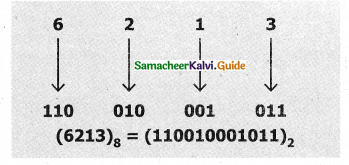
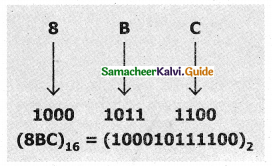
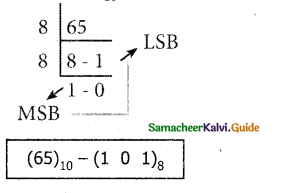
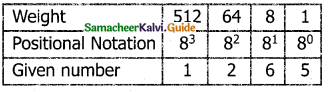
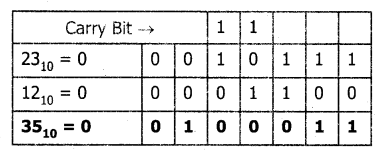
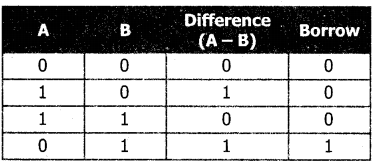
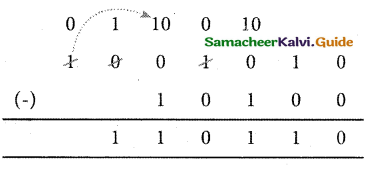
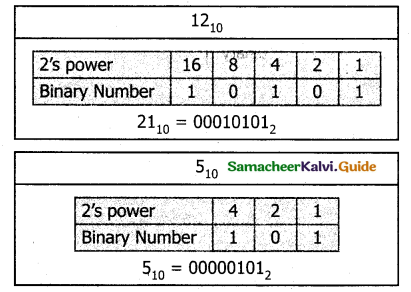
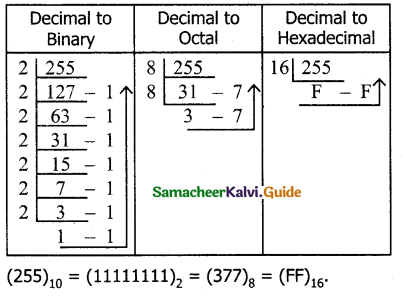
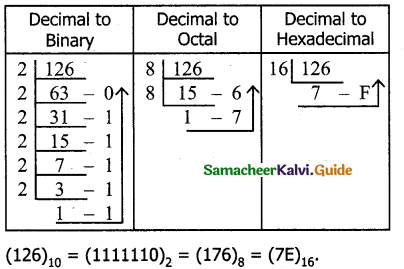
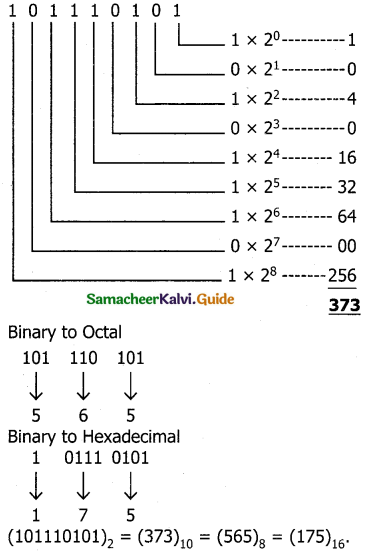
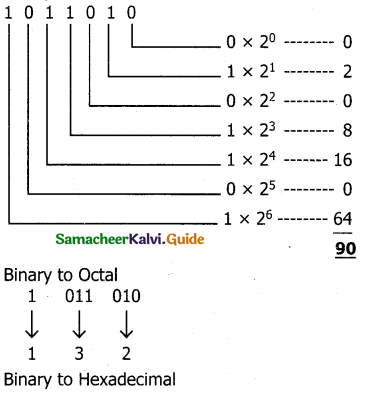
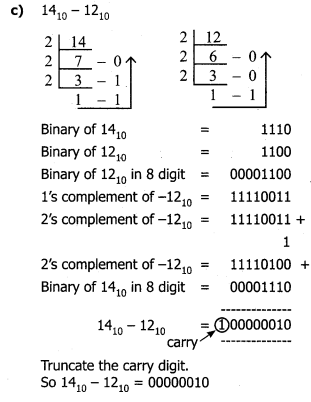
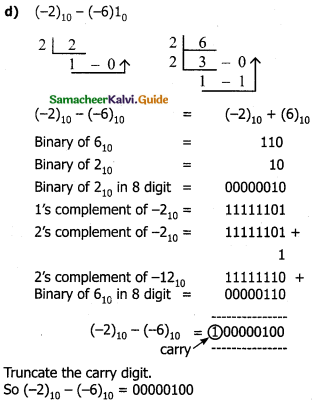
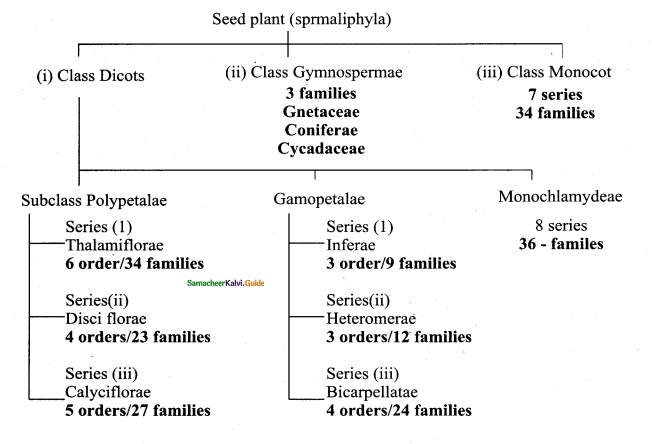
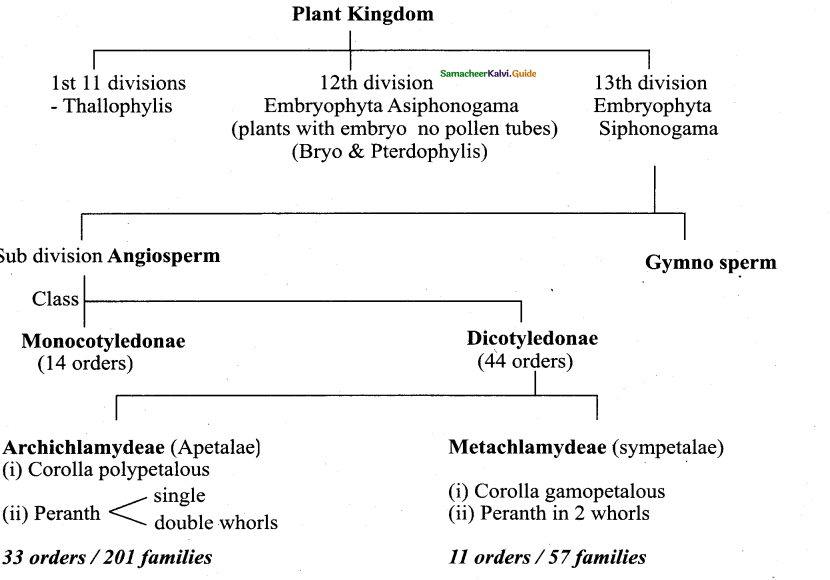
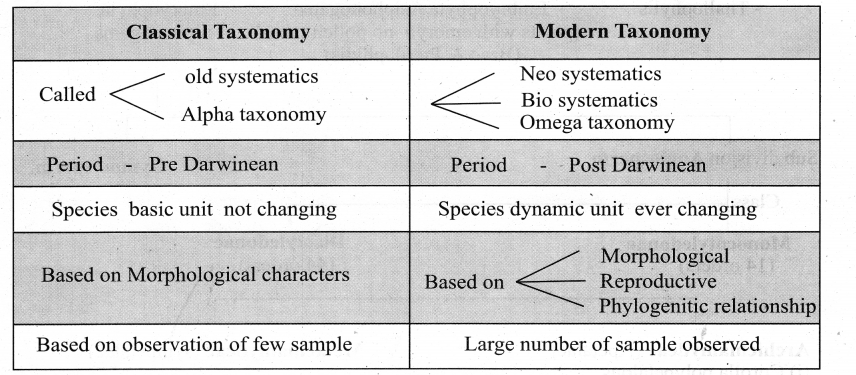
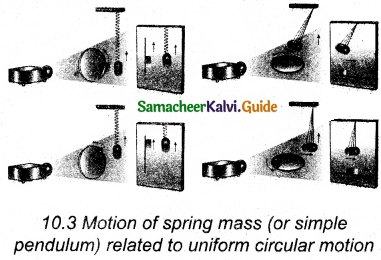
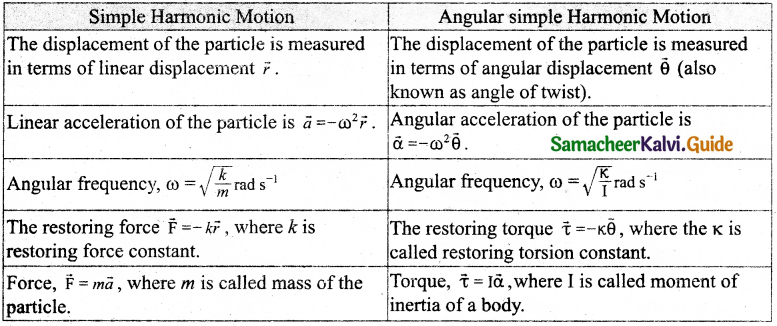
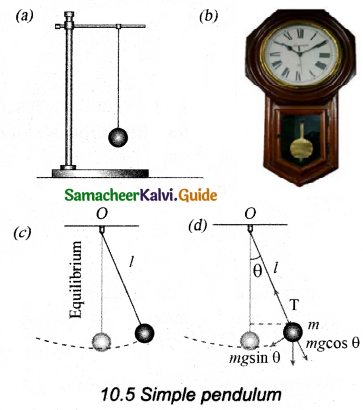
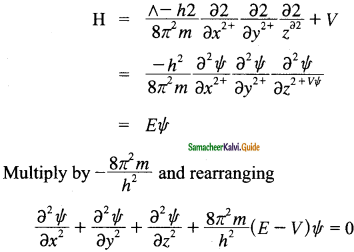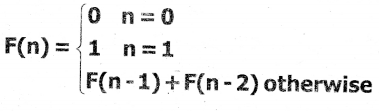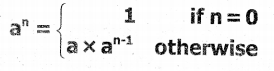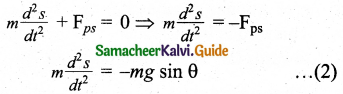Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Guide Pdf Chapter 2 Number Systems Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
