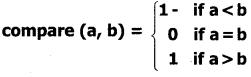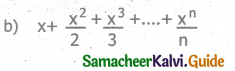Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Guide Pdf Chapter 11 Functions Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Solutions Chapter 11 Functions
11th Computer Science Guide Functions Text Book Questions and Answers
Book Evaluation
Part I
Choose The Correct Answer
Question 1.
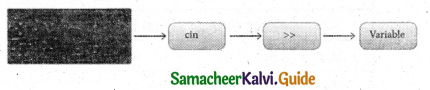
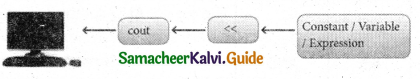
Which of the following header file defines the standard I/O predefined functions ?
a) stdio.h
b) math.h
c) string.h
d) ctype.h
Answer:
a) stdio.h
Question 2.
Which function is used to check whether a character is alphanumeric or not ?
a) isalpha( )
b) isdigit( )
c) isalnum( )
d) islower( )
Answer:
c) isalnum( )
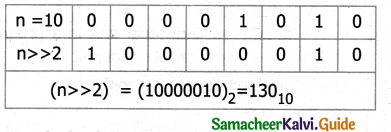
![]()
Question 3.
Which function begins the program execution ?
a) isalpha( )
b) isdigit( )
c) main( )
d) islower( )
Answer:
c) main( )
Question 4.
Which of the following function is with a return value and without any argument ?
a) x=display(int/ int)
b) x=display( )
c) y=display(float)
d) display(int)
Answer:
b) x=display( )
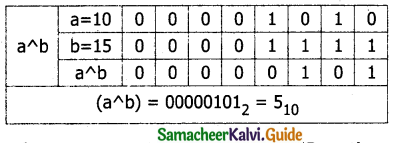
![]()
Question 5.
Which is return data type of the function prototype of add (int, int); ?
a) int
b) float
c) char
d) double
Answer:
a) int
Question 6.
Which of the following is the scope operator ?
a) >
b) &
c) %
d) ::
Answer:
d) ::
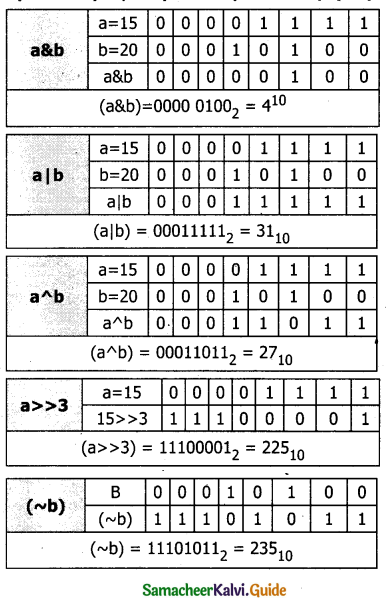
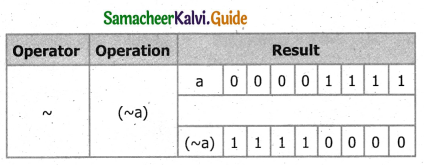
![]()
Part – II
Very Short Answers
Question 1.
Define Functions.
Answer:
A large program can typically be split into small subprograms (blocks) called functions where each sub-program can perform some specific functionality. Functions reduce the size and complexity of a program, make it easier to understand, test, and check for errors.
Question 2.
Write about strlen() function.
Answer:
The strlen() takes a null-terminated byte string source as its argument and returns its length. The length does not include the null(\0) character.
Example:
char source[ ] = “Computer Science”;
cout<<“\nGiven String is “<<source<<” its Length is “<<strlen(source);
Output
Given String is Computer Science its Length is 16
Question 3.
What are the importance of void data type?
Answer:
void type has two important purposes:
- To indicate the function does not return a value.
- To declare a generic pointer.
![]()
Question 4.
What is Parameter and list its types?
Answer:
Arguments or parameters are the means to pass values from the calling function to the called function.
Types:
- The variables used in the function definition as parameters are known as formal parameters.
- The constants, variables, or expressions used j in the function call are known as actual parameters.
Question 5.
Write a note on Local Scope.
Answer:
- A local variable is defined within a block. A block of code begins and ends with curly braces { }.
- The scope of a local variable is the block in which it is defined.
- A local variable cannot be accessed from outside the block of its declaration.
- A local variable is created upon entry into its block and destroyed upon exit
![]()
Part – III
Short Answers
Question 1.
What is Built-in functions?
Answer:
The functions which are available by default are known as “Built-in” functions. Ready-to-use subprograms are called pre-defined functions or built-in functions.
Question 2.
What is the difference between isupper() and toupper() functions?
Answer:
isupper():
- This function is used to check the given character is uppercase.
- This function will return 1 if true otherwise 0.
toupper():
- This function is used to convert the given character into its uppercase.
- This function will return the upper case equivalent of the given character. If the given character itself is in upper case, the output will be the same.
![]()
Question 3.
Write about strcmp( ) function.
Answer:
strcmp( )
The strcmp( ) function takes two arguments: string 1 and string2. It compares the contents of string 1 and string2 lexicographically.
The strcmp() function returns a:
- Positive value if the first differing character in string 1 is greater than the corresponding character in string2. (ASCII values are compared)
- Negative value if the first differing character in string 1 is less than the corresponding character in string2,
- 0 if string1 and string2 are equal.
Example:
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char string1[ ] = “Computer”;
char string2[ ] = “Science”;
int result;
result = strcmp(string1,string2);
if(result==0)
{
cout<<“String1 : “<<string1<<” and String2 : “<<string2 <<“Are Equal”;
}
else
{
cout<<“String1 :”<<string1<<” and String2 : “<<string2’ <<“ Are Not Equal”;
}
}
Output
String1 : Computer and String2 : Science Are Not Equa1
![]()
Question 4.
Write short note on pow( ) function in C++.
Answer:
pow( ) function:
The pow( ) function returns base raised to the power of exponent. If any argument passed to pow( ) is long double, the return type is promoted to long double. If not, the return type is double.
The pow( ) function takes two arguments:
- base – the base value
- exponent – exponent of the base
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
int main ( )
{
double base, exponent, result;
base = 5;
exponent = 4;
result = pow(base, exponent);
cout << “pow(“< double x = 25;;
result = sin(x);
cout << “\nsin(“<<x<<“)= “<<result;
return 0;
}
Output
pow(5^4) = 625
sin(25) = -0.132352
![]()
Question 5.
What are the information the prototype provides to the compiler?
Answer:
The prototype above provides the following information to the compiler:
- The return value of the function is of type long.
- Fact is the name of the function.
- The function is called with two arguments:
- The first argument is of int data type.
- The second argument is of double data type, int display(int, int) // function prototype//.
The above function prototype provides details about the return data type, name of the function and a list of formal parameters or arguments.
Question 6.
What is default arguments ? Give example.
Answer:
default arguments:
In C++, one can assign default values to the formal parameters of a function prototype. The default arguments allows to omit some arguments when calling the function.
When calling a function,
For any missing arguments, complier uses the values in default arguments for the called function.
