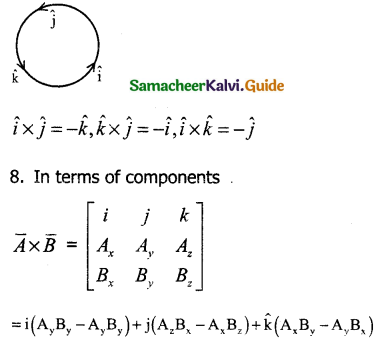
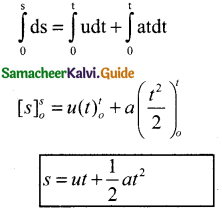
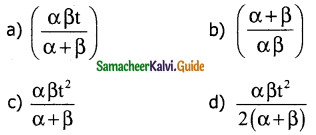
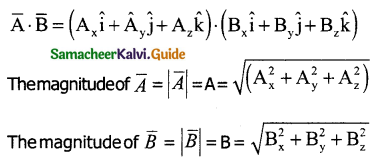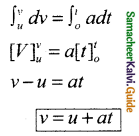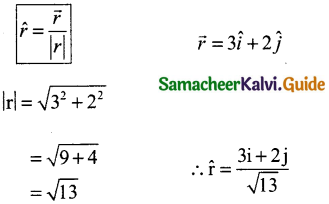Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Guide Pdf Chapter 1 Historical Background of Commerce in the Sub-Continent Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Commerce Solutions Chapter 1 Historical Background of Commerce in the Sub-Continent
11th Commerce Guide Historical Background of Commerce in the Sub-Continent Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the Correct Answer
Question 1.
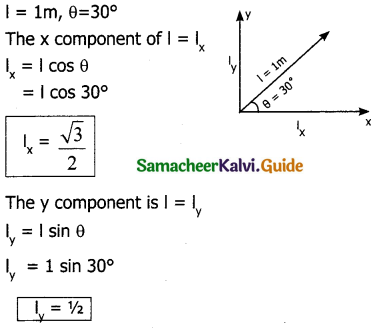
The place where the goods are sold is ………………
a) Angadi
b) Market .
c) Nalangadi
d) Allangadi
Answer:
a) Angadi
Question 2.
Hindrance of place is removed by ……………………….
a) Transport
b) Warehouse
c) Salesman
d) Insurance
Answer:
a) Transport
![]()
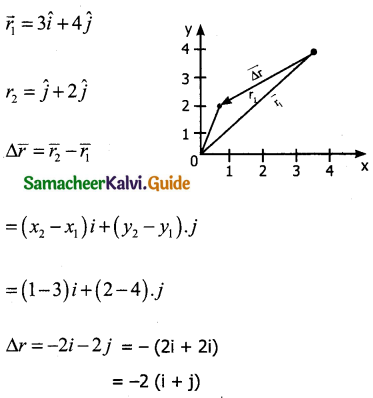
Question 3.
Who wrote “Arthasasthra”?
a) Kautilya
b) Chanakiya
c) Thiruvalluvar
d) Elangovadiga
Answer:
a) Kautilya
Question 4.
Trade and Commerce was common to …………………….. Dynasty.
a) pallava
b) Chola
c) Panidya
d) Chera
Answer:
c) Panidya
![]()
Question 5.
…………………….. was first sultan who paved way in the dense forest and helped traders to move from one market place to others place for
their commercial caravans.
a) Balban
b) Vascoda Gama
c) Akbar
d) Alauddin Khilij
Answer:
a) Balban
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is meant by the Barter system?
Answer:
Goods were exchanged for goods prior to the invention of money.
Question 2.
What is meant by Nallangadi?
Answer:
According to St.Poet Ilango, in Silapathigaram, a Day Market was called Nalangadi.
![]()
Question 3.
What is meant by Allangadi?
Answer:
The night market was called Allangadi according to Saint Poet Ilango in Silapathigaram, Madurai-Kanchi.
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Explain the meaning of the term “Vanigam”.
Answer:
The word vaniyam or vanipam would have had a Dravidian origin. The early Tamils produced their products and goods in their lands and bartered their surplus and that is how the trade came into existence. The word ‘Vanigam is used in Sangam literature like Purananuru and Thirukkural.
