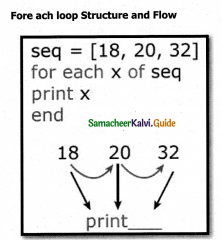
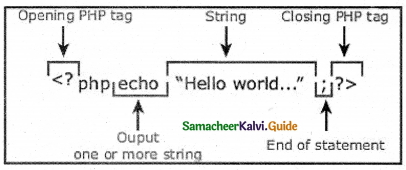
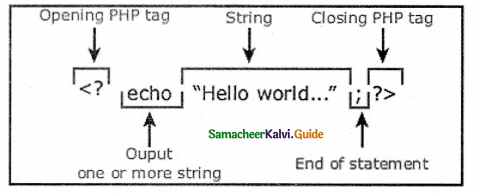
Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Guide Pdf Chapter 8 Forms and Files Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Applications Solutions Chapter 8 Forms and Files
12th Computer Applications Guide Forms and Files Text Book Questions and Answers
Part I
Choose The Correct Answers
Question 1.
When you use the $_GET variable to collect data, the data is visible to.
a) none
b) only you
c) everyone
d) selected few
Answer:
c) everyone
![]()
Question 2.
Which one of the following should not be used while sending passwords or other sensitive information?
a) GET
b) POST
c) REQUEST
d) NEXT
Answer:
a) GET
Question 3.
Which directive determines whether PHP scripts on the server can accept file up¬loads?
a) file_uploads
b) file_upload
c) file_input
d) fiie_intake
Answer:
a) file_uploads
Question 4.
In HTML form cinput type=”text”> is used for
a) One line text
b) Block of text
c) One paragraph
d) None
Answer:
a) One line text
![]()
Question 5.
HTML classes that are already defined and allow us to apply styles on it are called as
a) Pseudo classes
b) Css classes
c) Javascript classes
d) None
Answer:
b) Css classes
Question 6.
If you would like to read a file character by character which function do you use?
a) fopen ()
b) fread ()
c) fgetc ()
d) file ()
Answer:
c) fgetc ()
Question 7.
PHP is a ……………… typed language.
a) User
b) Loosely
c) Server
d) System
Answer:
b) Loosely
Question 8.
What does fopen() function do in PHP?
a) It used to open files in PHP
b) It used to open Remote Server
c) It used to open folders in PHP
d) It used to open Remote Computer
Answer:
a) It used to open files in PHP
![]()
Question 9.
How PHP files can be accessed?
a) Through Web Browser
b) Through HTML files
c) Through Web Server
d) All of Above
Answer:
a) Through Web Browser
Question 10.
Which of the following functions reads the entire contents of a file?
a) fgets()
b) file_get_contents()
c) fread()
d) readfile()
Answer:
b) file_get_contents()
Part II
Short answers
Question 1.
Define HTML form controls.
Answer:
- Text inputs contain textbox and text area controls,
- Buttons may contain Submit button, Reset but-ton and Cancel Button,
- Checkbox is the important feature which selects more than one value from the HTML form,
- Radio box is simiiar to checkbox but one value can be chosen at a time,
- File select is the best feature to select one file from the local machine to server machine at a time.
- Form tag is used to mention a method (POST or GET) and control the entire form controls in the HTML document.
Question 2.
Define for Form Handling method in PHP.
Answer:
- Form tag is used to mention a method (POST or GET) and control the entire form controls in the HTML document.
- All input values are synchronized and sent to the server via the POST or GET method.
![]()
Question 3.
What is Form Validation In RHP?
Answer:
- Validation is a process of checking the input data submitted by the user from the client machine.
- There are two types of validation available in PHP. They are as follows, Client-Side Validation, Server Side Validation.
Question 4.
List out HTML control to support PHP language.
Answer:
- Text inputs
- Buttons
- Checkbox
- Radio box
- File Select
- Form Tag
Question 5.
Write Syntax of Text box in HTML,
Answer:
| Type | Description |
| <input type=”text”> | Defines a one-line text input field |
![]()
Question 6.
Define File handling in PHP.
Answer:
Files: File handling is an important activity of all web application development process.
Files are processed for different tasks using the following events:
- PHP Open a File
- PHP Read a File
- PHP Close a File
- PHP Write a File
- PHP Appending a File and
- PHP uploading a File.
