Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Botany Guide Pdf Chapter 6 Cell The Unit of Life Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Bio Botany Solutions Chapter 6 Cell The Unit of Life
11th Bio Botany Guide Cell The Unit of Life Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Choose The Right Answers:
Question 1.
The two subunits of ribosomes remain united at a critical level of
a) Magnesium
b) Calcium
c) Sodium
d) Ferrous
Answer:
a) Magnesium
Question 2.
Sequence of which of the following is used to know the phylogeny
a) mRNA
b) rRNA
c) tRNA
d) HnRNA
Answer:
d) HnRNA
![]()
Question 3.
Many cells function properly and divide mitotically even they do not have
a) Plasma membrane
b) Cyto skeleton
c) Mitochondria
d) Plastids
Answer:
d) Plastids
Question 4.
Keeping in view the Fluid mosaic model for the structure of cell membrane which one of the following statements is correct with respect to the movement of lipids & Proteins from one lipid mono layer to the other
a) Neither lipid nor protein can flip flop
b) Both lipid and protein can flip flop
c) While lipid can rarely flip flop proteins cannot
d) While proteins can flip flop but lipids cannot ,
Answer:
c) While lipids can rarely flip-flop proteins cannot
![]()
Question 5.
Match the columns and identify the correct option:
Answer:
|
Column I |
Column II |
| a. Thylakoids | Disc shaped sacs in Golgi apparatus |
| b. Cristae | Condensed structure of DNA |
| c. Cistemae | Flat membrane sacs in stroma |
| d. Chromatin | In folding in Mitochondria |
(a) (b) (c) (d)
(1) (iii) (iv) (ii) (i)
(2) (iv) (iii) (i) (ii)
(3) (iii) (iv) (j) (ii)
(4) (iii) (i) (iv) (ii)
Answer:
(3) (iii) (iv) (i) (ii)
Question 6.
Bring out the significance of Phase Contrast Microscope
Answer:
Phase-contrast microscope is used to observe living cells, tissues and the cells cultured invitro during mitosis.
![]()
Question 7.
State the Protoplasm theory
Answer:
- Fischer in 1894 & Hardy ( 1899 ) Proposed the Colloidal theory of Protoplasm (the physical basis of life)
- It is a colloidal system with water, many biological import things, glucose, fatty acids, amino acids minerals, vitamins hormones & enzymes are seen.
- Homogenous -These solutes are soluble
- Heterogenous – Solutes are not soluble – This Forms the basis for its colloidal nature.
- Protoplasm occur in 2 states but interconvertible

Question 8.
Distinguish between Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes.
Answer:
|
Prokaryotes |
Eukaryotes |
|
| Size of cell | 1-5 cm | 10 -100 cm True Nucleus |
| Nuclear character | Nucleoid or incipient nucleus only (No nuclear membrane or Nucleolus | Nucleolus & Nuclear membrane present |
| DNA | Usually Circular without histone protein | Usually linear with histone proteins |
| RNA/ Protein synthesis | Couples in Cytoplasm | RNA Synthesis inside Nucleus / Protein synthesis in the cytoplasm) |
| Ribosomes | 50 s +30 s (70s) | 60s + 40s ( 80s) |
| Organelles | Absent | Numerous |
| Cell Movement | Flagella | Flagella & Celia |
| Organisation | Usually unicellular | Single, Colonial and multicellular |
| Cell division | Binary Fission | Mitosis & Meiosis |
| Example | Bacteria & Archae Bacteria | Fungi, Plants, and Animals |
Question 9.
Difference between plant and animal cell:
Answer:
|
Plant Cell |
Animal Cell |
| 1.Usually they are large than animal cell | Usually smaller than plant cell |
| 2. Cell wall present in addition to plasma membrane and consists of middle lamellae. Primary and secondary walls | Cell wall absent |
| 3. Plasmaodesmata present | Plasmodesmata absent |
| 4. Chloroplast present | Chloroplast absent |
| 5. Centrioles absent except motile cells of lower plants | Vacuole small and temporary |
| 6. Vacuole larger and pennanent | Tonoplast absent |
| 7. Tonoplast present around vacuole | Centrioles present |
| 8. Nucleus present along the periphery of the cell | Nucleus at the centre of the cell |
| 9. Lysosomes are rare | Lysosomes present |
Question 10.
Draw the ultrastructure of a plant cell:
Answer:
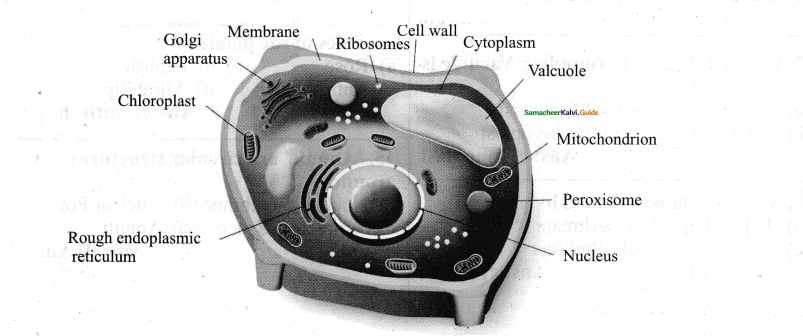
Part-A
Choose The Right Answer:
Question 1.
Scientist who named the unicellular particles as ‘animalcules’ …………… .
(a) Aristotle
(b) Robert Brown
(c) Antonie von Leeuwenhoek
(d) Robert Hooke
Answer:
(c) Antonie van Leeuwenhoek
Question 2.
Compound microscope was invented by
a) Robert brown
b) Z. Sigmody
c) Z. Jansen
d) Zenike
Answer:
C) Z. Jansen
![]()
Question 3.
Micrometry is a technique of measurement of
a) Microtomy
b) Nanoparticles
c) Microscopic Objects
d) Moving objects
Answer:
c) Microscopic Objects
Question 4.
Which of the following electron opaque chemical is used in Electron microscope?
(a) Strontium
(b) Deuterium
(c) Palladium
(d) Uranium
Answer:
(c) Palladium
![]()
Question 5.
Who first observed Protoplasm
a) Corti
b) Felix Dujardin
c) Hugo Van Mohl
d) O. Hertwig
Answer:
a) Corti
Question 6.
Dinoflagellates and Protozoa are kept under
a) MegaKaryotes
b) Prokaryotes
c) Eukaryotes
d) Mesokaryola
Answer:
d) Mesokaryota
![]()
Question 7.
Which among the following is NOT an exception to cell theory?
(a) Viruses
(b) Viroids
(c) Prions
(d) Fungi
Answer:
(d) Fungi
Question 8.
Michondria was named by
a) A.kolliker
b) Altmann
c) Benda
d) Purkinje
Answer:
c) Benda
![]()
Question 9.
When Thylakoids are stacked together like a pile of coins known as
a) Grana
b) Cistemae
c) Quantosomes
d) Polysomes
Answer:
a) Grana
Question 10.
Dense particulars or granules observed by George Palade is known as
a) Cirtemae
b) Lamella
c) Locules
d) Ribosomes
Answer:
d) Ribosomes
![]()
Question 11.
