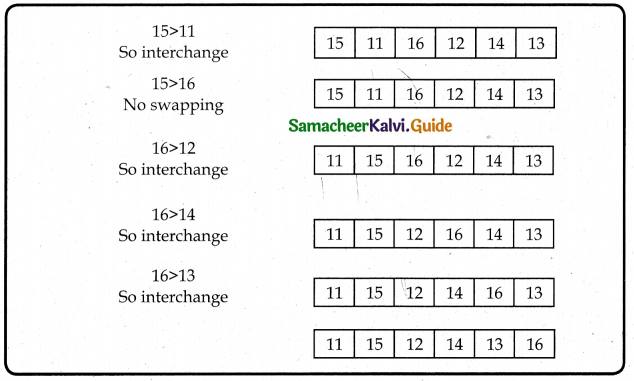
Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Science Guide Pdf Chapter 6 Control Structures Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Computer Science Solutions Chapter 6 Control Structures
12th Computer Science Guide Control Structures Text Book Questions and Answers
I. Choose the best answer (1 Mark)
Question 1.
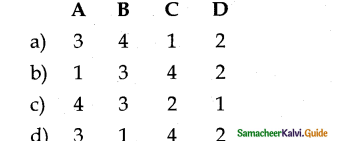
How many important control structures are there in Python?
a) 3
b) 4
c) 5
d) 6
Answer:
a) 3
Question 2.
elif can be considered to be abbreviation of
a) nested if
b) if..else
c) else if
d) if..elif
Answer:
c)else if
![]()
Question 3.
What plays a vital role in Python programming?
a) Statements
b) Control
c) Structure
d) Indentation
Answer:
d) Indentation
Question 4.
Which statement is generally used as a placeholder?
a) continue
b) break
c) pass
d) goto
Answer:
c) pass
Question 5.
The condition in the if statement should be in the form of
a) Arithmetic or Relational expression
b) Arithmetic or Logical expression
c) Relational or Logical expression
d) Arithmetic
Answer:
c) Relational or Logical expression
![]()
Question 6.
Which is the most comfortable loop?
a) do..while
b) while
c) for
d) if..elif
Answer:
c) for
Question 7.
What is the output of the following snippet?
i=l
while True:
if i%3 ==0:
break
print(i/end=”)
i +=1
a) 12
b) 123
c) 1234
d) 124
Answer:
a) 12
![]()
Question 8.
What is the output of the following snippet?
T=1
while T:
print(True)
break
a) False
b) True
c) 0
d) no output
Answer:
b) True
Question 9.
Which amongst this is not a jump statement ?
a) for
b) goto
c) continue
d) break
Answer:
a) for
![]()
Question 10.
Which punctuation should be used in the blank?
if < condition >
statements-block 1
else:
statements-block 2
a) ;
b) :
c) ::
d) !
Answer:
b) :
II. Answer the following questions (2 Marks)
Question 1.
List the control structures in Python.
Answer:
There are three important control structures
- Sequential
- Alternative or Branching
- Iterative or Looping
Question 2.
Write note on break statement.
Answer:
- The break statement terminates the loop containing it.
- Control of the program flows to the statement immediately after the body of the loop.
- When the break statement is executed, the control flow of the program comes out of the loop and starts executing the segment of code after the loop structure.
- If break statement is inside a nested loop (loop inside another loop), break will terminate the innermost loop.
![]()
Question 3.
Write is the syntax of if..else statement
Answer:
Syntax:
if:
statements – block 1
else:
statements – block 2
Question 4.
Define control structure.
Answer:
A program statement that causes a jump of control from one part of the program to another is called a control structure or control statement.
Question 5.
Write note on range () in loop
Answer:
Usually in Python, for loop uses the range() function in the sequence to specify the initial, final and increment values. range() generates a list of values starting from start till stop – 1.
![]()
III. Answer the following questions (3 Marks)
Question 1.
Write a program to display
Answer:
A
AB
ABC
ABCD
ABCDE
For i in range (1,6,1):
ch=65
for j in range (ch,ch+i,1):
a=chr(j)
print (a, end =’ ‘)
print ()
Question 2.
Write note on if..else structure.
Answer:
The if-else statement provides control to check the true block as well as the false block. Following is the syntax of ‘if-else’ statement.
Syntax:
if:
statements – block 1
else:
statements – block 2
![]()
Question 3.
Using if..else..elif statement write a suitable program to display largest of 3 numbers.