Question 7.
Define Browse button in HTML.
Answer:
- It is one of the types of button, which is used to upload a single file or multiple files.
- The <input type=”file”> defines a file-select field and a “Browse” button for file uploads.
- To define a file-select field that allows multiple files to be selected, add the “multiple” attribute.
Question 8.
Write Syntax of Browse button in HTML.
Answer:
Syntax:
cinput type=”file” name=”myFile”>
Question 9.
Compare Text box and Text area
Answer:
| Text box | Text Area |
| They are generally used for collecting information such as names, email addresses, URLs, etc. | These are larger versions of the TEXT BOX. They give more room for visitors input. TEXTAREAs are generally used to gather feedback or comments. |
| The <input> tag specifies an input field where the user can enter data. | The <textarea> tag defines a multi-line text input control. |
![]()
Question 10.
Usage of File open function.
Answer:
- fopen( ) is a system function available in PHP.
- This function helps to open a file in the server.
- It contains two parameters one for the file and the other one specifies in which mode the file should be opened (Read/Write).
Part III
Explain in brief answer
Question 1.
Write the features Form Handling.
Answer:
- HTML Forms are required, when you want to collect some data from the site visitor.
- A form will take input from the site visitor and then will post it to a back-end application such as CGI, ASP Script or PHP script etc.
- The back-end application will perform required processing on the passed data based on defined business logic inside the application.
Question 2.
Write the purpose Get method and Post method.
Answer:
All input values are synchronized and sent to the server via POST method or GET method. Method is an attribute form tag in HTML. Once the data reaches the server, two PHP variables such as $_POST and $_GET collects the data and prepares the response accordingly.
Post Method:
The input data sent to the server with POST method is stored in the request body of the client’s HTTP request.
Get Method:
The input data sent to the server with POST method via URL address is known as query string. All input data are visible by user after they clicks the submit button.
Question 3.
Differentiate Get and Post Method
Answer:
| Get Method | Post method |
| It is designed to get data from server | It is designed to send data to the server |
| It is suitable to carry limited data | It can carry unlimited of data |
| Faster to send the request | It is little slow compare to get method |
![]()
Question 4.
Write short notes on File handling.
Answer:
- File handling is an important activity of all web application development process.
- It is needed for any application. For some tasks to be done file needs to be processed.
- File handling in PHP is similar as file handling is done by using any programming language.
Question 5.
Write short notes on File handling functions.
Answer:
- fopen( ) – PHP Open a File
- fread( ) – PHP Read a File,
- fclose( ) – PHP Close a File,
- fwrite( ) – PHP Write a File,
- file_put_contents( ) – PHP Appending a File
![]()
Part IV
Explain in detail
Question 1.
Explain Form handling methods.
Answer:
PHP Basic Form Handling
- When the user keying the input data in HTML controls and clicks the submit button the request will be generated and reaches a PHP file which is mentioned in the FORM tag under the Action attribute.
- All input values are synchronized and sent to the server via POST method or GET method.
- Method is an attribute form tag in HTML. Once the data reaches the server, two PHP variables such as $_POST and $_GET collects the data and prepares the response accordingly.
Post Method:
- The input data sent to the server with POST method is stored in the request body of the client’s HTTP request.
Get Method:
- The input data sent to the server with POST method via URL address is known as query string.
- All input data are visible by user after they clicks the submit button.
Question 2.
Discuss in detail about HTML form controls.
Answer:
| Value of type attribute | Description |
| Text | Create a Text Box. The element used to get all kind of text input such as name, address etc., |
| Password | Similar as Text box. But, while entering data, the characters are appearing as coded symbois such as asterisk. |
| Checkbox | Check box is an element appearing like a small square box. When the user dick on the square a tiny tick mark will appear inside the square. This element is used to select multiple options. |
| Radio Button | Radio button is used to select any one of the multiple options from the list. This element locks like a small circle, when the user select an item, a tiny dot will appear within the circle. If the user selects another option, previously selected option will be deselected. This means, user can select any one of the given option form a group. |
| Reset | It is a special command button used to dear ail the entries made in the form. |
| Submit | It is also a special command button used to submit all the entries made in the form to the backend server. |
| Button | This is a standard graphical button on the form used to call functions on click. |
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the process File handling.