Histone proteins are seen in the DNA of …………… .
(a) Pseudokaryotes
(b) Prokaryotes
(c) Mesokaryotes
(d) Eukaryotes
Answer:
(d) Eukaryotes
Question 12.
These are also known as Microbodies
a) Mitochondrial & Ribosomes
b) Ribosomes & Cistemao
c) Polysomes & Vacuoles
d) Peroxisomes & Glyoxysomes
Answer:
d) Peroxisomes & Glyoxysomes
![]()
Question 13.
The organelle made up of nine triplet peripheral fibrils are known as
a) Microbodies
b) Tululin
c) Centrosome
d) Centroles
Answer:
d) Centroles
Question 14.
Fungal cell wall is made of …………… .
(a) Cutin
(b) Chitin
(c) Hemicellulose
(d) Pectin
Answer:
(b) Chitin
![]()
Question 15.
‘Annule’ are circular structure seen around
a) Nuclear membrane
b) Nuclear Pore
c) Perinuclear Space
d) Annuli
Answer:
d) Annuli
Question 16.
The Chromosome that occur in the oocyte of Salamander and in Giant nucleus of Acetabularia is known as
a) Polytene Chromosome
b) Lamp brush chromosome
c) Mitochondrial chromosome
d) Chloroplast chromosome
Answer:
b) Lamp brush chromosome
![]()
Question 17.
Ordinary microscope can be made into Dark Field Microscope (DFM) by means of a special component is called
a) Patch stop carrier
b) Secondary Magnification lens
c) Stage
d) Phase plate
Answer:
a) Patch stop Carrier
Question 18.
In-plant cells, golgi bodies are found as small vesicles called …………… .
(a) Polysomes
(b) Cytosomes
(c) Cytosol
(d) Dictyosomes
Answer:
(d) Dictyosomes
![]()
Question 19.
Cisternae, tubule and Vesicles occur in which of the following:
a) Golgi apparatus
b) Lysosomes
c) Endoplasmic reticulum
d) Glyoxysomes
(i) a & b
(ii) b & c
(iii) c & d
(iv) a & c
Answer:
(iv) a & c
Question 20.
The Golgi apparatus in plant is known as
a) Dictyosomes
b) Glyoxysomes
c) Neo-particles
d) Microvesides
Answer:
a) Dictyosomes
![]()
Question 21.
Which of the three, come under the system of the membrane in Eukaryotic cell
a) Mitochondria
b) Nuclear Membrane
c) Golgi apparatus
d) Endoplasmic reticulum
(i) a, b & c
(ii) b, c & d
(iii) a, c & d
(iv) a, b & d
Answer:
(ii) b, c & d
Question 22.
DNA of mitochondrion is …………… .
(a) Helical
(b) Dumbbell
(c) Circular
(d) Spiral
Answer:
(c) Circular
![]()
Question 23.
Fluid droplets are engulfed by membrane, which form vesicles around them
a) Phagocytosis
b) Exocytosis
c) Endocytosis
d) Pinocytosis
Answer:
d) Pinocytosis
Question 24.
The 60 s large subunit of Eukaryotes contain
a) 23 s & 5 s – large subunit
b) 16 s r RNA in large subunit
c) 18 s r RNA in large subunit
d) 28 s, 5-8 sand 5 s in large subunit
Answer:
d) 28 s, 5-8 sand 5 s in large subunit
![]()
Question 25.
Elaioplasts store …………….
(a) Starch
(b) Lipid
(c) Protein
(d) Chlorophyll
Answer:
(b) Lipid
II. State whether the following statement True or False with reference to the origin of Eukaryotes.
1. A Prokaryote grow in size and develop infoldings in its cell membrane to increase surface area to volume ratio
2. Aerobic protea bacterium enter eukaryote as prey or parasite and become an endosymbiont
3. Proteobacteria eventually assimilated and became mitochondria
4. Some Prokaryotes go on to acquire additional Exo symbionts the cyanobacteria evolve to become chloroplasts.
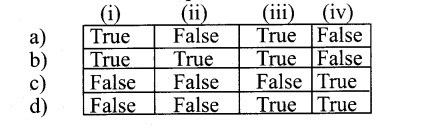
Answer:
b) True, True, True, False
![]()
Question 2.
Find out the true and false statements from the following and on that basis And the correct answer.
(i) In Prokaryotes the flagellar rotation, only proton movements are involved & not ATP.
(ii) In Eukaryotes to shift the adjacent microtubules to bend cilia or flagella, dynein use energy from ATP
(iii) Bacterial flagella are made up of helical polymers of protein known as Tubulin
(iv) In Eukaryotes the flagella are made up of microtubules and proteins known as dynein and nexin.
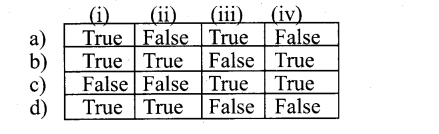
Answer:
b) True True False True
Question 3.
With reference to Eukaryotic flagellum Find out the true or false statements from the following and on that basis find the correct answer
(i) Flagellum is shorter than cilia as short as 200 µm
(ii) Flagella are microtubule projection of plasma membrane
(iii) Flagella composed of 8 pairs of microtubules with 2 pairs of microtubules in the center
(iv) Structure of Flagella has Axoneme made up of microtubules & protein tubules
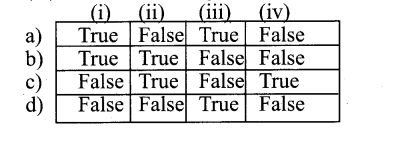
Answer:
c) False True False True
![]()
Question 4.
(i) Cytoplasm is the physical basis of life
(ii) Cytoplasm inheritance occurs only through the plasma genes
(iii) Cytoplasm serves as a molecular soup where all the cellular organelles are suspended and bound together by a lipid bilayer plasma membrane
(iv) Cytoplasm is a very bad conductor of electricity.
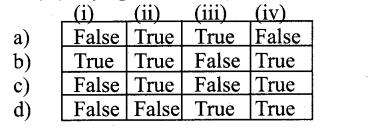
Answer:
a) False True True False
Question 5.
Find out the true or false statements from the following and on that basis find the correct answer
(i) The contractibility of protoplasm is important for the absorption and removal of water, especially in stomatal operations
(ii) The viscosity of protoplasm is 2-20centipoises
(iii) The protoplasm is made of 10-20% of water
(iv) Brownian movement and Tyndall effect are colloidal properties, so not applicable to protoplasm
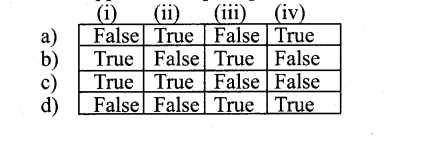
Answer:
d) True True False False
![]()
II. Choose The Wrong Match
Question 1.
(a) Cytoplith – Hypodermal leaf cells of ficus bengaliensis
(b) Raphides – Eichhomia leaves
(c) Sphaero raphides – Colocasia
(d) Silica – Oryza sativa
Answer:
d) Silica – Oryza sativa
Question 2.
