Students can download 6th Science Term 1 Chapter 4 The Living World of Plants Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science Solutions Term 1 Chapter 4 The Living World of Plants
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science The Living World of Plants Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The pond is an example of ………
(a) Marine habitat
(b) Freshwater habitat
(c) Deserts
(d) Mountain
Answer:
(b) Freshwater habitat
Question 2.
The important function of stomata is ______
(a) Conduction
(b) Transpiration
(c) Photosynthesis
(d) Absorption
Answer:
(b) Transpiration
![]()
Question 3.
Organs of absorption are ………
(a) Root
(b) Stem
(c) Leaf
(d) Flower
Answer:
(a) Root
Question 4.
The habitat of water hyacinth is ______
(a) Aquatic
(b) Terrestrial
(c) Desert
(d) Mountain
Answer:
(a) Aquatic
II. True or False – If false give the correct answer.
- Plants can live without water.
- All plants have chlorophyll.
- Plants have three parts; the root, the stem, and the leaves.
- Mountain is an example of a freshwater habitat.
- Root is modified into spines.
- Green plants need sunlight.
Answer:
- False – They need water to carry out various functions.
- False – Only green plants have chlorophyll.
- True
- False – Mountain is an example of Terrestrial habitat.
- False – Spines are usually modifications of leaves.
- True
III. Fill in the blanks.
- Earth’s surface is covered by ……….. % of water.
- The driest places on earth are ……….
- Fixation and absorption are the main functions of ……….
- Primary organs of photosynthesis are ………..
- Taproot system present in ……….. plants.
Answer:
- 70%
- Deserts
- roots
- leave
- dicot.
![]()
IV. Match the following:
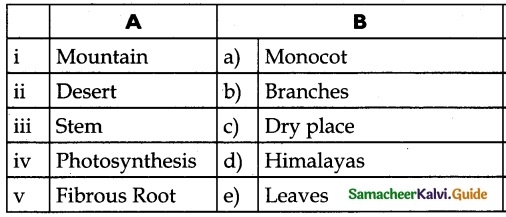
Answer:
(i) – d
(ii) – c
(iii) – b
(iv) – e
(v) – a
V. Arrange in the correct sequence.
Question 1.
Leaf – Stem – Root – Flower
Answer:
root – stem – leaf – flower
Question 2.
Transpiration – Conduction – Absorption – Fixation.
Answer:
Fixation, Absorption, Conduction, Transpiration.
VI. Very short answer.
Question 1.
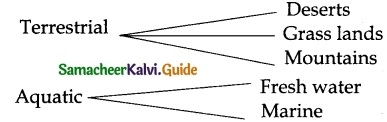
Classify plants on the basis of their habitat.
Answer:
Terrestrial and Aquatic are the 2 habitats
Question 2.
Identify the desert plant from the following – Cactus, Hydrilla, Mango, and Rose.
Answer:
Cactus plants – grow in deserts, and are able to store water in their stem.
Question 3.
Define the term habitat.
Answer:
Each and every organism needs a place to live and reproduce known as habitat.
The dwelling place of any organism is its habitat. Eg. Aquatic habitat
![]()
Question 4.
Relate the terms leaves and photosynthesis.
Answer:
Leaves are green in colour, they have chlorophyll and do photosynthesis.
VII. Short answer.
Question 1.
Why do you call Jasmine plants a twiner?
Answer:
Weak plant, cannot stand on its own, must climb on any support to survive.
Question 2.
Compare the taproot and fibrous root systems.
Answer:
Taproot system:
- Consists of a single root.
- it grows straight down in the ground
- Seen in misogynous plants.
Fibrous root system:
- Consists cluster of roots.
- It is thin and uniform in size.
- Seen in monocotyledonous plants.
Question 3.
Distinguish between terrestrial and aquatic habitats.
Answer:
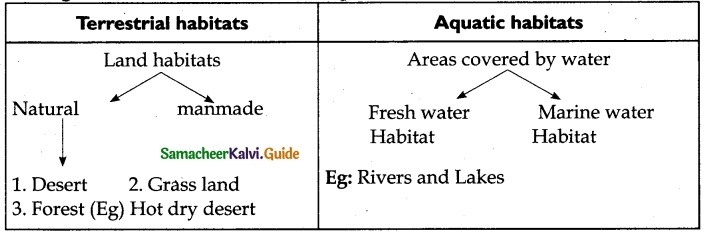
Question 4.
List out the plants present in your school garden.
Answer:
Mango tree, Neem tree, Water lily, Clitoria, Hibiscus
![]()
VIII. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
Make a list of functions of root & stem.
Answer:
Functions of root:
The root,
- Fixes the plant to the soil.
- Absorbs water and minerals from the soil.
- Stores food in some plants like carrots and beetroot.
Functions of stem:
The stem,
- Supports the branches, leaves, flowers, and fruits.
- Transports water and minerals from roots to upper aerial plant parts.
- Transports the prepared food from leaves to other parts.
- Stores food as in the case of sugarcane.
Question 2.
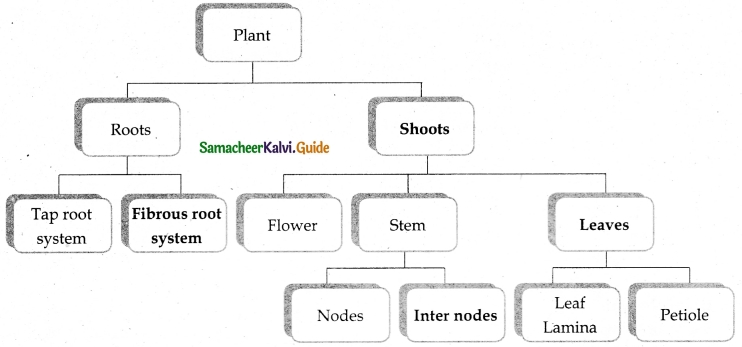
Study the given concept map. Connect them correcting by drawing arrow marks. Complete the map by filling in the blanks.