Answer:
a = int (input (“Enter number 1″)
b = int (input (” Enter number 2″)
c = int (input (” Enter number 3″)
if a > b and a > c:
put (” A is greatest”)
elif b > a and b > c:
print (“B is greatest”)
else:
print (“C is greatest”)
Question 4.
Write the syntax of while loop.
Answer:
The syntax of while loop in Python has the following syntax:
Syntax:
while:
statements block 1
[else:
statements block 2]
Question 5.
List the differences between break and continue statements.
Answer:
Break | Continue |
| Break statement terminates the loop containing it and control reaches after the body of the loop | Continue statement skips the remaining part of a loop and start with next iteration. |
![]()
IV. Answer the following questions (5 Marks)
Question 1.
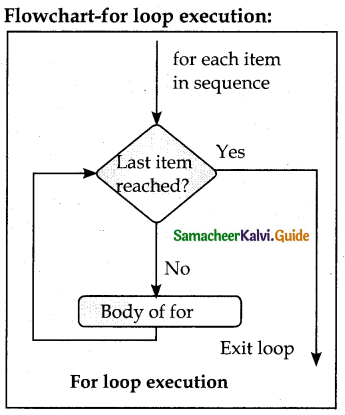
Write a detail note on for loop
Answer:
for loop:
- for loop is the most comfortable loop. It is also an entry check loop.
- The condition is checked in the beginning and the body of the loop
(statements-block 1) is executed if it is only True otherwise the loop is not executed.
Syntax:
for counter_variable in
sequence:
statements – block 1
[else: # optional block statements – block 2]
- The counter, variable mentioned in the syntax is similar to the control variable that we used in the for loop of C++ and the sequence refers to the initial, final and increment value.
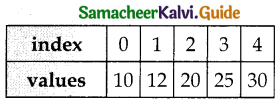
- Usually in Python, for loop uses the range () function in the sequence to specify the initial, final and increment values, range () generates a list of values starting from start till stop-1.
The syntax of range() follows:
range (start, stop, [step])
Where,
start – refers to the initial value
stop – refers to the final value
step – refers to increment value,
this is optional part.
Examples for range():
range (1,30,1) – will start the range of values from 1 and end at 29 range (2,30,2) – will start the range of values from 2 and end at 28 range (30,3,-3) – will start the range of values from 30 and end at 6E range (20) – will consider this value 20 as the end value ( or upper limit) and starts the range count from 0 to 19 (remember always range () will work till stop -1 value only)
Example-Program:
#Program to illustrate the use of for loop – to print single digit even number
for i in range (2,10,2):
print (i, end=”)
Output:
2468
![]()
Question 2.
Write a detail note on if..else..elif statement with suitable example.
Answer:
- When we need to construct a chain of if statement(s) then ‘elif’ clause can be
used instead of ‘else’.
Syntax:
if < condition -1>:
statements-block 1
elif< condition -2>:
statements-block 2
else:
statements-block n - In the syntax of if..elif ..else mentioned above, condition -1 is tested if it is true then statements-block 1 is executed, otherwise, the control checks condition-Z, if it is true statements- block2 is executed and even if it fails statements-block n mentioned in else part is executed.
- ‘elif’ clause combines if..else- if ..else statements to one if..elif … else, “elif’ can be considered to be abbreviation of ‘else if’. In an’if’ statement there is no limit of ‘elif’ clause that can be used, but an clause if used should be placed at the end.
Example:
# Program to illustrate the use of nested if statement
Average – Grade
> =80 and above A
> =70 and above B
> =60 and <70 C
> =50 and <60 D
Otherwise E
Example-program
m1 = int (input(“Enter mark in first subject:”))
m2 = int (input(” Enter mark in second subject:”))
avg = (ml+ml)/2
if avg> =80:
print (“Grade: A”)
elif avg> =70 and avg< 80:
print (“Grade: B”)
elif avg> =60 and avg< 60:
print (“Grade: C”)
elif avg> =50 and avg< 60: .
print (“Grade: D”)
else:
print(“Grade: E”)
Output 1:
Enter mark in first
subject: 34
Enter mark in second
subject: 78
Grade: D
![]()
Question 3.
Write a program to display all 3 digit odd numbers.
Answer:
Odd Number (3 digits)
for a in range (100, 1000)
if a % 2 = = 1:
print b
Output:
101, 103, 105, 107, .. …… 997, 999
Question 4.
Write a program to display multiplication table for a given number.