The default value is given in the form of variable initialization.
Example:
void defaultvalue(int n1=10, n2=100);
The default arguments facilitate the function call statement with partial or no arguments or complete arguments.
Example:
defaultvalue(x,y);
defaultvalue(200,150);
defaultvalue(150);
defaultvalue( );
The default values can be included in the function prototype from right to left, i.e., we cannot have a default value for an argument in between the argument list.
Example:
void defaultvalue(int n1 = 10, n2);//invalid prototype
void defaultvalue(int n1, n2 = 10);//valid prototype
![]()
Part – IV
Explain in Detail
Question 1.
Explain the Call by value method with a suitable example.
Answer:
Call by value method:
This method copies the value of an actual parameter into the formal parameter of the function. In this case, changes made to the formal parameter within the function will have no effect on the actual parameter.
Example:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void display(int x)
{
int a = x * x;
cout<<“\n\nThe Value inside display function
(a * a):”<<a;
}
int main( )
{
int a;
cout<<“\nExample : Function call by value:”;
cout<<“\n\nEnter the Value for A cin>>a;
display(a);
cout<<”\n\nThe Value inside main function “<<a;
return (0);
}
Output:
Example: Function call by value Enter the Value for A : 5
The Value inside display function (a * a) : 25
The Value inside main function 5
Question 2.
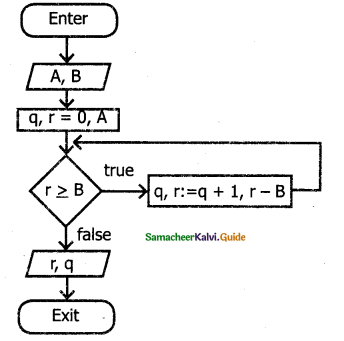
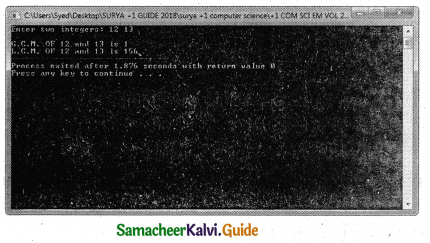
What is Recursion? Write a program to find GCD using recursion.
Answer:
A function that calls itself is known as a recursive function. And, this technique is known as recursion.
Finding GCD of any to number using Recursion:
GCD – Greatest Common Divisor or HCF (Highest Common Factor) or GCM – Greatest Common Measure)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//Function to find HCF or GCD OR GCM // int gcd(int n1, int n2)
{
if (n2 != 0)
return gcd(n2, n1 % n2); //Recursive call of gcd function
else
return n1;
}
int main( )
{
int num1, num2;
cout << “Enter two positive integers: “;
cin >> num1 >> num2;
cout << “Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) of ” << num1;
cout<< ” & ” << num2 << ” is: ” << gcd(num1, num2);
return 0;
}
Output :
Enter two positive integers: 350 100
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) of 350 & 100 is: 50
![]()
Question 3.
What are the different forms of function return? Explain with example.
Answer:
Different forms of User-defined Function declarations:
Function without return value and without parameter
The following program is an example of a function with no return and no arguments passed.
The name of the function is display( ), its return data type is void and it does not have any argument.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void display( )
{
cout<<“Function without parameter and return value”;
}
int main()
{
display( ); // Function calling statement//
return(O);
}
Output :
Function without parameter and return value
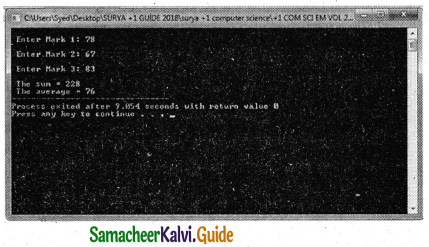
A Function with return value and without parameter
The name of the function is display(), its return type is int and it does not have any argument. The return statement returns a value to the calling function and transfers the program control back to the calling statement.
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int display( )
{
int a, b, s;
cout<<“Enter 2 numbers:
cin>>a>>b;
s=a+b;
return s;
}
int main( )
{
int m=display( );
cout<<“\nThe Sum=”<<m;
return(0);
}
OUTPUT :
Enter 2 numbers: 10 30
The Sum = 40
![]()
Question 4.
Explain scope of variable with an example.
Answer:
Scope refers to the accessibility of a variable.
There are four types of scopes in C++
- Local Scope
- Function Scope
- File Scope
- Class Scope
1. Local Scope:
- A local variable is defined within a block. A block of code begins and ends with curly braces {}.
- The scope of a local variable is the block in which it is defined.
- A local variable cannot be accessed from outside the block of its declaration.
- A local variable is created upon entry into its block and destroyed upon exit;
Example:
int main( )
{
int a,b; //Local variable
}
2. Function Scope:
- The scope of a variable within a function is extended to the function block and all sub-blocks therein.
- The lifetime of a function scope variable is the lifetime of the function block.
Example:
int. sum(int x, int y); //x and y has function scope.
3. File Scope:
- A variable declared above all blocks and functions (including main()) has the scope of a file.
- The lifetime of a file scope variable is the lifetime of a program.
- The file scope variable is also called a global variable.
Example:
#include
using namespace std;
int x,y; //x and y are global variable
void main()
{
……..
}
4. Class Scope:
- Data members declared in a class has the class scope.
- Data members declared in a class can be accessed by all member functions of the class.
Example:
Class example
{
int x,y; //x and y can be accessed by print() and void():
void print();
Void total();
};
Class Scope:
A class is a new way of creating and implementing a user-defined data type. Classes provide a method for packing together data of different types.
Data members are the data variables that represent the features or properties of a class.
| class student } private: int mark1, mark2, total; }; | The class student contains mark1, mark2, and total are data variables. Its scope is within the class of students only. |
![]()
Question 5.
Write a program to accept any integer number and reverse it.
Answer:
PROGRAM:
using namespace std;
#include <iostream>
int reverse(int num)
{
int r=0,d;
while(num>0)
{
d = num%10;
r = r*10+d;
num = num/10;
}
return (r);
}
int main( )
{
intx;
cout<<“\nEnter a number”;
cin>>x;
cout<<“\nReverse of the number is “<<reverse(x);
return 0;
}
OUTPUT

11th Computer Science Guide Functions Additional Questions and Answers
Choose The Correct Answer 1 Mark
Question 1.
………………. is the name of the function.
(a) Predefined
(b) Built-in
(c) Library
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question 2.
…………….. reduce the size and complexity of a program, makes it easier to understand, test, and check for errors.
a) Arrays
b) Functions
c) Structures
d) Unions
Answer:
b) Functions
Question 3.
The strcpy() function takes two arguments of ……………….
(a) target and source
(b) upper and lower
(c) base and exponent
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) target and source
![]()
Question 4.
Functions which are available in the C++ language standard library is known as ……………… functions.
a) Built-in
b) User-defined
c) Either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Built-in
Question 5.
The pow() function takes the two arguments of ……………….
(a) target and source
(b) upper and lower
(c) base and exponent
(d) source and exponent
Answer:
(c) base and exponent
Question 6.