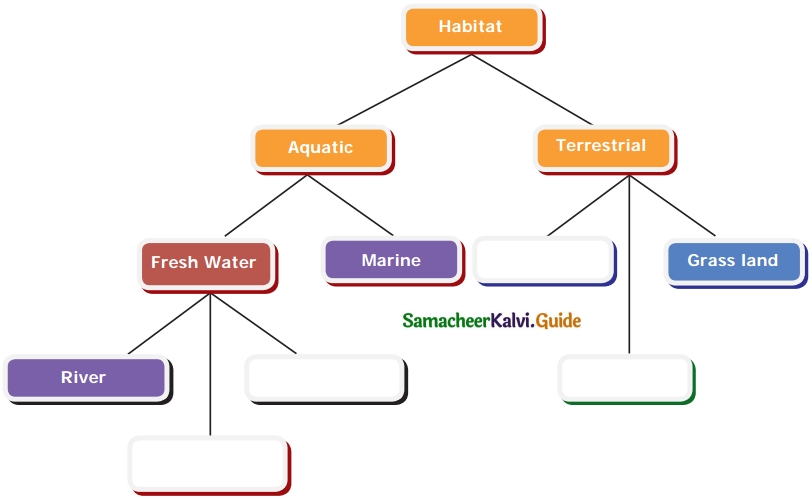
Answer:
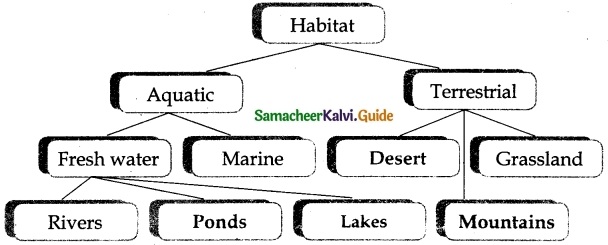
Samacheer Kalvi 6th Science The Living World of Plants Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Multiple Choice Questions.
Question 1.
Maize has ……….
(a) taproot
(b) fibrous root
(c) Adventitious root
(d) Fasciculate root
Answer:
(b) fibrous root
Question 2.
The underground part of the main axis of a plant is known as ______
(a) shoot
(b) node
(c) root
(d) leaf
Answer:
(c) root
![]()
Question 3.
The stalk of the leaf is known
(a) peduncle
(b) rachis
(c) pedicel
d) petiole
Answer:
(d) petiole
Question 4.
On the lower side of the leaf, there are tiny pores or openings known as ______
(a) Leaf base
(b) midrib
(c) petiole
(d) stomata
Answer:
(d) stomata
Question 5.
The diameter of the leaf of Victoria amazonica is
(a) 2 meters
(b) 2.5 cm
(c) 3 meters
(d) 1 meter
Answer:
(c) 3 meters
II. Fill in the blanks.
- Special features in plants which help them to survive in the habitats they live are known as ……….
- The Great Indian Desert is an arid region of rolling sandhills on the Indian sub continent is known as ……….
- ………. is the main vein of the lamina of the leaf.
- A change in an organism caused by environmental factors is known as ………
Answer:
- Adaptations
- Thar desert
- Midrib
- Modification
III. Arrange in the correct sequence.
Question 1.
Sea – Lake – River – Pond
Answer:
Pond – Lake – River – Pond.
Question 2.
Internode – Node – Axillary Bud – Terminal Bud
Answer:
Terminal Bud – Axillary Bud – Node – Internodes.
![]()
IV. Very short answer.
Question 1.
Draw the structure of a leaf and neatly label the parts.
Answer:
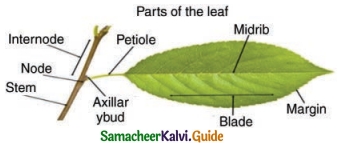
Question 2.
List the main part of a flowering plant.
Answer:
The flowering plant consists of two main parts. They are
- Root system
- Shoot system
Question 3.
Differentiate between Gymnosperm and Angiosperm.
Answer:
Both groups produces seeds.
Gymnosperms – Non flowering but produce naked seeds Eg. Pinus, Cycas.
Angiosperms – Flowering and produce closed seeds Eg. Mango – Rose
Question 4.
Give some examples of monocotyledonous plants and dicotyledonous plants.
Answer:
Monocotyledonous plant – Grass, Paddy, Maize
Dicotyledonous plant – Bean, Mango, Neem
Question 5.
Notes on Thorns or Spines.
Answer:
Some plants leave – modified into sharp structures known as Thorns or Spines help to reduce water loss.
Eg – Agave – (leaf apex & margin modified into spines).
V. Answer in Details.
Question 1.
Explain Tendril climber.
Answer:
Tendril a twining climbing organ of some weak stemmed plants.
It coils around support and helps the plant to climb.
- Sweet peas – Here leaflets are modified into tendrils.
- Bitter gourd – Axillary buds of plant-modified into tendril, help climb up.
![]()
Question 2.
Write about Desert Habitat.
Answer:
- Dry places on earth
- Less rainfall – less than 25 cm annually.
- Deserts cover 20% of the earth’s surface.
- Plants – Adapted to withstand severe heat.
Thick leaves help them to store water and minerals. Eg. Aloe
- Stems modified to store water. Eg. Cactus
- Leaves – modified into spines – Opuntia.
Question 3.
Study was given concept map. Connect them by drawing marks- for example, the map by filling the blanks.
Answer: