.
A mobile phone tower transmits a wave signal of frequency 900 MHz, the length of the transmitted from the mobile phone tower ……………………
(a) 0.33 m
(b) 300 m
(c) 2700 × 108m
(d) 1200 m
Hint:
f = 900 MHz = 900 × 106 Hz
Speed of wave (c) = 3 × 106 ms-1
λ = \(\frac{v}{f}\) = \(\frac { 3\times 10^{ 8 } }{ 900\times 10^{ 6 } } \) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) = 0.33m
Answer:
(a) 0.33 m
![]()
Question 11.
The displacement y of a wave travelling in the x direction is given by
y = (2 × 10-3) sin (300 t – 2x + \(\frac { \pi }{ 4 } \)), where x and y are measured in metres and t in second. The speed of the wave is …………………
(a) 150 ms-1
(b) 300 ms-1
(c) 450 ms-1
(d) 600 ms-1
Hint:
From standard equation of wave, Y = a sin (ωt – kx + ϕ)
ω = 300 ; k = 2
Speed of wave, V = \(\frac{ω}{k}\) = \(\frac{300}{2}\) = 150ms-1
Answer:
(a) 150 ms-1
Question 12.
The increase in internal energy of a system is equal to the workdone on the system. The process does the system undergoes is ……………………
(a) Isochoric
(b) Adiabatic
(c) Isobaric
(d) Isothermal
Answer:
(d) Isothermal
Question 13.
The minimum velocity with which a body of mass m must enter a vertical loop of radius R so that it can complete the loop is ……………………..
(a) \(\sqrt{2gR}\)
(b) \(\sqrt{3gR}\)
(c) \(\sqrt{5gR}\)
(d) \(\sqrt{gR}\)
Answer:
(c) \(\sqrt{5gR}\)
![]()
Question 14.
If the rms velocity of the molecules of a gas in a container be doubled then the pressure of the gas will.
(a) Becomes 4 times of the previous value
(b) Becomes 2 times of its previous value
(c) Remains same
(d) Becomes \(\frac{1}{4}\) of its previous value
Hint:
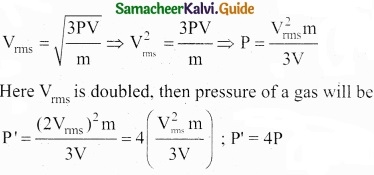
Answer:
(a) Becomes 4 times of the previous value
Question 15.
Gravitational mass is proportional to gravitational ………………….
(a) Intensity
(b) Force
(c) Field
(d) All of these
Answer:
(b) Force
PART – II
Answer any six questions in which Q. No 23 is compulsory. [6 × 2 = 12]
Question 16.
Write any four postulates of Kinetic theory of gases?
Answer:
- A gas consists of a very large number of molecules. Each one is a perfectly identical elastic sphere.
- The molecules of a gas are in a state of continuous and random motion. They move in all directions with all possible velocities.
- The size of each molecule is very small as compared to the distance between them. Hence, the volume occupied by the molecule is negligible in comparison to the volume of the gas:
- There is no force of attraction or repulsion between the molecules and the walls of the container.
![]()
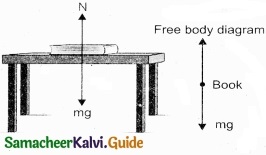
Question 17.
Draw the free body diagram of the book at rest on the table?
Answer:
Question 18.
Three block are connected as shown in fig on a horizontal frictionless table. If m1 = 1 kg, m2 = 8 kg, m3 = 27 kg and T3 = 36 N then calculate tension T2?
Answer:
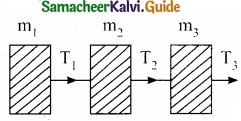
Acceleration acquired by all blocks a = \(\frac { T_{ 3 } }{ m_{ 1 }+m_{ 2 }+m_{ 3 } } \) = \(\frac{36}{36}\) = 1ms-2
∴ Tension T2 = (m1 + m2) a
= (1 + 8) × 1 = 9N
![]()
Question 19.
What is power? Give its dimensional formula?
Answer:
The rate of work done is called power. Dimensional formula of power is ML2 T-3
Question 20.
What are geostationary and polar satellites?
Answer:
Geostationary Satellite: It is the satellite which appears at a fixed position and at a definite height to an observer on Earth.
Polar Satellite: It is the satellite which revolves in polar orbit around the Earth.
Question 21.
An iceberg of density 900 kg m-3 is floating in water of density 1000 kg m-3. What is the percentage of volume of iceberg outside the water?
Answer:
Fraction of volume inside water = Relative density of the body
\(\frac { V’ }{ V } \) = \(\frac { \rho }{ \rho ‘ } \) = \(\frac{900}{1000}\) = 0.9
Fraction of volume outside water = 1 – 0.9 = 0.1
Percentage of volume outside water = 0.1 × 100 = 10%
![]()
Question 22.
State stoke’s law and define terminal velocity?
