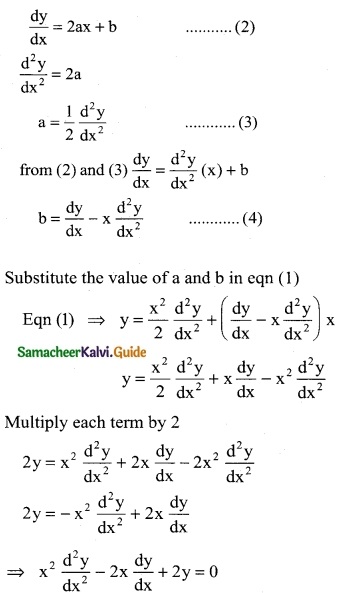
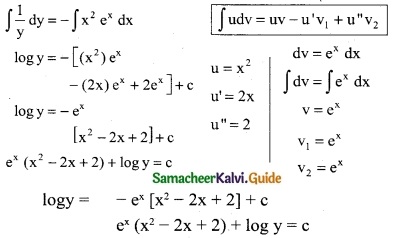
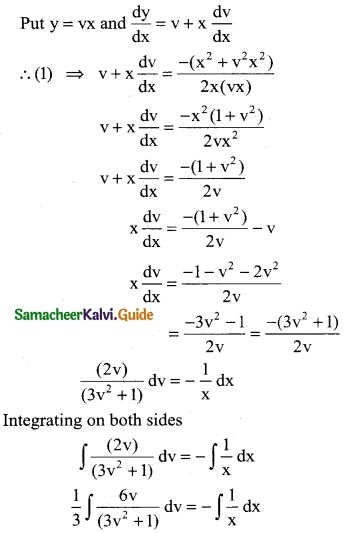
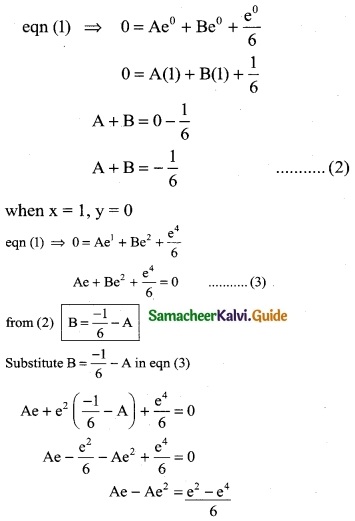
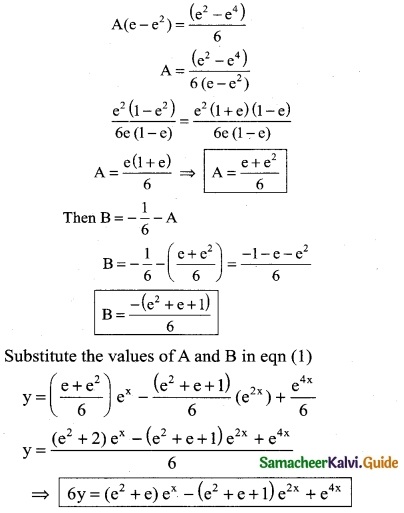
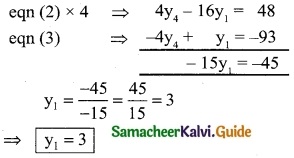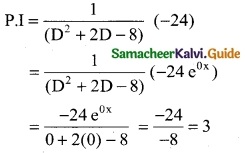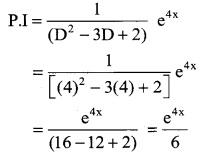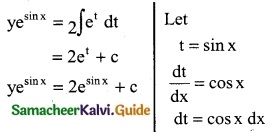Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Business Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 5 Numerical Methods Ex 5.2 Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Business Maths Solutions Chapter 5 Numerical Methods Ex 5.2
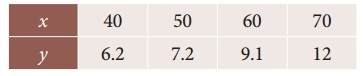
Question 1.