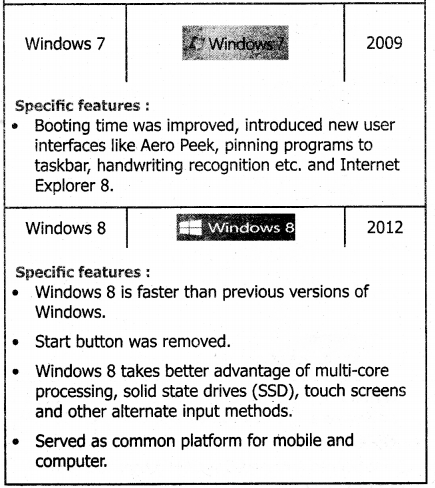
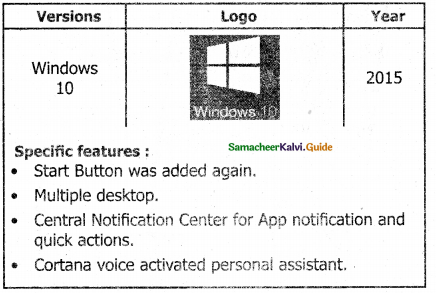
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Computer Science Solutions Chapter 2 Number Systems
11th Computer Science Guide Number Systems Text Book Questions and Answers
![]()
Part – I
I. Choose The Correct Answer :
Question 1.
Which is a basic electronic circuit which operates on one or more signals?
a) Boolean algebra
b) Gate
c) Fundamental gates
d) Derived gates
Answer:
b) Gate
![]()
Question 2.
Which gate is called as the logical inverter?
a) AND
b) OR
c) NOT
d) XNOR
Answer:
c) NOT
Question 3.
A + A = ?
a) A
b) O
c) 1
d) A
Answer:
a) A
Question 4.
NOR is a combination of ?
a) NOT(OR)
b) NOT(AND)
c) NOT(NOT)
d) NOT(NOR)
Answer:
a) NOT(OR)
Question 5.
NAND is called as _______ Gate
a) Fundamental Gate
b) Derived Gate
c) Logical Gate
d) Electronic gate
Answer:
b) Derived Gate
Part II
Short Answers:
Question 1.