Why functions are needed?
a) Divide and conquer the purpose
b) Reusability of code
c) Reduce the complexity of a program
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
![]()
Question 7.
The C++ program always has a main() function to begin the program execution.
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) null
Answer:
(a) 1
Question 8.
Ready-to-use subprograms are called ………………..
a) Pre-defined functions
b) Built-in functions
c) Either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Either A or B
Question 9.
In C++ the arguments can be passed to a function in ………………. ways.
(a) 2
(b) 1
(c) 3
(d) 7
Answer:
(a) 2
![]()
Question 10.
A header file can be identified by their file extension ……………..
a) .head
b) .h
c) .hf
d) None of these
Answer:
b) .h
Question 11.
…………… is a header file contains pre-defined standard input/output functions.
a) conio.h
b) istream.h
c) iostream.h
d) stdio.h
Answer:
d) stdio.h
Question 12.
stdio.h header file defines the standard I/O predefined function ……………
a) getchar()
b) putchar()
c) getsQ and puts()
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
![]()
Question 13.
The predefined function ……………. is used to get a single character from the keyboard.
a) getchar()
b) putchar()
c) gets() and puts()
d) puts()
Answer:
a) getchar()
Question 14.
The predefined function …………… is used to display a single character.
a) getchar( )
b) putchar( )
c) gets( )
d) puts( )
Answer:
b) putchar( )
Question 15.
Function ……………… reads a string from standard input and stores it into the string pointed by the variable.
a) getchar( )
b) putchar( )
c) gets( )
d) puts( )
Answer:
c) gets( )
![]()
Question 16.
Function …………….. prints the string read by gets() function in a newline.
a) getchar( )
b) putchar( )
c) gets( )
d) puts( )
Answer:
d) puts( )
Question 17.
……………. header file defines various operations on characters.
a) conio.h
b) ctype.h
c) iostream.h
d) stdio.h
Answer:
b) ctype.h
Question 18.
……………… function is used to check whether a character is alphanumeric or not.
a) isalnum( )
b) isalpha( )
c) isdigit( )
d) None of these
Answer:
a) isalnum( )
![]()
Question 19.
………….. function returns a non-zero value if the given character is a digit or a letter, else it returns 0.
a) isalnum( )
b) isaipha( )
c) isdigit( )
d) None of these
Answer:
a) isalnum( )
Question 20.
The ……………… function is used to check whether the given character is an alphabet or not.
a) isalnum( )
b) isalpha( )
c) isdigit( )
d) None of these
Answer:
b) isalpha( )
Question 21.
………….. function will return 1 if the given character is an alphabet, and 0 otherwise 0.
a) isalnum( )
b) isalpha( )
c) isdigit( )
d) None of these
Answer:
b) isalpha( )
![]()
Question 22.
………… function is used to check whether a given character is a digit or not.
a) isalnum( )
b) isalpha( )
c) isdigit( )
d) None of these
Answer:
c) isdigit( )
Question 23.
……………. function will return 1 if the given character is a digit, and 0 otherwise.
a) isalnum( )
b) isalpha( )
c) isdigit( )
d) None of these
Answer:
c) isdigit( )
Question 24.
………………. function is used to check whether a character is in lower case (small letter) or not.
a) islower( )
b) tolower( )
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
a) islower( )
![]()
Question 25.
……………. functions will return a non-zero value if the given character is a lower case alphabet, and 0 otherwise.
a) islower( )
b) tolower( )
c) toupper( )
d) isupper( )
Answer:
a) islower( )
Question 26.
……………. function is used to check the given character is uppercase.
a) islower( )
b) tolower( )
c) toupper( )
d) isupper( )
Answer:
d) isupper( )
Question 27.
……………. function will return 1 if the given character is an uppercase alphabet otherwise 0.
a) islower( )
b) tolower( )
c) toupper( )
d) isupper( )
Answer:
d) isupper( )
![]()
Question 28.
…………. function is used to convert the given character into its uppercase.
a) islower( )
b) tolower( )
c) toupper( )
d) isupper( )
Answer:
c) toupper( )
Question 29.
………….. function will return the upper case equivalent of the given character.
a) islower( )
b) tolower( )
c) toupper( )
d) isupper( )
Answer:
c) toupper( )
Question 30.
………………… function is used to convert the given character into its lowercase.
a) islower( )
b) tolower( )
c) toupper( )
d) isupper( )
Answer:
b) tolower( )
Question 31.
………………. function copies the character string pointed by the source to the memory location pointed by the target.
a) strcpy( )
b) strcat( )
c) strcmp( )
d) strlen( )
Answer:
a) strcpy( )
Question 32.
The …………………. function takes a null-terminated byte string source as its argument and returns its length.
a) strcpy( )
b) strcat( )
c) strcmp( )
d) strlen( )
Answer:
d) strlen( )
![]()
Question 33.
The length of the string does not include the _______ character.
a) Null(\0)
b) Blank space
c) White space
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Null(\0)
Question 34.
………………. function compares the contents of string1 and string2 lexicographically.
a) strcpy( )
b) strcat( )
c) strcmp( )
d) strlen( )
Answer:
c) strcmp()
Question 35.
The Strcmp( ) function returns a ………………. value if the first differing character in string1 is greater than the corresponding character in string2.
a) Positive
b) Negative
c) Zero
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Positive
Question 36.
The Strcmp() function returns a …………….. value if the first differing character in stringl is less than the corresponding character in string2.
a) Positive
b) Negative
c) Zero
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Negative
![]()
Question 37.
………………. function appends copy of the character string pointed by the source to the end of string pointed by the target.
a) strcpy( )
b) strcat( )
c) strcmp( )
d) strlen( )
Answer:
b) strcat( )
Question 38.
The …………….. function is used to convert the given string into Uppercase letters.
a) strupr( )
b) toupper( )
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
a) strupr( )
Question 39.
The …………….. function is used to convert the given string into Lowercase letters.
a) tolower( )
b) strlwr( )
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
b) strlwr( )
![]()
Question 40.
The cos( ) function takes a single argument in ………………
a) Radians
b) Degree
c) Either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Radians
Question 41.
The cos( ) function returns the value in the range of ……………
a) [0, 1]
b) [-1, 1]
c) [1,-1]
d) None of these
Answer:
b) [-1, 1]
Question 42.
The cos( ) function returns the value in ……………….
a) double
b) float
c) long double
d) Either A or B or C
Answer:
d) Either A or B or C
![]()
Question 43.
The sqrt( ) function takes a …………… argument.
a) single non-negative
b) single negative
c) double non-negative
d) double negative
Answer:
a) single non-negative
Question 44.
If a negative value is passed as an argument to sqrt( ) function, a …………….. occurs,
a) Data type mismatch
b) Domain error
c) Prototype mismatch
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Domain error
Question 45.
The ………….. function returns, the value in the range of [-1,1].
a) cos( )
b) sin( )
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 46.
The …………….. function returns base raised to the power of the exponent.
a) exponent( )
b) power( )
c) pow( )
d) None of these
Answer:
c) pow( )
![]()
Question 47.