Using graphic method, find the value of y when x = 48 from the following data:
Solution:
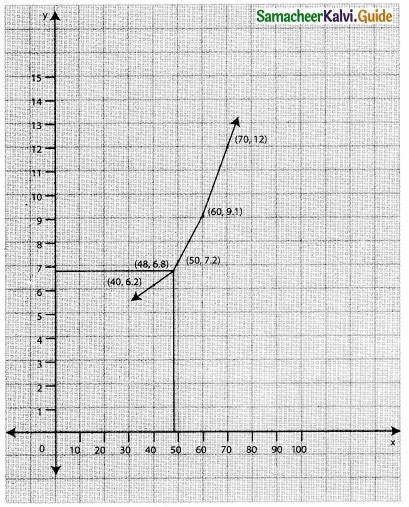
The value of y when x = 48 is 6.8
![]()
Question 2.
The following data relates to indirect labour expenses and the level of output
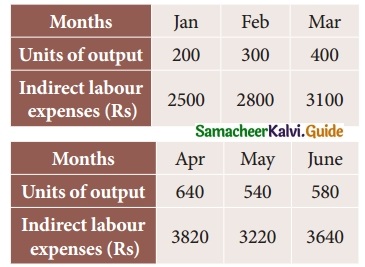
Estimate the expenses at a level of output of 350 units, by using graphic method.
Solution:
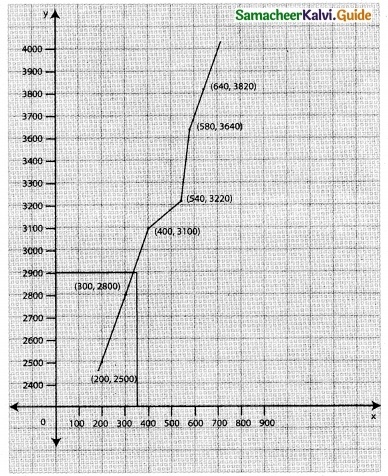
![]()
Question 3.
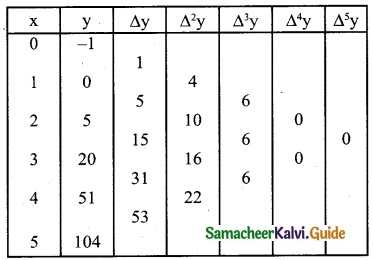
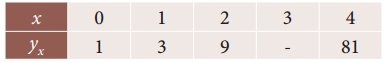
Using Newton’s forward interpolation formula find the cubic polynomial.
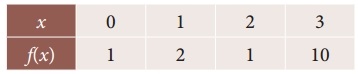
Solution:
Since we use the Newton’s forward interpolation formula.
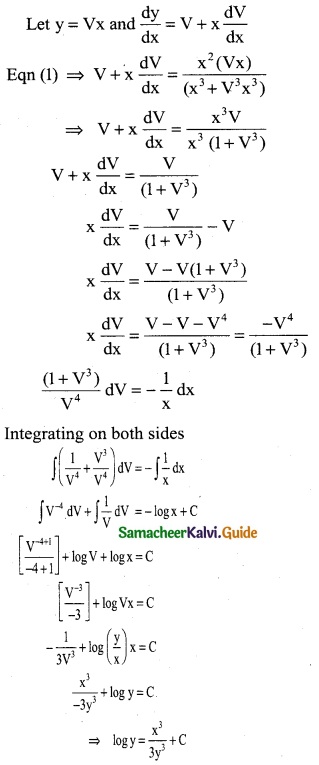
y(x= x0+nh) = y0 + \(\frac { n }{1!}\) Δy0 + \(\frac { n(n-1) }{2!}\) Δ²y0 + \(\frac { n(n-1)(n-2) }{3!}\) Δ³y0 + ………
To find y at x
∴ x0 + nh = x
0 + n(1) = x
∴ n = x
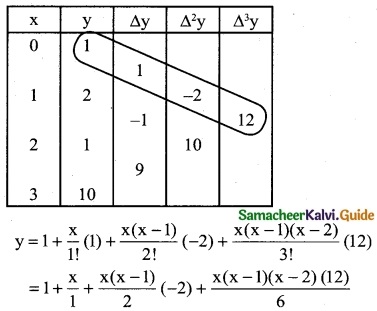
= 1 + x + (x² – x) (-1) + 2x (x² – 3x + 2)
y = 1 + x – x² + x + 2x³ – 6x² + 4x
y = 2x³ – 7x² + 6x + 1
∴ f(x) = 2x³ – 7x² + 6x + 1
![]()
Question 4.