Answer:
Stoke’s law:
When a body falls through a highly viscous liquid, it drags the layer of the liquid immediately in contact with it. This results in a relative motion between the different layers of the liquid. As a result of this, the falling body experiences a viscous force F.
Stoke performed many experiments on the motion of small spherical bodies in different fluids and concluded that the viscous force F acting on the spherical body depends on
- Coefficient of viscosity q of the liquid
- Radius a of the sphere and
- Velocity v of the spherical body
Dimensionally it can be proved that ∴ F = k ηav
Experimentally Stoke found that k = 6π
This is Stoke’s law
Terminal velocity:
Terminal velocity of a body is defined as the constant velocity acquired by a body while falling through a viscous liquid.
![]()
Question 23.
The Earth without its atmosphere would be hospitably cold. Explain why?
Answer:
The lower layers of Earth’s atmosphere reflect infrared radiations from Earth back to the surface of Earth. Thus the heat radiation received by the earth from the Sun during the day are kept trapped by the atmosphere. If atmosphere of Earth were not there, its surface would become too cold to live.
Question 24.
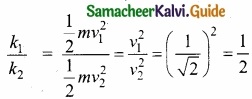
A body A is projected upwards with velocity v1 Another body B of same mass is proj eeted at an angle of 45°. Both reach the same height. Calculate the ratio of their initial kinetic energies?
Answer:
As A and B attain the same height therefore vertical component of initial velocity of B is equal to initial velocity of A
v2 cos 45° = V1 (or) \(\frac { v_{ 2 } }{ \sqrt { 2 } } \) = v1
PART – III
Answer any six questions in which Q.No. 29 is compulsory. [6 × 3 = 18]
Question 25.
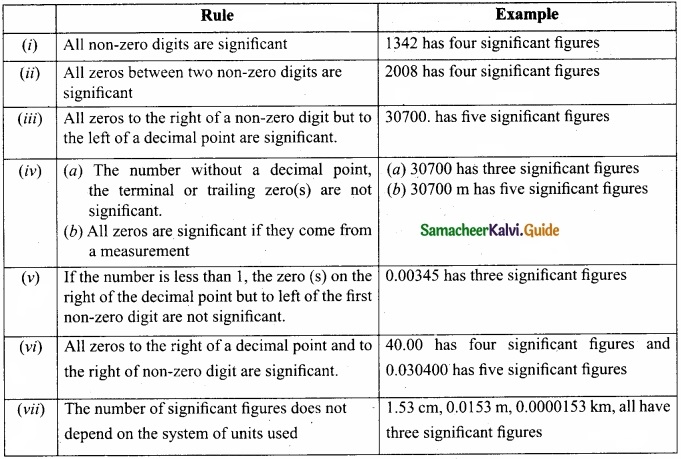
Explain the rules for counting significant figures with examples?
Rules for counting significant figures:
Answer:
Question 26.
Elastic headon collision, consider two particles one is moving and another one is stationary with their respective masses m and \(\frac { M }{ m } \). A moving particle meets collides elastically on stationary particle in the opposite direction. Find the kinetic energy of the stationary particle after a collision?
Answer:
mass of the moving particle m1 = m (say)
mass of the stationary particle m1 = \(\frac { 1 }{ m } \) M
Velocity of the moving particle before collision = v1i (say)
Velocity of the stationary particle before collision = v2i = 0
Velocity of the stationary particle after collision = v2f (say)

Kinetic energy of the stationary particle after a collision

Question 27.
Calculate the angle for which a cyclist bends when he turns a circular path of length 34.3 m in \(\sqrt{22}\) s?
Answer:
Given Data:
l = 34.3 m, t = \(\sqrt{22}\) , g = 9.8 ms-2, θ = ?
If r is radius of circular path, then length of path = 2πr = 34.3 m
r = \(\frac { 33.4 }{ 2\pi } \) and time taken t = \(\sqrt{22}\)s
As tan θ = \(\frac { v^{ 2 } }{ rg } \)
∴ tan θ = (\(\frac { 34.3 }{ \sqrt { 22 } } \))2 × \(\frac { 2\pi }{ 34.3\times 9.8 } \)
tan θ = \(\frac { 34.3\times 34.3 }{ 22 } \) × \(\frac{2×22}{7×343×9.8}\) = \(\frac{34.3×2}{68.6}\) = 1 [∴θ = 45°]
![]()
Question 28.
Explain how density, moisture affect the velocity of sound in gases?
Answer:
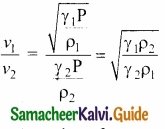
Effect of density:
Let us consider two gases with different densities having same temperature and pressure. Then the speed of sound in the two gases are

Taking ratio of equation (1) and equation (2) we get
For gases having same value of γ,
\(\frac { v_{ 1 } }{ v_{ 2 } } \) = \(\sqrt { \frac { \rho _{ 2 } }{ \rho _{ 1 } } } \)
Thus the velocity of sound in a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of the density of the gas.