If any argument passed to pow() is long double, the return type is promoted to ……………..
a) long double
b) int
c) double
d) char
Answer:
a) long double
Question 48.
The pow( ) function takes ……………… argument.
a) base
b) exponent
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
Question 49.
The …………….. function in C++ seeds the pseudo-random number generator used by the rand() function.
a) srand( )
b) sran( )
c) rands( )
d) None of these
Answer:
a) srand( )
Question 50.
The srand( ) function is defined in ……………. header file.
a)
b) <stdlib)h>
c) or<stalib)h>
d) None of these
Answer:
c) or<stalib)h>
![]()
Question 51.
C++ program can contain ……………. main”() function.
a) Only one
b) No
c) More than one
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Only one
Question 52.
In C++,……………… function begins the program execution.
a) void
b) main( )
c) User-defined
d) Built-in
Answer:
b) main( )
Question 53.
………………. data type is used to indicate the function does not return a value.
a) int
b) double
c) void
d) unsigned
Answer:
c) void
Question 54.
……………… data type is used to declare a generic pointer.
a) int
b) double
c) void
d) unsigned
Answer:
c) void
Question 55.
The user-defined function should be called explicitly using its ………………
a) Name
b) Arguments to be passed
c) Both A and B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A and B
![]()
Question 56.
Which of the following calling the function have a return value and with arguments?
a) display( );
b) display(x,y);
c) x = display( );
d) x = display(x,y);
Answer:
d) x = display(x,y);
Question 57.
Which of the following calling function have no return value and no argument?
a) display( );
b) display(x,y);
c) x = display();
d) x = display(x,y);
Answer:
a) display( );
Question 58.
Which of the following calling the function have no return value and with arguments?
a) display( );
b) display(x,y);
c) x = display();
d) x = display(x,y);
Answer:
b) display(x,y);
![]()
Question 59.
Which of the following calling the function have a return value and no argument?
a) display();
b) display(x,y);
c) x = display();
d) x = display(x,y);
Answer:
c) x = display();
Question 60.
…………………. are the means to pass values from the calling function to the called function.
a) Arguments
b) Parameters
c) Arguments or Parameters
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Arguments or Parameters
Question 61.
The variables used in the function definition as parameters are known as ……………. parameters.
a) Formal
b) Actual
c) Ideal
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Formal
![]()
Question 62.
The parameters used in the function call are known as ………………. parameters.
a) Formal
b) Actual
c) Ideal
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Actual
Question 63.
The ……………… can be used in the function call as parameters.
a) Constants
b) Variables
c) Expressions
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 64.
The …………….. arguments allow omitting some arguments when calling the function.
a) Default
b) Actual
c) Formal
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Default
![]()
Question 65.
The default value is given in the form of …………………….
a) Variable declaration
b) Variable initialization
c) void
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Variable initialization
Question 66.
The default arguments facilitate the function call statement with ………………. arguments.
a) Partial
b) No
c) Complete
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 67.
The default values can be included in the function prototype from ……………….
a) Left to Right
b) Right to Left
c) Center to Left
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Right to Left
![]()
Question 68.
The constant variable can be declared using the…………… keyword.
a) constant
b) Const
c) const
d) CONST
Answer:
c) const
Question 69.
The …………….. keyword makes variable value stable.
a) constant
b) Const
c) const
d) CONST
Answer:
c) const
Question 70.
The ……………… modifier enables to assign an initial value to a variable that cannot be changed later inside the body of the function,
a) void
b) Const
c) const
d) Unsinged
Answer:
c) const
![]()
Question 71.
In C++, the arguments can be passed to a function in ……………. ways.
a) three
b) two
c) four
d) None of these
Answer:
b) two
Question 72.
In C++, the arguments can be passed to a function in ……………… method.
a) Call by value
b) Call by reference
c) Either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Either A or B
Question 73.
………………. method copies the value of an actual parameter into the formal parameter of the function.
a) Call by value
b) Call by reference
c) Either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Call by value
![]()
Question 74.
In ……………. method, changes made to the formal parameter within the function will have no effect on the actual parameter.
a) Call by value
b) Call by reference
c) Either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Call by value
Question 75.
………… method copies the address of the actual argument into the formal parameter.
a) Call by value
b) Call by reference
c) Either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Call by reference
Question 76.
In the…………….. method, any change made in the formal parameter will be reflected back in the actual parameter.
a) Call by value
b) Call by reference
c) Either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Call by reference
![]()
Question 77.
The definition of the functions is stored in …………….
a) Array
b) Call by reference
c) Structures
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Call by reference
Question 78.
………….. functions can be used to reduce the overheads like STACKS for small function definition.
a) Inline
b) Built-in
c) User-defined
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Inline
Question 79.
……………. reduces the speed of program execution.
a) Array
b) Stacks
c) Structures
d) Unions
Answer:
b) Stacks
![]()
Question 80.
A(n) ………….. function looks like a normal function in the source file but inserts the function’s code directly into the calling program.
a) inline
b) Built-in
c) User-defined
d) None of these
Answer:
a) inline
Question 81.
To make a function inline, one has to insert the keyword …………….. in the function header.
a) Inline
b) Insert
c) INLINE
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Inline
Question 82.
……………. functions execute faster but require more memory space.
a) User-defined
b) Built-in
c) Inline
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Inline
![]()
Question 83.
The inline function reduces the complexity of using …………………
a) Array
b) Stacks
c) Structures
d) Unions
Answer:
b) Stacks
Question 84.
Returning from the function is done by using the ……………… statement.
a) return
b) goto
c) break
d) continue
Answer:
a) return
Question 85.
The …………….. statement stops execution and returns to the calling function.
a) return
b) goto
c) break
d) continue
Answer:
a) return
![]()
Question 86.
Identify the true statement from the following.
a) A return may or may not have a value associated with it.
b) If the return has a value associated with it, that value becomes the return value for the calling statement.
c) The return statement is used to return from a function.
d) AN the above
Answer:
d) AN the above
Question 87.
The functions that return no value are declared as ……………..
a) Null
b) void
c) Empty
d) None of these
Answer:
b) void
Question 88.
The data type of a function is treated as …………….. if no data type is explicitly mentioned.
a) Null
b) void
c) Empty
d) int
Answer:
d) int
![]()
Question 89.
What is the return type of the following function prototype? add (int, int);
a) Null
b) void
c) Empty
d) int
Answer:
d) int
Question 90.
What is the return type of the following function prototype? double add (int, int);
a) float
b) void
c) double
d) int
Answer:
c) double
Question 91.
What is the return type of the following function prototype?
char *display();
a) float
b) string
c) double
d) char
Answer:
b) string
![]()
Question 92.
A function that calls itself is known as ………….. function.
a) recursive
b) nested
c) invariant
d) variant
Answer:
a) recursive
Question 93.
A function that calls itself using …………. technique.
a) recursive
b) variant
c) invariant
d) recursion
Answer:
d) recursion
Question 94.
………………. is mandatory when a function is defined after the main() function.
a) Function prototype
b) Function parameters
c) Return statement
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Function prototype
![]()
Question 95.