What is Boolean Algebra?
Answer:
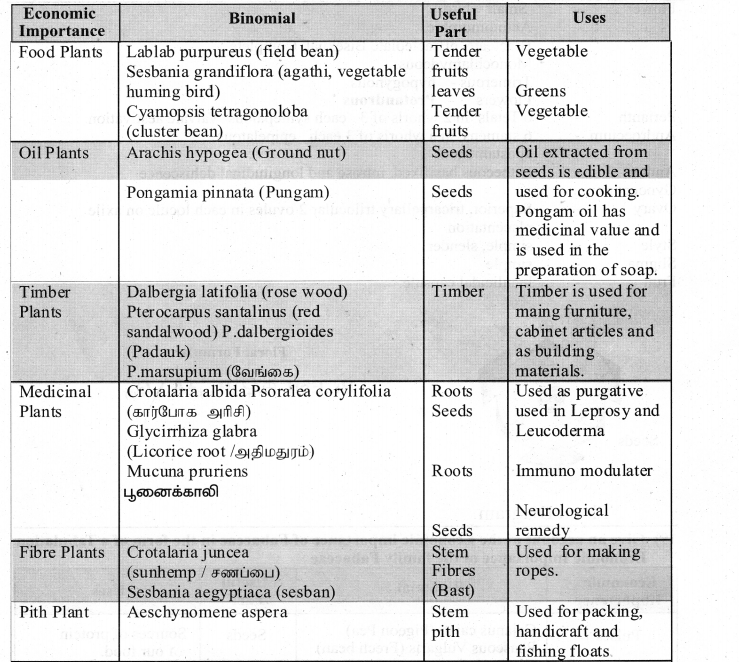
Boolean algebra is a mathematical discipline that is used for designing digital circuits in a digital computer. It describes the relationship between inputs and outputs of a digital circuit.
![]()
Question 2.
Write a short note on NAND Gate.
Answer:
The NAND gate operates an AND gate followed by a NOT gate. It acts in the manner of the logical operation “AND” followed by an inversion. The output is “false” if both inputs are “true” otherwise, the output is “true”. In other words, the output of the NAND gate is 0 if and only if both the inputs are 1, otherwise the output is 1.
The logical symbol of the NAND gate is
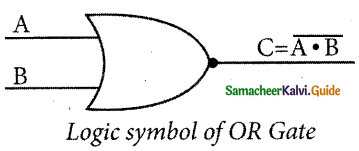
The truth table for NAND gate is
| Input | Output | |
| A | ‘ B | C |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Question 3.
Draw the truth table for the XOR gate.
Answer:
The truth table for XOR gate is
| In put | Output | |
| A | ‘ B | C |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Question 4.
Write the associative laws?
Answer:
A + (B + C) = (A + B) + C
A.(B.C) = (A.B).C
Question 5.
What are derived gates?
Answer:
The logic gates which are derived from the fundamental gates are called derived gates. Ex. NAND, NOR, XOR and XNOR are derived gates.
![]()
Part – III
Explain In Brief
Question 1.
Write the truth table of fundamental gates.
Answer:
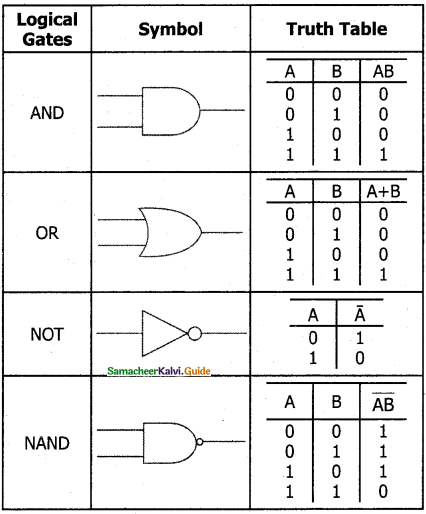
The fundamental logic gates are AND, OR, and NOT gates.
The truth table for AND Gate is
| Input | Output | |
| A | B | C |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
The truth table for OR gate is
| Input | Output | |
| A | B | C |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
The truth table for NOT gate is
| Input | Output |
| A | C |
| 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 |
Question 2.
Write a short note on the XNOR gate.
Answer:
The XNOR (exclusive – NOR) gate is a combination XOR gate followed by an inverter. Its output is “true” if the inputs are the same, and “false” if the inputs are different. In simple words, the output is 1 if the input is the same, otherwise, the output is 0. The logic symbol of the XNOR gate is
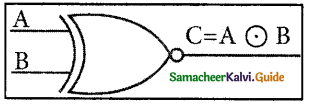
The truth table for XNOR Gate is
| Input | Output | |
| A | B | C |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Question 3.
Reason out why the NAND and NOR are called universal gates?
Answer:
NAND and NOR gates are called Universal gates because the fundamental logic gates can be realized through them.
![]()
Question 4.
Give the truth table of XOR gate.
Answer:
The truth table for XOR Gate is
| Input | Output | |
| A | B | C |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Question 5.
Write the De Morgan’s law.
Answer:
De Morgan’s \(\overline{\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{B}}\) = \(\overline{\mathrm{A}}\) . \(\overline{\mathrm{B}}\)
(\(\overline{\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{B}}\)) = \(\overline{\mathrm{A}}\) + \(\overline{\mathrm{B}}\)
Part IV
Explain In Detail
Question 1.
Explain the fundamental gates with an expression and truth table.
Answer:
A gate is a basic electronic circuit which operates on one or more signals to produce an output signal. There are three fundamental gates namely AND, OR and NOT.
AND Gate
The AND gate can have two or more input signals and produce an output signal. The output is “true” only when both inputs are “true” otherwise, the output is “false”. In other words the output will be 1 if and only if both inputs are 1; otherwise, the output is 0.
The logical symbol of the AND gate is
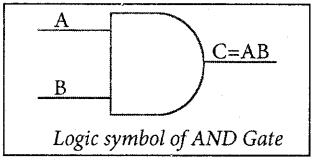
The output of the AND gate is C = A . B or C = AB
The truth table for AND Gate is
| Input | Output | |
| A | B | C |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
OR Gate
The OR gate gets its name from its behaviour like the logical inclusive “OR”. The output is “true” if either or both of the inputs are “true”. If both inputs are “false” then the output is “false”. In other words, the output will be 1 if and only if one or both inputs are 1; otherwise, the output is 0.