![]()
Question 2.
State the meaning of Maruvurapakkam and Pattinapakkam.
Answer:
Big cities like Poompuhar had the ‘Maruvurappakam’ (inland town) and ‘Pattinapakkam’ (coastal town), had markets and bazaars where many merchants met one another for the purpose of selling or buying different kinds of commodities and foodstuff.
Question 3.
What is the role of Sangam in trade development of ancient Tamilnadu?
Answer:
Trade in Sangam period was both internal and external. It was conducted by means of barter (Pandamattru). Honey, roots, fruits, cattle and paddy served as a medium of exchange for certain period. Sangam work refers to great traders, their caravans, their security force, markets, marts and guilds of such traders. There was dependence and interdependence among the people in matters of trade and commerce. Coins were used later for the purpose of exchange of goods.
![]()
Question 4.
What are the ports developed by Pandiya kingdom?
Answer:
Port towns like Tondi, Korkai, Puhar, and Muziri were always seen as busy with marts and markets with activities related to imports and exports. In such a brisk trade, people of the coastal region engaged themselves in coastal trade and developed their intercontinental trade contacts.
Question 5.
What was focused in Arthasasthra about creation of wealth?
Answer:
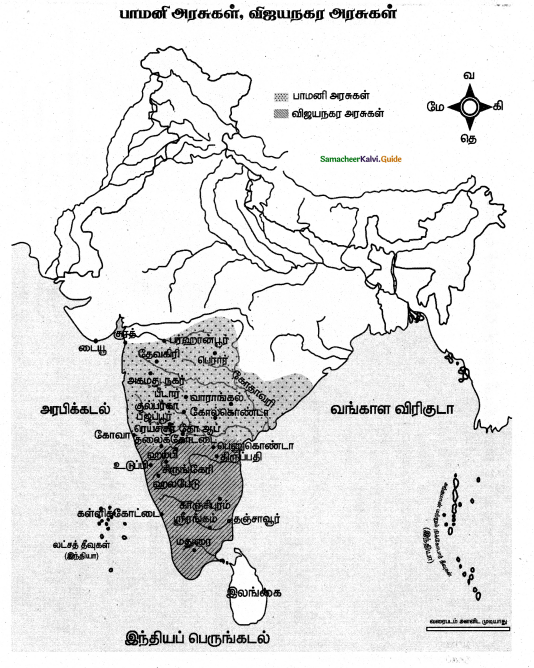
Kautilya’s Arthasasthra describes the economy in Mauriyan time. Kautilya gave importance to the state in relation to treasury, taxation, industry, commerce, agriculture, and conservation of natural resources. Arthasastra focused on the creation of wealth as the means to promote the well-being of the state. It advocated the maintenance of a perfect balance between the state government and people’s welfare through trading activities.
IV. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
What are the hindrances of business?
Answer:
Hindrances of business:
- Hindrance of Person: Manufacturers do not know the place and face of the consumers. It is the retailer who knows the taste, preference, and location of the consumers. The chain of middlemen consisting of wholesalers, agents, and retailers establish the link between the producers and consumers.
- Hindrance of Place: Production takes place in one centre and consumers are spread throughout the country and world. Rail, air, sea, and land transports bring the products to the place of the consumer.
- Hindrance of Time: Consumers want products whenever they have money, time, and willingness to buy. Goods are produced in anticipation of such demands.
- Hindrance of risk of deterioration in quality: Proper packaging and modern air-conditioned storage houses ensure that there is no deterioration in the quality of products.
- Hindrance of risk of loss: Fire, theft, floods, and accidents may bring huge losses to the business.
- Hindrance of knowledge: Advertising and communication help in announcing the arrival of new products and their uses to the people.
- Hindrance of exchange: Money functions as a medium of exchange and enables the buying and selling of any product or service by payment of the right price.
- Hindrance of finance: Producers and traders may not have the required funds at the time of their need.
- Hindrance of developing the exact product: Research and development help in developing the exact product or service which can satisfy the specific wants of consumers and thus improve the standard of living of the people.
- Hindrance of both selection and delivery at doorsteps: E-Commerce enables the consumer to select the product on the website, place online orders, and make payment after receiving the product at the doorstep.
Question 2.
State the constraints in the barter system.
