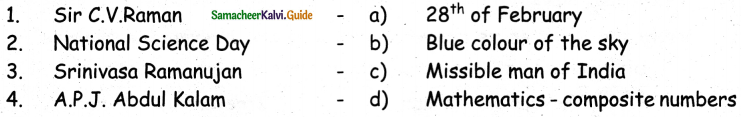Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 5th Science Guide Pdf Term 2 Chapter 1 Food Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 5th Science Solutions Term 2 Chapter 1 Food
Samacheer Kalvi 5th Science Guide Food Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The biotic factor which spoils the food item is
a) drying
b) temperature
c) humidity
d) bacteria
Ans:
(d) bacteria
![]()
Question 2.
Grains are preserved by
a) drying
b) freezing
c) adding sugar
d) adding salt
Answer:
(a) drying
Question 3.
Anaemia is a disease which occurs due to lack of
a) Vitamin-A
b) Vitamin-B
c) Iron
d) Vìtamin-D
Answer:
(c) Iron
Question 4.
Storage of excess fat in the body is known as
a) obesity
b) headache
c) fever
d) stomach pain
Answer:
(a) obesity
Question 5.
Carbohydrates are rich in
a) ghee
b) fruits
c) rice
d) oil
Answer:
(c) rice
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
Night blindness is caused by the lack of_________.
Answer:
Vitamin A
Question 2.
Marasmus is a __________ deficiency disease.
Answer:
protein
Question 3.
Bad smell from the food item is due to _________.
Answer:
Evaporation
Question 4.
Humidity in air is one of the _________ factor, which spoils food.
Answer:
Decompose
Question 5.
Using low-quality gas tubes in the gas stove may lead to _________ leakage.
Answer:
Gas
![]()
III. Match the following:

Answer:

![]()
IV. Say True or False:
Question 1.
Vinegar is added as a preservative for pickles.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Irradiation affects the taste of food materials.
Answer:
False
Question 3.
In case of gas leakage, we can continue to use electrical appliances.
Answer:
False
Question 4.
Deficiency due to iodine is called beriberi.
Answer:
False
Question 5.
Growing children need more proteins in their food.
Answer:
True
![]()
V. Answer briefly:
Question 1.
Define deficiency disease.
Answer:
Deficiency in one or more of the nutrients causes various diseases. These are called deficiency diseases.
Question 2.
What is known as balanced diet?
Answer:
The food we normally eat in a day is our diet. For growth and maintenance of good health, our diet should have all the nutrients that our body needs, in right quantities. Such a diet is called a balanced diet.
Question 3.
How can we prevent obesity?
Answer:
- Avoid fast foods, fried items and meat with more fat.
- Eat fruits and vegetables, legumes, whole grains and nuts.
- Do regular physical exercises.
- Don’t play games in computer and mobile phones.
- Have proper sleep time.
Question 4.
What should we do in case of minor burns?
Answer:
In case of minor burns, the burnt area should be held under cool running water for some time and proper medical treatment should be given.
Question 5.
Define spoilage of food.
Answer:
The change in the normal state of the food is called spoilage of food.
Question 6.
What is the purpose of food preservation?
Answer:
- To retain the colour, taste and nutritive value of the food.
- To make food available throughout the year.
- To prevent the growth of micro-organisms like bacteria and fungi in the food items.
- To reduce the wastage of food materials.
- Preserving food not only protects our health but also makes food available to the people who need it.
![]()
VI. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
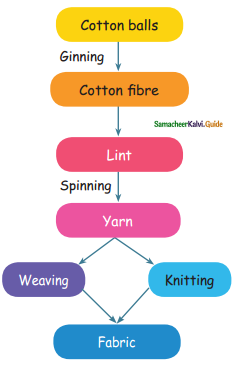
Write about food preservation methods.
Answer:
Drying: It is the removal of water content from the food by drying it in the sunlight.
E.g. Grains.
Addition of salt: When salt is added to food, it removes the water from the food.
E.g. Fish, Pickles.
Addition of sugar: When sugar is added to food, it dissolves in the water content of the food and preserves the food items from spoilage.
E.g. Jam, Fruit juices.
Freezing: The microbial growth and the enzyme activity on the frozen food items can be prevented by this method. E.g. Fruits, Vegetables.
Boiling: It kills the micro-organisms present in the food materials.
E.g. Milk, Water.
Canning and bottling: In this method, food is packed in airtight cans so that germs do not grow on them.
E.g. Milk powder.
Addition of chemical preservatives: Chemical preservatives are added to stop the growth of micro-organisms in certain food materials.