Scope refers to the accessibility of a ……………..
a) Function
b) Class
c) Variable
d) Constant
Answer:
c) Variable
Question 96.
There are ………… types of scopes in C++.
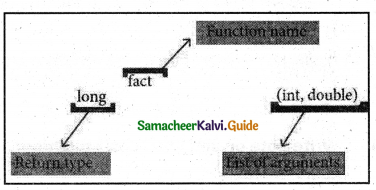
a) five
b) two
c) three
d) four
Answer:
d) four
Question 97.
…………….. is a type of variable scope.
a) Local
b) Function / File
d) Class
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
![]()
Question 98.
A …………… is a region or life of the variable and broadly speaking there are three places, where variables can be declared.
a) Scope
b) Access specifier
c) Location
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Scope
Question 99.
Variables inside a block are called …………… variables.
a) Local
b) Function
c) Class
d) File
Answer:
a) Local
Question 100.
Variables inside a function are called ………….. variables.
a) Local
b) Function
c) Class
d) File
Answer:
b) Function
![]()
Question 101.
Variables outside of ail functions are called ………….. variables.
a) Local
b) Function
c) Class
d) Global
Answer:
d) Global
Question 102.
Variables inside a class are called ……………
a) Class variable
b) Data members
c) Member functions
d) Either A or B
Answer:
d) Either A or B
Question 103.
The scope of formal parameters is …………… scope.
a) Local
b) Function
c) Class
d) File
Answer:
b) Function
![]()
Question 104.
A variable declared above all blocks and functions (including main ()) has the …………… scope.
a) Local
b) Function
c) Class
d) File
Answer:
d) File
Question 105.
The lifetime of a ………….. scope variable is the lifetime of a program.
a) Local
b) Function
c) Class
d) File
Answer:
d) File
Question 106.
The file scope variable is also called as ………….. variable.
a) Global
b) General
c) Void
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Global
![]()
Question 107.
…………… provides a method for packing together data of different types.
a) Enumeration
b) Array
c) Class
d) All the above
Answer:
c) Class
Question 108.
……………… represent the features or properties of a class.
a) Member function
b) Data member
c) Global variable
d) None of these
Answer:
b) Data member
Question 109.
…………….. is a scope resolution operator.
a) ? :
b) #
c) : :
d) &&
Answer:
c) : :
Question 110.
The …………… operator reveals the hidden scope of a variable.
a) ? :
b) &&
c) : :
d) #
Answer:
c) : :
![]()
Very Short Answers (2 Marks)
Question 1.
Write about reusability.
Answer:
- Few lines of code may be repeatedly used in different contexts. Duplication of the same code can be eliminated by using functions which improve the maintenance and reduce program size.
- Some functions can be called multiple times with different inputs.
Question 2.
Why functions are needed?
Answer:
To reduce the size and complexity of the program functions are used.
Question 3.
What are constant arguments and write their syntax?
Answer:
The constant variable can be declared using the const keyword. The const keyword makes variable, value stable. The constant variable should be initialized while declaring. The const modifier enables the assignment of an initial value to a variable that cannot be changed later inside the body of the function.
Syntax: (const )
![]()
Question 4.
Write a note on the reusability of the code.
Answer:
Reusability:
- Few lines of code may be repeatedly used in different contexts. Duplication of the same code can be eliminated by using functions which improve the maintenance and reduce program size.
- Some functions can be called multiple times with different inputs.
Question 5.
What is function scope?
Answer:
Function Scope:
- The scope of variables declared within a function is extended to the function block and all sub-blocks therein.
- The lifetime of a function scope variable is the lifetime of the function block. The scope of.
Question 6.
What is the header file?
Answer:
C++ provides a rich collection of functions ready to be used for various tasks. The tasks to be performed by each of these are already written, debugged, and compiled, their definitions alone are grouped and stored in files called header files
![]()
Question 7.
What is a built-in function?
Answer:
The ready-to-use subprograms are called pre-defined functions or built-in functions.
Question 8.
What is a user-defined function?
Answer:
C++ provides the facility to create new functions for specific tasks as per user requirements. The name of the task and data required is decided by the user and hence they are known as User-defined functions.
Question 9.
How a header file is identified?
Answer:
A header file can be identified by their file extension .h.
Example:
stdio.h
![]()
Question 10.
Write note on stdio.h header file.
Answer:
This header file defines the standard I/O predefined functions getchar(), putchar(), gets(), puts() and etc.
Question 11.
What is the purpose of getchar() and putchar() functions?
Answer:
The predefined function getchar() is used to get a single character from the keyboard and putchar() function is used to display it.
Question 12.
What is the purpose of gets() and puts() functions?
Answer:
Function gets( ) reads a string including balance spaces from standard input and stores it into the string pointed by the variable. Function puts() prints the string read by gets() function in a newline.
Question 13.
Write note on isalpha( ) function.
Answer:
The isalpha( ) function is used to check whether the given character is an alphabet or not.
Syntax:
int isalpha(char c);
This function will return 1 if the given character is an alphabet, and 0 otherwise 0. The following statement assigns 0 to the variable n, since the given character is not an alphabet.
int n = isalphaC3′);
The statement is given below displays 1, since the given character is an alphabet.
cout << isalpha(‘a’); .
![]()
Question 14.
Write the use of isdigit() function.
Answer:
This function is used to check whether a given character is a digit or not. This function will return 1 if the given character is a digit, and 0 otherwise.
Syntax:
int isdigit(char c);
When the following code is executed, the value of the variable n will be 1, since the given character is a digit.
char ch = ‘3’;
n = isdigit (ch);
Question 15.
How to copy a string into another string?
Answer:
The srcpy() function copies the character string pointed by the source to the memory location pointed by the target. The strcpy() function takes two arguments: target and source. The null terminating character (\0) is also copied.
Example:
char source[ ] = “Computer Science”;
char target[20]=”target”;
strcpy(target,source);
Question 16.
What is the purpose of strupr( ) and strlwr( ) functions?
Answer:
- The strupr( ) function is used to convert the given string into Uppercase letters.
- The strlwr( ) function is used to convert the given string into Lowercase letters.
![]()
Question 17.
What is the use of return statement in a function?
Answer:
Returning from the function is done by using the return statement.
The return statement stops execution and returns to the calling function. When a return statement is executed, the function is terminated immediately at that point.
Question 18.
Write note on scope resolution operator.
Answer:
The scope operator reveals the hidden scope ‘ of a variable. The scope resolution operator (::) is used for the following purposes.
To access a Global variable when there is a Local variable with same name. An example using Scope Resolution Operator.
PROGRAM :
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int x=45; // Global Variable x
int main()
{
int x = 10; // Local Variable x
cout << “\nValue of global x is ” << ::x;
cout << “\nValue of local x is ” << x;
return 0;
}
Output :
Value of global x is 45
Value of local x is 10
![]()
Short Answers (3 Marks)
Question 1.
What is divide and conquer?
Answer:
Divide and Conquer:
- Complicated programs can be divided into manageable sub-programs called functions.
- A programmer can focus on developing, debugging, and testing individual functions.
- Many programmers can work on different functions simultaneously.
