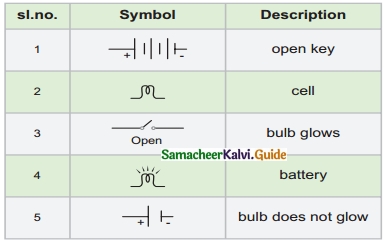
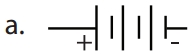Students can download 6th Social Science Term 1 Geography Chapter 2 Land and Oceans Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Geography Solutions Term 1 Chapter 2 Land and Oceans
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Land and Oceans Text Book Back Questions and Answers
A. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
Which of the following is the smallest ocean on Earth?
(a) The Pacific Ocean
(b) The Indian Ocean
(c) The Atlantic Ocean
(d) The Arctic Ocean
Answer:
(d) The Arctic Ocean
Question 2.
The Malacca Strait connects
(a) The Pacific and Atlantic Oceans
(b) The Pacific and Southern Oceans
(c) The Pacific and Indian Oceans
(d) The Pacific and Arctic Oceans
Answer:
(c) The Pacific and Indian Oceans
![]()
Question 3.
Which of the following oceans is the busiest ocean?
(a) The Pacific Ocean
(b) The Atlantic Ocean
(c) The Indian Ocean
(d) The Arctic Ocean
Answer:
(b) The Atlantic Ocean
Question 4.
The frozen continent is
(a) North America
(b) Australia
(c) Antarctica
(d) Asia
Answer:
(c) Antarctica
Question 5.
A narrow strip of water that connects two large water bodies?
(a) A Strait
(b) An Isthmus
(c) An Island
(d) A Trench
Answer:
B. Fill in the blanks
- The world’s largest continent is …………….
- ……………. is the mineral-rich plateau in India.
- The largest ocean is …………….
- Deltas are ……………. order landforms ……………..
- The Island continent is …………….
Answer:
- Asia
- Chotanagpur Plateau
- The Pacific ocean
- Third
- Australia
C. Circle the odd one out

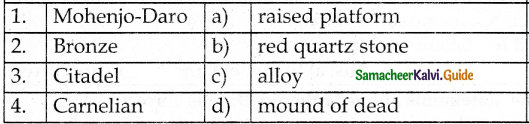
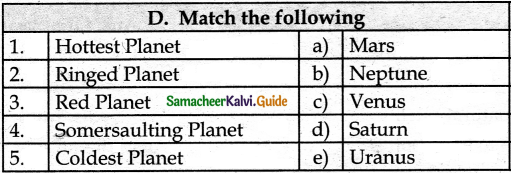
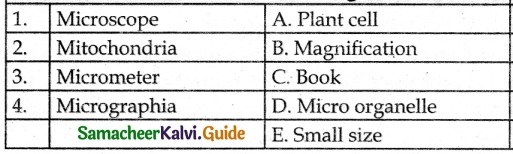
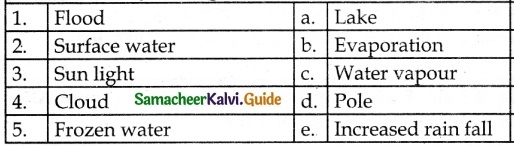
D. Match the following
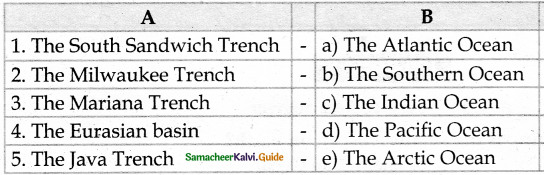
Answer:
1. – b
2. – a
3. – d
4. – e
5. – c
E. (i) Consider the following statements
1. Plains are formed by rivers.
2. The ‘South Sandwich Trench’ is found in the Indian Ocean.
3. Plateaus have steep slopes.
Choose the correct answer using the codes given below.
(a) 1 and 3
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 2 only
Answer:
(a) 1 and 3
(ii) Consider the following statements
Statement I : Mountains are second order landforms.
Statement II : The Mariana Trench is the deepest trench in the world.
Which of the statement(s) is/are true?
(a) I is true; II is wrong
(b) I is wrong; II is true
(c) Both the statements are true
(d) Statements I and II are wrong.
Answer:
(c) Both the statements are true
F. Answer in a word
Question 1.
Which is the highest plateau in the world?
Answer:
Tibetan Plateau.
Question 2.
Name a second-order landform.
Answer:
Mountains or Plateaus or Plains
Question 3.