Effect of moisture (humidity):
We know that density of moist air is 0.625 of that of dry air, which means the presence of moisture in air (increase in humidity) decreases its density. Therefore, speed of sound increases with rise in humidity. From equation:
v = \(\sqrt { \frac { \gamma \rho }{ \rho } } \)
Let ρ1, v1 = and ρ2, v2 be the density and speeds of sound in dry air and moist air, respectively.

Since P is the atmospheric pressure, it can be shown that
\(\frac { \rho _{ 2 } }{ \rho _{ 1 } } \) = \(\frac { P }{ p_{ 1 }+0.625p_{ 2 } } \)
where p1 and p2 are the partial pressures of dry air and water vapour respectively. Then
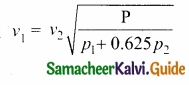
Question 29.
Explain
(a) Why there are no lunar eclipse and solar eclipse every month?
(b) Why do we have seasons on earth?
Answer:
(a) If the orbits of the Moon and Earth lie on the same plane, during full Moon of every month, we can observe lunar eclipse. If this is so during new Moon we can observe solar eclipse.
But Moon’s orbit is tilted 5° with respect to Earth’s orbit. Due to this 5° tilt, only during certain periods of the year, the Sun, Earth and Moon align in straight line leading to either lunar eclipse or solar eclipse depending on the alignment.
(b) The common misconception is that ‘Earth revolves around the Sun, so when the Earth is very far away, it is winter and when the Earth is nearer, it is summer’.
Actually, the seasons in the Earth arise due to the rotation of Earth around the Sun with 23.5° tilt. Due to this 23.5° tilt, when the northern part of Earth is farther to the Sun, the southern part is nearer to the Sun. So when it is summer in the northern hemisphere, the southern hemisphere experience winter.
![]()
Question 30.
When a person breathes, his lungs can hold up to 5.5 1 of air at body temperature 37°C and atmospheric pressure (1 atm = 101 kPa). This air contains 21% oxygen, calculate the number of oxygen molecules in the lungs?
Answer:
We can treat the air inside the lungs as an ideal gas. To find the number of molecules, we can use the ideal gas law.
PV = NkT
Here volume is given in the Litre. 1 Litre is volume occupied by a cube of side 10 cm
1 Litre = 10 cm × 10 cm × 10 cm = 10-3m-3
N = \(\frac{PV}{kT}\) = \(\frac { 1.01\times 10^{ 5 }\times 5.5\times 10^{ -3 } }{ 1.38\times 10^{ -23 }\times 310 } \)
= 1.29 × 1023 × \(\frac{21}{100}\)
Number of oxygen molecules = 2.7 × 1022 molecules
Question 31.
Give any five properties of vector product of two vectors?
Answer:
(I) The vector product of any two vectors is always another vector whose direction is perpendicular to the plane containing these two vectors, i.e., orthogonal to both the vectors \(\vec { A } \) and \(\vec { B } \), even though the vectors AandB may or may not be mutually orthogonal.
(II) The vector product of two vectors is not commutative, i.e., \(\vec { A } \) × \(\vec { B } \) ≠ \(\vec { B } \) × \(\vec { A } \) . But, \(\vec { A } \) × \(\vec { B } \) = –\(\vec { B } \) × \(\vec { A } \).
Here it is worthwhile to note that |\(\vec { A } \) × \(\vec { B } \)| = |\(\vec { B } \) × \(\vec { A } \)| = AB sin θ i.e., in the case of the product vectors \(\vec { A } \) × \(\vec { B } \) and \(\vec { B } \) × \(\vec { A } \), the magnitudes are equal but directions are opposite to each other.
(III) The vector product of two vectors will have maximum magnitude when sin 0 = 1, i.e., θ = 90° i.e., when the vectors \(\vec { A } \) and \(\vec { B } \) are orthogonal to each other.
(\(\vec { A } \) × \(\vec { B } \))max = AB\(\hat { n } \)
(IV) The vector product of two non-zero vectors will be minimum when sin 0 = 0, i.e., 0 = 0° or 180°
(\(\vec { A } \) × \(\vec { B } \))max = 0
i.e., the vector product of two non-zero vectors vanishes, if the vectors are either parallel or antiparallel.
(V) The self-cross product, i.e., product of a vector with itself is the null vector
\(\vec { A } \) × \(\vec { A } \) = AA sin 0°\(\hat { n } \) = \(\vec { 0 } \)
In physics the null vector \(\vec { 0 } \) is simply denoted as zero.
![]()
Question 32.
Why does a porter bend forward w hile carrying a sack of rice on his back?
Answer:
When a porter carries a sack of rice, the line of action of his centre of gravity will go away from the body. It affects the balance, to avoid this he bends. By which centre of gravity will realign within the body again. So balance is maintained.
Question 33.
A piece of wood of mass m is floating erect in a liquid whose density is p. If it is slightly pressed down and released, then executes simple harmonic motion. Show that its time period of oscillation is T = 2π\(\sqrt{m/Agρ}\)
Answer:
Spring factor of liquid(k) = Aρg
Inertia factor of wood = m
Time period T = 2π = image 12
T = 2π\(\sqrt{m/Aρg}\)
PART – IV
Answer all the questions. [5 × 5 = 25]
Question 34 (a).
