Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Guide Pdf History Term 1 Chapter 1 What is History?Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Solutions History Term 1 Chapter 1 What is History?
6th Social Science Guide What is History? Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
What was the step taken by the early man to collect his food?
(a) trade
(b) hunting
(c) painting
(d) rearing of animals
Answer:
(b) hunting
II. Match the statement with the reason. Tick the appropriate answer
Question 1.
Statement: Pre historic man went along with the dog for hunting.
Reason: Dogs with its sniffing power would find out other animals.
(a) Statement is true, but reason is wrong.
(b) Statement and reason are correct.
(c) Statement is wrong, but reason is correct.
(d) Both statement and reason are wrong.
Answer:
(b) Statement and reason are correct
Question 2.
Statement: The objects used by the early man are excavated. They are preserved to know the lifestyle of the people.
Find out which of the following is related to the statement.
(a) Museum
(b) Burial materials
(e) Stone tools
(d) Bones
Answer:
(a) Museum
![]()
Question 3.
Find out the wrong pair:
(a) Old stone age – Stone tools
(b) Rock paintings – Walls of the caves
(c) Copper plates – A source of history
(d) Cats – First domesticated
Answer:
(d) Cats – First domesticated
Question 4.
Find the odd one:
(a) Paintings were drawn on rocks and caves.
(b) There were paintings depicting hunting scenes.
(c) It was drawn to show his family members about hunting.
(d) The paintings were painted by using many colours.
Answer:
(c) It was drawn to show his family members about hunting.
III. Fill in the blanks
- The Old Stone age man lived mostly in ………………
- ……………… is the Father of history.
- ………………was the first animal tamed by Old Stone Age man.
- Inscriptions are ……………… sources
- Ashoka Chakra has ……………… spokes.
Answer:
- Caves
- Herodotus
- Dog
- archaeological
- 24
IV. State True or False
- Stone tools belonging to the Old Stone age have been excavated at Athtirampakkam near Chennai.
- The materials used by the ancient people are preserved in the museums by the Archaeological Department.
- During the period of Ashoka, Buddhism spread across the country.
Answer:
- True
- True
- True
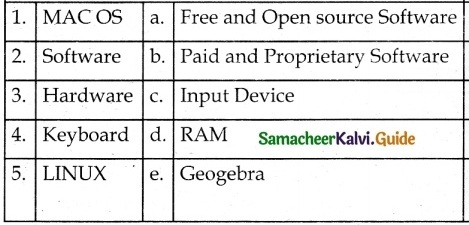
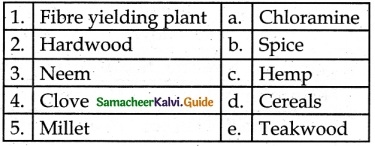
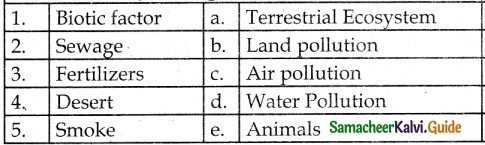
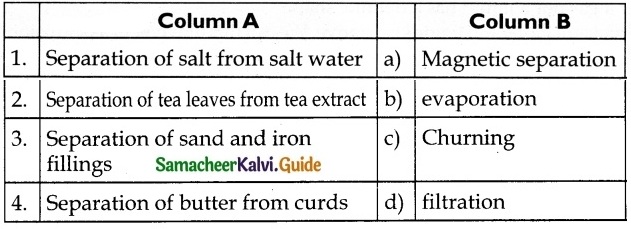
V. Match the following
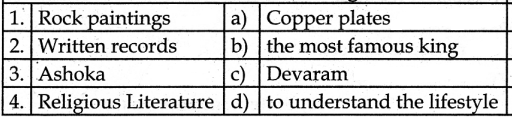
1. – d
2. – a
3. – b
4. – c
VI. Answer in one word
Question 1.
Can you say any two advantages of writing a diary?
Answer:
- Diary writing helps to record the events.
- It reveals the lifestyle of people of that period.
![]()
Question 2.
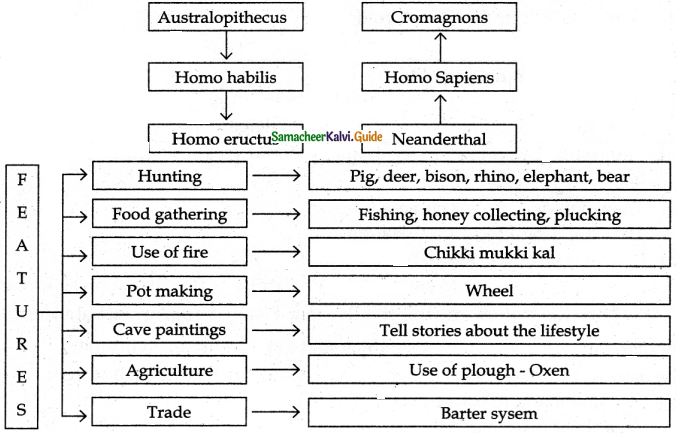
How do we know the people’s lifestyle of the Old Stone Age?