Which ocean is named after a country?
Answer:
Indian Ocean.
![]()
Question 4.
Name the island located in the Arabian Sea.
Answer:
Lakshadweep islands
Question 5.
What is the deepest part of the ocean called?
Answer:
Trench
G. Answer in brief
Question 1.
What is a continent?
Answer:
The vast landmasses on Earth are called Continents.
Question 2.
Name the continents which surround the Atlantic Ocean.
Answer:
The Atlantic ocean is bounded by North America and South America in the West, and ( Europe and Africa in the East)
Question 3.
What are the oceans?
Answer:
Oceans are a vast expanse of water.
![]()
Question 4.
List out the names of continents according to their size
Answer:
From the largest to the smallest, they are Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia.
Question 5.
Name the oceans which surround North America and South America.
Answer:
North America: On the west by the Pacific Ocean, on the east by Atlantic ocean and on the north by Arctic ocean
South America: On the west by the Pacific Ocean, on the east by Atlantic ocean.
H. Distinguish between
Question 1.
A Mountain and a Plateau?
Answer:
Mountains
- A landform that rises over 600 meters above its surroundings and has steep slopes is called a mountain.
- Example: Himalayas
Plateaus
- Plateaus are the elevated portions of the Earth that have flat surfaces bounded by steep slopes. The elevation of plateaus maybe a few hundred metres or several thousand metre.
- Example: Chotanagpur Plateau
![]()
Question 2.
An ocean and a sea
Answer:
Ocean
- Oceans are a vast expanse of water.
- Eg. the Pacific Ocean
Sea
- Seas are water bodies partially or fully enclosed by land.
- Eg: Bay of Ben, Arabian Sea.
I. Answer the following questions in detail
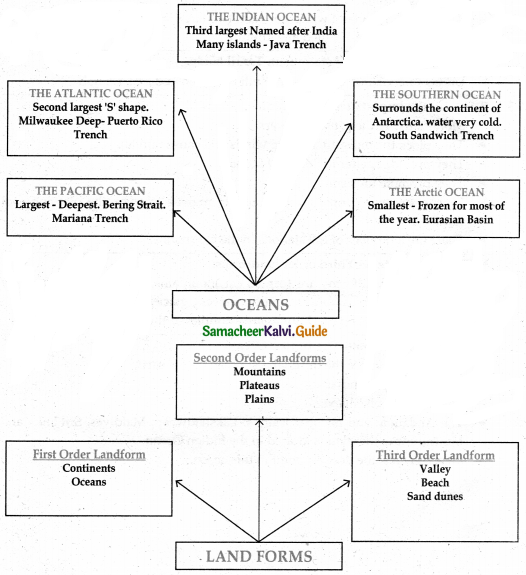
Question 1.
Mention the classification of landforms.
Answer:
First-order landforms:
- Continents and oceans are grouped as first-order landforms.
- The vast landmasses on Earth are called Continents and huge water bodies are called Oceans.
- There are seven continents in the world. They are Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe and Australia.
- The five oceans are the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern, and Arctic Oceans.
Second-order landforms:
- Mountains, Plateaus, and Plains are grouped as second-order landforms.
- A landform that rises 600 meters above its surroundings and has steep slopes is called a mountain. Example:
- The Himalayas, the Rocky Mountains, and the Andes.
- Plateaus are the elevated portions of the Earth that have flat surfaces bounded by steep slopes. Example:
- Tibetan plateau and Deccan plateau.
- Plains are flat and relatively low-lying lands. These plains are used extensively for agriculture. Example: Indo – Gangetic plain.
Third-order landforms:
- Third-order landforms are formed on mountains, plateaus, and plains mainly by erosional and depositional activities of rivers, glaciers, winds, and waves.
- Example: Valleys, beaches, and sand dunes.
Question 2.
Write a note on plateaus.
Answer:
Ocean:
- An ocean is a vast expanse of water.
- Oceans are very deep.
- Example: The Pacific Ocean
Sea:
- A sea is a water body partially or fully enclosed by land.
- Seas are not so deep as oceans
- Example: The Arabian sea
Question 3.
Plains are highly populated. Give reasons.
Answer:
- Plains are flat and relatively low-lying lands.
- Plains are formed by rivers and their tributaries and distributaries.
- Plains are used extensively for agriculture due to the availability of water and fertile soil.
- Plains are most suitable for human inhabitation. Hence, they are highly populated.
![]()
Question 4.
Give the important features of the Pacific Ocean,
Answer:
- The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest ocean on Earth.