The logical symbol of the OR gate is
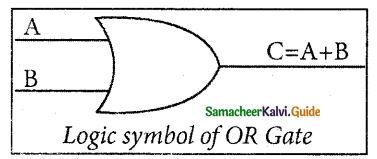
The OR gate output is C = A OR B. We use the + sign to denote the OR function. Therefore, C = A + B.
The truth table for OR Gate is
| Input | Output | |
| A | B | C |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
NOT Gate
The NOT gate, called a logical inverter, has only one input. It reverses the logical state. In other words the output C is always the complement of the input.
The logical symbol of the NOT gate is
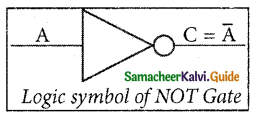
The boolean function of NOT gate is C = NOT A. In boolean algebra, the overbar stands for NOT operation. Therefore, \(C=\bar{A}\)
The truth table for NOT gate is
| Input | Output |
| A | C |
| 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 |
![]()
Question 2.
How AND and OR can be realized using NAND and NOR gate.
Answer:
NAND and NOR gates are called Universal gates because the fundamental logic gates can be realized through them.
NAND gates can be used to implement the fundamental logic gates NOT, AND, and OR.
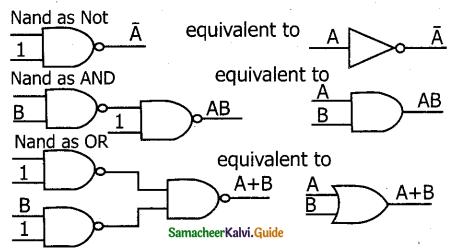
NOR gates can also be used to implement NOT, OR and AND gates.
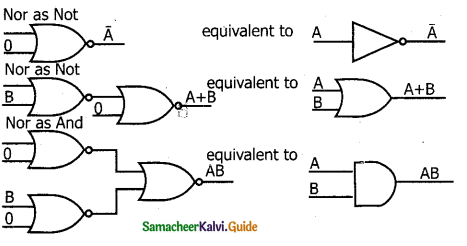
Question 3.
Explain the Derived gates with expression and truth table.
Answer:
The other logic gates like NAND, NOR, XOR, and XNOR are derived gates which are derived from the fundamental gates.
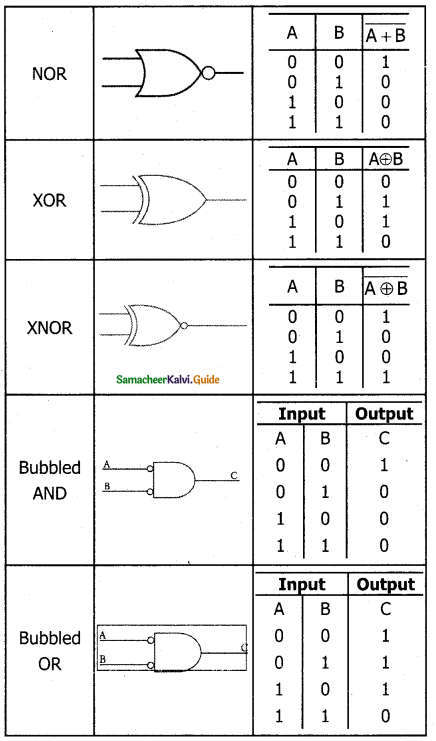
NOR Gate
The NOR gate circuit is an OR gate followed by an inverter. Its output is “true” if both inputs are “false” Otherwise, the output is “false”. In other words, the only way to get ‘1’ as output is to have both inputs ‘O’. Otherwise, the output is 0. The logic circuit of the NOR gate is
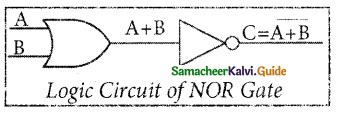
The logic symbol of NOR gate is
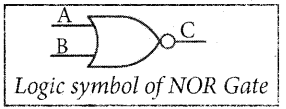
The output of the NOR gate is C = A + B
The truth table for NOR gate is
| Input | Output | |
| A | B | C |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
NAND Gate
The NAND gate operates an AND gate followed by a NOT gate. It acts in the manner of the logical operation “AND” followed by an inversion. The output is “false” if both inputs are “true” otherwise, the output is “true”. In other words, the output of the NAND gate is 0 if and only if both the inputs are 1, otherwise the output is 1. The logic circuit of the NAND gate is
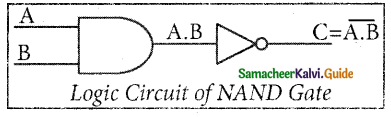
The logical symbol of NAND gate is
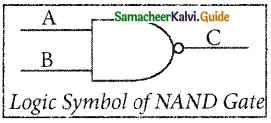
The output of the NAND gate is \(C=\overline{A . B}\)
The truth table for NAND gate is
| Input | Output | |
| A | B | C |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
XOR Gate
The XOR (exclusive – OR) gate acts in the same way as the logical “either/or.” The output is “true” if either, but not both, of the inputs, are “true”. The output is “false” if both inputs are “false” or if both inputs are “true.” Another way of looking at this circuit is to observe that the output is 1 if the inputs are different, but 0 if the inputs are the same. The logic circuit of the XOR gate is
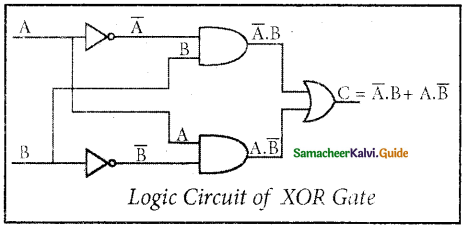
The logical symbol of XOR gate is
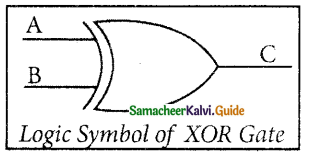
The output of the XOR gate is
\(\begin{aligned}
C &=A \oplus B \\
&=\bar{A} \cdot B+A \cdot \bar{B}
\end{aligned}\)
The truth table for XOR gate is
| Input | Output | |
| A | B | C |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
XNOR Gate
The XNOR (exclusive – NOR) gate is a combination XOR gate followed by an inverter. Its output is “true” if the inputs are the same, and “false” if the inputs are different. In simple words, the output is 1 if the input are the same, otherwise the output is 0. The logic circuit of XNOR gate is
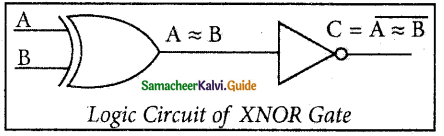
The Logic Symbol is
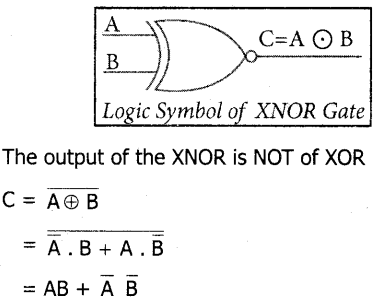
In boolean algebra, \(\mathrm{A} \odot \mathrm{B}\) or “included dot” stands for the XNOR.