E.g. Sodium benzoate is added with fruits, Sulphur dioxide is added with dry fruits, Vinegar is added with pickles.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the different types of food.
Answer:
Different types of food
- Grains
- Vegetables
- Fruits
- Milk
- Meat, Fish, Egg
- Fat/Oil, Salt and Sugar
Some major food items are given in the table below.
| Major Food Items | Sources |
| Carbohydrates | Honey, Sugarcane, Fruits, Whole grains, Vegetables, Rice |
| Proteins | Legumes, Pulses, Nuts, Soya bean, Green leafy vegetables, Fish, Egg, Milk |
| Fats | Egg yolk, Saturated oil, Meat |
Question 3.
Write about kitchen safety.
Answer:
Kitchen is an important place in our homes. We prepare our food in the kitchen. We use gas cylinders for cooking. Some of us may use electric stoves. The equipment and the environment in the kitchen may be little dangerous. So we need to be cautious and careful.
The following table gives what should we do and what we shouldn’t do while handling gas cylinders.
| Do’s | Don’ts |
| Keep the cylinder in vertical position at plain level and in a well-aired place. | Do not keep the cylinder in horizontal or inverted position. |
| Keep the lighter ready and then turn on the gas stove knob. | Do not turn the knob before lighting the lighter. It may lead to gas leakage. |
| Keep the windows and doors open to ensure ventilation in case of gas leakage. | Do not turn off an electrical appliance in the kitchen. If there is a gas leakage it may lead to fire. |
| Always use I.S.I standard gas stoves, regulators and gas tubes. | Don’t use low quality gas stoves, tubes and regulators. It may lead to gas leakage. |
![]()
VII. Higher order thinking questions:
Question 1.
Ram put water over a burning wood in the kitchen. The fire is put off. How the water was able to put out the fire?
Answer:
When Ram put water on fire it does two things. It displaces the free oxygen molecules (which have two atoms of oxygen) so that it is not available to participate in the burning process and it turns to steam, carrying heat away from the fire, cooling it to the point where it can no longer burn.
Activities:
Activity 1.
Classify the following into perishable and non-perishable food items. Salt, Sugar, Apple, Corn, Orange, Wheat, Pulses, Tomato, Papaya, Rice, Cucumber.
Answer:
| Perishable | Non-perishable |
| Apple | Salt |
| Corn | Sugar |
| Orange | Wheat |
| Tomato | Pulses |
| Papaya | Rice |
| Cucumber |
![]()
Activity 2.
Look at the fruits and vegetables in your house. Is there any spoiled one? Find out the reason for that.
Answer:
| Item | Symptom | Reason |
| 1. Banana | 1. Skin becomes wrinkled 2. Shrinks in size | Moisture loss |
| 2. Bread | Greenish patch | Growth of Fungus |
| 3. Potato | Shrinking in size, bad smell. | Change in temperature, humidity. |
![]()
Activity 3.
Find your B.M.I
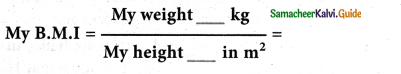
Answer:
Activity to be done by students.
Activity 4.
Find out the common disease prevalent in your area. Find out the reason for them an discuss with your teacher how to get remedy for them.
Answer:
| Disease | Reason | Remedy |
| Dengue fever | Virus spread by Mosquitoes | Protect from mosquito bites. Use mosquito repellents. |
Samacheer Kalvi 5th Science Guide Food Additional Questions and Answers
I.Choose the correct Answer:
Question 1.
Microorganisms present in spoiled foods may cause _________ diseases.
(a) foodborne
(b) Diabetes
(c) Colour blindness
(d) Cholera
Answer:
(a) foodborne
Question 2.
_______ disease is spread from one person to another.
(a) Heart disease
(b) Common cold
(c) Marasmus
(d) Diabetes
Answer:
(b) Common cold
Question 3.
Kwashiorkor is a _______ deficiency disease.
(a) Vitamin – A
(b) Iodine
(c) protein
(d) Iron
Answer:
(c) protein
Question 4.
Beri beri is a disease which occurs due to lack of _______.
(a) Vitamin-A
(b) Vitamin -B
(c) Iron
(d) Vitamin-D
Answer:
(b) Vitamin-B
Question 5.
Type of Fire Extinguisher for the fire caused by Liquid, Gaseous fuels is _________.
(a) Carbon dioxide
(c) Water
(b) Oxygen
(d) Dry chemical
Answer:
(a) Carbon dioxide
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
BMI=_____
Answer:
Weight In kg / Height In m2
Question 2.
Food is exposed to _________ rays or _________ rays.