Answer:
We understand the lifestyle of people of the Old Stone Age from used stone tools, their paintings on the rocks and walls of the caves.
Question 3.
Is inscription a written record?
Answer:
Yes. The inscription is a written record.
Question 4.
What is proto history?
Answer:
Protohistory is the period between prehistory and history.
![]()
Question 5.
Name an epic.
Answer:
Silapadhikaram.
VII. Answer the following
Question 1.
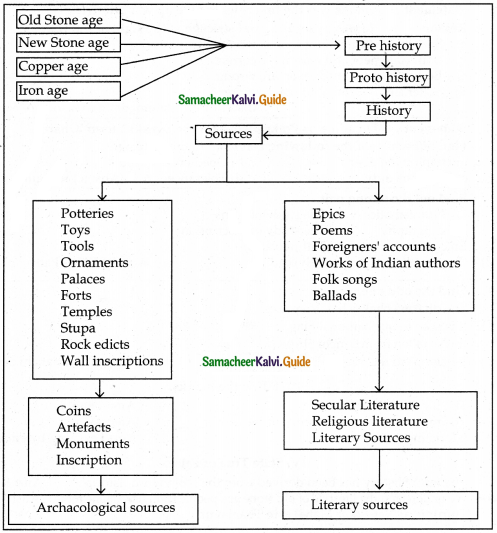
What is history?
Answer:
- History is a record of past events in chronological order.
- The term History has been derived from the Greek word Istoria which means learning by enquiry.
Question 2.
What do you know about the prehistoric period?
Answer:
- The period between the use of the first stone tools and the invention of writing systems is pre-history.
- Stone tools excavated materials, and rock paintings are the major sources of pre-history
Question 3.
What are the sources available to know about the prehistoric period?
Answer:
Paintings on the rocks and the walls of the caves, stone tools, excavated materials are the sources available to know about the pre-historic period.
![]()
Question 4.
Mention the places from where we got pre-historic tools.
Answer:
We find the pre-historic tools at Kondapur, Nevasa, Mehrgash, Rock shelters of Bhimbetka, and Edakkal caves in India. In Tamilnadu Attirampakkam, Ariyalur, Perambulur, Adichanalur are the places where we came across the pre-historic tools.
Question 5.
What are the benefits of a museum?
Answer:
- Museums are community centres designed to inform and teach the public.
- The educational benefit of a museum is academic learning.
- Museums are the caretakers of history as much as they offer connections to history.
- Museums are full of stories, and it is interesting for students to hear these stories.
- Museums offer opportunities for children to compare and contrast leading to critical thinking skills.
- Children’s curiosity comes out in the form of questions.
- Students are exposed to new ideas and concepts.
- Museums inspire students to wonder, imagine, and dream Of possibilities that are beyond what they know.
- Students are exposed to opportunities that spark creative moments.
Question 6.
Name some tools used by early man to hunt animals.
Answer:
- Blade cores were used. These were chunks of Sharp rocks.
- An end scraper is a tear-drop shaped piece of stone used to scrap fur and fatty tissue from the hides of animals.
- Burins were stone tools with a rounded grasping end and at the sharp, razor-like working end.
- Awls were small circular stone flakes.
Question 7.
Why were paintings drawn on rocks?
Answer:
- Paintings could have been drawn or rocks to convey their lifestyles to future generations.
- They might have wished to record their activities through their paintings.
Question 8.
Name any two artifacts.
Answer:
Potteries, Toys, Tools, and Ornaments.
- An artefact is something made or given shape by men, such as a tool or a work of art, especially an object of archaeological interest.
- Some of the artefacts are potteries, toys, tools, and ornaments.
VIII. HOTS
Question 1.
How dogs were useful to prehistoric man?
Answer:
- Dogs with their sniffing power helped them find out other wild animals.
- Dog helped them prevent the entry of dangerous animals.
- Thus dogs helped them in hunting and protection.
![]()
Question 2.
Compare the lifestyle of Old. Stone Age man with present-day lifestyle.
Answer:
Old Stone age man
- He was a nomad.
- Took shelter on branches of trees, in holes and caves.
- Wore dresses made out of leaves, the skin of animals, and barks of trees.
- Ate vegetables, fruits, and roots which he gathered from jungles.
- Not civilized.
Present-day man:
- Settled in villages and towns.
- Lives in well-built houses.
