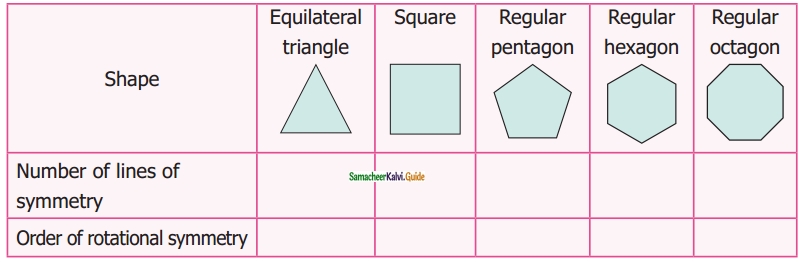
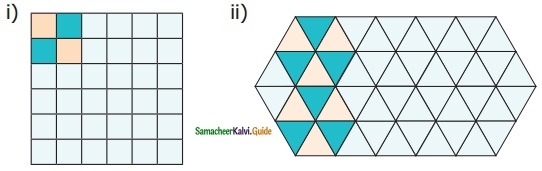
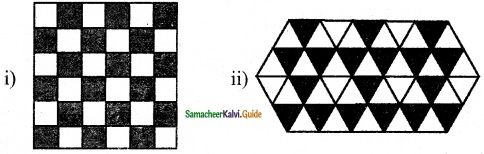
Students can download 6th Science Term 2 Chapter 1 Heat Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 2 Chapter 1 Heat
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Heat Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
When an object is heated, the molecules that make up the object
(a) begin to move faster
(b) lose energy
(c) become heavier
(d) become lighter
Answer:
(a) begin to move faster
Question 2.
The unit of heat is
(a) newton
(b) joule
(c) volt
(d) Celsius
Answer:
(b) joule
![]()
Question 3.
One litre of water at 30°C is mixed with one litre of water at 50°C. The temperature of the mixture will be
(a) 80°C
(b) More than 50°C but less than 80°C
(c) 20°C
(d) around 40°C
Answer:
(d) around 40° C
Question 4.
An iron ball at 50°C is dropped in a mug containing water at 50°C. The heat will
(a) flow from iron ball to water.
(b) not flow from iron ball to water or from water to iron ball.
(c) flow from water to iron ball.
(d) increase the temperature of both.
Answer:
(b) not flow from iron ball to water or from water to iron ball.
II. Fill in the Blanks
- Heat flows from a ……….. body to a ………… body.
- The hotness of the object is determined by its ………..
- The SI unit of temperature is …………
- Solids ……….. on heating and ………… on cooling.
- Two bodies are said to be in the state of thermal ………… if there is no transfer of heat taking place.
Answer:
- hot, cold
- temperature
- Kelvin
- expand, contract
- equilibrium
![]()
III. True or False. If False, give the correct answer.
- Heat is a kind of energy that flows from a hot body to a cold body.
- Steam is formed when heat is released from water.
- Thermal expansion is always a nuisance.
- Borosilicate glass do not expand much on being heated.
- The unit of heat and temperature are the same.
Answer:
- True
- False – Steam is formed when the heat is absorbed from the water.
- False – Thermal expansion is always not a nuisance.
- True
- False – Unit of heat and temperature are different.
IV. Give reasons for the following
Question 1.
An ordinary glass bottle cracks when boiling water is poured into it, but a borosilicate glass bottle does not.
Answer:
The reason is that the borosilicate glass does not expand much on being heated and therefore they do not crack.
Question 2.
The electric wire which sag in summer become straight in winter.
Answer:
- During summer thermal expansion takes place in electric wire.
- In winter it contracts so it becomes straight.
Question 3.
Rivet is heated before fixing in the hole to join two metal plates.
Answer:
- When we heat rivet expansion takes place and becomes soft.
- One end of the rivet is hammered to form a new head.
- When cooled, the rivet will contract and hold tightly.
![]()
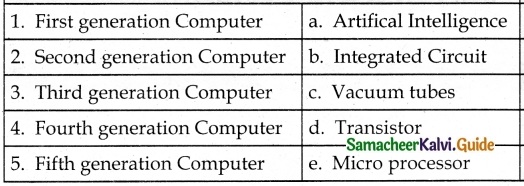
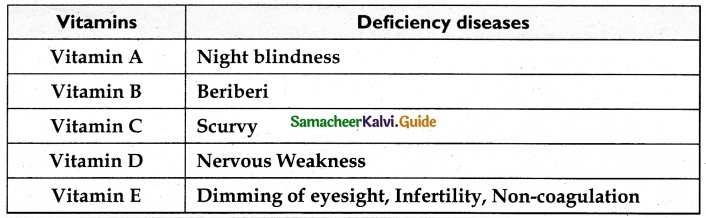
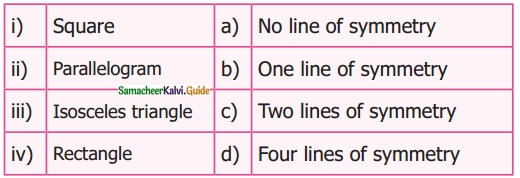
V. Match the following
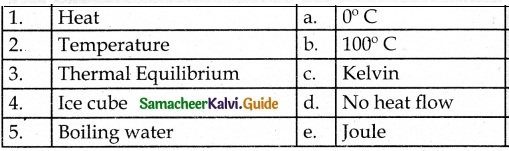
Answer:
1. – e
2. – c
3. – d
4. – a
5. – b
VI. Analogy
- Heat: Joule :: Temperature : ………
- Ice cube : 0°C :: Boiling water : ………..
