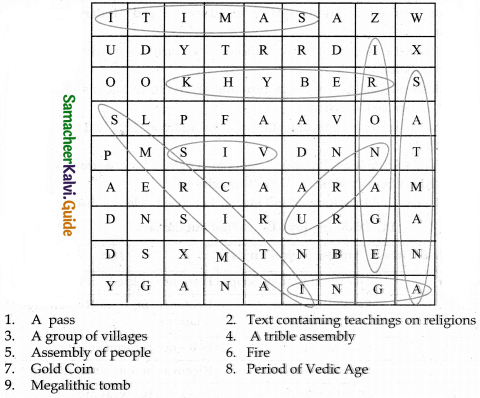
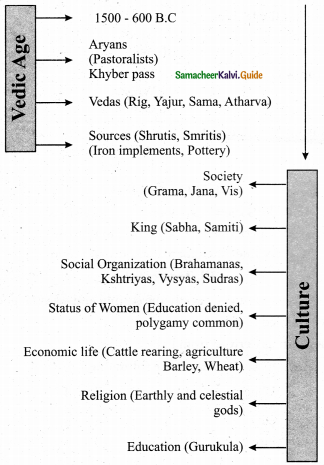
Students can download 6th Social Science Term 3 Civics Chapter 1 Democracy Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Civics Solutions Term 3 Chapter 1 Democracy
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Democracy Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The early man settled near ……………….. and practiced agriculture.
(a) plains
(b) bank of rivers
(c) mountains
(d) hills
Answer:
(b) bank of rivers
Question 2.
The birth place of democracy is ________
(a) China
(b) America
(c) Greece
(d) Rome
Answer:
(c) Greece
![]()
Question 3.
……………….. is celebrated as the International Democracy Day.
(a) September 15
(b) October 15
(c) November 15
(d) December 15
Answer:
(a) September 15
Question 4.
Who has the right to work in a direct Democracy?
(a) Men
(b) Women
(c) Representatives
(d) All eligible voters
Answer:
(d) All eligible voters
II. Fill in the blanks
- Direct Democracy is practiced in ………………
- The definition of democracy is defined by ………………
- People choose their representatives by giving their ………………
- In our country ……………… democracy is in practice.
Answer:
- Switzerland
- Abraham Lincoln
- Votes
- Parliamentary
III. Answer the following
Question 1.
What is Democracy?
Answer:
- The citizens of a country select their representatives through elections.
- Thus they take part in the direct governance of a country. This is termed democracy.
Question 2.
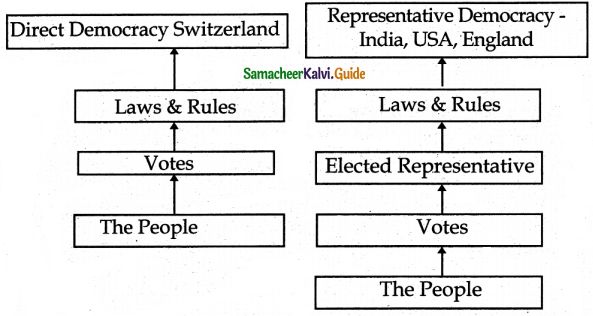
What are the types of democracy?
Answer:
- There are various types of democracy in practice around the world.
- Among those, direct democracy and representative democracy are the most popular forms of government.
Question 3.
Define: Direct Democracy
Answer:
- In a direct democracy, only the citizens can make laws.
- All changes have to be approved by the citizens.
- The politicians only rule over parliamentary procedure. Eg. Switzerland.
![]()
Question 4.
Define Representative Democracy.
Answer:
- In a representative democracy, all the members should be represented by a group of representatives.
- To select their representative’s elections are held.
- On behalf of people, these representatives obtain the power to take decisions in a democratic manner.
- This is termed Representative Democracy.
Question 5.
What are the salient features of our constitution that you have understood?
Answer:
- The Constitution of India guides the Indians in all aspects and maintains law and order.
- It ensures freedom, equality and justice to everyone.
- It defines the political principles, the structure of government, the powers and responsibilities.
- It fixes the Rights and Duties and Directive Principles of the Citizens.
- It is the longest written constitution in the world.
IV. HOTS
Question 1.
Compare and contrast direct democracy and representative democracy.
Answer:
V. Activity
Question 1.
Find out your area’s representative’s names and write down
- MP
- MLA
- Local body member
Answer:
- MP – KRPPrabakara
- MLA – TPM Mohideenkhan
- Local body member – A. Radhakrishnan
![]()
Question 2.
Discuss about the merits and demerits of democracy.
Answer:
The merits of democracy are :
- A democratic government is better form of government because it is more accountable form of government.
- Democracy improves the quality of decision making,
- Democracy enhances the dignity of citizens.
- Poor and least educated has the same status as the rich and educated.
- Democracy allows us to correct own mistake.
Demerits:
- Leaders keep on changing leading to instability.
- Democracy in all about political competition and power play and there is no scope for mortality.
- So many people have to be consulted in a democracy that it lead to delays.
- Democracy leads to corruption for it is based on electoral competition.
- Ordinary people do not know what is good for them, they should not decide anything
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Democracy Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Fill in the blanks Answer
- The UNO General Assembly resolved to observe 15th September as the International Day of Democracy in ………………
- ……………… constitution is the longest written constitution in the world.
- The Drafting committee of the Constituent Assembly was headed by ………………
- In India, all the people above ……………… years of age enjoy universal Adult Franchise.
- The oldest and longest functioning parliament in the world is ………………
Answer:
- 2007
- Indian
- Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
- 18
- The Iceland Democracy
II. Choose the Correct answer
Question 1.