- It covers about one-third of the Earth’s total area.
- It is bounded by Asia and Australia in its west and North America and South America in its east.
- On its apex is the Bering Strait. It connects the Pacific Ocean with the Arctic Ocean.
- The deepest point Mariana Trench is located in the Pacific Ocean.
- A chain of volcanoes is located around the Pacific Ocean.
Question 5.
Write above the importance of oceans.
Answer:
- Oceans are the first order landform.
- 71% of the earth’s surface is covered with water.
- Oceans influence man in various ways, from the climate he experiences to the food he eats.
- Oceans are a major source of salt, valuable minerals, petroleum, pearls, and diamonds.
- Ocean currents affect the climate of neighbouring areas.
- Ocean trade plays an important role in the world economy.
- Ocean currents can be converted into electricity.
J. Picture Study
Question 1.
Name the landform.
Answer:
Sand dune
Question 2.
What order of a landform is this?
Answer:
Third-order landform
Question 3.
By which activity of river is this landform formed?
Answer:
Deposition

K. (i) Activity (Activity to be done by students)
Trip to the nearby area to appreciate the physical features of any kind of landform.
Conduct a quiz on landforms and oceans.
(ii) Activity
Question 1.
Give examples for the following using an Atlas.
Answer:
- Bay: Hudson Bay, Bay of Bengal, Bay of Biscay
- Gulf: the Persian Gulf, Gulf of Kutch, Gulf of Mannar
- Island: Srilanka, Australia, Maldives
- Straits: Palk strait, Bering strait, Magellan strait
Question 2.
Map reading (with the help of an atlas)
Answer:
- A sea in the east of India – Bay of Bengal
- Continents in the west of Atlantic Ocean – North America, South America
- Continents in the south of Arctic Ocean – Europe, Asia
- A strait between India and Sri Lanka – Palk strait
- Oceans which surround Australia – Indian ocean, Pacific ocean
- Find out the Isthmusses – Isthmus of Panama, Isthmus of Avalon, Isthmus of La Dune
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Social Science Land and Oceans Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
International Mountain Day is ……………..
(a) June 15
(b) April 11
(c) November 11
(d) December 11
Answer:
(d) December 11
Question 2.
Andes mountain is located in
(a) North America
(b) South America
(c) Asia
(d) Europe
Answer:
(b) South Amei leaf
![]()
Question 3.
The highest plateau in the world is …………….
(a) Ladakh plateau
(b) Tibetan plateau
(c) Deccan plateau
(d) Chotanagpur plateau
Answer:
(b) Tibetan plateau
Question 4.
The International Mountain Day is
(a) December 10th
(b) December 11th
(c) December 12th
(d) December 13th
Answer:
(b) December 11th
Question 5.
It connects the Pacific Ocean with the Arctic ocean.
(a) Bering strait
(b) Magellan strait
(c) Gibraltar strait
(d) Palk strait
Answer:
(a) Bering strait
II. Fill in the blanks
- The sea around Pangea is called ……………….
- The smallest continent is ……………….
- The smallest ocean is ……………….
- ………………. is called the Roof of the world
- The deepest point in the Indian ocean is ……………….
Answer:
- Panthalasa
- Australia
- Arctic ocean
- Tibetan Plateau
- Java trench
III. Answer in brief
Question 1.
What is an Isthmus?
Answer:
A narrow strip of land which connects two large landmasses or separates two large water bodies is called an Isthmus.
Question 2.
What are the Second-order landforms?
Answer:
The Second-order landforms are categorised as mountains, plateaus, and plains.
![]()
Question 3.
Bring out the importance of mountains.
Answer:
- Mountains are the source of rivers.
- They block the moisture-bearing winds and cause rainfall.
- They provide shelter to flora and fauna.
- They promote tourism.
- During summer people go to mountain regions to enjoy the pleasing cool weather.
- There are a number of hill stations in the mountains.
Question 4.
Mention some of the early civilizations.
Answer:
The Indus valley civilization, the Mesopotamian civilization, The Egyptian civilization, and the Chinese civilization. Where some of the early civilizations?
Question 5.
Write a few lines about The Indian Ocean.
Answer:
- The Indian Ocean is the third largest ocean on the earth.
- It is named after India.
- It is triangular in shape.
- The Andaman and Nicobar Islands, Lakshadweep, Maldives, Sri Lanka, and Mauritius are the islands located in the Indian Ocean.
- Java Trench is the deepest point in this ocean.
IV. Mind Map