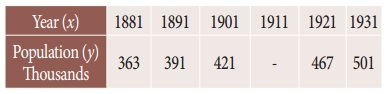
The population of a city in a censes taken once in 10 years is given below. Estimate the population in the year 1955.
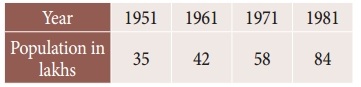
Solution:
Let the year be x and population be y. To find the population for the year 1955.
(ie) The value of y at x = 1955
Since the value of y is required near the beginning of the table, we use the Newton’s forward interpolation formula.
y(x= x0+nh) = y0 + \(\frac { n }{1!}\) Δy0 + \(\frac { n(n-1) }{2!}\) Δ²y0 + \(\frac { n(n-1)(n-2) }{3!}\) Δ³y0 + ………
To find y at x = 1955
∴ x0 + nh = 1955; x0 = 1951, h = 10
⇒ 1951 + n(10) = 1955
10n = 1955 – 1951 ⇒ 10n = 4
n = \(\frac { 4 }{10}\) = 0.4
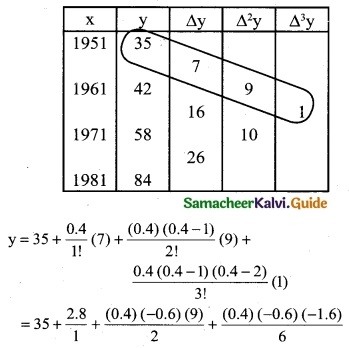
y = 35 + 2.8 – 1.08 + 0.064
= 37.864 – 1.08
y = 36.784
∴ Population in the year 1955 is 36.784 (lakhs)
![]()
Question 5.
In an examination the number of candidates who secured marks between certain interval were as follows:
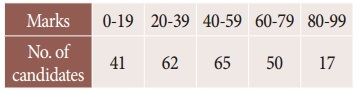
Estimate the number of candidates whose marks are lessthan 70.
Solution:
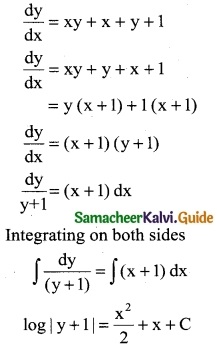
Since the required mark is at the end of the table, we apply Backward interpolation formula. Let the marks be x and No. of candidates be y.
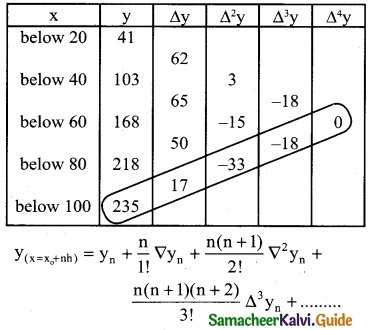
To find y at x = 70
x = x0 + nh ⇒ 70 = 100 + n(20)
70 – 100 = 20n
20n = -30 ⇒ n = \(\frac { -30 }{20}\)
n = -1.5
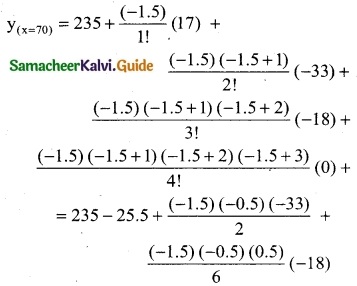
= 235 – 25.5 – 12.375 – 1.125
= 235 – 39
= 196
∴ 196 candidates secured less than 70 marks
Question 6.
