Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Biology Model Question Paper 1 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th Biology Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
TN State Board 11th Biology Model Question Paper 1 English Medium
General Instructions:
-
- The question paper comprises of four parts. Questions for Botany and Zoology are asked separately.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 8 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each. These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer.
- Question numbers 9 to 14 in Part II are two-marks questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 15 to 19 in Part III are three-marks questions. These are to be answered in about three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 20 and 21 in Part IV are five-marks questions. These are to be answered in detail. Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3:00 Hours
Maximum Marks: 70
Bio – Botany [Maximum Marks: 35]
PART – 1
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer. [8 × 1 = 8]
Question 1.
Syphilis is caused by …………………..
(a) Mycococcus candisans
(b) Treponema pallidum
(c) Yersinia pestis
(d) Mycobacterium leprae
Answer:
(b) Treponema pallidum
Question 2.
Who is called as the Father of Indian Phycology?
(a) M.O. Parthasarathy
(b) Y. Bharadwaja
(c) V.S. Sundaralingam
(d) V. Desikachary
Answer:
(a) M.O. Parthasarathy
![]()
Question 3.
Which of the following plant possess sessile leaves?
(a) Hibiscus
(b) Mangifera
(c) Psidium
(d) Gloriosa
Answer:
(d) Gloriosa
Question 4.
Histone proteins are seen in the DNA of …………………..
(a) Pseudokaryotes
(b) Prokaryotes
(c) Mesokaryotes
(d) Eukaryotes
Answer:
(d) Eukaryotes
![]()
Question 5.
Number of fatty acids in triglyceride is ……………………
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer:
(c) 3
Question 6.
Principle behind the desalination of sea water is ……………………
(a) Endosmosis
(b) Diffusion
(c) Reverse osmosis
(d) Deplasmolysis
Answer:
(c) Reverse osmosis
Question 7.
In Emerson’s first effect, the photosynthetic yield was dropped in the region above ……………………
(a) 720 nm
(b) 620 nm
(c) 680 nm
(d) 600 nm
Answer:
(d) 600 nm
![]()
Question 8.
Which of the following plant hormone functions against auxin?
(a) Gibberellin
(b) Cytokinin
(c) Ethylene
(d) Abscissic acid
Answer:
(d) Abscissic acid
PART – II
Answer any four of the following questions. [4 × 2 = 8]
Question 9.
What is Porin? How it helps the bacteria?
Answer:
Porin is an abundant polypeptide present in bacterial cell walls. It helps in the diffusion of solutes.
![]()
Question 10.
Mention various types of stem seen in angiosperms?
Answer:
Majority of angiosperm possess upright, vertically growing erect stem. They are
- Excurrent
- Decurrent
- Caudex and
- Culm.
Question 11.
How will you define inflorescence?
Answer:
An inflorescence is a group of flowers arising from a branched or unbranched axis with a definite pattern.
![]()
Question 12.
List out the disadvantages of Amitosis?
Answer:
- Causes unequal distribution of chromosomes.
- Can lead to abnormalities in metabolism and reproduction.
Question 13.
State Relay Pump theory?
Relay pump theory of Godlewski (1884)
Answer:
Periodic changes in osmotic pressure of living cells of the xylem parenchyma and medullary ray act as a pump for the movement of water.
![]()
Question 14.
Define anaerobic photosynthesis?
Answer:
In some bacteria, oxygen is not evolved and is called as non-oxygenic and anaerobic photosynthesis. Examples: Green sulphur, Purple sulphur and green filamentous bacteria.
PART – III
Answer any three questions in which question number 19 is compulsory. [3 × 3 = 9]
Question 15.
Who is called as founder of modern bacteriology? Mention his contribution?
Answer:
Robert Heinrich Hermann Koch is considered as the founder of modem bacteriology. He identified the causal organism for Anthrax, Cholera and Tuberculosis. He proved experimental evidence for the concept of infection (Koch’s postulates).
![]()
Question 16.
List down the key difference between roots and shoots?
Answer:
|
Roots |
Shoots |
| 1. Positively geotropic | 1. Negatively geotropic |
| 2. Negatively phototropic | 2. Positively phototropic |
| 3. Non-green in colour | 3. Green in colour |
| 4. Nodes, intemodes and buds are absent. | 4. Nodes, intemodes and buds are present |
![]()
Question 17.
Differentiate between Taxonomy & Systematics?