Therefore, C = \(\mathrm{A} \odot \mathrm{B}\)
The truth table for XNOR gate is
| Input | Output | |
| A | B | C |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
11th Computer Science Guide Number Systems Additional Questions and Answers
Part I
I. Choose The Correct Answer :
Question 1.
_______ is used for designing digital circuits in a digital computer.
a) Boolean algebra
b) Calculus
c) Iteration
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Boolean algebra
![]()
Question 2.
_______describes the relationship between inputs and outputs of a digital circuit.
a) Boolean algebra
b) Calculus
c) Iteration
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Boolean algebra
Question 3.
Who proposed the basic principles of boolean algebra?
a) George Boole
b) Charles Babbage
c) John Napier
d) Lady Ada Lovelace
Answer:
a) George Boole
Question 4.
The sentences which can be determined to be True or False are called _______ .
a) Logical Statement
b) Truth Functions
c) Either A or B
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Logical Statement
Question 5.
The results of a logical statement True or False are called _______
a) Truth Values
b) Constant
c) True value
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Truth Values
![]()
Question 6.
The truth values depicted by logical constant as_________ .
a) 1
b) 0
c) 1 and 0
d) None of these
Answer:
c) 1 and 0
Question 7.
The truth value depicted by logical constant 1 means _______
a) False
b) True
c) Either True or False
d) None of these
Answer:
b) True
Question 8.
The truth value depicted by logical constant 0 means _______
a) False
b) True
c) Either True or False
d) None of these
Answer:
a) False
Question 9.
The variable which can store truth values are called _______ variables.
a) Logical
b) Binary valued
c) Boolean
d) A OR B OR C
Answer:
a) Logical
Question 10.
Boolean algebra makes use of _______
a) variables
b) operations
c) Both A AND B
d) None of these
Answer:
c) Both A AND B
Question 11.
The basic logical operation is _______
a) AND
b) OR
c) NOT
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
![]()
Question 12.
The basic logical operation AND is symbolically represented by _______.
a) dot (.)
b) plus ( + )
c) over bar / single apostrophe
d) None of these
Answer:
a) dot (.)
Question 13.
The basic logical operation OR is symbolically represented by _______.
a) dot (.)
b) plus ( + )
c) over bar / single apostrophe
d) None of these
Answer:
b) plus ( + )
Question 14.
The basic logical operation NOT is symbolically represented by
a) dot (.)
b) plus ( + )
c) over bar / single apostrophe
d) None of these
Answer:
c) over bar / single apostrophe
Question 15.
_______symbol is called as Logical Operator.
a) dot (.)
b) plus ( + )
c) over bar / single apostrophe
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 16.
A represents all the possible values of logical variables or statements along with all the possible results of a given combination of truth values.
a) Truth table
b) Log table
c) I/O Table
d) None of these
Answer:
a) Truth table
Question 17.
_______boolean operator is similar to multiplication in ordinary algebra.
a) AND
b) OR
c) NOT
d) All the above
Answer:
a) AND
![]()
Question 18.
The AND operator takes _______inputs.
a) only one
b) only two
c) two or more
d) None of these
Answer:
c) two or more
Question 19.
The _______operator output is true only if all the inputs are true.
a) AND
b) OR
c) NOT
d) All the above
Answer:
a) AND
Question 20.
The OR operator takes _______ inputs.
a) only one
b) only two
c) two or more
d) None of these
Answer:
c) two or more
Question 21.
The _______ operator output is true if at least one input is true.
a) AND
b) OR
c) NOT
d) All the above
Answer:
b) OR
Question 22.
The _______operator has one input and one output
a) AND
b) OR
c) NOT
d) All the above
Answer:
c) NOT
![]()
Question 23.
The ______operator inverts the input.
a) AND
b) OR
c) NOT
d) All the above
Answer:
c) NOT
Question 24.
Identify the true statements from the following.
a) The NOT operator input is either true or false and the output is always the opposite.
b) Boolean algebra is a mathematical discipline that is used for designing digital circuits.
c) The AND operator will give only one output
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 25.
The_________is the combination of NOT and AND.
a) NOR
b) NAND
c) XNOR
d) Bubbled AND
Answer:
b) NAND
Question 26.
The _________is generated by inverting the output of an OR operator.
a) NOR
b) NAND
c) XNOR
d) Bubbled AND
Answer:
b) NAND
Question 27.
The algebraic expression of the NAND function is:
a) \(Y=\overline{A . B}\)
b) \(Y=\overline{A+B}\)
c) \(Y=\overline{\bar{A} \cdot \bar{B}}\)
d) \(Y=\bar{A} \cdot \bar{B}\)
Answer:
a) \(Y=\overline{A . B}\)
![]()
Question 28.
The _________ is the combination of NOT and OR.
a) NOR
b) NAND
c) XNOR
d) Bubbled AND
Answer:
a) NOR
Question 29.
The ____________ is generated by inverting the output of an AND operator.
a) NOR
b) NAND
c) XNOR
d) Bubbled AND
Answer:
a) NOR
Question 30.
The algebraic expression of the NOR function is:
a) \(Y=\overline{A . B}\)
b) \(Y=\overline{A+B}\)
c) \(Y=\overline{\bar{A} \cdot \bar{B}}\)
d) \(Y=\bar{A}+\bar{B}\)
Answer:
b) \(Y=\overline{A+B}\)
Question 31.
_________ is a fundamental logic gate.
a) AND
b) NAND
c) NOT
d) Bubbled AND
Answer:
d) Bubbled AND
![]()
Question 32.
is a derived gate.
a) NOR
b) NAND
c) XNOR
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 33.
is not a derived gate.
a) BUBBLED AND
b) NAND
c) XNOR
d) NOT
Answer:
d) NOT
Question 34.