![]()
Question 2.
Write about islower( ) function.
Answer:
islower( )
This function is used to check whether a character is in lower case (small letter) or not.
This function will return a non-zero value, if the given character is a lower case alphabet, and 0 otherwise.
Syntax:
int islower(char c);
After executing the following statements, the value of the variable n will be 1 since the given character is in lower case
char ch = ‘n’;
int n = islower(ch);
The statement given below will assign 0 to the variable n, since the given character is an uppercase alphabet.
int n = islower(‘P’);
Question 3.
What is digit()? Give example.
Answer:
This function is used to check whether a given character is a digit or not. This function will return 1 if the given character is a digit, and 0 otherwise.
Example:
using namespace std;
#include
#include int main( )
{
char ch;
cout << “\n Enter a Character:”; cin >> ch;
cout << “\n The Return Value of isdigit(ch) is << isdigit(ch);
}
Output – 1
Enter a Character: 3
The Return Value of isdigit(ch) is: 1
Output – 2
Enter a Character: A
The Return Value of isdigit(ch) is: 0
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the method of comparing two strings.
Answer:
strcmp( ) function compares the contents of string 1 and string2 lexicographically. The strcmp() function takes two arguments: stringl and string2.
The strcmp( ) function returns a:
- Positive value if the first differing character in stringl is greater than the corresponding character in string2. (ASCII values are compared)
- Negative value if the first differing character in stringl is less than the corresponding character in string2.
- 0 if stringl and string2 are equal.
Example:
#include <string.h>
#inciude <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char string1[ ] = “Computer”;
char string2[ ] = “Science”;
int result;
result = strcmp(string1,string2);
if(result==0)
{
cout<<“String1: “<<string1<<“and String2 : “<<string2 <<“Are Equal”;
}
else
{
cout<<“String1 :”<<string1<<” and String2 : “c<<string2<<” Are Not Equal”;
}
}
Output
String1 : Computer and String2 : Science Are Not Equal
![]()
Question 5.
What is a return statement with an example?
Answer:
The return statement stops execution and returns to the calling function. When a return statement is executed, the function is terminated immediately at that point. The return statement is used to return from a function. It is categorized as a jump statement because it terminates the execution of the function and transfers the control to the called statement.
Example:
return(a + b); return(a);
return; // to terminate the function
Question 6.
Write note on sin() and cos() functions.
Answer:
cos() function
The cos() function takes a single argument in radians. The cosQ function returns the value in the range of [-1, 1], The returned value is either in double, float, or long double.
Example:
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double x = 0.5, result;
result = cos(x);
cout << “COS(“<<x<<“)= “<<result;
}
Output
COS(0.5)= 0.877583
sin( ) function:
The sin() function takes a single argument in radians. The sin( ) function returns the value in the range of [-1, 1]. The returned value is either in double, float, or long double.
![]()
Question 7.
Write about sqrt( ) and pow( ) functions.
Answer:
sqrt( ) function:
The sqrt( ) function returns the square root of the given value of the argument. The sqrt( ) function takes a single non-negative argument. If a negative value is passed as an argument to sqrt( ) function, a domain error occurs.
Example:
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
double x = 625, result;
result = sqrt(x);
cout << “sqrt(“<<x<<“) = “<<result;
return 0;
}
Output
sqrt(625) = 25
pow( ) function:
The pow( ) function returns base raised to the power of exponent. If any argument passed to pow() is long double, the return type is promoted to long double. If not, the return type is double.
The pow() function takes two arguments:
base – the base value
exponent – exponent of the base Example:
#include <iostream>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
int main ( )
{
double base, exponent, result;
base = 5;
exponent = 4;
result = pow(base, exponent);
cout << “pow(“< << “) = ” << result;
double x = 25;;
result = sin(x);
cout << “\nsin(“<<x<<“)= “<<result;
return 0;
}
Output
pow(5 ^ 4) = 625 sin(25)= -0.132352
![]()
Question 8.
How will you generate a random numbers?
Answer:
The srand( ) function in C++ seeds the pseudo random number generator used by the rand( ) function. The seed for rand( ) function is 1 by default. It means that if no srand( ) is called before rand(), the rand() function behaves as if it was seeded with srand(1).
The srand( ) function takes an unsigned integer as its parameter which is used as seed by the rand() function. It is defined inor <stdlib,h>header file.
Example:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int random = rand(); /* No srand() calls before rand(), so seed = 1 */
cout << “\nSeed = 1, Random number = ” << random;
srand(10);
/* Seed = 10 */
random = rand( );
cout << “\n\nSeed = 10, Random number=” << random;
return 0;
}
Output
Seed = 1, Random number = 41
Seed =10, Random number =71
![]()
Question 9.
Write note on function prototype.
Answer:
Function Prototype:
C++ program can contain any number of functions. But, it must always have only one main( ) function to begin the program execution. We can write the definitions of functions in any order as we wish.
We can define the main( ) function first and all other functions after that or we can define all the needed functions prior to main( ). Like a variable declaration, a function must be declared before it is used in the program.
The declaration statement may be given outside the main( ) function.
Example:
long fact (int, double);
Question 10.
Explain Formal Parameters and Actual Parameters or Arguments.
Answer:
Formal Parameters and Actual Parameters or Arguments:
Arguments or parameters are the means to pass values from the calling function to the called function.
- The variables used in the function definition as parameters are known as formal parameters.
- The constants, variables or expressions used in the function call are known as actual parameters.
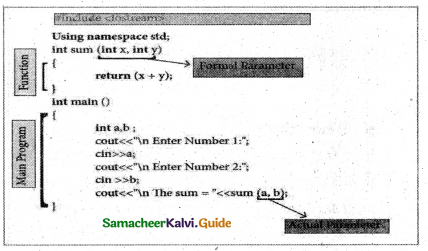
![]()
Explain in Detail (5 Marks)
Question 1.
Explain about generating random numbers with a suitable program.
Answer:
The srand() function in C++ seeds the pseudo-random number generator used by the rand() function. The seed for rand() function is 1 by default. It means that if no srand() is called before rand(), the rand() function behaves as if it was seeded with srand( 1). The srand() function takes an unsigned integer as its parameter which is used as seed by the rand() function. It is defined inor header file.
#include
#include using namespace std; int main()
{
int random = rand(); /* No srand() calls before rand(), so seed = 1*/
cout << “\nSeed = 1, Random number =” << random;
srand(10);
/* Seed= 10 */
random = rand();
cout << “\n\n Seed =10, Random number =” << random;
return 0;
}
Output:
Seed = 1, Random number = 41
Seed =10, Random number 71
![]()
Question 2.
How will access function? Explain in detail.
Answer:
Accessing a function:
The user-defined function should be called explicitly using its name and the required arguments to be passed. The compiler refers to the function prototype to check whether the function has been called correctly.
If the argument type does not match exactly with the data type defined in the prototype, the compiler will perform type conversion, if possible. If type conversion is impossible, the compiler generates an error message.