Answer:
|
Taxonomy |
Systematics |
| 1. Discipline of classifying organisms into taxa. | 1. Broad field of biology that studies the diversification of species. |
| 2. Governs the practices of naming, describing, identifying and specimen preservation. | 2. Governs the evolutionary history and phylogenetic relationship in addition to taxonomy |
| 3. Classification + Nomenclature = Taxonomy | 3. Taxonomy + Phylogeny = Systematics |
Question 18.
What do you mean by Phloem loading?
Answer:
The movement of photosynthates (products of photosynthesis) from mesophyll cells to phloem sieve elements of mature leaves is known as phloem loading.
![]()
Question 19.
Define Dark Reaction?
Answer:
Fixation and reduction of CO2 into carbohydrates with the help of assimilatory power produced during light reaction. This reaction does not require light and is not directly light driven. Hence, it is called as Dark reaction or Calvin-Benson cycle.
PART – IV
Answer all the questions. [2 × 5 = 10]
Question 20.
List out the salient features of Basidiomycetes?
Answer:
- Basidiomycetes include puffballs, toad stools, Bird nest’s fungi, Bracket fungi, stink horns, rusts and smuts.
- The members are terrestrial and lead a saprophytic and parasitic mode of life.
- The mycelium is well developed, septate with dolipore septum (bracket like). Three types of mycelium namely primary (Monokaryotic), secondary (Dikaryotic) and tertiary are found.
- Clamp connections are formed to maintain dikaryotic condition.
- Asexual reproduction is by means of conidia, oidia or budding.
- Sexual reproduction is present but sex organs are absent. Somatogamy or spermatisation results in plasmogamy. Karyogamy is delayed and – dikaryotic phase is prolonged. Karyogamy takes place in basidium and it is immediately followed by meiotic division.
- The four nuclei thus formed are transformed into basidiospores which are borne on sterigmata outside the basidium (Exogenous). The basidium is club shaped with four basidiospores, thus this group of fungi is popularly called “Club fungi”. The fruit body formed is called Basidiocarp.
[OR]
List out the general characters of Pteridophytes?
Answer:
General characteristic features of Pteridophytes:
- Plant body is sporophyte (2n) and it is the dominant phase. It is differentiated into root, stem and leaves.
- Roots are adventitious.
- Stem shows monopodial or dichotomous branching.
- Leaves may be microphyllous or megaphyllous.
- Stele is protostele but in some forms siphonostele is present (Marsilea)
- Tracheids are the major water conducting elements but in Selaginella vessels are found.
- Sporangia, spore bearing bag like structures are borne on special leaves called sporophyll. The sporophylls gets organized to form cone or strobilus. e.g., Selaginella and Equisetum.
- They may be homosporous (produce one type of spores – Lycopodium) or Heterosporous (produce two types of spores -Selaginella). Heterospory is the origin for seed habit.
- Development of sporangia may be eusporangiate (development of sporangium from group of initials) or leptosporangiate (development of sporangium from single initial).
- Spore mother cells undergo meiosis and produce spores (n).
- Spore germinates to produce haploid, multicellular green, cordate shaped independent gametophytes called prothallus.
- Fragmentation, resting buds, root tubers and adventitious buds help in vegetative reproduction.
- Sexual reproduction is Oogamous. Sex organs, namely antheridium and archegonium are produced on the prothallus.
- Antheridium produces spirally coiled and multiflagellate antherozoids.
- Archegonium is flask shaped with broad venter and elongated narrow neck. The venter possesses egg or ovum and neck contain neck canal cells.
- Water is essential for fertilization. After fertilization a diploid zygote is formed and undergoes mitotic division to form embryo.
- Pteridophytes show apogamy and apospory.
![]()
Question 21.
Draw a flow chart of Kreb’s cycle?