Answer:
Coding:
num=int(input(“Display Multiplication Table of “))
for i in range(1,11):
print(i, x ,num, ‘=’, num*i)
Output:
Display Multiplication Table of 2
1 x 2 = 2
2 x 2 = 4
3 x 2 = 6
4 x 2 = 8
5 x 2 = 10
6 x 2 = 12
7 x 2 =14
8 x 2 = 16
9 x 2 =18
10 x 2 = 20
>>>
![]()
12th Computer Science Guide Control Structures Additional Questions and Answers
I. Choose the best answer ( I Mark)
Question 1.
Executing a set of statements multiple times are called…………………………..
(a) Iteration
(b) Looping
(c) Branching
(d) Both a and b
Answer:
(d) Both a and b
Question 2.
………… important control structures are available in python.
a) 2
b) 3
c) 4
d) many
Answer:
b) 3
![]()
Question 3.
Identify which is not a control structure?
(a) Sequential
(b) Alternative
(c) Iterative
(d) Break
Answer:
(d) Break
Question 4.
To construct a chain of if statement, else can be replaced by
a) while
b) ifel
c) else if
d) elif
Answer:
d) elif
Question 5.
Branching statements are otherwise called……………………………
(a) Alternative
(b) Iterative
(c) Loop
(d) Sequential
Answer:
(a) Alternative
![]()
Question 6.
Which statement is used to skip the remaining part of a loop and start with the next iteration?
a) continue
b) break
c) pass
d) condition
Answer:
a) continue
Question 7.
In the …………….. loop, the condition is any valid Boolean expression returning True or false.
a) if
b) else
c) elif
d) while
Answer:
d) while
Question 8.
How many blocks can be given in Nested if.. elif.. else statements?
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) n
Answer:
(d) n
![]()
Question 9.
A loop placed within another loop is called as …………… loop structure.
a) entry check
b) exit check
c) nested
d) conditional
Answer:
c) nested
Question 10.
What types of Expressions can be given in the while loop?
(a) Arithmetic
(b) Logical
(c) Relational
(d) Boolean
Answer:
(d) Boolean
![]()
II. Answer the following questions (2 and 3 Marks)
Question 1.
Write a note on sequential statements?
Answer:
A sequential statement is composed of a sequence of statements which are executed one after another. A code to print your name, address, and phone number is an example of a sequential statement.
Question 2.
Write the syntax of for loop.
Answer:
Syntax:
for counter_variable in sequence:
statements-block 1
[else: # optional block
statement-block 2]
Question 3.
Define loops?
Answer:
Iteration or loop are used in a situation when the user needs to execute a block of code several times or till the condition is satisfied. A loop statement allows executing a statement or group of statements multiple times.
Question 4.
What is meant by Nested loop structure?
Answer:
- A loop placed within another loop is called a nested loop structure.
- A while; within another while; for within another for;
- For within while and while within for to construct nested loops.
![]()
Question 5.
Give the syntax of range O in for loop?
Answer:
The syntax of range ( ) is as follows:
range (start, stop, [step] )
Where,
start – refers to the initial value
stop – refers to the final value
step – refers to increment value, this is an optional part.
Question 6.
Write a note on the pass statement.
Answer:
- pass statement in Python programming is a null statement.
- pass statement when executed by the interpreter it is completely ignored.
- Nothing happens when the pass is executed, it results in no operation.
III. Answer the following questions (5 Marks)
Question 1.
Explain the types of alternative or branching statements provided by Python?
Answer:
The types of alternative or branching statements provided by Python are:
- Simple if statement
- if..else statement
- if..elif statement
1) Simple if statement
Simple if is the simplest of all decision-making statements. The condition should be in the form of relational or logical expression.
Syntax:
if:
statements-block1
Example:
x=int (input(“Enter your age :”))
if x > =18:
print (“You are; eligible for voting”)
Output:
Enter your age :34
You are eligible for voting
2) if..else statement
The if.. else statement provides control to check the true block as well as the false block. Following is the syntax of ‘if..else statement.
Syntax:
if:
statements-block 1
else:
statements-block 2
Example:
a = int(input(” Enter any number :”))
if a%2==0:
print (a, ” is an even number”) else:
print (a, ” is an odd number”)
Output 1:
Enter any number:56
56 is an even number
Output 2:
Enter any number:67
67 is an odd number
Flowchart- if..else statement Execution
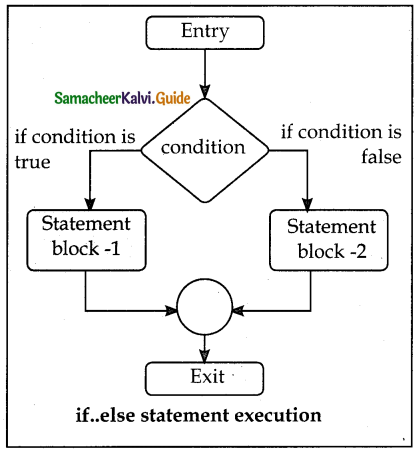
3) Nested if..elif…else statement:
- When we need to construct a chain of if statement(s) then ‘elif’ clause can be used instead of ‘else.