Example :
| 1. | display( ) | calling the function without a return value and without any argument. |
| 2. | display (x, y) | calling the function without a return value and with arguments. |
| 3. | x = display() | calling the function with a return value and without any argument. |
| 4. | x = display (x, y) | calling the function with a return value and with arguments. |
![]()
Question 3.
Explain constant argument in detail.
Answer:
Constant Arguments:
The constant variable can be declared using const keyword. The const keyword makes variable value stable. The constant variable should be initialized while declaring. The const modifier enables to assign an initial value to a variable that cannot be changed later inside the body of the function.
Syntax:
<returntype> <functionname> (const <datatype variable=value>)
Example:
int minimum(const int a=10);
float area(const float pi=3.14, int r=5);
PROGRAM
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; ,
double area(const double r,const double pi=3.14)
{
return(pi*r*r);
}
int main ( )
{
double rad,res;
cout<<‘AnEnter Radius :”;
cin>>rad;
res=area(rad);
cout << “\nThe Area of Circle =”<<res;
return 0;
}
OUTPUT:
Enter Radius: 5
The Area of Circle =78.5
If the variable value “r” is changed as r=25;
inside the body of the function “area” then compiler will throw an error as “assignment of
read-only parameter ‘r’ “.
double area (const double r, const double pi= 3.14)
{
r=25;
return(pi*r*r);
}
![]()
Question 4.
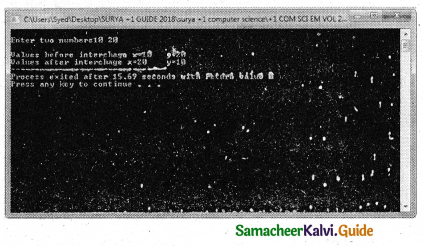
Explain about address method.
Answer:
This method copies the address of the actual argument into the formal parameter. Since the address of the argument is passed, any change made in the formal parameter will be reflected back in the actual parameter.
#include
using namespace std;
void display(int & x) //passing address of a//
{
x = x*x;
cout << “\n\n The Value inside display function (n1 x n1) :”<< x ;
}
int main()
{
intn 1;
cout << “\n Enter the Value for N1 cin >> n1;
cout << “\n The Value of N1 is inside main function Before passing:” << n1;
display(n1);
cout << “\n The Value of N1 is inside main function After passing (n1 x n1):”<< n1; retum(O);
}
Output:
Enter the Value for N1: 45
The Value of N1 is inside the main function Before passing: 45
The Value inside display function (n1 x n1) : 2025
The Value ofNl is inside the main function After passing (n1 x n1): 2025
![]()
Question 5.
Explain inline function in detial.
Answer:
Inline function:
An inline function looks like normal function in the source file but inserts the function’s code directly into the calling program. To make a function inline, one has to insert the keyword inline in the function header.
This reduces the speed of program execution. Inline functions can be used to reduce the overheads like STACKS for small function definition.
Syntax:
inline return type function name (data type parametername1,… datatype parameternameN)
Advantages of inline functions:
- Inline functions execute faster but requires more memory space.
- Reduce the complexity of using STACKS.
PROGRAM
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
inline float simpleinterest (float pi, float nl, float r1)
{
float si1=(p1*n1*r1)/100;
return(si1);
}
int main ( )
{
float si,p,n,r;
cout<<“\nEnter the Principle Amount Rs. :”;
cin> >p;
cout<<“\nEnter the Number of Years:”;
cin>>n;
cout<<“\nEnter the Rate of Interest :”;
cin>>r;
si=simpleinterest(p,n,r);
cout << “\nThe Simple Interest = Rs,”<<si;
return 0;
}
Output:
Enter the Principle Amount Rs. :60000
Enter the Number of Years :10
Enter the Rate of Interest :5
The Simple Interest = Rs.30000
Though the above program is written in the normal function definition format during compilation the function code (p1*n1*r1)/100 will be directly inserted in the calling statement i.e. si=simpleinterest(p,n,r);
This makes the calling statement to change as si= (p1*n1*r1)/100;
![]()
Hands-On Practice
Write C++ program to solve the following problems:
Question 1.
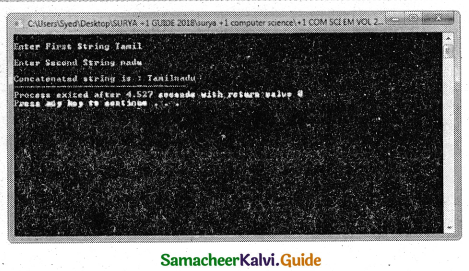
Program that reads two strings and appends the first string to the second. For example, If the first string Is entered as Tamil and the second string is Nadu, the program should print Tamilnadu. Use string library header.
Answer:
PROGRAM :
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char firststr[50],secondstr[50];
cout<<“\nEnter First String “; cin> >firststr;
cout<<“\nEnter Second String”; cin>>secondstr;
strcat(firststr,secondstr); //concatenation process
cout << ”\nConcatenated string is : ” <<firststr;
return 0;
}
Output:
Question 2.
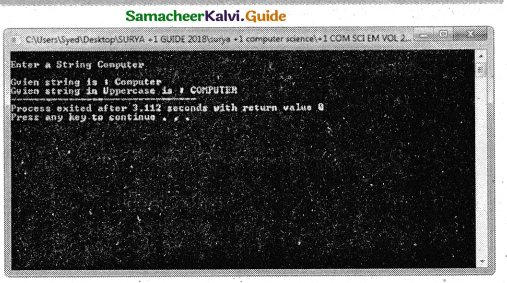
Program that reads a string and converts it to uppercase. Include required header files.
Answer:
PROGRAM :
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char str[50];
cout<<“\nEnter a String
cin>>str;
cout << “\nGvien string is : “<<str; strupr(str);
cout << “\nGvien string in Uppercase is :”<<str;
return 0;
}
Output :
![]()
Question 3.
Program that checks whether a given character is an alphabet or not. If It is an alphabet, whether It Is lowercase character or uppercase- character? Include required header files.
Answer:
PROGRAM :
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main( )
{
char ch;
cout<<“\nEnter a Character”;
cin>>ch;
if(isalpha(ch))
if(islower(ch))
cout << “\nGiven Character is an Alphabet and in Lowercase”;
else
cout << “\nGiven Character is an Alphabet and in Uppercase “;
else
cout << “\nGiven Character in not an Alphabet”;
return 0;
Output

![]()
Question 4.