Answer:
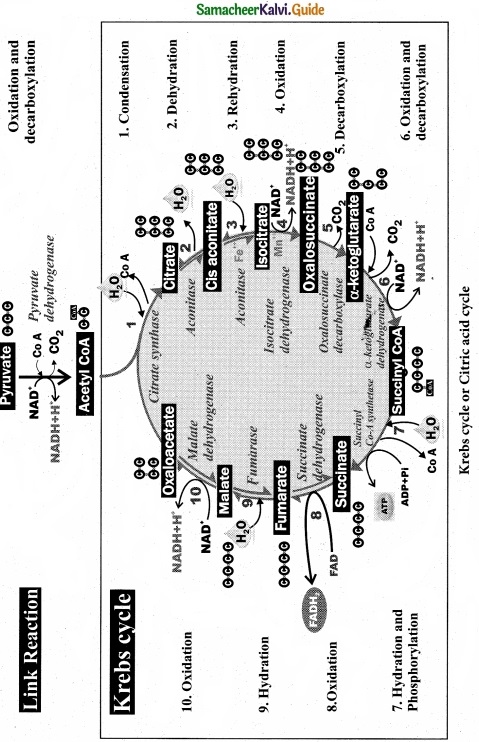
[OR]
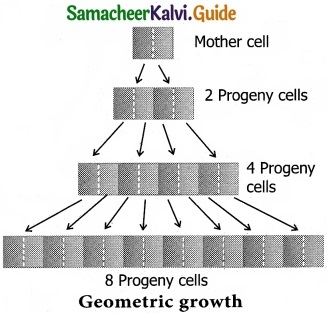
Give a detailed account on geometric growth rate?
Answer:
This growth occurs in many higher plants and plant organs and is measured in size or weight. In plant growth, geometric cell division results if all cells of an organism or tissue are active mitotically. Example: Round three in the given figure 15.5, produces 8 cells as 23 58 and after round 20 there are 220 5 1,048,576 cells.
The large plant or animal parts are produced this way. In fact, it is common in animals but rare in plants except when they are young and small. Exponential growth curve can be expressed as,
W1 = W0ert
W1 = Final size at the beginning of the period
W0 = Initial size at the beginning of the period
r = Growth rate
t = Time of growth
e = Base of the natural logarithms
Here ‘r’ is the relative rate and also a measure of the ability of the plant to produce new plant material, reffered to as efficiency index. Hence, the final size of W1 depends on the initial size W0.
Bio – Zoology [Maximum marks: 35]
PART – 1
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer. [8 × 1 = 8]
Question 1.
Which class of protozoa is totally parasitic …………………….
(a) Sporozoa
(b) Mastigophora
(c) Ciliate
(d) Sarcodina
Answer:
(a) Sporozoa
![]()
Question 2.
Medusa is the Reproductive organs of ……………………..
(a) Hydra
(b) Aurelia
(c) Obelia
(d) Sea anemone
Answer:
(b) Aurelia
Question 3.
Match the List I and List II.
|
List I |
List II |
| 1. Ball and socket | (i) Knee |
| 2. Hinge | (ii) Humerous and pectoral of girdle |
| 3. Pivot | (iii) Carpal and metacarpal of thumb |
| 4. Saddle | (iv) Atlas and axis |
(a) 1 – (i), 2 – (ii), 3 – (iii), 4 – (iv)
(b) 1 – (ii), 2 – (i), 3 – (iv), 4 – (iii)
(c) 1 – (iv), 2 – (iii), 3 – (i), (4) – (ii)
(d) 1 – (iii), 2 – (iv), 3 – (ii), 4 – (i)
Answer:
(b) 1 – (ii), 2 – (i), 3 – (iv), 4 – (iii)
![]()
Question 4.
LH – stands for ………………………
(a) Luteinising hormone
(b) Langerhans hormome
(c) Low secretion hormone
(d) Luteotrophic hormone
Answer:
(a) Luteinising hormone
Question 5.
Which of the following statement is correct?
(a) Calcitonin and thymosin are thyroid hormones.
(b) Pepsin and prolactin are selected in stomach.
(c) Secretin and rhodopsin are polypeptide hormones.
(d) Cortisol and aldosterone are steroid hormones.
Answer:
(d) Cortisol and aldosterone are steroid hormones.
![]()
Question 6.
Which of the following statement is incorrect regard to species …………………….
(a) They have similar morphological
(b) They are reproductively isolated
(c) They produce viable young ones
(d) They have similar anatomical features
Answer:
(b) They are reproductively isolated
Question 7.
The kidney of adult mammals is ……………………
(a) Opisthonephron
(b) Pronephros
(c) Mesonephros
(d) Metanephros
Answer:
(d) Metanephros
![]()
Question 8.
Deficiency of calciferol causes ………………………
(a) Scurvy
(b) Leucopenia
(c) Leukaemia
(d) Rickets
Answer:
(d) Rickets
PART – II
Answer any four of the following questions. [4 × 2 = 8]
Question 9.
Why mule is sterile in nature?
Answer:
Mule gets one set of chromosomes (32) from male parent, horse and one set of chromosomes (31) from female parent, donkey. These two sets of chromosomes do not match with each other and cannot produce gametes by meiosis. Hence mule is sterile in nature.