A . is a basic electronic circuit which operates on one or more signals to produce an output signal.
a) logic gate
c) boolean algebra
c) boolean gate
d) None of these
Answer:
a) logic gate
Question 35.
_________gate is called universal gate.
a) NAND
b) NOR
c) NAND and NOR
d) None of these
Answer:
c) NAND and NOR
Question 36.
The fundamental logic gates can be realized through _________gate.
a) NAND
b) NOR
c) NAND and NOR
d) None of these
Answer:
c) NAND and NOR
![]()
Question 37.
The _________ gate has only one input.
a) NAND
b) NOR
c) NOT
d) XNOR
Answer:
c) NOT
Question 38.
A bubbled AND gate produces the same output as a _________gate.
a) NAND
b) NOR
c) NOT
d) XNOR
Answer:
b) NOR
Question 39.
We can replace e.v H NOR gate by a _________gate.
a) NAND
b) NOR
c) Bubbled AND
d) Bubbled OR
Answer:
c) Bubbled AND
Question 40.
The output of NOR gate is _________if both inputs are “false”.
a) true
b) false
c) either true or false
d) None of these
Answer:
a) true
Question 41.
The output of the NAND gate is 0 if and only if both the inputs are _________
a) 0
b) 1
c) false
d) None of these
Answer:
b) 1
![]()
Question 42.
The truth tables of the bubbled OR gate and _________ gates are identical.
a) NAND
b) NOR
c) Bubbled AND
d) XOR
Answer:
a) NAND
Question 43.
We can replace each NAND gate by a _________gate.
a) NAND
b) NOR
c) Bubbled AND
d) Bubbled OR
Answer:
d) Bubbled OR
Question 44.
A+B represents _________ gate
a) XOR
b) NOR
c) NOT
d) XNOR
Answer:
a) XOR
Question 45.
In XOR gate, the output is _________ if the inputs are different.
a) 0
b) 1
c) 1 or 0
d) None of these
Answer:
b) 1
Question 46.
In XOR gate, the output is _________if the inputs are same.
a) 0
b) 1
c) 1 or 0
d) None of these
Answer:
a) 0
![]()
Question 47.
The _________gate is a combination XOR gate followed by an Inverter.
a) XOR
b) NOR
c) NOT
d) XNOR
Answer:
d) XNOR
Question 48.
A ® B represent _________gate.
a) XOR
b) NOR
c) NOT
d) XNOR
Answer:
d) XNOR
Question 49.
Identify the true statement from the following.
a) Using a combination of logic gates, complex operations can be performed.
b) Arrays of logic gates are found in digital integrated circuits.
c) In boolean algebra, © or “included dot” stands for the XNOR.
d) All the above
Answer:
d) All the above
Question 50.
AB + \(\overline{\mathbf{A}} \overline{\mathbf{B}}\) is the equation for gate.
a) XOR
b) NOR
c) NOT
d) XNOR
Answer:
d) XNOR
Question 51.
\(\bar{A} B+A B\) is the equation for _________gate.
a) XOR
b) NOR
c) NOT
d) XNOR
Answer:
a) XOR
![]()
Question 52.
The logical symbol of XOR gate is _________.
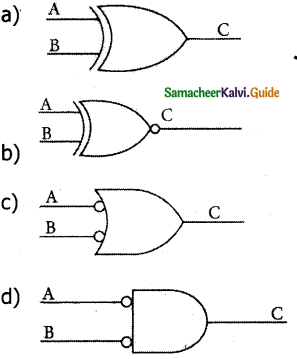
Answer:
a
Part II
Short Answers:
Question 1.
What are the logical operations?
Answer:
The basic logical operations are AND, OR, and NOT, which are symbolically represented by a dot ( . ), plus ( + ), and over bar / single apostrophe respectively. These symbols are also called “Logical Operators”.
Question 2.
What is Truth Table?
Answer:
A truth table represents all the possible values of logical variables or statements along with all the possible results of a given combination of truth values.
Question 3.
Write a note on NOT operator.
Answer:
The NOT operator has one input and one output. The input is either true or false, and the output is always the opposite, that is, the NOT operator inverts the input.
The truth table for a NOT operator where A is the input variable and Y is the output is shown below:
| A | Y |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
The NOT operator is represented algebraically by the Boolean expression: Y = A.
The truth table for NAND gate is \(\mathbf{Y}=\overline{\mathbf{A}}\)
Question 4.
What are the universal gates? Why it is called so?
Answer:
NAND and NOR gates are called Universal gates because the fundamental logic gates can be realized through them.
![]()
Question 5.
What is logic gate? What are the fundamental logic gates?
Answer:
A gate is a basic electronic circuit which operates on one or more signals to produce an output signal.
There are three fundamental gates namely AND, OR, and NOT.
Question 6.
Write the commutative theorem of boolean algebra.
Answer:
i) A + B = B + A
ii) A . B = B . A.
Question 7.
Write the associative theorem of boolean algebra.
Answer:
i) A + (B + C) = (A + B) + C
ii) A . (B . C) = (A . B) . C.
Question 8.
Write the distributive theorem of boolean algebra.
Answer:
i) A . (B + C) = A . B + A . C
ii) A + (B . C) = (A + B) . (A + C).
Question 9.
Write the absorption theorem of Boolean algebra.
Answer:
i) A + (A . B) = A
ii) A . (A + B) = A.
Question 10.
Write the 3rd distributive theorem of Boolean algebra.
Answer:
A + A 1 B = A + B
Question 11.
Write the De Morgan’s theorems of Boolean algebra.
\(i) \overline{\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{B}}=\overline{\mathrm{A}} \cdot \overline{\mathrm{B}}
ii) \overline{\mathrm{A} \cdot \mathrm{B}}=\overline{\mathrm{A}}+\overline{\mathrm{B}}\)
Question 12.
Write the Null element theorem of Boolean algebra.
Answer:
i) A + 1 = 1
ii) A . 0 = 0
Question 13.
Write the Identity theorem of Boolean algebra.
Answer:
i) A + 0 = A
ii) A . 1 = A
![]()
Question 14.
Write the complement theorem of Boolean algebra.
Answer:
i) A + A = 1
ii) A . A = 0.
Part – III
Explain In Brief
Question 1.
Write note on AND operator.