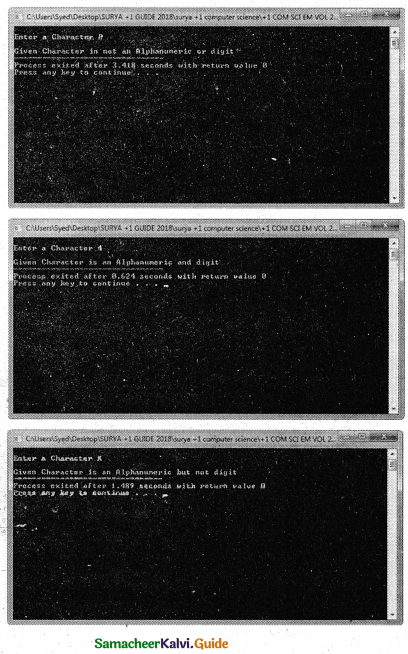
Program that checks whether the given character is alphanumeric or a digit Add appropriate header file
Answer:
PROGRAM :
#include <string.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char ch;
cout<<“\nEnter a Character”;
cin>>ch;
if(isalnum(ch))
if(isdigit(ch))
cout << “\nGiven Character is an Alphanumeric and digit”;
else
cout << “\nGiven Character is an Alphanumeric but not digit”;
else
cout << “\nGiven Character in not an Alphanumeric or digit”;
return 0;
}
Output:
![]()
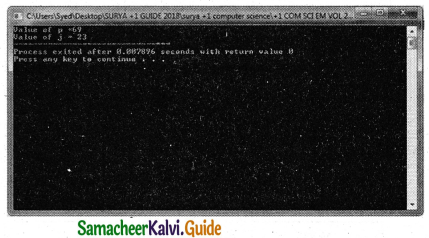
Question 5.
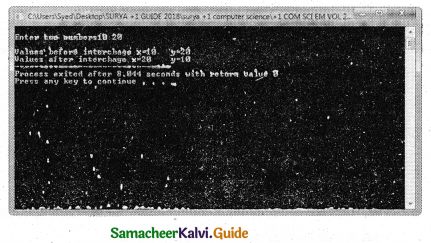
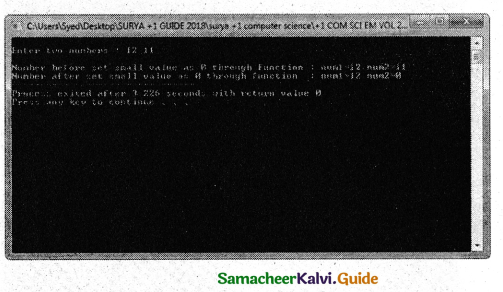
Write a function called zero_small ( ) that has two integer arguments being passed by reference and sets smaller of the two numbers to 0. Write the main program to access this function.
Answer:
PROGRAM
using namespace std;
#include <iostream>
void zero_small(int &a, int &b)
{
if (a<b)
a= 0;
else
b=0;
}
int main( )
{
int num1,num2;
cout<<“\nEnter two numbers :”; cin>>num1>>num2;
cout<<“\nNumber before set small value as 0 through function : num1=” <<num1<<” num2=”<<num2;
zero_small(num1,num2);
cout<<“\nNumber after set small value as 0 through function : num1=” <<num1<<” num2=”<<num2;
}
Output :

![]()
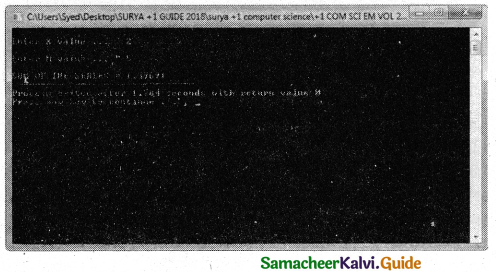
Question 6.
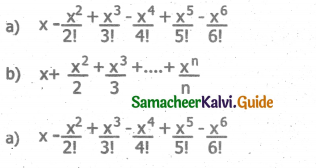
Write definition for a function sumseries ( ) in C++ with two arguments/ parameters – double x and int n. The function should return a value of type double and it should perform sum of the following series:
x-x2 /3! + x3 / 5! – x4 / 7! + x5 / 9! upto n terms.
Answer:
PROGRAM :
using namespace std;
#indude
double sumseries(double x, int n)
{
double sum=0,t;
int f=1,sign=1;
t=x;
inti=1‘,j=1;
while(i<=n)
{
sum = sum + sign * t/f;
j=j + 2;
i++;
f = f*j*(j-1);
t = t * x;
sign = -sign;
}
return(sum);
}
int main()
{
int i,x,n,f=1,sign=1;
cout<<“\nEnter X value …”;
cin>>x;
cout<<“\nEnter N value …”;
cin>>n;
cout<<“\nSUM OF THE SERIES = “<<sumseries(x,n);
return 0;
}
Output :
![]()
Question 7.
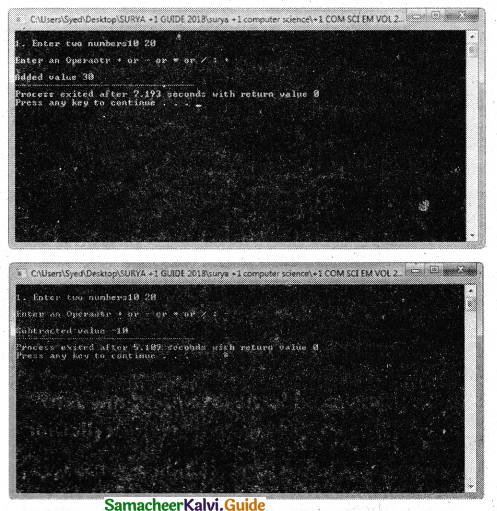
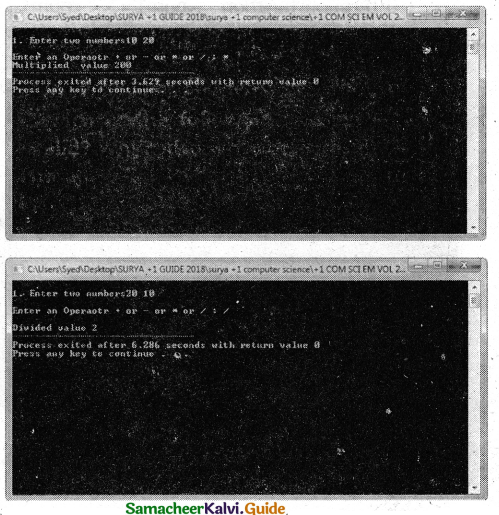
Program that Invokes a function calc ( ) which intakes two integers and an arithmetic operator and prints the corresponding result.
Answer:
PROGRAM :
using namespace std;
#include
void calc(int numl,int num2,char op)
{
int result;
switch(op)
{
case’+’:
result = num1 + num2;
cout<<“\nAdded value “<<result;
break;
case’-‘:
result = num1 – num2;
cout<<“\nSubtracted value “<< result;
break;
case’*’:
result = num1 * num2;
cout<<“\Multiplied value”<<result;
break;
case ‘/’:
result = num1 / num2;
cout<<“\nDivided value “<<result;
break;
default:cout<<“\nPROCESS COMPLETED”;
}
}
int main()
{
float n1,n2;
char op;
cout<<“\nl. Enter two numbers”; cin>>n1>>n2;
cout<<“\nEnter an Operaotr + or – or * Or / :”; cin>>op;
calc(nl,n2,op);
}
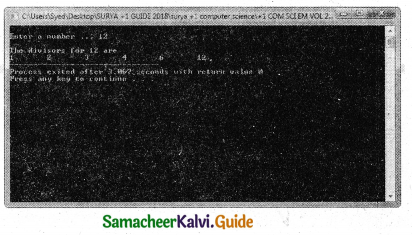
Output :