Answer:
- File handling is an important part of any web ap¬plication. You often need to open and process a file for different tasks.
- File handling is needed for any application. For some tasks to be done file needs to be processed.
- File handling in RHP is similar as file handling is done by using any programming language like C.
Five major operations can he performed on file are:
- Creation of a new file.
- Opening an existing file.
- Reading data from a file.
- Writing data in a file.
- Closing a file.
Steps for Processing a Fite
- Declare a file pointer variable.
- Open a file using open() function.
- Process the file using the suitable function.
- Close the file using fclose() function.
Question 4.
Explain concepts of HTTP Uploading process.
Answer:
File Upload:
- File upload is the best feature to select one file from the local machine to server machine. Form tag is used to mention a method as POST or GET and encrypt attribute mentioned as “multipart/form-data”.
- In the <Input> tag mention type=”file” attribute shows the input field as a file-select control, with a “Browse” button next to the input control.
- The form above sends data to a file called “Student_photo_upload.php”.
- First, ensure that PHP is configured to allow file uploads.
- In Server machine “php.ini” file, search for the file_uploads directive, and set it to On: “file_upIoads = On”
- After submitting the upload button the request reaches to Student_photo_upload.php file. In the file $_FILES variable collects all uploaded file information such as the name of the file, size of the file and extension of the file etc.
- All the details are checked thoroughly and the errors are saved in an array variable.
- The file finally moves under the image directory if the array error variable is empty.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain in detail of File handling functions.
Answer:
- PHP Manipulating Files: PHP has several functions for creating, reading, uploading, and editing files.
- PHP readfile() Function: The readfile() function reads a file and writes it to the output buffer.
- PHP Open File – fopen(): A better method to open files is with the fopen() function.
This function gives you more options than the readfile() function. - PHP Read File – read(): The fread() function reads from an open file.
- PHP Close File – close(): The fclose() function is used to close an open file.
- PHP Create File – fopen(): The fopen() function is also used to create a file.
- Maybe a little confusing, but in PHP. a file is created using the same function used to open files.
- PHP Write to File – write(): The fwrite() function is used to write to a file.
12th Computer Applications Guide Forms and Files Additional Important Questions and Answers
Part A
Choose the correct answers:
Question 1.
The main objective of PHP and HTML form controls are …………..
a) To collect data from users.
b) To create data from users.
c) To delete data from users.
d) to manipulate data from users.
Answer:
a) To collect data from users.
![]()
Question 2.
Pick the odd one out.
(a) Submit
(b) Reset
(c) File
(d) Cancel
Answer:
(c) File
Question 3.
Match the following:
(A) Check box – (1) Query String
(B) Email – (2) Client’s Request
(C) POST – (3) Should require @ and .strings
(D) GET – (4) Must be checkable minimum one value

Answer:
(D) GET – (4) Must be checkable minimum one value
![]()
Question 4.
…………………………. is used to select one value can be chosen at a time.
(a) Checkbox
(b) Radio box
(c) Textbox
(d) File
Answer:
(b) Radio box
Question 5.
…………….. and ……………. are the most important concepts that the PHP web development processes.
a) Forms and files
b) Tables and Links
c) Both a and b
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Forms and files
Question 6.
……………. is a process of checking the input data submitted by the user from the client machine.
a) File
b) Form
c) Validation
d) All of these
Answer:
c) Validation
![]()
Question 7.
Which tag is used to mention POST or GET method?
(a) Frame
(b) Form
(c) File
(d) Input
Answer:
(b) Form
Question 8.
Which of the following is a back-end application?
a) CGI
b) ASP Script
c) PHP Script
d) All of these
Answer:
d) All of these
Question 9.
……………….. is the best feature to select one file from the local machine to server machine,
a) File upload
b) Files
c) Forms
d) All of these
Answer:
a) File upload
![]()
Question 10.
………………………. is a process of checking the input data submitted by the user from the client machine.