Choose the wrong match with reference to mitochondria
(a) Protein – 73%
(b) Lipids – 25-30%
(c) DNA – 12%
(d) RNA – 5-7%
Answer:
c) DNA-12%
![]()
Question 3.
(i) Centrosome give rise to spindle fibers in Animal cell
(ii) Golgibodies play important role in packaging and secretion
(iii) Endoplasmic reticulum-SER is involved in protein synthesis
(iv) Vacuoles facilitate the transport of ions and materials in plant cell
Answer:
(iii) Endoplasmic reticulum SER is involved in protein synthesis
Question 4.
(i) The magnification of SEM & its resolving power is – 200000 &5-20nm
(ii) The magnification &resolution power of temis – 1 – 300000&2-10A
(iii) The magnification power of TEM is – 100000 then the light microscope
(iv) The magnification power of phase-contrast – 3 – 40000 & 8-10A microscope &its resolution power
Answer:
(iv) The magnification power contrast is microscope & its resolution power – 3-400000 & 8-10A
IV. Choose The Right Match From The Following
Question 1.
(i) Size of mycoplasma – 0.15-0.03 µm
(ii) Size of BGA – 60mm
(iii) Size of RBC – 0.25-0.06 µm
(iv) Size of chick egg – 7-811mm
Answer:
(i) Size of mycoplasma – 0.15-0.03µm
![]()
Question 2.
Choose the right match:
(i) Volutin granules occurin -Bacteria
(ii) Ttannin – Cassia auriculata
(iii) Calcium carbonate – Mimosa pudica
(iv) Heavy metals – Erchhornia
Answer:
(i) Volutin granules- Bacteria
Question 3.
Choose the right match:
(i) Cell theory – Cortix
(ii) Protoplasm theory – Max Schultze
(iii) Chromosomes physical carriers of genes – Strasburger
(iv) Endoplasmic reticulum word coined by – Benda
Answer:
(ii) Protoplasm theory – Max Schultze
V. Match The Following And Find The Correct Answer:
Question 1.
(i) Harry Beevers – (A) identified Lysosomes a Peroxisomes
(ii) Christian Do Duve – (B) Discovered Glycoxysome c
(iii) A-F-U- Schimper – (C) Coined the word Chromosome
(iv) Waldeyer – (D) Coined the word Plastids
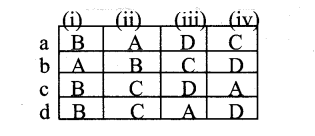
Answer:
a) B A D C
![]()
Question 2.
(i) When the small pieces of golgibody pinches off from its tubules to form – A. Chioroplast
(ii) Fernandez moran particles occur in – B. Golgi apparatus
(iii) Zymogen granules occur in – C. Lysosome
(iv) Quantosomes are present in – D. Mitochondria
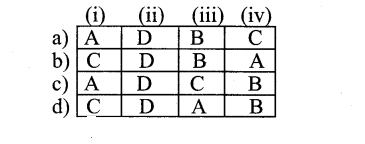
Answer:
b) C D B A
Question 1.
ASSERTION (A): A cell membrane shows fluid behavior
REASON (R): A membrane is- a mosaic or composite of diverse lipids and proteins
a) Assertion and Reason are correct ‘R’ explaining ‘A’
b) A and R-correct ‘R’ not explaining A
c) A is true, but R is wrong
d) A is true but R is not explaining A
Answer:
(a) Assertion A & Reason R are correct R is explaining A
![]()
Question 2.
Assertion (A): Chloroplast is an important cell organelle performing photosynthesis in plants
Reason (R): An organelle is a distinct part of a cell which has a particular structure and function.
a) A and R are correct R explaining A
b) A and R correct and R not explaining A
c) A is true, but R is wrong
d) A is true but R is not explaining A
Answer:
b) A and R correct R not explaining A
Question 3.
Assertion (A): The inheritance of Mitochondria is uniparental
Reason (R): Mitochondria of any one of the parenting divide and gets distributed to daughter cells.
a) A and R are correct R explaining A
b) A and R are correct R not explaining A
c) A is true but R is wrong
d) A is true but R is not explaining A
Answer:
(c) A is true but R is wrong
![]()
Question 4.
Assertion (A): The objective of optic lenses of a microscope are interchanged, then it can work as a telescope
Reason (R): The objective of the telescope has a small focal length
(a) A and R are correct R explaining A
(b) A and R are correct R not explaining A
(c) A is true but R is wrong
(d) A is true but R is not explaining A
Answer:
(d) A is true but R is not explaining A
Question 5.
Assertion (A): A polytene achieved by repeated replication of chromosomal DNA without nuclear division. The daughter chromatids aligned side by side called Endomitosis
Reason (R): Polytenes is observed in the salivary glands of Drosophila by C.G.Balbiani. 1881.
a) A and R are correct R explaining A
b) A and R are correct R not explaining A
c) A is true but R is wrong
d) A is true but R is not explaining A
Answer:
(b) A and R correct R not explaining A
![]()
Two Marks Questions
Question 1.
Name the scientist who proposed the cell theory.
Answer:
Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann.
Question 2.
ER- can be referred to as the endoskeleton of the cell. Justify.
Answer:
- Yes. It connects plasma membrane & nuclear membrane, giving support to the Cytosol so we can call it the endoskeleton of the cell.
- It also helps in the exchange of substances in and out of the cell.
![]()
Question 3.
Why do we say that viruses are an exception to its cell theory?
Answer:
Viruses lack protoplasm, the essential parts of the cell, and are existing as obligate parasites (i.e)(subcellular particles).
Question 4.
Who said that different kinds of plastids can transform into one another?
Answer:
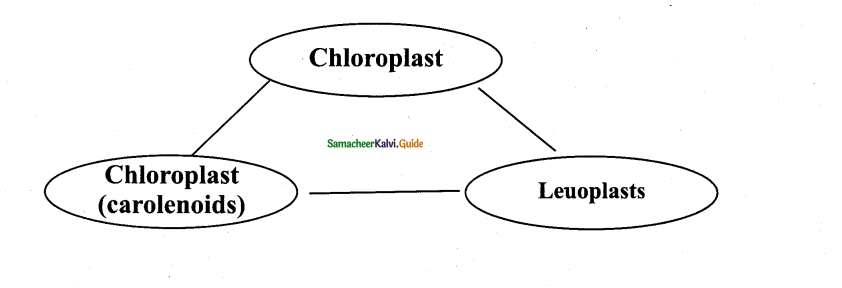
A-F-U Schimper said that the 3 different kinds of plastids can transform into one another according to the need or demand of the plant body.
![]()
Question 5.
In a Bright field microscope, where does the primary & secondary magnification occurs?
Answer:
Primary magnification is obtained through, objective lens, and secondary magnification is obtained through an eye piece lens.
Question 6.
State the functions of chloroplast
Answer:
- They are organs of Photosynthesis.
- Light reactions & dark reactions take place in the granum & stroma respectively.
- Chloroplast also play important role in the Photorespiration or C2 cycle.