![]()
Question 10.
Define macrophages?
Answer:
Macrophages are Immune cells derived from monocytes; engaged in phagocytosis of microbes and debris.
Question 11.
Differentiate between peristomium and prostomium in earthworm?
Answer:
|
Peristomium |
Prostomium |
| 1. The first segment of the body of earthworm is called peristomium. | 1. A small flap overhanging the mouth is called prostomium or upper lip. |
Question 12.
Draw the diagram of structure of alveoil?
Answer:
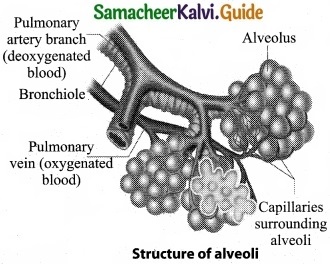
Question 13.
How is urea formed in the human body?
Answer:
More toxic ammonia produced as a result of breakdown of amino acids is converted into less toxic urea in the liver by a cyclic process called Ornithine cycle.
![]()
Question 14.
Write the symptoms of cretinism?
Answer:
Cretinism is caused due to hypothyroidism in infants. A cretin child shows the following symptoms
- Retarded skeletal growth
- Absence of sexual maturity
- Retarded mental ability
- Thick and short limbs
- Thick wrinkled skin
- Bloated face
- Protruded enlarged tongue
- Low BMR, slow pulse rate, subnormal body temperature and elevated blood cholesterol levels
PART – III
Answer any three questions in which question number 19 is compulsory. [3 × 3 = 9]
Question 15.
What is Canal system?
Answer:
The water transport system in sponges through which water enters through minute pores and goes out through the large opening called osculum. It helps is nutrition, circulation, respiration and excretion.
![]()
Question 16.
Draw the diagram of structure of the heart?
Answer:
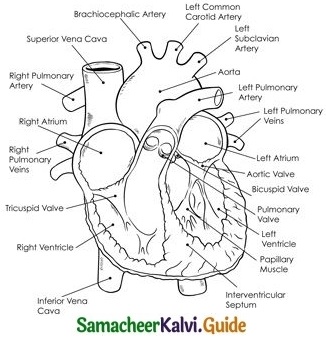
Question 17.
What are spinal nerves?
Answer:
The 31 pairs of nerves which emerge out from the spinal cord through spaces called the intevertebral foramina found between the adjacent vertebrae are the spinal nerves.
![]()
Question 18.
Classify organisms on the basis of seven kingdom system?
Answer:
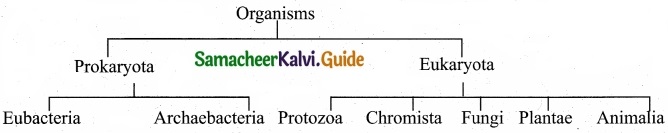
Question 19.
Distinguish between exocrine glands and endocrine glands?
Answer:
|
Exocrine glands |
Endocrine glands |
| 1. These glands release their products through ducts. | 1. These are ductless gland and their secretions are released directly into the blood, |
| 2. These secrete mucous, saliva, ear wax, oil, milk, digestive enzyme etc. e.g. Salivary glands. | 2. These secrete hormones, e.g. Pituitary gland. |
PART – IV
Answer all the questions. [2 × 5 = 10]
Question 20.
Explain the conditions which creates problems in oxygen transport?
Answer:
When a person travels quickly from sea level to elevations above 8000 ft, where the atmospheric pressure and partial pressure of oxygen are lowered, the individual responds with symptoms of acute mountain sickness (AMS)- headache, shortness of breath, nausea and dizziness due to poor binding of O2 with haemoglobin.
When the person moves on a long – term basis to mountains from sea level is body begins to make respiratory and haematopoietic adjustments. To overcome this situation kidneys accelerate production of the hormone erythropoietin, which stimulates the bone marrow to produce more RBCs.
When a person descends deep into the sea, the pressure in the surrounding water increases which causes the lungs to decrease in volume.
This decrease in volume increases the partial pressure of the gases within the lungs. This effect can be beneficial, because it tends to drive additional oxygen into the circulation, but this benefit also has a risk, the increased pressure can also drive nitrogen gas into the circulation.
This increase in blood nitrogen content can lead to a condition called nitrogen narcosis. When the diver ascends to the surface too quickly a condition called ‘bends’ or decompression sickness occurs and nitrogen comes out of solution while still in the blood forming bubbles.