- Total Kinetic Energy of molecules: Heat:: Average Kinetic Energy : …………….
Answer:
- Kelvin
- 100° C
- Temperature
VII. Give Very Short Answer:
Question 1.
Make a list of electrical types of equipment at home from which we get heat.
Answer:
Water heater, Iron box, Electric kettle, Micro oven.
Question 2.
What is the temperature?
Answer:
The measurement of the warmness or coldness of a substance is known as its temperature.
Question 3.
What is thermal expansion?
Answer:
The expansion of a substance on heating is called thermal expansion.
![]()
Question 4.
What do you understand by thermal equilibrium?
Answer:
When two objects in thermal contact, no longer affect each other’s temperature, there exists Thermal equilibrium.
VIII. Give Short Answer:
Question 1.
What difference do you think heating the solid will make in their molecules?
Answer:
- When we heat solids the vibrations and movement of molecules will increase.
- The temperature of the object increases.
- The distance between molecules will increase.
Question 2.
Distinguish between heat and temperature.
Answer:
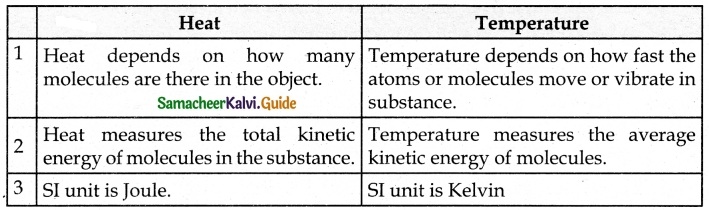
IX. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
Explain thermal expansion with suitable examples.
Answer:
Thermal expansion: The expansion of a substance on heating is called, the thermal expansion of that substance.
Fitting the iron rim on the wooden wheel:
- The diameter of the iron ring is slightly less than that of the wooden wheel.
- So, it cannot be easily slipped on from the rim of a wooden wheel.
- The iron ring is, therefore, first heated to a higher temperature so that it expands in size and the hot ring is then easily slipped over to the rim of the wooden wheel.
- Coldwater is now poured on the iron ring so that it contracts in size and holds the wooden wheel tightly.
Rivetting:
- Rivets are used to join two steel plates together.
- Hot rivet is driven through the hole in the plates.
- One end of the rivet is hammered to form a new rivet head.
- When cooled, the rivet will contract and hold the two plates tightly together.
Cracking of a thick glass tumbler:
- Glass is a poor conductor of heat.
- When hot liquid is poured into the tumbler, the inner surface of the tumbler becomes hot and expands while the outer surface remains at room temperature and does not expand.
- Due to this unequal expansion, the tumbler cracks.
![]()
X. Questions based on Higher Order Thinking Skills
Question 1.
When a window is accidentally left open on a winter night, will you feel uncomfortable because the cold is getting in, or because the heat is escaping from the room?
Answer:
- When a window is left open on a winter night I will feel uncomfortable because the heat is escaping from the room.
- The heat will transfer from high temperature to low temperature.
- During winter cold air enters the room, so room temperature will decrease.
Question 2.
Suppose your normal body temperature was lower than what it is. How would the sensation of hot and cold change?
Answer:
- When our body temperature is lower than normal temperature, We feel hot from the surrounding.
- Because the surrounding temperature will be high compare to our body.
Question 3.
If you heat a circular disk with a hole, what change do you expect in the diameter of the hole? Remember that the effect of heating increases the separation between any pair of particles.
Answer:
Many of us “expect” that the diameter of the hole will decrease because the circular disk is free to expand in all directions as well. Note that expansion of metal due to heating is not like gas spreading out wherever space is available. The correct way to think about it is as follows: Hole size is irrelevant in this case. So we can think that hole is very large.
If we carve a hole so large that its radius is slightly less than that of the circular disk itself, then we will have a ring. It is obvious that the radius of the ring will increase, as atoms have more energy so their oscillation amplitude will increase. As the diameter of the ring increases, the diameter of the hole will also increase.