Answer:
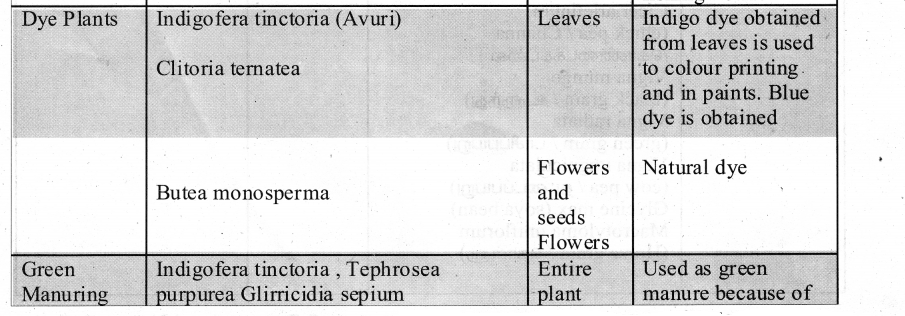
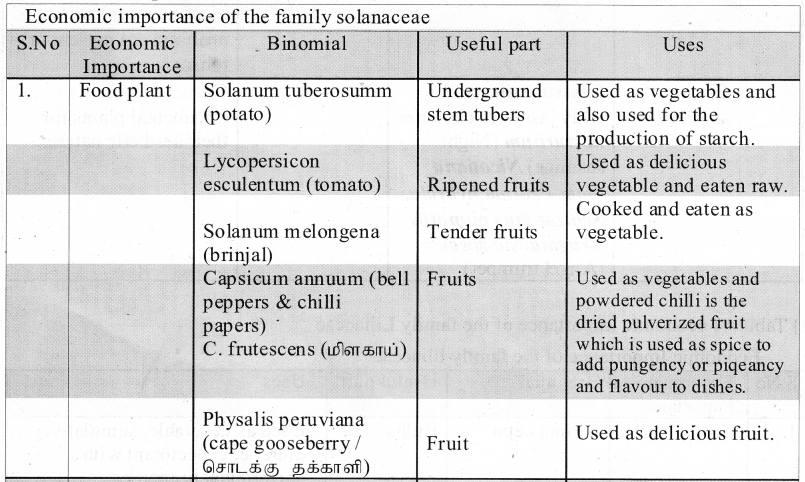
The AND operator is defined in Boolean algebra by the use of the dot (.) operator. It is similar to multiplication in ordinary algebra. The AND operator combines two or more input variables so that the output is true only if all the inputs are true. The truth table for a 2-input AND operator is shown as follows:
| A | B | Y |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| .1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
The above 2-input AND operation is expressed as:
Y = A . B.
Question 2.
Write note on OR operator.
Answer:
The plus sign is used to indicate the OR operator. The OR operator combines two or more input variables so that the output is true if at least one input is true. The truth table for a 2-input OR operator is shown as follows:
| A | B | y |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
The above 2-input OR operation is expressed as Y = A + B.
![]()
Question 3.
Write a note on the NAND operator.
Answer:
The NAND is the combination of NOT and AND. The NAND is generated by inverting the output of an AND operator. The algebraic, expression of the NAND function is: Y = \(\overline{\mathrm{A}, \mathrm{B}}\)
The NAND function truth table is shown below:
| A | B | y |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
A NAND B = NOT (A AND B).
Question 4.
Write a note on the NOR operator.
Answer:
The NOR is the combination of NOT and OR. The NOR is generated by inverting the output of an OR operator. The algebraic expression of the NOR function is: Y = \(\overline{A+B}\)
The NOR function truth table is shown below:
| A | B | y |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
A NOR B = NOT (A OR B).
Question 5.
Explain AND gate with its symbols and truth table.
Answer:
The AND gate can have two or more input signals and produce an output signal. The output is “true” only when both inputs are “true” otherwise, the output is “false”. In other words, the output will be 1 if and only if both inputs are 1; otherwise, the output is 0.
The output of the AND gate is represented by a variable say C, where A and B are two and if input boolean variables. In boolean algebra, a variable can take either of the values ‘0’ or ‘1’. The logical symbol of the AND gate is
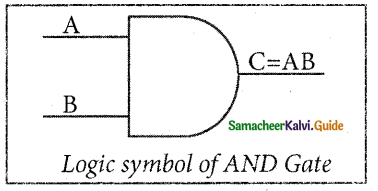
One way to symbolize the action of an AND gate is by writing the boolean function.
C = A AND B
In Boolean algebra, the multiplication sign stands for the AND operation. Therefore, the output of the AND gate is
C = A . B or simply C = AB
The truth table for AND Gate is
| Input | Output | |
| A | B | C |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
![]()
Question 6.
Explain OR gate with its symbols and truth table.
Answer:
The OR gate gets its name from its behaviour like the logical inclusive “OR”. The output is “true” if either or both of the inputs are “true”. If both inputs are “false” then the output is “false”. In other words, the output will be 1 if and only if one or both inputs are 1; otherwise, the output is 0. The logical symbol of the OR gate is
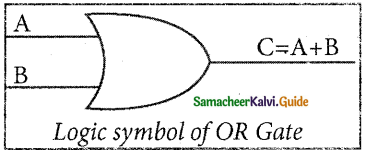
The OR gate output is C = A OR B
We use the + sign to denote the OR function.
Therefore, C = A + B
The truth table for OR gate is
| Input | Output | |
| A | B | C |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
The boolean function of NOT gate is C = NOT A In boolean algebra, the overbar stands for NOT operation. Therefore, \(C=\bar{A}\)
Question 7.
Explain NOT gate with its symbols and truth table.
Answer:
The NOT gate, called a logical inverter, has only one input. It reverses the logical state. In other words, the output C is always the complement of the input. The logical symbol of the NOT gate is

The boolean function of NOT gate is C = NOT A
In boolean algebra, the overbar stands for NOT operation. Therefore, \(C=\bar{A}\)
The truth table for NOT gate is
| Input | Output |
| A | C |
| 1 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 |
![]()
Question 8.
Explain NOR gate with its symbols and truth table.
Answer:
The NOR gate circuit is an OR gate followed by an inverter. Its output is “true” if both inputs are “false” Otherwise, the output is “false”. In other words, the only way to get ‘1’ as output is to have both inputs ‘O’. Otherwise, the output is 0. The logic circuit of the NOR gate is
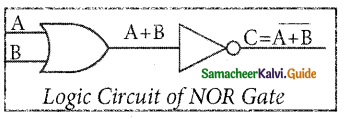
The Logic Symbol of NOR Gate is
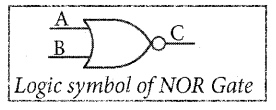
The output of NOR gate is \(C=\overline{A+B}\)
The truth table for NOR gate is
| Input | Output | |
| A | ‘ B | C |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Question 9.