Find the value of f(x) when x = 32 from the following table
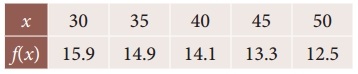
Solution:
Since the value of f(x) is required near the beginning of the table, we use the Newton’s forward interpolation formula.
y(x= x0+nh) = y0 + \(\frac { n }{1!}\) Δy0 + \(\frac { n(n-1) }{2!}\) Δ²y0 + \(\frac { n(n-1)(n-2) }{3!}\) Δ³y0 + ………
To find y at x = 32
∴ x0 + nh = 32;
30 + n(5) = 32
5n = 32 – 30 ⇒ 5n = 2
n = \(\frac { 2 }{5}\)
∴ n = 0.4
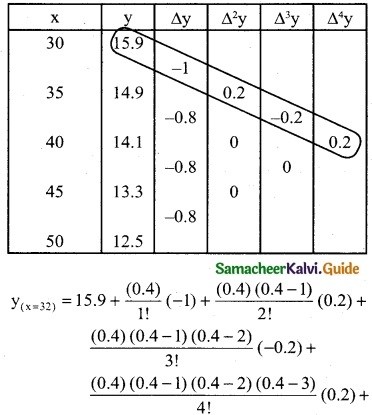
= 15.9 – 0.4 – 0.024 – 0.0128 – 0.00832
15.9 – 0.44512 = 15.45488
= 15.45
∴ when x = 32, f(x) = 15.45
![]()
Question 7.
The following data gives the melting point of a alloy of lead and zinc where ‘t’ is the temperature in degree c and p is the percentage of lead in the alloy
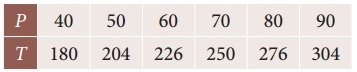
Find the melting point of the alloy containing 84 percent lead.
Solution:
Since the required value is at the end of the table, apply backward interpolation formula. To find T at p = 84
T(p= p0+nh) = Tn + \(\frac { n }{1!}\) ∇Tn + \(\frac { n(n+1) }{2!}\) ∇²T0 + \(\frac { n(n+1)(n+2) }{3!}\) Δ³T0 + ………
To find T at P = 84
Pn + nh = 84
90 + n(10) = 84
10n = 84 – 90
10n = -6 ⇒ n = \(\frac { -6 }{10}\)
n = -0.6
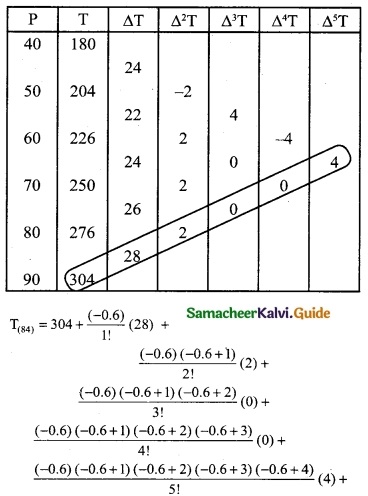
= 304 – 16.8 – 0.24 – 0.091392
= 304 – 17.131392
= 286.86
Hence the melting point of the alloy is 286.86° c.
![]()
Question 8.
Find f(2.8) from the following
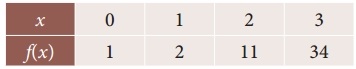
Solution:
Since the required value is at the end of the table, apply backward interpolation formula.
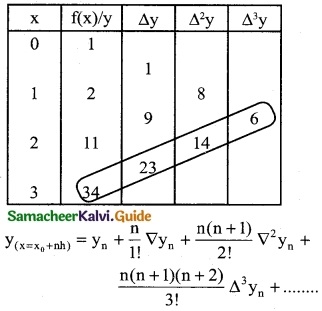
To find y at x = 2.8
∴ x0 + nh = 2.8
∴ 3 + n(1) = 2.8
n = 2.8 – 3
n = -0.2
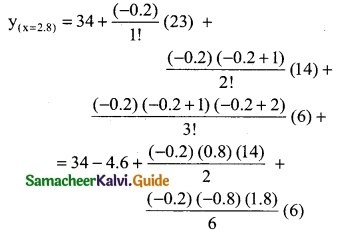
= 34 – 4.6 – 1.12 – 0.288
= 34 – 6.008
= 27.992
∴ f(2.8) = 27.992
![]()
Question 9.