(a) collection
(b) verification
(c) validation
(d) Report
Answer:
(c) validation
Choose odd man out:
1. a) Submit
b) Cancel
c) File select
d) Reset
Answer:
c) File select
2. a) file_put_contents()
b) fopen ()
c) fread ()
d) fgetc ()
Answer:
d) fgetc ()
![]()
3. a) Append
b) Frame
c) File select
d) Form Tag
Answer:
a) Append
4. a) File
b) Data
c) Mode
d) Action
Answer:
d) Action
5. a) PHP
b) AJAX
c) JSP
d) ASP
Answer:
b) AJAX
![]()
Very Short Answers
Question 1.
Give the syntax for fopen( ) function?
Answer:
Syntax:
$file_Object= fopen(“FileName”, “ReadAVriteMode”) or die(“Error Message!”);
Question 2.
What is the main objective of PHP and HTML?
Answer:
The main objective of PHP and HTML form controls is to collect data from users.
Question 3.
What is fopen() function?
fopen() is a system function available in PHP.
Question 4.
What is the purpose of fopen() function?
Answer:
fopen function helps to open a file in the server.
![]()
Question 5.
How many parameters are there in fopen() function?
Answer:
There are two parameters in fopen() function.
Question 6.
What is the purpose of fread() function?
Answer:
The fread() function reads from an open file.
Question 7.
How files are uploaded to the server?
Answer:
A PHP script can be used with an HTML form to allow users to upload files to the server.
Question 8.
What is file handling?
Answer:
File handling is used to open and process a file for different tasks.
![]()
Question 9.
What is the purpose of form validation?
Answer:
To protect your form from hackers and spammers!
Question 10.
What is HTML?
Answer:
HTML is the standard markup language for creating web pages and web applications.
Question 11.
Expand HTML.
Answer:
HTML stands Hypertext Markup Language.
Question 12.
What are the methods to be used to upload data?
Answer:
GET and POST methods are used to upload the data most frequently.
Question 13.
What is the purpose of encrypting attribute?
Answer:
This attribute is used to specify, how the browser encodes the data before it sends it to the server.
![]()
Question 14.
Expand AJAX.
Answer:
Asynchronous JavaScript And XML.
Question 15.
IS AJAX, a programming language?
Answer:
AJAX is not a programming language.
Match the following:
1. Text – More than one value
2. Buttons – Only one value
3. Checkbox – Post and Get
4. Radio box – Select file
5. File Select – Submit Reset and Cancel.
6. Form – Textbox and text area
7. URL address – _blank, _se!f, __parent
8. Target window – Query string
9. file_put_contents() – php.ini
10. Server machine – Append
Answer:
1. Textbox and text area
2. Submit, Reset and Cancel.
3. More than one value
4. Only one value
5. Select file
6. Post and Get
7. Query string
8. _blank, _self, _parent
9. Append
10. php.ini
![]()
Syntax
1. fopen():
$file_Object= fopen(“FileName”, “Read/Write-Mode”) or die(“Error Message!”);
2. fread():
fread($file_Object,filesize(“FileName”));
3. fcloseQ:
fclose($file_Object);
4. fwriteQ:
fwrite($myfile, $txt);
Additional programs using forms:
1. Sample’PHP program to open and dosing a file:
i) Text(Notepad) file:
AJAX = Asynchronous JavaScript and XML CSS = Cascading Style Sheets HTML = Hyper Text Markup Language PHP = PHP Hypertext Preprocessor SQL = Structured Query Language SVG = Scalable Vector Graphics XML = Extensible Markup Language
ii) PHP File:
<?php
$myfile = fopen(“webdictionary.txt”, “r”) or dieC’Unable to open file!”); echo fread($myfile,filesize(“webdictionary. txt”)); fclose($myfile);
?>
![]()
iii) OUTPUT
AJAX = Asynchronous JavaScript and XML CSS = Cascading Style Sheets HTML = Hyper Text Markup Language PHP = PHP Hypertext Preprocessor SQL = Structured Query Language SVG = Scalable Vector Graphics XML = Extensible Markup Language
2. An HTML code to demonstrate Form and Form controls (Login form)
<html>
<head>
<title> Login Form </title>
<body>
<h3 align=center> TamilNadu State Council of Educational Research and Training, Chennai </h3>
<Form Action = “mailto:abcd.xyz@com” method=post >
<p> User Name:
<Input type = text name=”user_name” size = 20 maxlength = 15> </p>
<p> Password:
clnputtype = password name=”pass”size = 20 maxlength = 15> </p>
<Input type = reset value = “Clear”>
<Input type = submit value = “Login”> </Form>
</body>
</html>
Output:
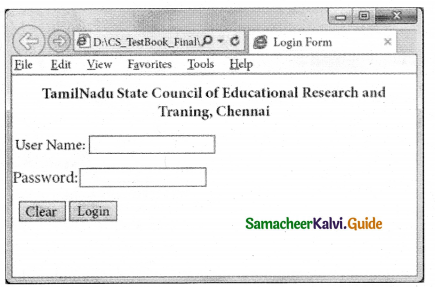
![]()
Part B
Short Answers
Question 1.