Describe the vertical oscillations of a spring?
Answer:
Vertical oscillations of a spring: Let us consider a massless spring with stiffness constant or force constant k attached to a ceiling as shown in figure. Let the length of the spring before loading mass m be L.
If the block of mass m is attached to the other end of spring, then the spring elongates by a length. Let F, be the restoring force due to stretching of spring. Due to mass m, the gravitational force acts vertically downward. We can draw free-body diagram for this system as shown in figure. When the system is under equilibrium,
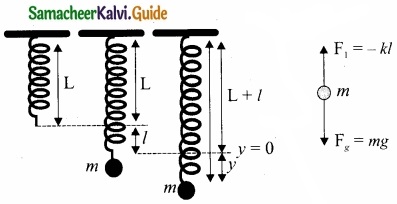
F1 + mg = 0 ……………… (1)
But the spring elongates by small displacement 1, therefore,
F1 ∝ l ⇒ F1 = -kl ……………….. (2)
Substituting equation (2) in equation (1) we get
-kl + mg = 0
mg = kl or
\(\frac{m}{k}\) = \(\frac{l}{g}\) ………………….. (3)
Suppose we apply a very small external force on the mass such that the mass further displaces downward by a displacement y, then it will oscillate up and down. Now, the restoring force due to this stretching of spring (total extension of spring is y + 1) is
F2 ∝ (y + l)
F2 = -k(y + l) = -ky – kl …………………… (4)
Since, the mass moves up and down with acceleration \(\frac{d^{2} y}{d t^{2}}\), by drawing the free body diagram for this case we get
-ky – kl + mg = m \(\frac{d^{2} y}{d t^{2}}\) ……………………. (5)
The net force acting on the mass due to this stretching is
F = F2 + mg
F = -ky – kl + mg …………………… (6)
The gravitational force opposes the restoring force. Substituting equation (3) in equation (6), we get
F = – ky- kl + kl = -ky
Applying Newton’s law we get
m \(\frac{d^{2} y}{d t^{2}}\) = -ky
\(\frac{d^{2} y}{d t^{2}}\) = –\(\frac{k}{m}\)y ………………… (7)
The above equation is in the form of simple harmonic differential equation. Therefore, we get the time period as
T = 2π\(\sqrt{m/k}\) second ……………………. (8)
The time period can be rewritten using equation (3)
T = 2π\(\sqrt{m/k}\) = 2πl\(\frac{1}{g}\) second ……………………. (9)
The accleration due to gravity g can be computed by the formula
g = 4π2\((\frac { 1 }{ T } )^{ 2 }\)ms-2 …………………….. (10)
[OR]
(b) Derive poiseuille’s formula for the volume of a liquid flowing per second through a pipe under streamlined flow?
Answer:
Consider a liquid flowing steadily through a horizontal capillary tube. Let v = (\(\frac{1}{g}\)) be the volume of the liquid flowing out per second through a capillary tube. It depends on (1) coefficient of viscosity (η) of the liquid, (2) radius of the tube (r), and (3) the pressure gradient (\(\frac{P}{l}\)) . Then,
v ∝ηarb(\(\frac{P}{l}\))c
v = kηarb(\(\frac{P}{l}\))c …………………….. (1)
where, k is a dimensionless constant.
Therefore, [v] = \(\frac { Volume }{ Time } \) = [L3T-1]; [ \(\frac{dP}{dX}\) ] = \(\frac { Pressure }{ Distance } \) = [ML-2T-2]
[η] = [Ml-1T-1] and [r] = [L]
Substituting in equation (1)
[L3T-1] = [ML-1T-1]a[L]b [ML-2T-2]c
M0L3T-1 = Ma+bL-a+b-2cT-a-2c = -1
So, equating the powers of M, L and T on both sides, we get
a + c = 0, – a + b – 2c = 3, and – a – 2c = – 1
We have three unknowns a, b and c. We have three equations, on solving, we get
a = – 1, b = 4 and c = 1
Therefore, equation (1) becomes,
v = kη-1r4(\(\frac{P}{l}\))1
Experimentally, the value of k is shown to be , we have \(\frac{π}{8}\), we have
v = \(\frac{\pi r^{4} \mathrm{P}}{8 \eta /}\)
The above equation is known as Poiseuille’s equation for the flow of liquid through a narrow tube or a capillary tube. This relation holds good for the fluids whose velocities are lesser than the critical velocity (vc).
![]()
Question 35 (a).
Describe briefly simple harmonic oscillation as a projection of uniform circular motion?
Answer:
Consider a particle of mass m moving with unifonn speed v along the circumference of a circle whose radius is r in anti-clockwise direction (as shown in figure). Let us assume that the origin of the coordinate system coincides with the center O of the circle.
If ω is the angular velocity of the particle and θ the angular displacement of the particle at any instant of time t, then θ = ωt. By projecting the uniform circular motion on its diameter gives a simple harmonic motion.