- Wears dresses made out of cotton and other materials.
- Eats all kinds of food grains.
- Well civilized.
IX. Activity (For Students)
- Write down the important events of your family with years. Draw a timeline with the help of your teacher of with your classmates.
- Early man used stones as a weapon. Make an album showing the various uses of stone.
- Identify the category of the following sources of history.
- Urns excavated from Adhichanallur.
- Copper plates of Velvikudi.
- Mahabharatha.
- Sanchi Stupa
- Pattinappaalai.
- The earthernwares form keezhadi
- Toys of Indus Civilisation.
- Big Temple of Thanjavur.
X. Life Skill (For Students)
- Make some weapon models used by the old stone Age man using clay.
- Discuss with your grandpa, grandma, neighbours, and teachers and collect information about your street, villages, town or school. With the collected data, try to write its history titling your writing as “I am a Historian”.
XI. Answer Grid
Question 1.
Early men scribbled and painted on me Today they used me to build houses and lay roads. Who am I?
Answer:
Rock.
Question 2.
Name any two archaeological sources?
Answer:
- Coins
- Inscriptions
Question 3.
Name the types of literary sources?
Answer:
- Secular literature
- Religious literature
![]()
Question 4.
Expand BC (BCE).
Answer:
Before the common era
Question 5.
What is the meaning of the Greek word “Istoria”?
Answer:
Learning by enquiry
Question 6.
Expand AD (CE).
Answer:
Common era
Question 7.
…………….. is the study of inscriptions..
Answer:
Epigraphy
Question 8.
…………….. is the study of coins.
Answer:
Numismatics
Question 9.
I can help you to talk, see, hear, write, and read. There is no world without me. Who am I?
Answer:
Mobile Phone
6th Social Science Guide What is History? Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Dhamma is a word.
(a) Prakrit
(b) Sanskrit
(c) Latin
(d) Greek
Answer:
(a) Prakrit
II. Match the statement with the reason
Question 1.
Statement: Ashoka was the first ruler to give up war after victory.
Reason: He was upset and grief-stricken at the sight of the war.
(a) Statement is true but the reason is wrong.
(b) Both statement and reason are correct.
(c) Both statement and reason are wrong.
(d) Statement is wrong but the reason is correct.
Answer:
(b) Both statement and reason are correct
Question 2.
(a) Statement: Archaeological sources help to know about the early man.
Find out which of the following is related to the statement.
(a) Monuments
(b) Pictures
(c) Metals
(d) Books
Answer:
(a) Monuments
![]()
Question 3.
Find out the wrong pair.
(a) Numismatics – The study of coins
(b) Epigraphy – The study of Inscription
(c) Epic – Pattinapaalai
(d) Copper plates – Velvikudi
Answer:
(c) Epic – Pattinapaalai
Question 4.
Find the odd one.
(a) The dharma chakra has 24 spokes.
(b) It is seen in our National Flag.
(c) It was taken from Sanchi Stupa.
(d) It belongs to the Mauryan period
Answer:
(c) It was taken from Sanchi Stupa
III. Fill in the blanks
- The Big Temple is in ……………
- The most famous ruler of ancient India was ……………
- Istoria means ……………
Answer:
- Thanjavur.
- Ashoka.
- Learning by enquiry.
IV. State True or False
- The term History has been derived from the Latin word ‘Istoria’.
- We understand the lifestyle of old stone age people from used stone tools.
- Thirumalai Nayakkar Mahal is in Thanjavur.
Answer:
- False
- True
- False
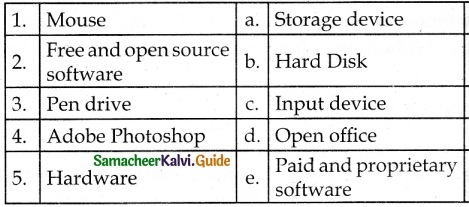
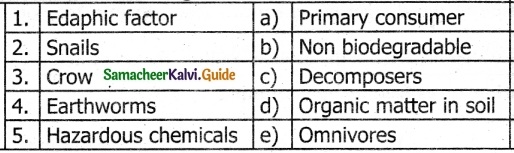
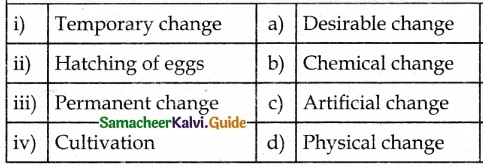
V. Match the following
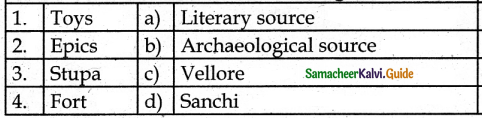
Answer:
1. – b
2. – a
3. – d
4. – c
VI. Mind Map