The Chief Architect of our constitution is ………………
(a) Dr. Rajendra Prasad
(b) Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
(c) Dr. S. Radhakrishnan
Answer:
(b) Dr. B.R. Ambedkar
Question 2.
USA follows ______
(a) Direct democracy
(b) Representative democracy
(c) Monarchy
(d) Dictatorship
Answer:
(b) Representative democracy
![]()
Question 3.
Presidential Democracy is practised in ………………
(a) USA
(b) Canada
(c) (a) and (b)
Answer:
(c) (a) and (b)
Question 4.
Presidential democracy is followed in
(a) USA
(b) India
(c) England
(d) Switzerland
Answer:
(a) USA
Question 5.
The Constitution of India guarantees ……………… fundamental rights to its citizens.
(a) 6
(b) 9
(c) 8
Answer:
(a) 6
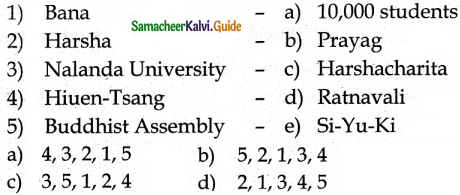
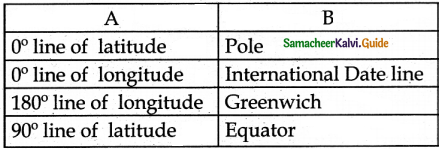
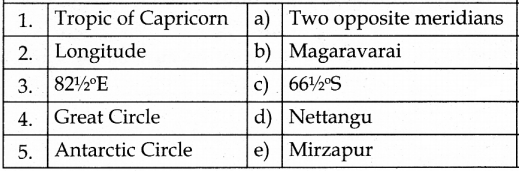
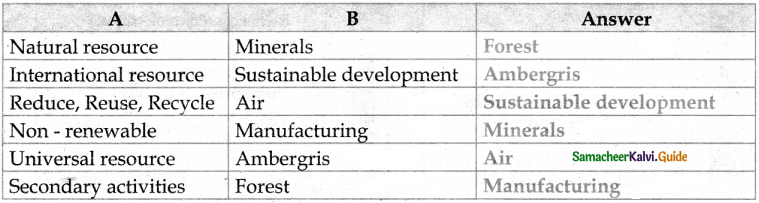
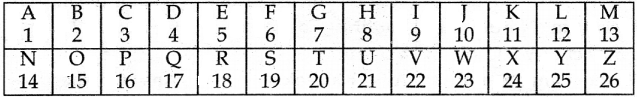
III. Match the following

Answer:
1. – d
2. – c
3. – b
4. – e
5. – a
IV. Answer the following questions
Question 1.
What is a Government
Answer:
A group of people with the authority to govern a country is called government.
Question 2.
How did Abraham Lincoln define democracy?
Answer:
Abraham Lincoln defined democracy as “Government of the people, by the people, and for the people”
![]()
Question 3.
What is meant by democratic decision making?
Answer:
- In the system of democracy, the power to take decisions does not lie with the head.
- All the members of the group hold open discussions and take final decisions only when everyone is convinced.
- This is called democratic way of decision making.
IV. Answer the following in detail
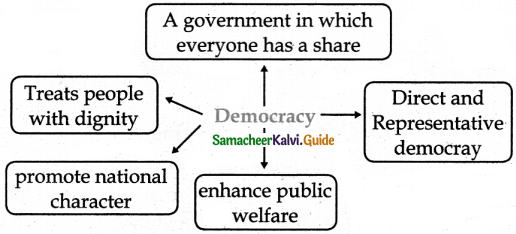
Question 1.
What are the Aims of Democracy?
Answer:
- To preserve and promote the dignity and fundamental rights of the individual
- To achieve Social justice and Social development of the Community.
- To establish the rule of law.
- To enable the People to choose their government.
- To work towards the development of the country with the help of People’s Participation.
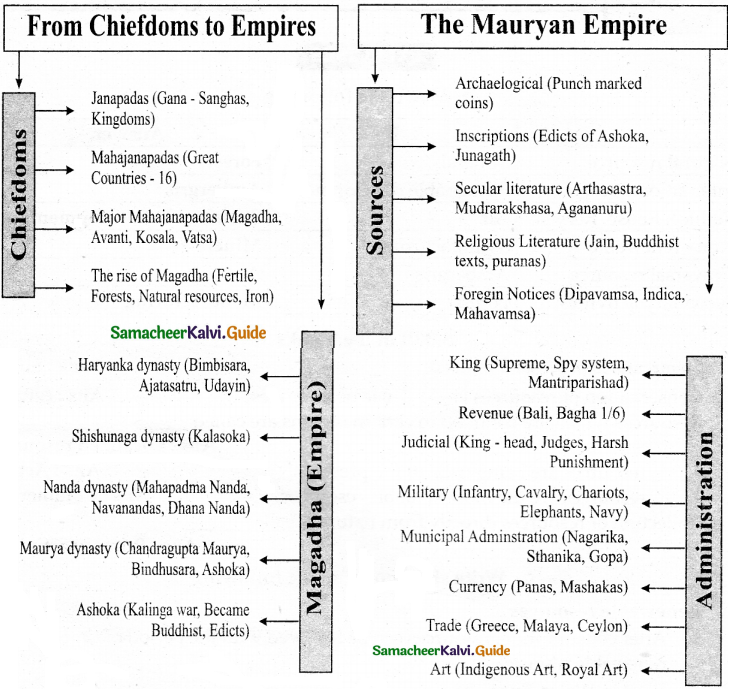
V. Mind map