For example, if you want to insert one hallow pipe inside another hollow pipe of the same diameter, just heat anyone and insert the second one into the heated pipe. This explains the answer in an easy way. So it says that diameter will increase with increasing temperature.
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Heat Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the right answer:
Question 1.
When an electric current is passing through the conductor …………… energy is produced.
(a) Electric
(b) Heat
(c) Chemical
(d) Kinetic energy
Answer:
(b) Heat
Question 2.
One day in 1922, the air temperature was measured at 59°C in the shade in Libya ________
(a) America
(b) Africa
(c) Antarctica
(d) Europe
Answer:
(b) Africa
![]()
Question 3.
The temperature of boiling water is …………..
(a) 0° C
(b) 32° C
(c) 100° C
(d) 110° C
Answer:
(c) 100°C
Question 4.
The temperature determines the direction flow of _______
(a) heat energy
(b) kinetic energy
(c) potential energy
(d) light energy
Answer:
(a) heat energy
Question 5.
When we cool the liquid it will become …………..
(a) Gas
(b) Solid
(c) Vapour
(d) None
Answer:
(b) Solid
II. Say True or False.
- Heat is measured in Celsius or centigrade.
- Temperature in the form of energy.
- The normal temperature of our body is 37°C.
- Two objects are said to be in thermal contact if they can exchange heat energy.
- When the vibrations move from one molecule to another molecule heat will flow.
Answer:
- False
- False
- True
- True
- True
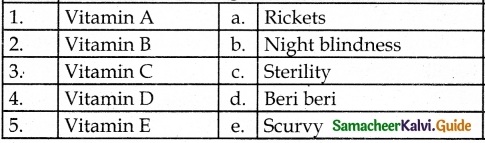
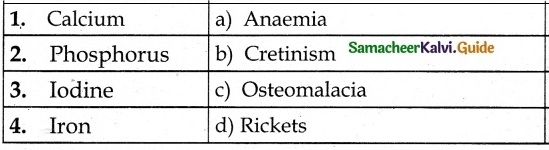
III. Match the Following:
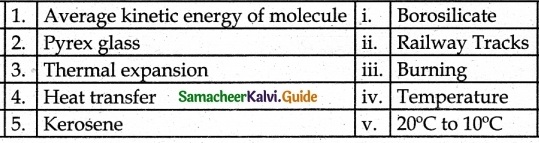
Answer
1. – iv
2. – i
3. – ii
4. – v
5. – iii
![]()
IV. Analogy
- Summer : Sag :: Winter : …………
- Evaporation : 100°C :: Freezing : …………
Answer:
- contract
- 0°C
V. Give reasons for the following:
Question 1.
Gaps are left in between rails while laying a railway track.
Answer:
Reason: During summer thermal expansion takes place.
Question 2.
Hot metal ball of 80° C is dipped into water of 80°C. The ball will not contract.
Answer:
Reason: Both are in same temperature.
VI. Very Short Answer:
Question 1.
What are the sources of heat?
Answer:
- The main source of heat is Sun.
- Other sources are combustion, friction and electricity.
Question 2.
Define – heat.
Answer:
Heat is an energy that raises the temperature of a thing by causing the molecules in that thing to move faster.
![]()
Question 3.
How will you identify two objects are said to be in thermal equilibrium?
Answer:
Two objects in thermal contact have same temperature they are said to be in thermal equilibrium.
Question 4.
What are the measuring unit of temperature?
Answer:
SI unit of temperature is kelvin. Celsius and Fahrenheit are the other units used.
Question 5.
What will determine the direction of flow of heat from one object to another?
Answer:
Temperature will determine the direction of the flow of heat.
VII. Long Answer Questions:
Question 1.
Explain linear expansion with an experiment.
Answer:
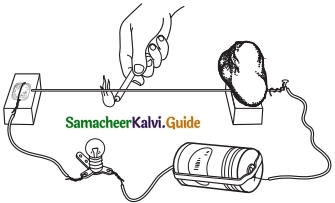
- The expansion in length is called linear expansion.
- Take a bulb, dry cell, candle, cycle spoke, coin, and two wooden boxes.
- Place one end of the cycle spoke on a wooden block and connect an electric wire to it. Put a stone over the spoke to hold it.
- The other one of the cycle spoke is placed on another wooden block.
- Wrap some electric wire around the coin and place it on the block. Put a stone over the coin to hold it in place.
- Connect bulb and dry cell to the free ends of wires connected to the coin and the spoke and make the circuit.
- When we heat the cycle spoke with a candle the length will expand and touches the coin.
- So the circuit completes, the bulb will glow.
- When we cool the spoke it contracts and does not touch the coin. So the circuit will disconnect, the bulb will not glow.
![]()