This means that we can associate a map (or a relationship) between uniform circular (or revolution) motion to vibratory motion. Conversely, any vibratory motion or revolution can be mapped to unifonn circular motion. In other words, these two motions are similar in nature.
Let us first project the position of a particle moving on a circle, on to its vertical diameter or on to a line parallel to vertical diameter as shown in figure. Similarly, we can do it for horizontal axis or a line parallel to horizontal axis.
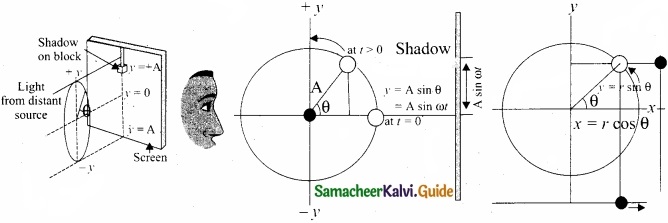
The projection of uniform circular motion on a diameter of SHM:
As a specific example, consider a spring mass system (or oscillation of pendulum). When the spring moves up and down (or pendulum moves to and fro), the motion of the mass or bob is mapped to points on the circular motion.
Thus, if a particle undergoes uniform circular motion then the projection of the particle on the diameter of the circle (or on a line parallel to the diameter) traces straight line motion which is simple harmonic in nature. The circle is known as reference circle of the simple harmonic motion. The simple harmonic motion can also be defined as the motion of the projection of a particle on any diameter of a circle of reference.
[OR]
(b) State and prove Bernoulli’s theorem for a flow of incompressible non viscous and stream lined flow of fluid?
Answer:
Bernoulli’s theorem:
According to Bernoulli’s theorem, the sum of pressure energy, kinetic energy, and potential energy per unit mass of an incompressible, non-viscous fluid in a streamlined flow remains a constant. Mathematically,
\(\frac{P}{ρ}\) + \(\frac{1}{2}\)v2 + gh – constant
This is known as Bernoulli’s equation.
Proof:
Let us consider a flow of liquid through a pipe AB. Let V be the volume of the liquid when it enters A in a time t. Which is equal to the volume of the liquid leaving B in the same time. Let aA, vA and PA be the area of cross section of the tube, velocity of the liquid and pressure exerted by the liquid at A respectively.
Let the force exerted by the liquid at A is
FA = PAaA
Distance travelled by the liquid in time t is d = vAt
Therefore, the work done is W = FAd = PAaAvAt
But aAvAt = aAd = V, volume of the liquid entering at A.
Thus, the work done is the pressure energy (at A), W = FAd = PAV
Pressure energy per unit volume at
A = \($\frac{\text { Pressure energy }}{\text { Volume }}$\) = \(\frac { P_{ A }V }{ V } \) = PA
Pressure energy per unit mass at
A = \($\frac{\text { Pressure energy }}{\text { Mass }}$\) = \(\frac { P_{ A }V }{ m } \) = \(\frac { P_{ A } }{ \frac { m }{ V } } \) = \(\frac { P_{ A } }{ \rho } \)
Since m is the mass of the liquid entering at A in a given time, therefore, pressure energy of the liquid at A is
EPA = PAV = PAV × (\(\frac{m}{m}\)) = m\(\frac { P_{ A } }{ \rho } \)
Potential energy of the liquid at A,
PEA = mghA
Due to the flow of liquid, the kinetic energy of the liquid at A,
KEA = \(\frac{1}{2}\)mv2A
Therefore, the total energy due to the flow of liquid at A,
EA = EPA + KEA + PEA
EA = \(m \frac{P_{A}}{\rho}+\frac{1}{2} m v_{A}^{2}+m g h_{A}\)
Similarly, let aB, VB and PB be the area of cross section of the tube, velocity of the liquid and pressure exerted by the liquid at B. Calculating the total energy at FB, we get .
\(\mathrm{E}_{\mathrm{B}}=m \frac{\mathrm{P}_{\mathrm{B}}}{\rho}+\frac{1}{2} m v_{\mathrm{B}}^{2}+m g h_{\mathrm{B}}\)
From the law of conservation of energy.
EA = EB
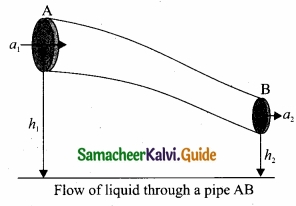
Thus, the above equation can be written as
\(\frac { P }{ \rho g } \) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac { v^{ 2 } }{ g } \) + h = Constant
The above equation is the consequence of the conservation of energy which is true until there is no loss of energy due to friction. But in practice, some energy is lost due to friction. This arises due to the fact that in a fluid flow, the layers flowing with different velocities exert frictional forces on each other. This loss of energy is generally converted into heat energy. Therefore, Bernoulli’s relation is strictly valid for fluids with zero viscosity or non-viscous liquids. Notice that when the liquid flows through a horizontal pipe, then
h = 0 ⇒ \(\frac { P }{ \rho g } \) + \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\frac { v^{ 2 } }{ g } \) = Constant
![]()
Question 36 (a).
Explain perfect inelastic collision and derive an expression for loss of kinetic energy in perfect inelastic collision?
Answer:
In a perfectly inelastic or completely inelastic collision, the objects stick together permanently after collision such that they move with common velocity. Let the two bodies with masses m1 and m2 move with initial velocities u1 and u2 respectively before collision. Aft er perfect inelastic collision both the objects move together with a common velocity v as shown in figure.
Since, the linear momentum is conserved during collisions,
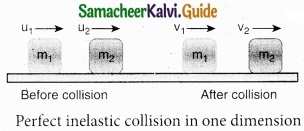
m1u1 + m2u2 = (m1 + m2) v
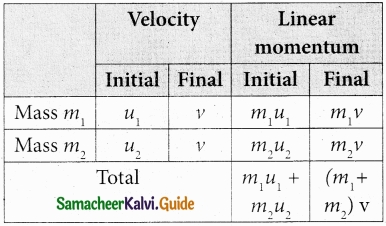
The common velocity can be computed by
v = \(\frac{m_{1} u_{1}+m_{2} u_{2}}{\left(m_{1}+m_{2}\right)}\) ………………….. (1)
Loss of kinetic energy in perfect inelastic collision;
In perfectly inelastic collision, the loss in kinetic energy during collision is transformed to another form of energy like sound, thermal, heat, light etc. Let KEi be the total kinetic energy before collision and KEf be the total kinetic energy after collision.
Total kinetic energy before collision,
KEe = \(\frac{1}{2} m_{1} u_{1}^{2}+\frac{1}{2} m_{2} u_{2}^{2}\) …………………… (2)
Total kinetic energy after collision,
KEf = \(\frac{1}{2}\left(m_{1}+m_{2}\right) v^{2}\) …………………….. (3)
Then the loss of kinetic energy is Loss of KE, ∆Q = KEf – KEi
= \(\frac{1}{2}\left(m_{1}+m_{2}\right) v^{2}-\frac{1}{2} m_{1} u_{1}^{2}-\frac{1}{2} m_{2} u_{2}^{2}\) ………………….. (4)
Substituting equation (1) in equation (4), and on simplifying (expand v by using the algebra (a + b)2 = a2 + b2 + 2ab), we get
Loss of KE, ∆Q = \(\frac{1}{2}\) \(\left(\frac{m_{1} m_{2}}{m_{1}+m_{2}}\right)\) (u1 – u2)2
[OR]
(b) Derive an expression for maximum height attained, time of flight, horizontal range for a projectile in oblique projection?
Answer:
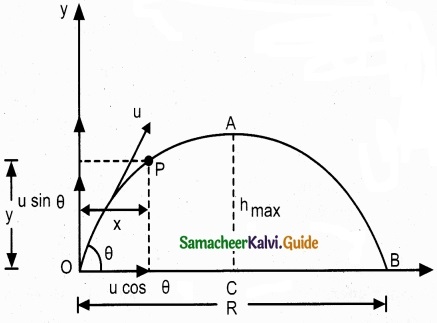
Maximum height (hmax):
The maximum vertical distance travelled by the projectile during the journey is called maximum height. This is determined as follows:
For the vertical part of the motion
\(v_{y}^{2}=u_{y}^{2}+2 a_{y} s\)
Here, uy= u sin θ, a = -g, s = hmax, and at the maximum height v = 0
Time of flight (Tf):
The total time taken by the projectile from the point of projection till it hits the horizontal plane is called time of flight. This time of flight is the time taken by the projectile to go from point O to B via point A as shown in figure.
We know that sy = uyt + \(\frac{1}{2}\)ayt2
Here, sy = y = 0 (net displacement in y-direction is zero), uy = u sin θ, ay = -g, t = Tf, Then
0 = u sin θ Tf – \(\frac{1}{2} g \mathrm{T}_{f}^{2}\)
Tf = 2u \(\frac{sin θ}{g}\) …………………….. (2)
Horizontal range (R):
The maximum horizontal distance between the point of projection and the point on the horizontal plane where the projectile hits the ground is called horizontal range (R). This is found easily since the horizontal component of initial velocity remains the same. We can write.
Range R = Horizontal component of velocity % time of flight = u cos θ × Tf = \(\frac{u^{2} \sin 2 \theta}{g}\)
The horizontal range directly depends on the initial speed (u) and the sine of angle of projection (θ). It inversely depends on acceleration due to gravity ‘g’.
For a given initial speed u, the maximum possible range is reached when sin 2θ is
maximum, sin 2θ = 1. This implies 2θ = π/2 or θ = π/4
This means that if the particle is projected at 45 degrees with respect to horizontal, it attains maximum range, given by
Rmax = \(\frac { u^{ 2 } }{ g } \).
![]()
Question 37 (a).
Explain the work-energy theorem in detail and also give three examples?
Answer:
- If the work done by the force on the body is positive then its kinetic energy increases.
- If the work done by the force on the body is negative then its kinetic energy decreases.