Answer:
The barter system visualises mutual exchange of one’s goods to another without the intervention of money as a medium of exchange. It imposes certain constraints in the smooth flow of trade as given below.
- Lack of double coincidence of Wants: Unless two persons who have surplus have the demand for the goods possessed by each other, barter could not materialize.
For instance ‘A’ is having a surplus of groundnut and ‘B’ is possessing rice in surplus. In this case A should be in need of rice possessed by B as the latter should - The non-existence of common measure of value: The barter system could not determine the value of commodities to be exchanged as they lacked commonly acceptable measures to evaluate each and every commodity. It was difficult to compare the values of all articles in the absence of an acceptable medium of exchange.
- Lack of direct contact between producer and consumers: It was not possible for buyers and sellers to meet face to face in many contexts
for exchanging the commodities for commodities. This hindered the process of barter in all practical sense. - Lack of surplus stock: The absence of surplus stock was one of the impediments in the barter system. If the buyers and sellers do not have a surplus then no barter was possible.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the development of Commerce and Trade in North India.
Answer:
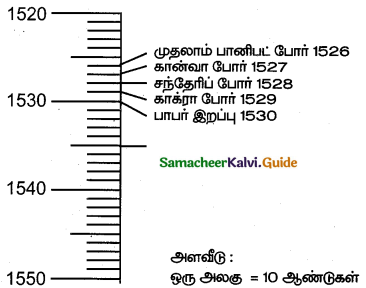
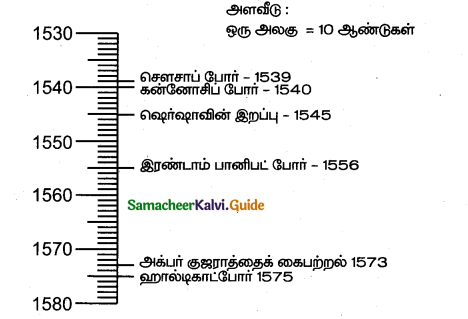
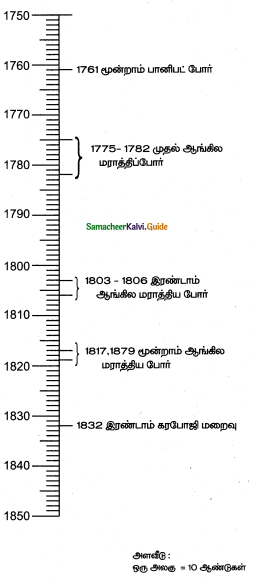
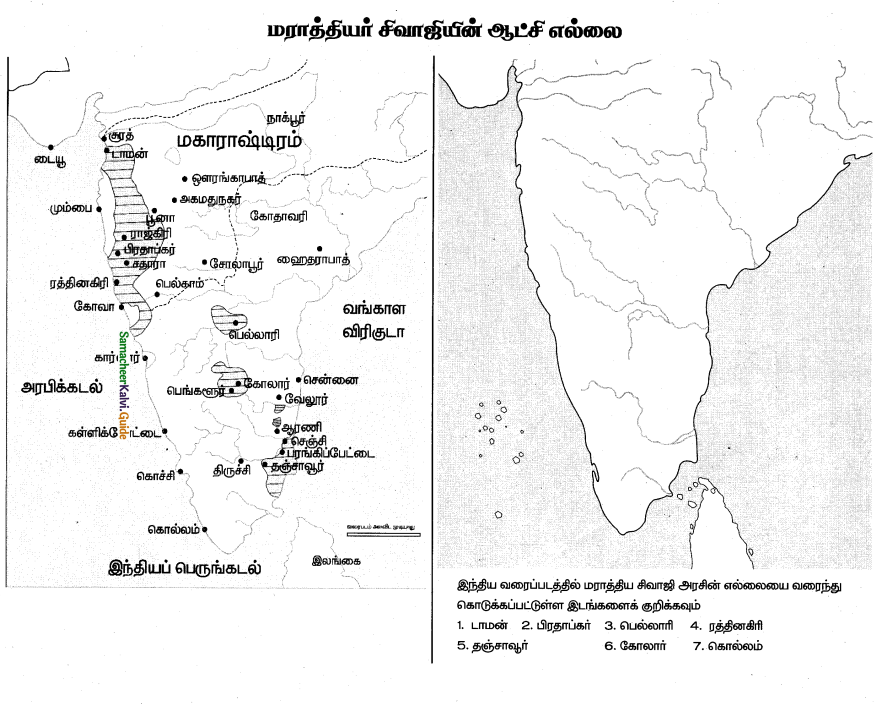
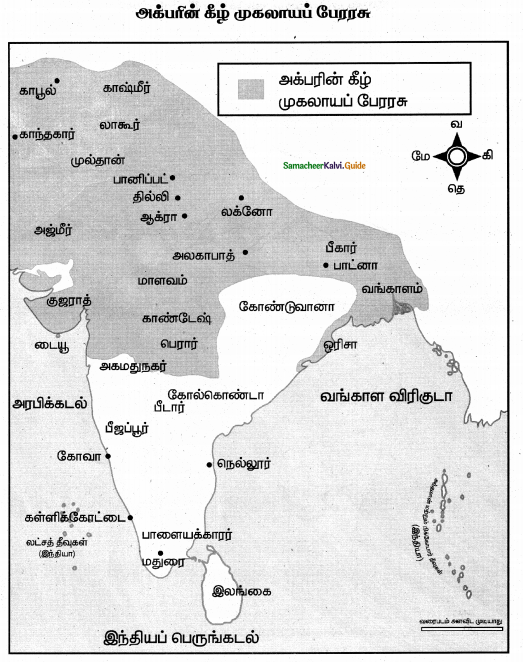
India was prosperous even during the medieval period from the 12th to 16th centuries despite political upheavals. Balban was the first sultan who paved the way in the dense forest and helped traders and their commercial caravans to move from one marketplace to another. Allauddin Khilji brought the price to a very low ebb. He encouraged the import of foreign goods from Persia and subsidized the goods.
Arabs were dominant players in India’s foreign trade. They never discouraged Indian traders like Tamils, Gujaratis, etc. The trade between the coastal ports was in the hands and Marwaris and Gujaratis, The overland trade with central and west Asia was in the hands of Multanis who were Hindus, and Khurasanis who were Afghans, Iranians, and so on.