Answer:
Gamma, ultra violet
Question 3.
Regular ________ can reduce obesity and overweight.
Answer:
physical activity
Question 4.
Infectious diseases are caused by _______.
Answer:
Micro-organisms
Question 5.
_______ are highly nutritive food materials.
Answer:
Spinach and Ponnanganni keerai.
![]()
III. Say True or False:
Question 1.
Spoiled foods are suitable to eat.
Answer:
False
Question 2.
People with BMIs between 18.5 and 25 have less chance of developing diseases like cancer.
Answer:
True
Question 3.
Do not operate electrical appliances with wet hands.
Answer:
True
Question 4.
Keep the inflammable materials near the gas stoves.
Answer:
False
Question 5.
Use proper fire extinguishers to put out the fire.
Answer:
True
![]()
IV. Match the following:
Question 1.
| 1. Metabolic factor | a. Cholera |
| 2. Genetic factor | b. Marasmus |
| 3. Microorganisms | c. Colour blindness |
| 4. Nutritional factor | d. Bacterial diseases |
| 5. Environment factor | e. Diabetes |
Answer:
- e
- c
- d
- b
- a
Question 2.
| 1. Vitamin – A | a. Cholera |
| 2. Vitamin – B | b. Marasmus |
| 3. Vitamin – C | c. Colour blindness |
| 4. Vitamin – D | d. Bacterial diseases |
| 5. Vitamin – E | e. Diabetes |
Answer:
- b
- a
- e
- c
- d
![]()
V. Answer briefly:
Question 1.
Which food items are called Perishable foods?
Answer:
Food items like fruits, vegetables, milk and meat will be fresh for a very short time. These are called perishable foods.
Question 2.
What is meant by the preservation of food?
Answer:
The process of keeping the food materials for a long time without getting spoiled is called preservation of food.
Question 3
What is Irradiation?
Answer:
Irradiation is a modern method by which, food is exposed to gamma rays or ultraviolet rays to kill the bacteria and the mould.
Question 4.
What are the sources to be removed to avoid fire?
Answer:
- Cut off the fuel.
- Cut off the air supply.
- Lower the temperature.
Question 5.
What is the Difference between Marasmus and Kwashiorkor?
Answer:
Marasmus:
- Marasmus is a protein deficiency disease.
- In marasmus, the child loses weight and it will appear as though bones are covered by skin.
Kwashiorkor:
In Kwashiorkor, the child develops an enlarged belly with swollen face and feet.
![]()
VI. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
What are the factors for food Spoilage?
Answer:
Food can be spoiled by factors like air and oxygen, moisture, light, micro-organisms, and temperature.
Air and Oxygen: When oxygen reacts with food contents, it produces changes in the colour and flavour of the food.
Moisture: Moisture keeps the food fresh. When the moisture is gone vegetables and fruits shrink. Due to evaporation, moisture loss occurs in foods like meat, fish and cheese. Enzymes: Enzymes break down the tissues and components of the food in different ways like oxidation, browning and ripening. So the food items decay.
Micro-organisms: Micro-organisms such as fungi, yeast and bacteria can grow well in low temperatures. They multiply in food and spoil them.
Light: Light produces colour changes and also vitamin loss.
Temperature: Sometimes the rise in temperature causes food spoilage.
Question 2.
Explain the different types of diseases.
Answer:
There are four main types of diseases. They are:
- Infectious diseases
- Hereditary diseases
- Physiological diseases
- Deficiency diseases.
a. Infectious diseases: Infectious diseases are caused by micro-organisms which invade our body and multiply inside them. These diseases are spread from one person to another. E.g. Common cold.
b. Hereditary diseases: Hereditary diseases are spread by abnormalities in the gene. These diseases are passed from parents to children. E.g. Heart disease.
c. Physiological diseases: Diseases which are caused due to malfunction of the body organs are called physiological diseases. E.g. Asthma.
d. Deficiency diseases: A diet which contains all essential nutrients in correct proportion is indispensable for maintaining good health. Deficiency in one or more of the nutrients causes various diseases. These are called deficiency diseases.
![]()
Question 3.
Write any 6 tips for fire protection and prevention.
Answer:
- Do not keep the inflammable materials like kerosene etc, near the gas stoves.
- In case of person’s clothes catching fire, cover the person with a thick blanket or carpet.
- If kerosene or oil catches fire, use sand to put out the fire.
- If solid materials like wood catch fire, use water to put out the fire.
- If an electrical appliance catches fire, unplug the appliances and disconnect the electricity.
- Use proper fire extinguishers to put out the fire.