![]()
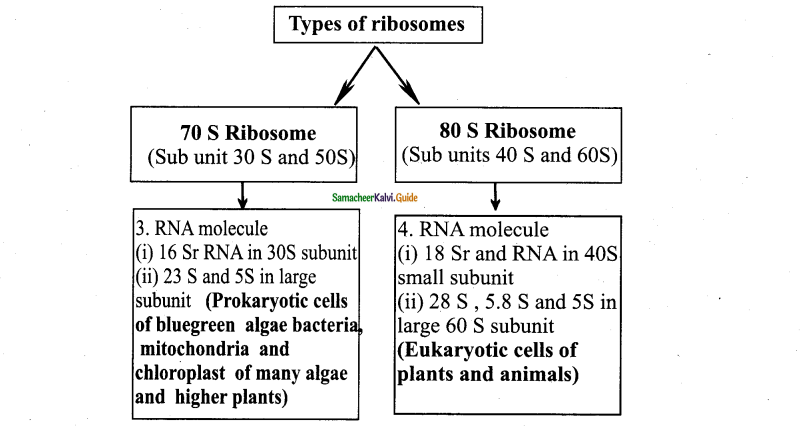
Question 7.
Distinguish between 70’s & 80’s Ribosomes.
Answer:
Question 8.
Name the types of cells based on nuclear characteristics.
Answer:
The types of cells based on nuclear characteristics:
- Prokaryotes
- Mesokaryotes and
- Eukaryotes.
Question 9.
Distinguish between glyoxysomes, peroxysomes & sphaerosomes
Answer:
| GLYOXYSOMES | PEROXYSOMES | SPHAEROSOMES |
| Single membrane-bound &sub cellular organelle | Single membrane-bound & subcellular organelle | Single membrane-bound & subcellular organelle |
| Contain enzymes of the glyoxylate pathway | Contain enzymes and play important role in C2 cycle or Photorespiration | They play important role in the storage of fats in the endoplasm cells of oilseeds |
| Beta oxidation of fatty acids occurs in the glyoxysomes of germinating seeds | ||
| Eg. Castor seeds | Eg. Occur in all green plants | Eg. Coconut Castor seeds |
Question 10.
Distinguish between Resolution & Magnification:
Answer:
| RESOLUTION | MAGNIFICATION |
| Ability of lenses to show the finest details between two points form Resolution R | It is the size of the image seen with eye, magnified by the microscope |
| Formula = \(R=\frac{0.61 \lambda}{(\mathrm{NA})}\) where,λ -wavelength of light NA-numerical aperture |
Formula = Size of image seen with microscope Size of image seen with normal eyes |
![]()
Question 11.
Differentiate 4 points of differences between Prokaryotes & Mesokaryotes
Answer:
|
PROKARYOTES |
MESOKARYOTES |
| Nucleoid no true nucleus | Nucleus with nuclear membrane |
| 1-5µm | 5- 10µm |
| DNA usually circular without | DNA linear but without |
| histone proteins | histone proteins |
| Ribosomes 50S+30S | 60S+40S |
| Organelles absent | Organelles present |
| Eg. bacteria & archaea | Eg. Dinoflagellate, Protozoa |
Question 12.
Write down any 4 functions of cell wall
Answer:
|
NAME OF THE CELL WALL |
FUNCTIONS OF THE CELL WALL |
| SHAPE | It offers definite Shape and Rigidity |
| BARRIER | It prevents the entry of several molecules into the cell |
| PROTECTION | Protects internal protoplasm against mechanical injury |
| Prevents cell from bursting | lit maintains osmotic pressure and prevent cell from bursting |
| DEFENSIVE DEVICE | It plays a major role by acting as a defensive device |
Question 13.
Differentiate between TEM and SEM:
Answer:
|
TEM |
SEM |
| It has a high resolving power | Resolving power Comparatively lower |
| Most commonly used | Occasionally used depending on the study |
| 2-dimensional image is provided | 3D image is provided |
| Magnification 1-3 lakhs times | Magnification 2 lakhs times |
| Resolving power 2-10A° | Resolving power 5-20 nm |
Question 14.
Explain signal transduction:
Answer:
DEFINITION:
- It is a process by which a cell receives information from outside and respond to it is called signal transduction
- Nitric oxide → is the main signally molecule
- Cell membrane → site of chemical interaction of signal transduction
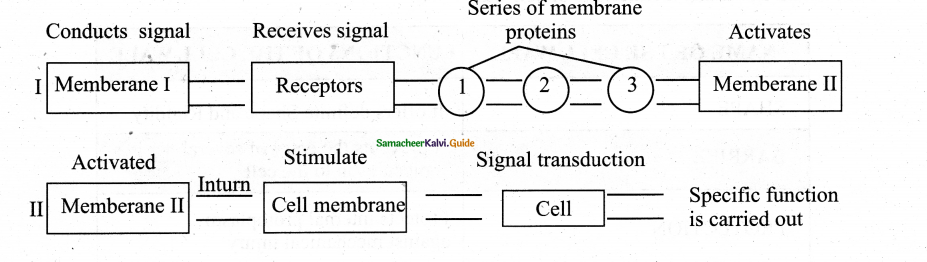
![]()
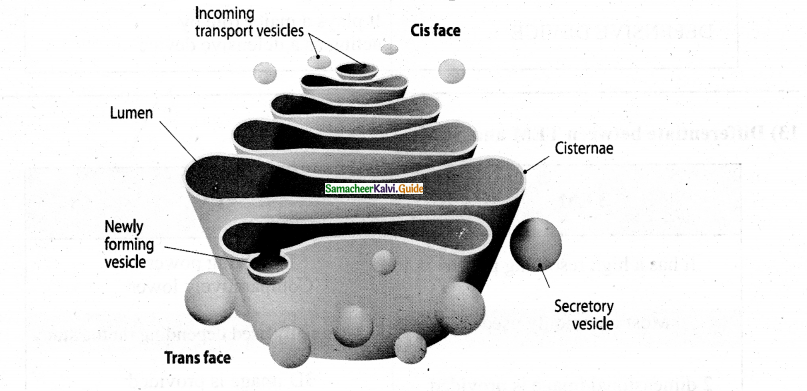
Question 15.
Draw the structure of the Golgi apparatus & label its parts.
Answer:
Question 16.
What is the cell wall composition of the following organism?
(a) Fungi
(b) Bacteria
(c) Algae
Answer:
(a) Fungi – Chitin and fungal cellulose.
(b) Bacteria – Peptidoglycan
(c) Algae – Cellulose, mannan and galactan.
![]()
Question 17.
What is meant by Holocentric chromosomes?
Answer:
If a chromosome has centromere activity distributed along the whole surface of the chromosome during mitosis (i.e) microtubules distributed all along the mitotic chromosome.
Eg. Caenorhabditis Elegans (transparent nematode) & many insects.
Question 18.
Differentiate between point centromere & Regional centromere.
Answer:
|
POINT CENTROMERE |
REGION AL CENTROMERE |
| The kinetochore is assembled as a result of protein recognition of specific DNA sequences Kinetochores assembled on point centromere bind a single microtubule localized, Centromere Eg. Budding Yeasts |
The kinetochore is assembled on a variable array of repeated DNA sequences Kinetochore assembled on regional centromeres, bind multiple microtubules Eg. Fission yeast cells, Human cells |
Question 19.