- ‘elif’ clause combines if..else-if.. elsestatements to one if ..elif… else. elif can be considered to be abbreviation of else if.
- In an ‘if statement there is no limit of ‘elif clause that can be used, but an ‘else clause if used should be placed at the end.
Syntax:
if<statements-block 1>:
elif :
statements-block 2
else:
statements-block n
Example:
a = int (input (“Enter number 1″)
b = int (input (” Enter number 2″)
c = int (input (” Enter number 3″)
if a > b and a > c:
put (” A is greatest”)
elif b > a and b > c:
print (“B is greatest”)
else:
print (“C is greatest”)
![]()
Question 2.
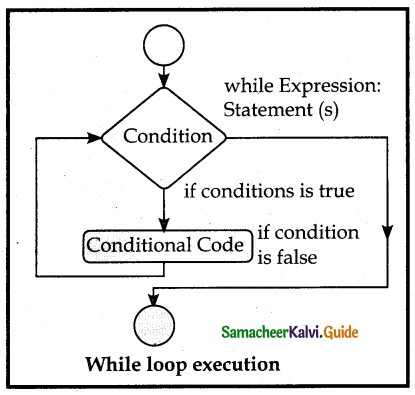
Explain while loop with example.
Answer:
- While loop belongs to entry check loop type, that is it is not executed even once
if the condition is tested False in the beginning. - In the while loop, the condition is any valid Boolean expression returning
True or False. - The else part of while is optional part of while. The statements blocki is kept
executed till the condition is True. - If the else part is written, it is executed when the condition is tested False.
Syntax:
while< condition >:
statements block 1
[else:
statements block 2]
Flowchart-while loop execution:
Example:
| i=10 | # intializing part of the control variable |
| while (i<=15): | # test condition |
| print (i,end=,\t/) | # statements – block1 |
| i=i+1 | # Updation of the control variable |
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the Jump statement in python.
Answer:
- The jump statement in Python is used to unconditionally transfer the control from one part of the program to another.
- There are three keywords to achieve jump statements. in Python: break, continue, pass.
Flowchart -Use of break, continue statement in loop structure:
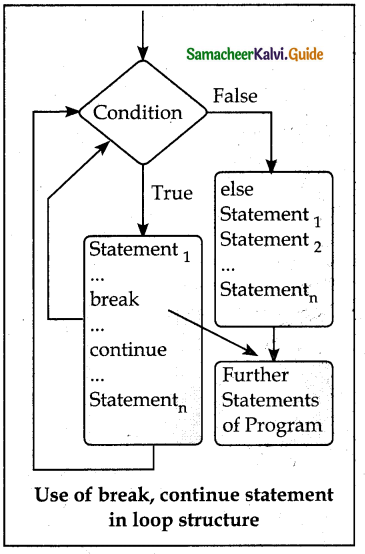
- break statement:
- The break statement terminates the loop containing it.
- Control of the program flows to the statement immediately after the body of the loop.
- A while or for loop will iterate till the condition is tested false, but one can even transfer the control out of the loop (terminate) with help of a break statement.
- When the break statement is executed, the control flow of the program comes out of the loop and starts executing the segment of code after the loop structure.
- If the break statement is inside a nested loop (loop inside another loop), the break will terminate the innermost loop. Syntax for break statement:
break
Example: for word in “Jump Statement”:
ifword = = “e”:
break print (word, end= “)
Output: Jump Stat
Flowchart- Working of break statement:
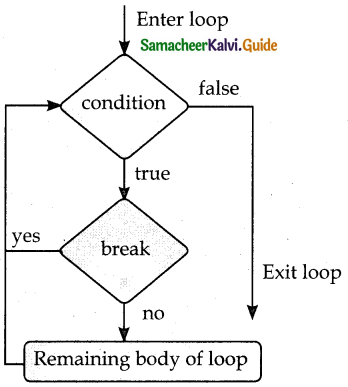
Working of break statement
continue statement: Continue statement unlike the break statement is used to skip the remaining part of a loop and start with the next iteration.