Using interpolation estimate the output of a factory in 1986 from the following data
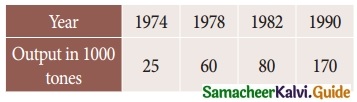
Solution:
Here the intervals are unequal. By Lagrange’s in-terpolation formula we have,
x0 = 1974, x1 = 1978, x2 = 1982, x3 = 1990
y0 = 25, y1 = 60, y2 = 80, y3 = 170, and x = 1986.
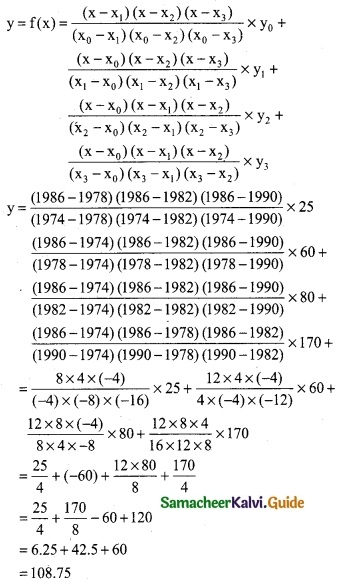
∴ output in 1986 is 108.75 (thousand tones)
Question 10.
Use lagrange’s formula and estimate from the following data the number of workers getting income not exceeding Rs. 26 per month.

Solution:
Here the intervals are unequal. By Lagrange’s In-terpolation formula we have,
x0 = 15, x1 = 25, x2 = 30, x3 = 35
y0 = 36, y1 = 40, y2 = 45, y3 = 48 and x = 26.
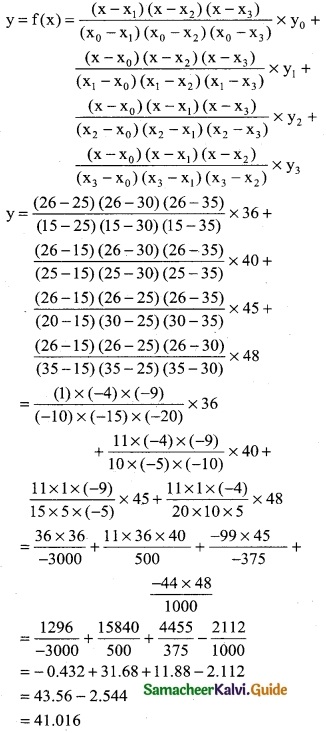
∴ Required No.of workers = 42 Persons (approximately)
![]()
Question 11.
Using interpolation estimate the business done in 1985 from the following data
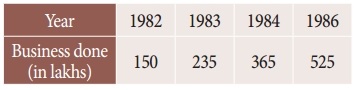
Solution:
Here the intervals are unequal. By Lagrange’s formula we have,
x0 = 1982, x1 = 1983, x2 = 1984, x3 = 1986
y0 = 150, y1 = 235, y2 = 365, y3 = 525 and x = 1985.
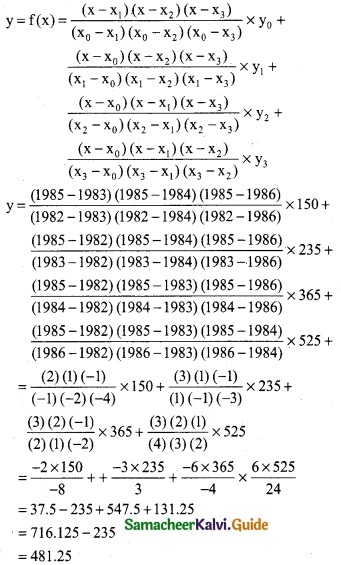
∴ Business done in the year 1985 is 481.25 lakhs.
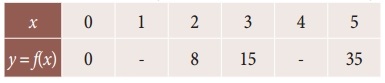
Question 12.
Using interpolation, find the value of f(x) when x = 15
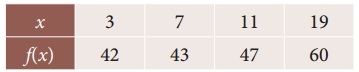
Solution:
Here the intervals are unequal, By Lagrange’s in-terpolation formula we have,
x0 = 3, x1 = 7, x2 = 11, x3 = 19
y0 = 42, y1 = 43, y2 = 47, y3 = 60 and x = 15.

![]()