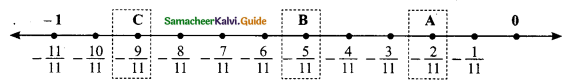
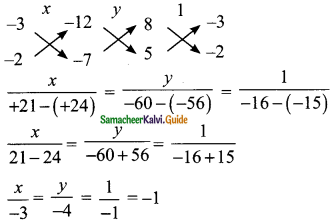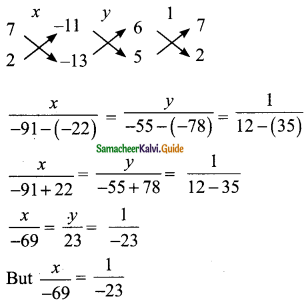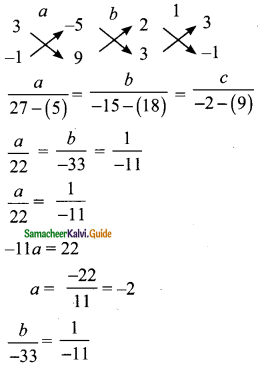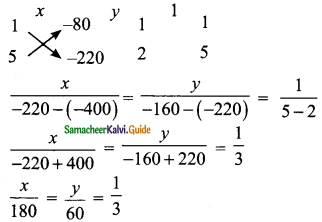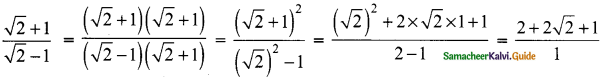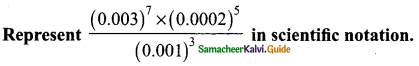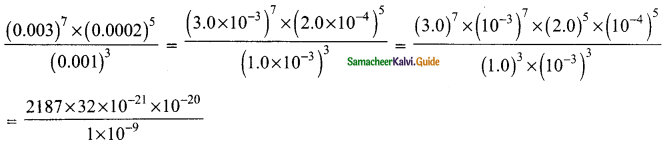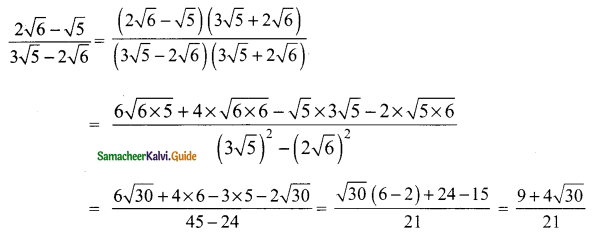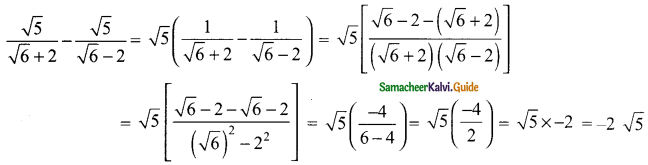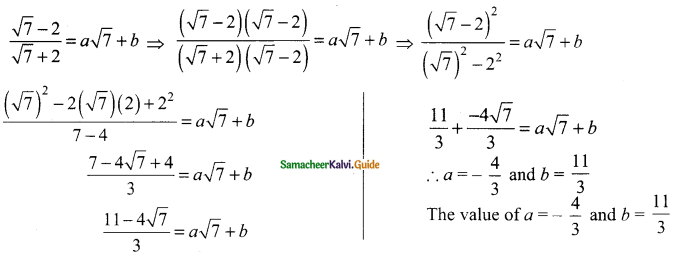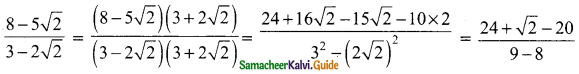Students can download Maths Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.9 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 3 Algebra Ex 3.9
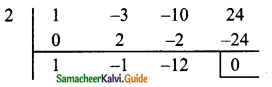
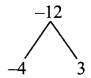
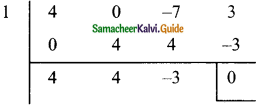
Question 1.