Explain Bubbled AND gate with its symbols and truth table.
Answer:
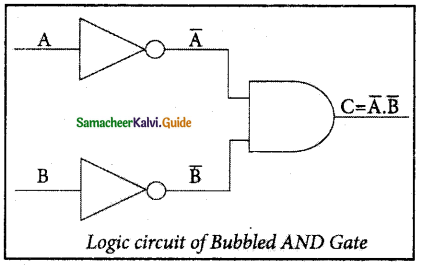
The Logic Circuit of Bubbled AND Gate
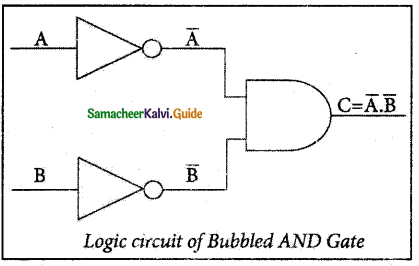
In the above circuit, inverters on the input lines of the AND gate gives the output as C = A.B.
The Logic symbol of Bubbled AND Gate is
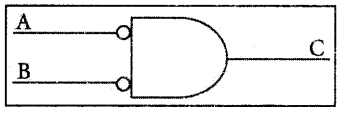
The truth table of Bubbled AND Gate is
| Input | Output | |
| A | B | C |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Part IV
Explain In Detail
Question 1.
Explain Bubbled OR gate with its symbols and truth table.
Answer:
The logic circuit of bubbled OR gate is
The output of this circuit can be written as \(C=\bar{A}+\bar{B}\)
The Logic symbol of Bubbled OR Gate is
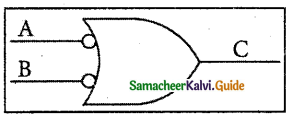
The truth table for the bubbled OR is
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the XOR gate with its symbols and truth table.
Answer:
The XOR (exclusive – OR) gate acts in the same way as the logical “either/or.” The output is “true” if either, but not both, of the inputs, are “true”. The output is “false” if both inputs are “false” or if both inputs are “true.”
Another way of looking at this circuit is to observe that the output is 1 if the inputs are different, but 0 if the inputs are the same.
The Logic circuit of XOR Gate is
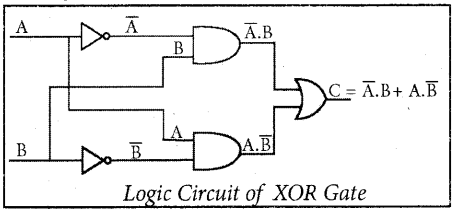
The output of the XOR gate is
\(C=A \oplus B=\bar{A} B+A B\)
The Logic symbol of XOR Gate is
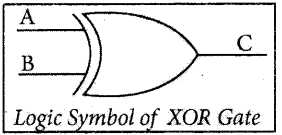
The truth table for XOR gate is
| Input | Output | |
| A | ‘ B | C |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Question 3.
Explain the XNOR gate with its symbols and truth table.
Answer:
The XNOR (exclusive – NOR) gate is a combination XOR gate followed by an inverter. Its output is
true” if the inputs are the same, and “false” if the inputs are different. In simple words, the output is 1 if the input are the same, otherwise, the output is 0.
The logic circuit of the XNOR gate is
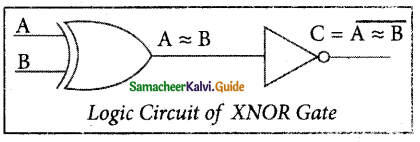
The output of the XNOR is NOT of XOR
\(C=(A \oplus B)^{\prime}=A B+\bar{A} \bar{B}\)
In boolean algebra, 0 or “included dot” stands for
the XNOR.
Therefore, C = \(\mathrm{A} \odot \mathrm{B}\)
The logical symbol is
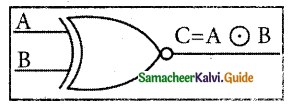
The truth table for the XNOR gate is
| Input | Output | |
| A | ‘ B | C |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
![]()
Question 4.
Write all the theorems of boolean algebra.
Answer:
Theorems of boolean algebra.
Identity
A + 0 = A
A • 1 = A
Complement
\(\begin{array}{l}
A+\bar{A}=1 \\
A \cdot \bar{A}=0
\end{array}\)
Commutative
A + B = B + A
A . B = B . A
Associative
A + (B + C) = (A + B) + C
A . (B . C) = (A; B) . C
Distributive
A-(B + C) = A- B + A- C
A + (B . C) = (A + B) . (A + C)
Null Element
A + 1 = 1
A . 0 = 0
Involution
\((\overline{\bar{A}})=A\)
Indempotence
A + A = A
A . A = A
Absorption
A + (A . B) = A
A . (A + B) = A
3rd Distributive
A + A.B = A + B
De Morgan’s
\(\begin{aligned}
\overline{A+B} &=\bar{A} \cdot \bar{B} \\
\overline{A . B} &=\bar{A}+\bar{B}
\end{aligned}\)
![]()
Question 5.
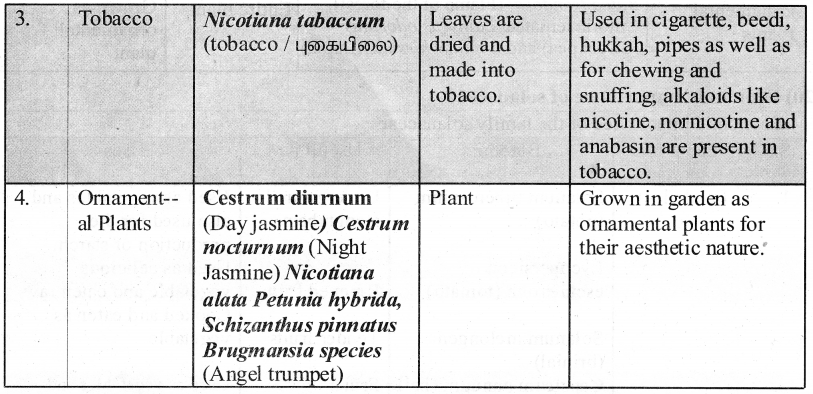
List all the logic gates with their symbols and truth tables.
Answer:
Logic Gates and their corresponding Truth Tables