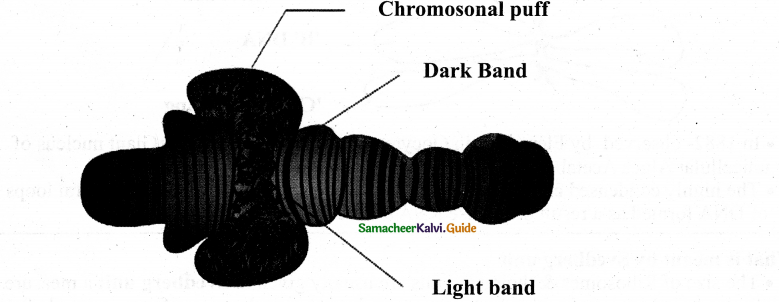
Draw the structure of the polytene chromosome:
Answer:
Question 20.
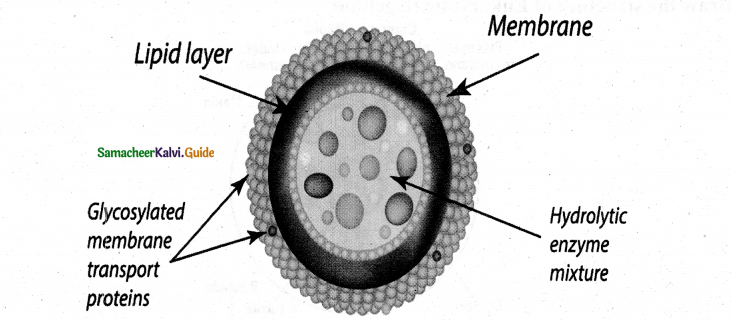
Draw the structure of the lysosome.
Answer:
Three Mark Questions
Question 1.
Distinguish between autosomes & allosomes.
Answer:
|
AUTOSOMES |
ALLOSOMES |
| In human diploid cells out of 46, only 44 chromosomes are Autosomes | Only 2 chromosomes are Allosomes or Sex chromosomes |
| They are controlling somatic characteristics of an organism | They are involved in Sex determination |
Question 2.
Explain lampbrush chromosomes:
Answer:
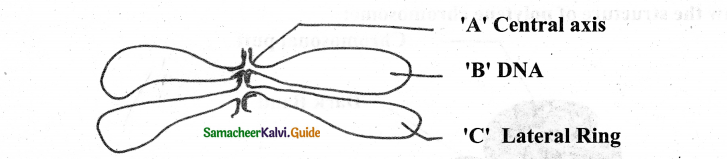
- In 1882- observed by Flemming in Oocytes of animal Salamander &Giant nucleus of unicellular Algae Acetabularia
- The highly condensed chromosomes form a chromosomal axis, from which lateral loops of DNA formed as a result of intense RNA synthesis
![]()
Question 3.
Define cytoplasmic streaming.
Answer:
Cytoplasmic streaming refers to the movement of the cytoplasm along with the cellular materials inside the cell.
![]()
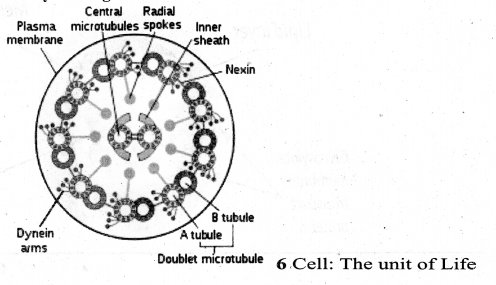
Question 4.
Draw the structure of the Eukaryotic flagellum.
Answer:
Question 5.
List out the functions of the Cell Wall.
Answer:
The cell wall plays a vital role in holding several important functions given below.
- Offers definite shape and rigidity to the cell.
- Serves as barrier for several molecules to enter the cells.
- Provides protection to the internal protoplasm against mechanical injury.
- Prevents the bursting of cells by maintaining the osmotic pressure.
- Plays a major role by acting as a mechanism of defense for the cells.
![]()
Question 6.
Explain in detail about Fluid mosaic model.
Answer:
Jonathan Singer and Garth Nicolson (1972) proposed fluid model: It is made up of lipids and proteins together with a little amount of carbohydrate. The lipid membrane is made up of phospholipid. The phospholipid molecule has a hydrophobic tail and hydrophilic head. The hydrophobic tail repels water and water-loving polar molecule are called hydrophilic molecule. They have polar phosphate group responsible for attracting water. Water-hating non – polar molecule are called as a hydrophobic molecules. They have fatty acid which is non – polar which cannot attract water.
Hydrophilic head attracts water. The proteins of the membrane are globular proteins which are found intermingled between the lipid bilayer most of which are projecting beyond the lipid bilayer. These proteins are called as integral proteins. Few are superficially attached on either surface of the lipid bilayer which are called as peripheral proteins. The proteins are involved in the transport of molecules across the membranes and also act as enzymes, receptors or antigens.
Question 7.
Draw the structure of the chromosome & neatly label the parts:
Answer:
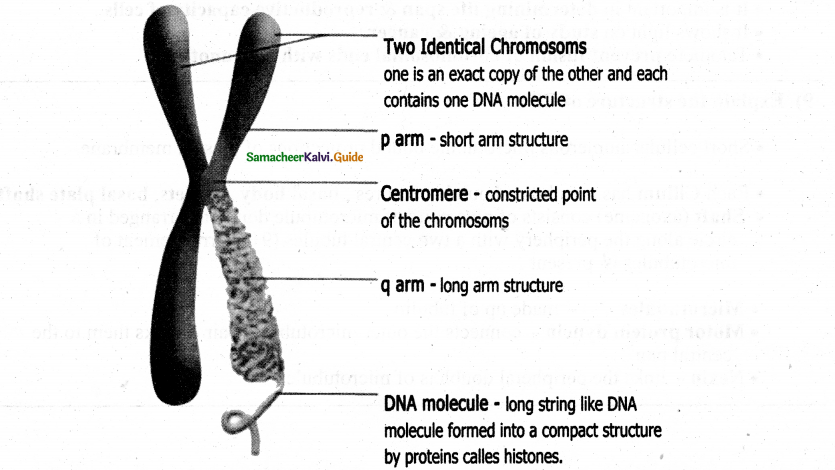
Question 8.
Based on the position of centromere classify the chromosomes with the help of diagrams.
Answer:
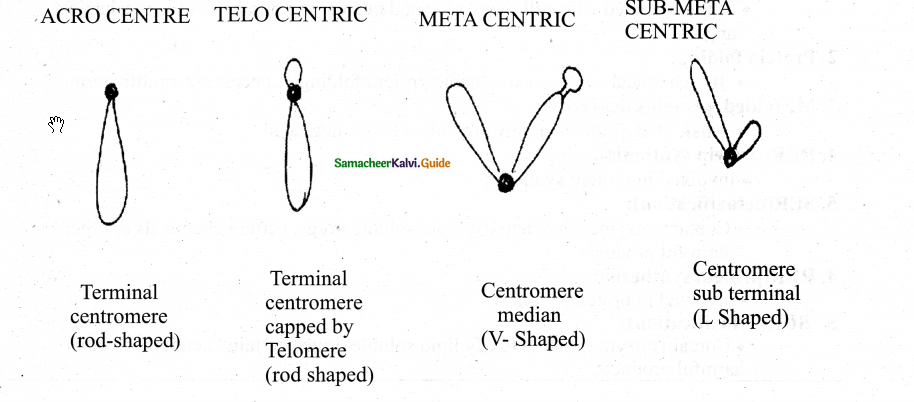
Eukaryotic chromosomes may be rod-shaped telo & acrocentric as well as meta & sub-meta-centric.