Question 4.
Briefly explain the coastal trade in ancient Tamilnadu.
Answer:
People of the coastal region engaged themselves in coastal trade and developed their intercontinental trade contacts. Big cities like Poompuhar had ‘Maruvurappakkam’(inland town) and ‘Pattinapakkam’(coastal Town), had markets and bazaars where many merchants met one another for the purpose of selling or buying different commodities and foodstuff. Port towns like Tondi, Korkai, Puhar, and Muziri were involved in imports and exports.
People were engaged in different kinds of fishing pearls, and conches and produced salts, and built ships. Boats like ‘Padagu’,’Thimil’,’Thoni’,’Ambu’, ‘Odampunai’ etc. were used to cross rivers for domestic trade while Kalam, Marakalam, Vangam, Navaietc were used for crossing oceans for foreign trade.
![]()
Question 5.
What do you know about the overseas trading partners of ancient Tamilnadu?
Answer:
Foreigners who transacted business were known as Yavanars. Arabs who traded with Tamil were called ‘Jonagar’. Pattinappalai praised Kaveripumpattinam as a city where various foreigners of high civilization speaking different languages assembled to transact business with the support of the then Kingdom.
Many ports were developed during the Sangam period. Kaveripumpattinam was the chief port of the Kingdom of Cholas while Nagapattinam, Marakannam, Arikamedu, etc., were other small ports on the east coast. Similarly, Pandiyas developed Korkai, Saliyur, Kayal, Marungaurpattinam, and Kumari for foreign trade. The State Governments installed check posts to collect customs along the highways and the ports.
11th Commerce Guide Historical Background of Commerce in the Sub-Continent Additional Important Questions and Answers
I Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
…………….. is part and parcel of human life.
(a) Commerce
(b) Banking
(c) Insurance
(d) Warehousing
Answer:
(a) Commerce
Question 2.
Most of the inland trade in the Sangam period was done in, ………………………………. as a medium of exchange under barter mode.
a) Salt
b) Coin
c) Milk
d) Gold
Answer:
a) Salt
![]()
Question 3.