- If there is no work done by the force on the body then there is no change in its kinetic energy, which means that the body has moved at constant speed provided its mass remains constant.
- When a particle moves with constant speed in a circle, there is no change in the kinetic energy of the particle. So according to work energy principle, the work done by centripetal force is zero.
[OR]
(b) (i) Define molar specific heat capacity?
Answer:
Molar specific heat capacity is defined as heat energy required to increase the temperature of one mole of substance by IK or 1°C
(ii) Derive Mayer’s relation for an ideal gas?
Mayer’s relation: Consider p mole of an ideal gas in a container with volume V, pressure P and temperature T.
When the gas is heated at constant volume the temperature increases by dT. As no work is done by the gas, the heat that flows into the system will increase only the internal energy. Let the change in internal energy be dU.
If CV is the molar specific heat capacity at constant volume, from equation.
CV = \(\frac { 1 }{ \mu } \) \(\frac{dU}{dT}\) …………………… (1)
dU = µCV dT ………………… (2)
Suppose the gas is heated at constant pressure so that the temperature increases by dT. If ‘Q’ is the heat supplied in this process and ‘dV’ the change in volume of the gas.
Q = pCpdT ……………. (3)
If W is the workdone by the gas in this process, then
W = P dV ………………….. (4)
But from the first law of thermodynamics,
Q = dU + W ………………… (5)
Substituting equations (2), (3) and (4) in (5), we get,
For mole of ideal gas, the equation of state is given by
\(\mu \mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{p}} d \mathrm{T}=\mu \mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{v}} d \mathrm{T}+\mathrm{P} d \mathrm{V}\)
Since the pressure is constant, dP = 0
CpdT = CVdT + PdV
∴ Cp = CV + R (or) Cp – CV = R …………………… (6)
This relation is called Mayer’s relation It implies that the molar specific heat capacity of an ideal gas at constant pressure is greater than molar specific heat capacity at constant volume.
The relation shows that specific heat at constant pressure (sp) is always greater than specific heat at constant volume (sv).
![]()
Question 38 (a).
Derive an expression of pressure exerted by the gas on the walls of the container?
Answer:
Expression for pressure exerted by a gas : Consider a monoatomic gas of N molecules each having a mass m inside a cubical container of side l.
The molecules of the gas are in random motion. They collide with each other and also with the walls of the container. As the collisions are elastic in nature, there is no loss of energy, but a change in momentum occurs.
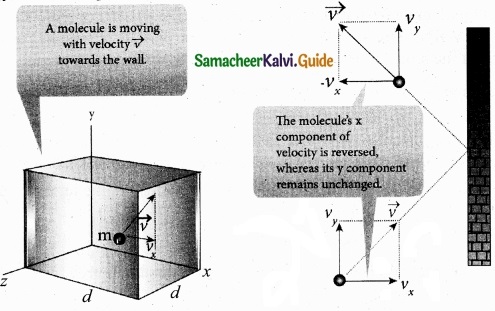
The molecules of the gas exert pressure on the walls of the container due to collision on it. During each collision, the molecules impart certain momentum to the wall. Due to transfer of momentum, the walls experience a continuous force. The force experienced per unit area of the walls of the container determines the pressure exerted by the gas. It is essential to determine the total momentum transferred by the molecules in a short interval of time.
A molecule of mass m moving with a velocity \(\vec { v } \) having components (vx, vy, vz) hits the right side wall. Since we have assumed that the collision is elastic, the particle rebounds with same speed and its x-component is reversed. This is shown in the figure. The components of velocity of the molecule after collision are (-vx, vy, vz).
The x-component of momentum of the molecule before collision = mvx
The x-component of momentum of the molecule after collision = – mvx
The change in momentum of the molecule in x direction
= Final momentum – initial momentum = – mvx – mvx = – 2mvx
According to law of conservation of linear momentum, the change in momentum of the wall = 2 mvx
The number of molecules hitting the right side wall in a small interval of time ∆t.
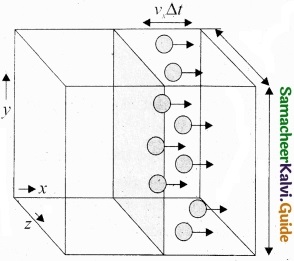
The molecules within the distance of vx∆t from the right side wall and moving towards the right will hit the wall in the time interval ∆t. The number of molecules that will hit the right side wall in a time interval ∆t is equal to the product of volume (Avx∆t) and number density of the molecules (n).
Here A is area of the wall and n is number of molecules per \(\frac{N}{V}\) unit volume. We have assumed that the number density is the same throughout the cube.
Not all the n molecules will move to the right, therefore on an average only half of the n molecules move to the right and the other half moves towards left side.
The number of molecules that hit the right side wall in a time interval ∆t
= \(\frac{n}{2}\) Avx∆t
In the same interval of time ∆t, the total momentum transferred by the molecules
\(\Delta \mathrm{P}=\frac{n}{2} \mathrm{A} v_{x} \Delta t \times 2 m v_{x}=\mathrm{A} v_{x}^{2} m n \Delta t\) ………………….. (2)
From Newton’s second law, the change in momentum in a small interval of time gives rise to force.