Write a note on client-side validation?
Answer:
Client-Side Validation: The input data validations are performed on the client machine’s web browsers using client-side scripts like Javascript or adding “required” attributes in HTML input tags.
Question 2.
What is the process of Server Side Validation:
Answer:
After the submission of data, validations are performed on the server-side using programming like PHP, ASP, or JSP, etc. available in the server machine.
![]()
Brief Answers
Question 1.
Write the Validation rules for HTML input fields.
Answer:
Validation rules for HTML input field
Name (Text Input) : Should require letters and white-spaces
Email (Text Input) : Should require @ and .strings
Website (Text Input) : Should require a valid URL
Radio: Must be selectable minimum one value
Check Box: Must be checkable minimum one value
Drop-Down Menu: Must be selectable minimum one value
![]()
Question 2.
Explain briefly about fopen() function.
Answer:
PHP Open a File
- fopen() is a system function available in PHP.
- This function helps to open a file in the server.
- It contains two parameters one for the file and the other one specifies in which mode the file should be opened (Read/Write).
Syntax:
$file_Object= fopen(“FileName” “Read/WriteMode”) or dieC’Error Message!”);
Example:
<?php
$myfile = fopen(“Student.txt”, “r”) or
die(“Unable to open file!”);
?>
![]()
Question 3.
Explain briefly about fread() function.
Answer:
PHP Read a File:
The fread() function reads from an open file. The file object comes from fopen function.
Syntax:
fread($file_Object,filesize(“FileName”));
Example:
<?php
fread($myfile,filesize(“Student.txt”));
?>
Question 4.
Explain briefly about fclose() function.
Answer:
PHP Close a File:
The fclose() function is used to close an opened file.
The file object comes from fopen function.
Syntax:
fclose($file_Object);
Example:
<?php
$myfile = fopenC’student.txt”, “r”);
// some code to be executed….
fclose($myfile);
?>
![]()
Question 5.
Explain briefly about fwrite() function.
Answer:
PHP write a File:
The fwrite() function is used to write to a file.
Syntax:
fwrite($myfile, $txt);
Example:
<?php
$myfile = fopen(“new_schooL_file.txt”, “w”)
or dieC’Unable to open file!”);
$txt = “School Name\n”;
fwrite($myfile, $txt);
$txt = “Student Name\n”;
fwrite($myfile, $txt);
fclose($myfile);
?>
Question 6.
Write a short note on Appending a File
Answer:
The file_put_contents() function is used to Ap-
pend to a file.
Syntax:
file_put_contents(file,data,mode,context)
Example:
<?php
$txt = “Student id “;
$myfile = file_put_contentsClogs.txt’, $txt.
PHP_EOL , FILE_APPEND | LOCK_EX);
?>
![]()
Part D
Detailed Answers
Question 1.
Explain the file uploading method in PHP.
Answer:
- File upload is the best feature to select one file from the local machine to the server machine.
- The form tag is used to mention a method as POST or GET and encrypt attribute mentioned as “multipart/form-data”.
- In the <Input> tag mention type=”file” attribute shows the input field as a file-select control, with a “Browse” button next to the input control.
- The form above sends data to a file.
- In Server machine “php.ini” file, search for the file_uploads directive, and set it to On: “file_up- loads = On”
- After submitting the upload button the request reaches the file.
- In the file $_FILES variable collects all uploaded file information such as the name of the file, size of the file and extension of the file, etc.
- All the details are checked thoroughly and the errors are saved in an array variable.
- The file finally moves under the image directory if the array error variable is empty.