Commerce activities are heading for a cashless system through ……………..
(a) e-commerce
(b) banking
(c) insurance
(d) warehousing
Answer:
(a) e-commerce
Question 4.
The night market was called…………………………..
a) Nalangadi
b) Angadi
c) Iravu Santhai
d) Allangadi
Answer:
d) Allangadi
![]()
Question 5.
Day market was called as ……………..
(a) Nalangadi
(b) Angadi
(c) Business
(d) Trade
Answer:
(a) Nalangadi
Question 6.
Foreigners who transacted business were known as ………………..
a) Jonagar
b) Sellers
c) Yavanars
d) Merchants
Answer:
c) Yavanars
![]()
Question 7.
Which is called a sleepless city?
(a) Chennai
(a) Allangadi
(c) Tuticorin
(d) Salem
Answer:
(a) Allangadi
Question 8.
………………………………. was the first sultan who paved in the dense forest and helped traders.
a) AlauddinKhilji
b) Balban
c) Suleiman I
d) Abdulaziz I
Answer:
c) Suleiman I
![]()
Question 9.
Boats like …………….. were used for crossing oceans for foreign trade.
(a) Vangam
(b) Thimil
(c) Ambu
(d) Thoni
Answer:
(a) Vangam
Question 10.
The hindrance of the place is removed by means of ……………….
a) Warehouse
b) Transport
c) Exchange of money
d) Insurance
Answer:
b) Transport
II. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
What is the cashless system?
Answer:
Commerce activities are heading for a cashless system through e-commerce which means business activities enabled through electronic modes like Online trading, Mobile banking, and e-marketing.
Question 2.
What do you mean by “Angadi”?
Answer:
The place where the goods were sold was called “ Angadi”.
![]()
Question 3.
Which city was called sleepless city?
Answer:
Madurai was called a sleepless city due to round-the-clock business activities.
Question 4.
What was advocated by Kautilya in Arthasasthra with regard to trade?
Answer:
In Arthasasthra Kautilya advocated the maintenance of perfect balance between State management and people’s welfare through trading activities.
![]()
Question 5.
What type of boats were used to cross oceans for foreign trade?
Answer:
Boats like ‘Kalam’, ‘Marakalam’, ‘Vangam’, ‘Navai’, etc., were used for crossing oceans for foreign trade.
Question 6.
Which are all considered the important trade centres in the 16th century?
Answer:
In 16th Century Delhi, Mumbai, Ahmedabad, Sonar, Sonargoon. Jaunpur and Lahore were considered as important trade centres.
![]()
Question 7.
What was the role of the state in trade?
Answer:
The role of the state in trade related to two aspects namely adequate infrastructure to sustain the trade and administrative machinery for taxation.
Question 8.
With whom Cholas had a strong trading relationship?
Answer:
Cholas had a strong trading relationship with the Chinese Song Dynasty.
III. Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
How has the commerce activities emerged how?
Answer:
The whole of commerce activity has emerged from the barter system into a multi-dimensional and multifaceted scientific system consisting of courses like Monetary system, Mail order business, Hire purchase system, Instalment purchase system and so on.
![]()
Question 2.
What are all the conditions under Barter System worked on?
Answer:
- Each party to barter must have surplus stocks for the trade to take place.
- Both the buyers and sellers should require the goods to each other desperately, i.e., double coincidence of wants.
- Buyer and seller should meet personally to affect the exchange.
IV. Long Answer Questions
Question 1.
How did the ancient Tamil country trade with Rome, China, and Europe?
Answer:
Roman and Greek traders frequented the ancient Tamil country and forged trade relationships with ancient Kings of Pandiya, Chola, and Chera dynasties. Cholas had a strong trading relationship with the Chinese Song Dynasty. The Cholas conquered the Sri Vijaya Empire of Indonesia and Malaysia to secure a sea trading route to China. During the 16th and 18th centuries, India’s overseas trade expanded due to trading with European companies. The discovery of new all sea routes from Europe to India via the Cape of Good Hope by Vasco da Gama had a far-reaching impact on the civilized world. The arrival of the Portuguese in India was followed by the advent of other European communities. They gained a strong foothold in India’s maritime trade by virtue of their strong naval power.
![]()