Find the GCD for the following:
(i) P5, P11, P3
Solution:
p5 = p5
p11 = p11
P9 = P9
G.C.D. is p5 (Highest common power is 5)
(ii) 4x3, y3, z3
Solution:
4x3 = 2 × 2 × x3
y3 = y3
z3 = z3
G.C.D. of 4x3, y3 and z3 = 1
![]()
(iii) 9a²b²c3, 15a3b2c4
Solution:
9a²b²c3 = 3 × 3 × a² × b² × c3
15a3b²c3 = 3 × 5 × a3 × b2 × c4
G.C.D = 3 × a2 × b2 × c3
= 3a2b2c3
(iv) 64x8, 240x6
Solution:
64x8 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × x8
= 26 × x8
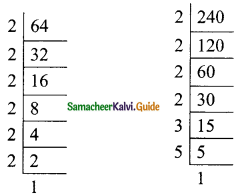
240x6 = 24 × 3 × 5 × x6
G.C.D = 24 × x6
= 16x6
![]()
(v) ab²c3, a²b3c, a3ac²
Solution:
ab²c3 = a × b² × c3
a²b3c = a² × b3 × c
a3bc² = a3 × b × c²
G.C.D. = abc
(vi) 35x5y3z4, 49x2yz3, 14xy2z2
Solution:
35x5y3z4 = 5 × 7 × x5 × y3 × z4
49x²yz3 = 7 × 7 × x2 × z3
14xy²z² = 2 × 7 × x × y² × z²
G.C.D. = 7 × x × y × z²
= 7xyz²
![]()
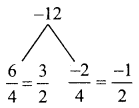
(vii) 25ab3c, 100a²bc, 125 ab
Solution:
25ab3c = 5 × 5 × a × b3 × c
100a²be = 2 × 2 × 5 × 5 × a² × b × c
125ab = 5 × 5 × 5 × a × b
G.C.D. = 5 × 5 × a × b
= 25ab
(viii) 3abc, 5xyz, 7pqr
Solution:
3abc = 3 × a × b × c
5xyz = 5 × x × y × z
7pqr = 7 × p × q × r
G.C.D. = 1
![]()
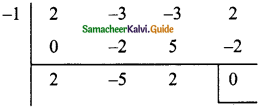
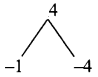
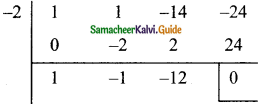
Question 2.
Find the GCD for the following:
(i) (2x + 5), (5x + 2)
(ii) am+1, am+2, am+3
(iii) 2a² + a, 4a² – 1
(iv) 3a², 5b3, 7c4
(v) x4 – 1, x² – 1
(vi) a3 – 9ax², (a – 3x)²
Solution:
(i) (2x + 5) = 2x + 5
5x + 2 = 5x + 2
G.C.D. = 1
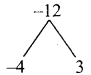
(ii) am+1 = am × a1
am+2 = am × a2
am+3 = am × a3
G.C.D.= am × a
= am+1
![]()
(iii) 2a² + a = a(2a + 1)
4a² – 1 = (2a)2 – 1
(Using a² – b² = (a + b)(a – b)
= (2a + 1)(2a – 1)
G.C.D. = 2a + 1
(iv) 3a² = 3 × a²
5b3 = 5 × b3
7c4 = 7 × c4
G.C.D. = 1
(v) x4 – 1 = (x²)² – 1
= (x² + 1 ) (x² – 1)
= (x² + 1 ) (x + 1 ) (x – 1 )
x² – 1 = (x + 1 ) (x – 1 )
G.C.D. = (x + 1 ) (x – 1 )
![]()
(vi) a3 – 9ax2 = a(a2 – 9x2)
= a[a2 – (3x)2]
= a(a + 3x)(a – 3x)
(a – 3x)2 = (a – 3x)2
G.C.D. = a – 3x