![]()
Question 9.
List out the functions of Golgi bodies.
Answer:
Functions of Golgi bodies:
- Glycoproteins and glycolipids are produced.
- Transporting and storing lipids.
- Formation of lysosomes.
- Production of digestive enzymes.
- Cell plate and cell wall formation
- Secretion of carbohydrates for the formation of plant cell walls and insect cuticles.
- Zymogen granules (proenzyme / pre-cursor of all enzymes) are synthesized.
Question 10.
Explain the structure of Cilia.
Answer:
- Short cellular-numerous microtubule bound projections of plasma membrane.
- Each Cilium has membrane-bound structures, basal body,rootlets, basal plate shaft
- Shaft (axoneme) consists of nine pairs of microtubule doublets, arranged in a
- circle along the periphery with a two central tubules (9+2) arrangement of microtubules is present.
- Microtubules – made up of tubulin.
- Motor protein dynein – connects the outer microtubules pair & links them to the central pair.
- Nexin – links the peripheral doublets of microtubules.
Question 11.
Write in detail about the 3 types of centromere in eukaryotes.
Answer:
There are three types of centromere in Eukaryotes. They are as follows:
- Point Centromere: The type of centromere in which the kinetochore is assembled as a result of protein recognition of specific DNA sequences. Kinetochores assembled on point centromere bind a single microtubule. It is also called a localized centromere. It occurs in budding yeasts.
- Regional Centromere: In regional centromere where the kinetochore is assembled on a variable array of repeated DNA sequences. Kinetochore assembled on regional centromeres bind multiple microtubules. It occurs in fission yeast cell, humans and so on.
- Holocentromere: The microtubules bind all along the mitotic chromosome. Example: Caenorhabditis Elegans (transparent nematode) and many insects.
![]()
Question 12.
Distinguish between primary wall & secondary wall of the plant cell wall.
Answer:
|
PRIMARY WALL |
SECONDARY WALL |
| First formed | Formed later |
| Thin elastic, extensible | Thick inelastic |
| Matrix made up of Hemi cellulose-bind micro, fibrils with matrix Pectinase- filling material, Glycoprotein-control orientation of microfibrils Water | Here cellulose & pectin compactly arranged with different orients giving a laminated structure to give strength to the cell wall. |
| Only one layer | Has three sub-layers s1,s2,s3. |
| Does not determine shape of cell | Determine shape of cell |
Question 13.
Describe the steps involved in cytological techniques.
Answer:
There are different types of mounting based on the portion of a specimen to be observed.
- Whole-mount: The whole organism or smaller structure is mounted over a slide and observed.
- Squash: This is a preparation where the material to be observed is crushed/squashed onto a slide so as to reveal its contents. Example: Pollen grains, mitosis, and meiosis in root tips and flower buds to observe chromosomes.
- Smears: Here the specimen is in the fluid (blood and microbial cultures etc) are scraped, brushed, or aspirated from the surface of the organ. Example: Epithelial cells.
- Sections: Freehand sections from a specimen and thin sections are selected, stained, and mounted on a slide. Example: Leaf and stem of plants.
![]()
Question 14.
List out any 3 stains used in histo- chemistry.
Answer:
| S.No | Stain | Colour of staining | Affinity |
| 1. | Eosin | Pink or red | Cytoplasm, Cellulose |
| 2. | Methylene blue | Blue | Nucleus |
| 3. | Saffranine | Red | Cell wall(lignin) |
| 4. | Janus green | Greenish blue | Mitochondria |
Question 15.
Identify the diagram and label the parts.
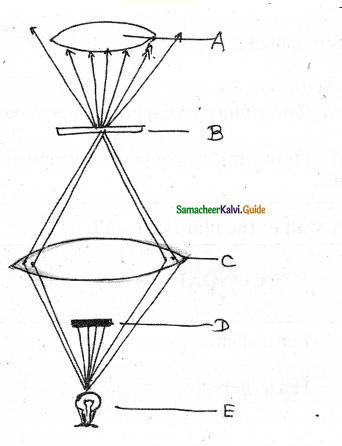
Answer:
This is a dark field microscope
A-objective lens
B-stage
C-condenser lens
D- patch stop
E-light source
Five Mark Questions
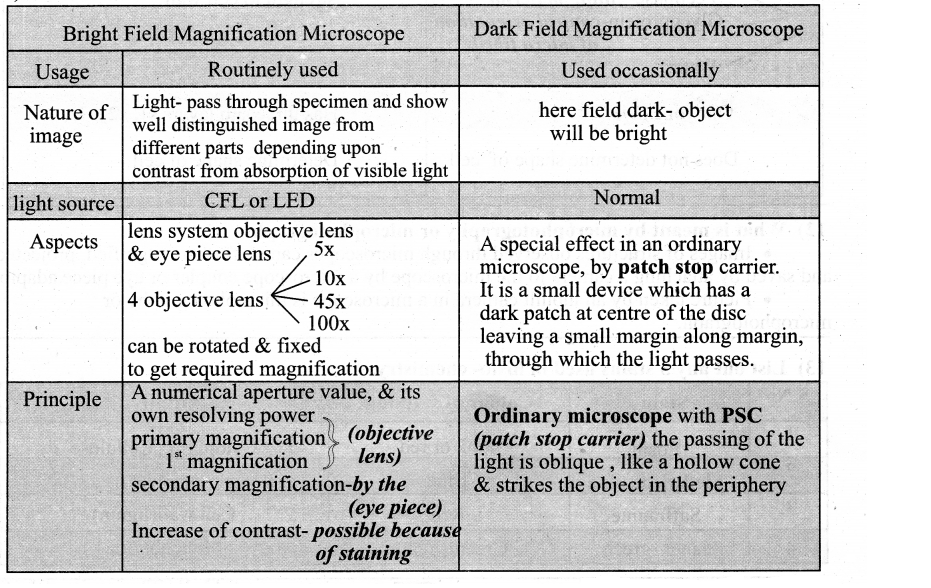
Question 1.
Differentiate between BFM & DFM.
Answer:
Question 2.
Differentiate between Light microscope & electron microscope.
Answer:
|
Light Microscope |
Electron Microscope |
| Another name = compound microscope | 1st introduced by Ernest Ruska & developed by G.Binnin & H. Roher (1981) |
| Principle | Principle |
| The transmission of visible light from the source of eye through a sample | It uses a beam of accelerated electrons as source of illumination. |
| Resolving power – Lesser | Resolving power – Higher |
| Magnification – Less | Magnification-1,00,000 times than the light |
| Purpose – studying in schools & college | Purpose Microscope Research purpose -can be seen in scientific laboratories |
| Pattern of working: The microscope transmits visible light from eye through sample where interaction occur and magnified image is visible. |
The specimen to be viewed under EM should be dehydrated and impregnated with election opaque chemicals like gold, palladium for withstanding electrons & also for contrast. |
| Types :1 Only one | Types: 2 types TEM, SEM |
Question 3.