The force exerted by the molecules on the wall (in magnitude)
F = \(\frac{∆p}{∆t}\) = nmAv2x ……………………. (3)
Pressure, P = force divided by the area of the wall
P = \(\frac{F}{A}\) = nmAv2x ……………………….. (4)
p = \(nm\bar{v}_{x}^{2}\)
Since all the molecules are moving completely in random manner, they do not have same . speed. So we can replace the term vnmAv2x by the average \(\bar { v } \)2x in equation (4).
P = nm\(\bar { v } \)2x ……………………. (5)
Since the gas is assumed to move in random direction, it has no preferred direction of motion (the effect of gravity on the molecules is neglected). It implies that the molecule has same average speed in all the three direction. So, \(\bar{v}_{x}^{2}\) = \(\bar{v}_{y}^{2}\) = \(\bar{v}_{z}^{2}\). The mean square speed is written as
\(\bar{v}^{2}\) = \(\bar{v}_{x}^{2}\) + \(\bar{v}_{y}^{2}\) + \(\bar{v}_{z}^{2}\) = 3\(\bar{v}_{x}^{2}\)
\(\bar{v}_{x}^{2}\) = \(\frac{1}{3}\) \(\bar{v}^{2}\)
Using this in equation (5), we get
P = \(\frac{1}{3} n m \bar{v}^{2} \quad \text { or } P=\frac{1}{3} \frac{N}{V} m \bar{v}^{2}\) ………………….. (6)
[OR]
(b) Discuss the simple pendulum in detail?
Answer:
Simple pendulum

A pendulum is a mechanical system which exhibits periodic motion. It has a bob with mass m suspended by a long string (assumed to be massless and inextensible string) and the other end is fixed on a stand. At equilibrium, the pendulum does not oscillate and hangs vertically downward.
Such a position is known as mean position or equilibrium position. When a pendulum is displaced through a small displacement from its equilibrium position and released, the bob of the pendulum executes to and fro motion. Let l be the length of the pendulum which is taken as the distance between the point of suspension and the centre of gravity of the bob. Two forces act on the bob of the pendulum at any displaced position.
- The gravitational force acting on the body (\(\vec { F} \) = m\(\vec { g } \)) which acts vertically downwards.
- The tension in the string T which acts along the string to the point of suspension.
Resolving the gravitational force into its components:
- Normal component: The component along the string but in opposition to the direction of tension, Fas = mg cos θ.
- Tangential component: The component perpendicular to the string i.e., along tangential direction of arc of swing, Fps = mg sin θ.
Therefore, The normal component of the force is, along the string,
\(\mathrm{T}-\mathrm{W}_{a s}=m \frac{v^{2}}{l}\)
Here v is speed of bob
T -mg cos θ = m \(\frac{v^{2}}{l}\)
From the figure, we can observe that the tangential component Wps of the gravitational force always points towards the equilibrium position i.e., the direction in which it always points opposite to the direction of displacement of the bob from the mean position. Hence, in this case, the tangential force is nothing but the restoring force. Applying Newton’s second law along tangential direction, we have
\(m \frac{d^{2} s}{d t^{2}}+\mathrm{F}_{p s}=0 \Rightarrow m \frac{d^{2} s}{d t^{2}}=-\mathrm{F}_{p s}\)
\(m \frac{d^{2} s}{d t^{2}}=-m g \sin \theta\) …………………. (1)
where, s is the position of bob which is measured along the arc. Expressing arc length in terms of angular displacement i.e.,
s = lθ ………………… (2)
then its acceleration, \(\frac{d^{2} s}{d t^{2}}=l \frac{d^{2} \theta}{d t^{2}}\) …………………. (3)
Substituting equation (3) in equation (1), we get
\(\begin{aligned}
l \frac{d^{2} \theta}{d t^{2}} &=-g \sin \theta \\
\frac{d^{2} \theta}{d t^{2}} &=-\frac{g}{l} \sin \theta
\end{aligned}\) ………………….. (4)
Because of the presence of sin θ in the above differential equation, it is a non-linear differential equation (Here, homogeneous second order). Assume “the small oscillation approximation”, sin θ ~ 0, the above differential equation becomes linear differential equation.
\(\frac{d^{2} \theta}{d t^{2}}=-\frac{g}{l} \theta\) …………………… (5)
This is the well known oscillatory differential equation. Therefore, the angular frequency of this oscillator (natural frequency of this system) is
ω2 = \(\frac{g}{l}\) …………………… (6)
∴ ω = \(\sqrt{g/l}\) in rad s-1 ……………….. (7)
The frequency of oscillation is
f = \(f=\frac{1}{2 \pi} \sqrt{\frac{g}{l}} \text { in } \mathrm{Hz}\) ………………… (8)
and time period of sscillations is
T = 2π\(\sqrt{l/g}\) in second. ……………….. (9)