Syntax of continue statement:
continue Example:
for word in “Jump Statement”:
if word = = “e”:
continue print (word, end=”)
print (“\n End of the program”)
Output:
Jump Statement
End of the program
pass statement:
- pass statement is generally used as a placeholder.
- When we have a loop or function that is to be implemented in the future and not now, we cannot develop such functions or loops with empty body segments because the interpreter would raise an error.
- So, to avoid this we can use a pass statement to construct a body that does nothing.
Syntax of pass statement:
pass
Example:
forval in “Computer”:
pass
print (“End of the loop, loop structure will be built in future”)
Output: End of the loop, loop structure will be built in future
![]()
Question 4.
What kind of Nested ioop structure can be created?
Answer:
- A loop placed within another loop is called a nested loop structure.
- A while; within another while; for within another for;
- for within while and while within to construct nested loops.
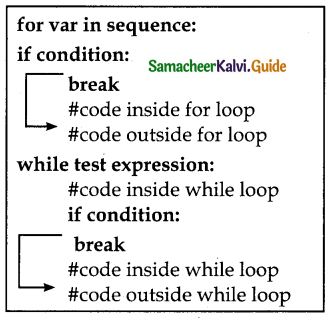
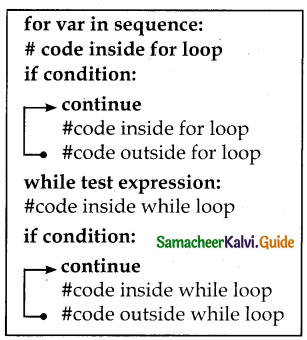
HANDS-ON PRACTICE
Question 1.
Write a program to check whether the given character is a vowel or not.
Answer:
Coding:
ch=input (“Enter a character :”)
# to check if the letter is vowel
if ch in (‘a’, ‘A’, e , E , i , I , o ,O , u’, ‘U’):
print (ch/ is a vowel’)
Output:
Enter a character:e
e is a vowel
![]()
Question 2.
(i) Write a program to display all 3 digit even numbers.
(ii) Write the output for the following program.
Answer:
i=1
while (i<=6):
for j in range (1, i):
print(j, end=’\t’)
print (end=’ \ n’)
i+=1
i) Python Program:
for i in range(100,1000,2):
Print(i)
ii) Output: 1
1 2
1 2 3
1 2 3 4
1 2 3 4 5
Question 3.
Write a program to check if a number is Positive, Negative or zero.
Answer:
Coding:
num = float(input(” Enter a number: “))
if num > 0:
print(“Positive number”)
elifnum == 0:
print(“Zero”)
else:
print(“Negative number”)
Output:
Enter a number:5
Positive number
![]()
Question 4.
Write a program to display Fibonacci series 0112345 (up to n terms)
Answer:
Coding:
Number = int(input(“\n Please Enter the Range Number: “))
i = 0
First_ Value = 0
Second-Value = 1
while(i < Number):
if(i <= 1):
Next = i else:
Next = First-Value + Second_Value
First_Value = Second_Value
Second_Value = Next
print(Next)
i = i + 1
Output:
Please Enter the Range Number: 4
0
1
1
2
3
Question 5.
Write a program to display sum of natural numbers, up to n.
Answer:
Coding:
number = int(input(“Please Enter any Number:”))
total = 0
for value in range(l, number + 1):
total = total + value
print(“The Sum of Natural Numbers is total)
Output:
Please Enter any Number:5
The Sum of Natural Numbers is : 15
![]()
Question 6.
Write a program to check if the given number is a palindrome or not.
Answer:
Coding:
n=int(input(“Enter number:”))
temp=n
rev=0
while(n>0):
dig=n%10
rev=rev*10+dig
n=n//10
if(temp==rev):
print(“The number is a palindrome!”)
else:
print(“The number isn’t a palindrome!”)
Output:
isn’t a palindrome!
Question 7.
Write a program to print the following pattern
* * * * *
* * * *
* * *
* *
*
Answer:
Coding:
number = int(input(“Please Enter Pattern Number: “))
for i in range(number,0,-l):
for j in range(1,i+1,1):
print(“*”, end”)
print()
Output:
Please Enter Pattern Number:5
* * * * *
* * * *
* * *
* *
*
![]()
Question 8.
Write a program to check if the year is leap year or not.
Answer:
Coding:
def leap_year(y):
.’ if (y % 400 = = 0):
print(y, “is the leap year”)
elif(y%4 = = 0):
print(y, “is the leap year”)
else:
print(y, “is not a leap year”)
year = int(input(“Enter a year…”)
print(leap_year(year))
Output:
Enter a year… 2007
2007 is the leap year