Write down the functions of the cell wall.
Answer:
|
NAME OF THE CELL WALL |
FUNCTIONS OF THE CELL WALL |
| SHAPE | It gives definite Shape and Rigidity to the ceil |
| BARRIER | It prevents several molecules from entering the cells |
| PROTECTION | To the internal protoplasm against mechanical injury |
| MAINTAIN ANCE | It maintains osmotic pressure So, prevent bursting of cells |
| DEFENCE | They are acting as a source of defense for cells |
Question 4.
Write down the functions of the Plasma Membrane or cell membrane.
Answer:
- Cell transport is the main function
- PM act as a channel of transport for molecules
- PM is selectively permeable to molecules
It transported by
- Energy-dependent processes,
- Energy independent processes Membrane proteins involved processes
- Endocytosis & Exocytosis large quantity of solids and liquids are transported into a cell or out of cells.
I. Endocytosis 2 types
a) Phagocytosis particle is engulfed by membrance which fold around it forming vesicles, enzymes digest and products are absorbed.
b) Pinocytosis Fluid droplets are engulfed by forming vesicles.
II. Exocytosis -Vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane and eject contents.
-This may be a secretion in the case of digestive enzymes hormones or mucus.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the fluid mosaic model of plasma membrane.
Answer:
- Jonathan Singer & Garth Nicolson (1972) proposed FM model.
- Plasma membrane made up of lipid (phospholipid), protein & little carbohydrate.
I. Phospholipid: Molecule has a hydrophobic tail(repel water) & hydrophilic head (water-loving)
II. Protein of membrane
- Globular in nature intermingles between lipid bipolar most perfect beyond Jt known
as (integral proteins)
Few are superficially attached on either surface of lipid bilayer (peripheral proteins)
- They are involved in transport of molecules across the membrane
- They acts as enzymes
- They acts as receptors or antigens.
III Carbohydrate
- They are short chain of polysaccharides.
(i.e) With protein glycoprotein With lipid glycolipids, glycocalyx
Flip Flapping:
- The movement of membrane lipids from one side of the membrane to the other side by vertical movement called flip-flap movement.
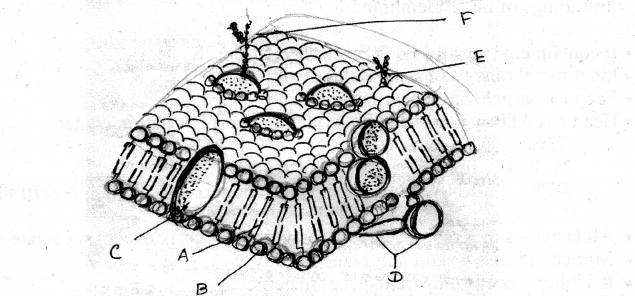
Answer:
A- hydrolipid tail,
B-hydrophilic head,} lipid
C-intrisic protein
D-extrinsic protein
This movement is very slow than lateral diffusion of lipid molecules.
- Phospholipids can flip flop due to smaller polar regions.
- Proteins cannot do so because of extensive polar regions.
Question 6.
Give an account of the structure and function of mitochondria.
Answer:
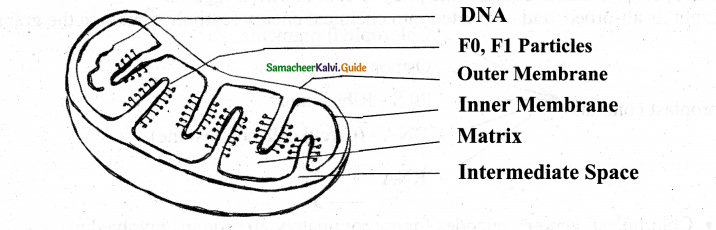
- 1st observed by A. Kolliker (1880)
- Altmann(1894) – named it as Bio-plasts
- Benda (1897) – named as Mitochondria
Structure
- Ovoid, rod-shaped, pleomorphic structures
- Double membrane
- Outer membrane smooth, & permeable- contain porins
2 compartments
1. outer chamber between 2 membranes
2. Inner chamber filled with matrix
Cristae – Infoldings of inner membrane:
- It contain enzymes for ETS(Electron Transport System)
- Inner membrane has FI particles or exosomes
- Each FI particle has a base, a stem & a rounded head
- Head has ATP synthetase to do oxidative phosphorylation content.
- 73% protein
- 25-30% lipids
- 5-7% RNA, DNA & enzymes(about 60 circular DNA &70’s Ribosomes.
- All enzymes of Kreb’s cycle are found in the matrix except succinate dehydrogenase.
- Mitochondria is a semi-autonomous body
- It’s inheritance is uniparental (i.e) maternal
- It is used to track recent evolutionary time because it mutates 5-10 times faster than DNA in the nucleus.
![]()
Question 7.
Structure of chloroplast
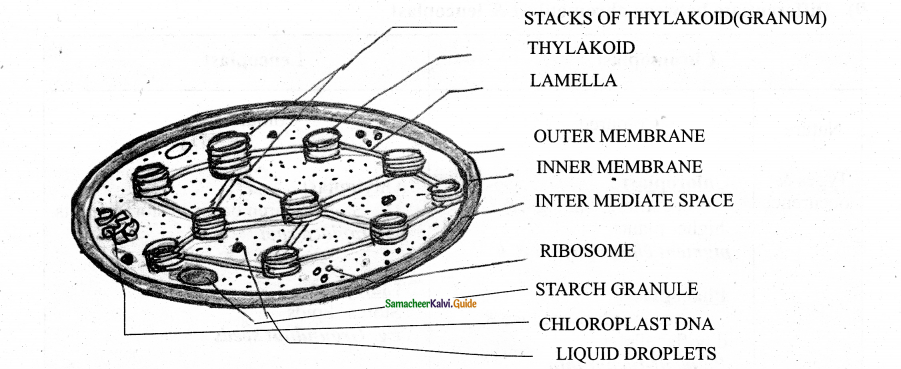
Answer:
- A vital organ of green plants.
- Double membrane-bound organelle peripheral space in between the membrane
- Inner chloroplast is filled with gelatinous stroma
- Inside the stroma interconnected sacs called Thylakoids
- Inner space of the thylakoid is the thylakoid lumen
- Thylakoids stacked together like piles of coins known as grana.
- Light is absorbed and converted into chemical energy (carbohydrates) in the granum
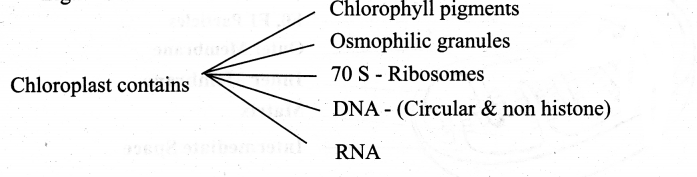
- Chloroplast genome encodes for approximately 30 proteins involved in photosystem I & II – cytochrome, b, f, complex and ATP synthase & also one of the subunits of RUBISCO is enclosed by it.