Small bubbles in the blood are not harmful, but large bubbles can lodge in small capillaries, blocking blood flow or can press on nerve endings. Decompression sickness is associated with pain in joints and muscles and neurological problems including stroke. The risk of nitrogen narcosis and bends is common in scuba divers.
During carbon-dioxide poisoning, the demand for oxygen increases. As the O2 level in the blood decreases it leads to suffocation and the skin turns bluish black.
[OR]
What is an epithelium? Enumerate the characteristic features of different epithelia?
Answer:
Simple epithelium is a simple layered sheet of cells that covers the body surface or lines the body cavity.
Types:
- Squamous epithelium: It is made of flattened cells with irregular boundaries. It is found in glomeruli, air sacs of lungs, lining of heart, blood vessels.
- Cuboidal epithelium: It is made of cube like cells. It is found in kidney tubules, ducts and glands. It is important for secretion and absorption.
- Columnar epithelium: It is made of column like cells. It lines the digestive tract. It is important for secretion and absorption.
- Ciliated epithelium: It has cilia at the free end. It is found in bronchi, uterine tubes. It is helpful in propelling materials.
- Glandular epithelium: Cuboidal or columnar epithelium specialized for secretion is called glandular epithelium. E.g., goblet cells and salivary gland.
Compound epithelium:
- Compound epithelium is made up of multilayered cells.
- These protect organs against chemical and mechanical stresses.
- These cover the dry surface of the skin, moist surface of the buccal cavity, pharynx, inner lining of ducts of salivary glands and pancreatic ducts.
Classification of Compound epithelium:
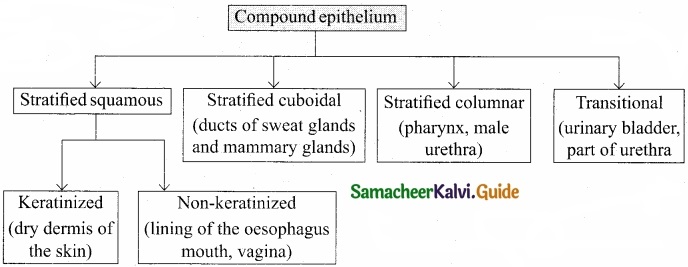
![]()
Question 21.
Write a detailed account of gastro intestinal tract hormones?
Answer:
Group of specialized endocrine cells present in gastro – intestinal tract secretes hormones such as gastrin, cholecystokinin (CCK), secretin and gastric inhibitory peptides (GIP). Gastrin acts on the gastric glands and stimulates the secretion of HCl and pepsinogen. Cholecystokinin (CCK) is secreted by duodenum in response to the presence of fat and acid in the diet.
It acts on the gall bladder to release bile into duodenum and stimulates the secretion of pancreatic enzymes and its discharge. Secretin acts on acini cells of pancreas to secrete bicarbonate ions and water to neutralize the acidity. Gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP) inhibits gastric secretion and motility.
[OR]
Discuss the various techniques adopted in cattle breeding?
Answer:
Methods of Animal breeding:
There are two methods of animal breeding, namely inbreeding and outbreeding
1. Inbreeding:
Breeding between animals of the same breed for 4-6 generations is called inbreeding. Inbreeding increases homozygosity and exposes the harmful recessive genes. Continuous inbreeding reduces fertility and even productivity, resulting in “inbreeding depression”.
This can be avoided by breeding selected animals of the breeding population and they should be mated with superior animals of the same breed but unrelated to the breeding population. It helps to restore fertility and yield.
2. Outbreeding:
The breeding between unrelated animals is called outbreeding. Individuals produced do not have common ancestors for 4-6 generations.
Outbreeding helps to produce new and favourable traits, to produce hybrids with superior qualities and helps to create new breeds. New and favourable genes can be introduced into a population through outbreeding.
(I) Out crossing:
It is the breeding between unrelated animals of the same breed but having no common ancestry. The offspring of such a cross is called outcross. This method is suitable for breeding animals that are below average in productivity.
(II) Cross breeding:
Breeding between a superior male of one breed with a superior female of another breed. The cross bred progeny has superior traits (hybrid vigour or heterosis.)
(III) Interspecific hybridization:
In this method of breeding mating is between male and female of two different species. The progeny obtained from such crosses are different from their parents, and may possess the desirable traits of the parents. Mule was produced by the process of interspecific hybridization between a male donkey and a female horse.