- RUBISCO- is the major protein component of the stroma single most abundant protein on earth
- The thylakoid contain small, rounded photosynthetic units called Quantosomes
- The chloroplast is semi-autonomous, divided by fission.
Question 8.
Give an account of Ribosomes:
Answer:
- 1953 – 1 observed by George Palade
- Dense particles in the EM not membrane-bound
Electron microscope observation
1. Made up of 2 round subunits one large layer & one small unit to form a complete unit
2. Mg++ is required for complete cohesion.
Biogenesis – denova formation, auto replication and nucleolar origin
Function – Sites of protein synthesis.
Content – consists of
- RNA 60%,
- Protein 40%
Polysemes:
In protein synthesizing cells, many ribosomes attached to single m RNA – to form polysomes’ main role in the formation of several copies of particular.
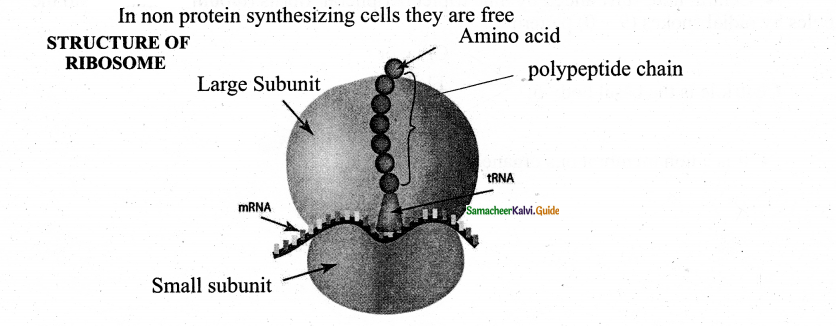
Question 9.
Differentiate between chromoplast & leucoplast
Answer:
|
Chromoplast |
Leucoplast |
|
| Nature | Coloured | Colourless |
| Types & occurence | Chloroplast: occur in green algae& higher plants. Pigment chlorophyll a & b Phaeoplast: occur in brown algae & dinoflagelletes Pigment-fucoanthin Rhodoplast: Occur in red algae Stores protein Pigment phycoerythrin |
Amyloplast Stores starch occur in storage parts Eg. Tapioca rootElaioplast Stores- lipids Eg. Groundnut seeds Aleuroplast or proteoplast Eg. Moon dhal |
Question 10.
State any 3 functions of Lysosomes
Answer:
polypeptide Intracellular digestion:
They digest carbohydrates, proteins & lipids present in the cytoplasm
Autophagy:
During the adverse condition, they digest their own organelles like mitochondria ER
Auto lysis:
Causes self-destruction of cell on the insight of disease
Aging:
Have autolytic enzymes that disrupts intracellular molecules.
![]()
Question 11.
Explain the structure of Centrioles
Answer:
- Central hub, surrounded by nine triplet peripheral fibrils (tubulin) connected to the tubules by radial spokes (9 + 0) pattern Cilia or Flagella Spindle fibres
- Centriole is the basal body of Flagella, Lilia or, Spindle fibers.
- It is a nonmembranous organelle
Question 12.
Differentiate between other inclusions of cells in Prokaryotes & Eukaryotes.
Answer:
|
Prokaryotes |
Eukaryotes |
|
| Reserse material | Phosphate granules & Cyanophycean granules | Starch grains Glycogen granules |
| Organic materials | Poly (3 hydroxyl granules sulphur granules, carboxysomes &Gas vacuoles | Aleurone grains, flat droplets |
| Other secretions | ……………………………. | Essential oil, resins, gums, latex and tannin |
| Inorganic inclusions | metachromatic granules- such as polyphosphate granules (volutin granules) & sulfur granules | Calcium carbonate crystals, Calcium oxalate crystals, Silica crystals Eg.cystolith- hypodermal cells of Ficus bengalensis (calcium carbonate) |
| Raphides- Eichhornia (calcium oxalate) | ||
| Prismatic crystals – dry scales ofAlliumcepa (calcium oxalate) |
Question 13.
Explain the structure of the Nucleus.
- It is important CPU of the cell, the largest part of it
- Control all activities of cell
- Hold the hereditary information
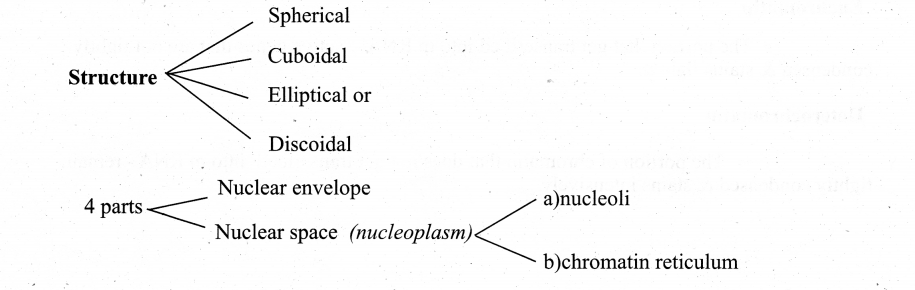 Nuclear envelope Nuclear space (nucleoplasm)
Nuclear envelope Nuclear space (nucleoplasm)
I Membrane:
Double membrane Nuclear envelope
a) Outer membrane
- Rough by the presence of ribosomes and with irregular intervals continues with ER
- It has nuclear pores that allow m RNA, ribosomal units, proteins & other macromolecules to pass in & out
- Nuclear pore enclosed by circular structure – annuli
b) Inner membrane:
Smooth without ribosomes in between the two membranes perinuclear space is present
II. Nucleoplasm:
A gelatinous matrix has 2 parts
- Nucleoli &
- Chromatin reticulum
a) Nucleoli:
- Small dense spherical structure occur in singly or in multiples.
- It possesses genes for r RNA &, tRNA
b) Chromatin network
- Uncoiled, indistinct , thread like structure(inter phase)
- Has little amount of RNA, DNA bound to histone proteins in Eukaryotes
- At the time of cell division – It get condensed to form Chromosome
Euchromatin With -2 parts
1. Euchromatin
2.Heterochromatin
- The portion that get transcribed into rn RNA – active genes that are not tightly condensed & stains lightly.
- Heterochromatin
- The portion of chromatin that does not get transcribed into m RNA – remain tightly condensed & stains intensively.
![]()
Question 14.
Explain the structure of Endoplasmic reticulum
Answer:
- The largest internal membrane (ER)
- Name given by K.R.Porter(1948)
Consists of Vesicles &Tubules, Cisternae
Cisternae:
- Long broad, flat sac-like structures arranged in stacks to form lamella.
- In between membrane is filled with fluid
Vesicles:
Oval membrane-bound vascular structure
Tubules:
Irregular shaped, branched, smooth-walled structure enclosing a space
Function:
- It is associated with nuclear membrane and cell surface membrane
- When ribosomes present on ER- it is known as (RER) Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
- When ribosomes absent on ER- it is known as Smooth Endoplasmic Retiöulum(SER).
![]()