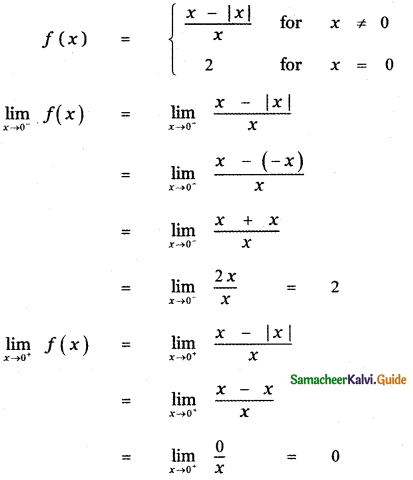
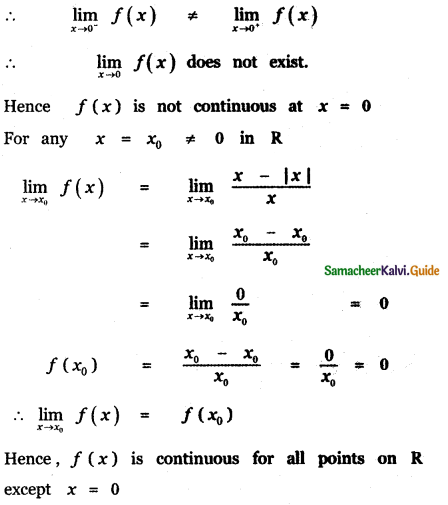
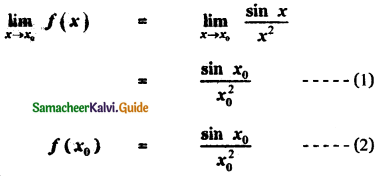
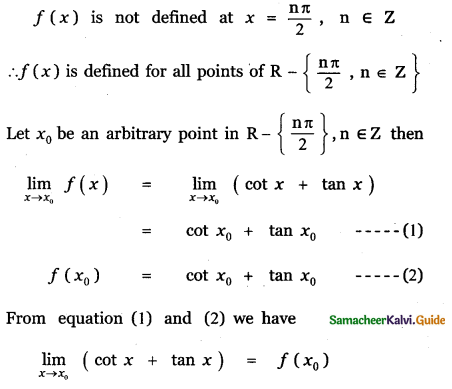
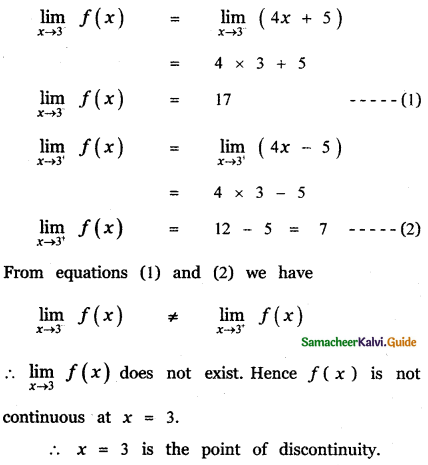
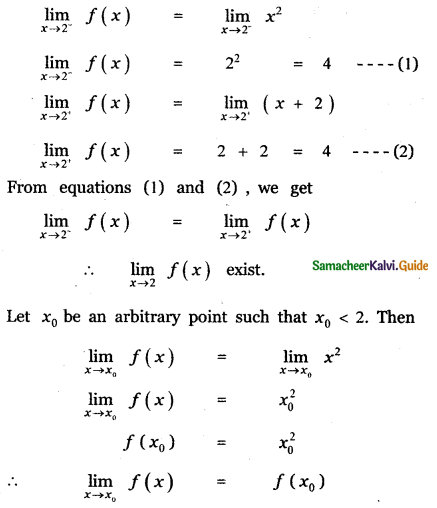
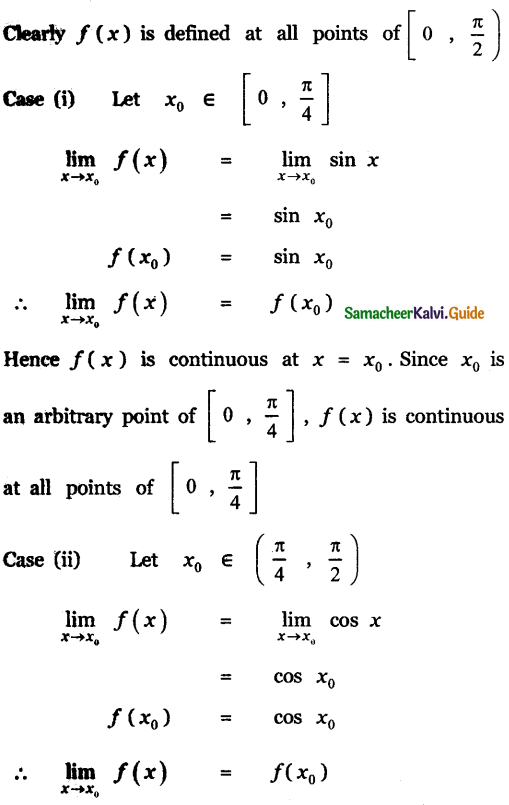
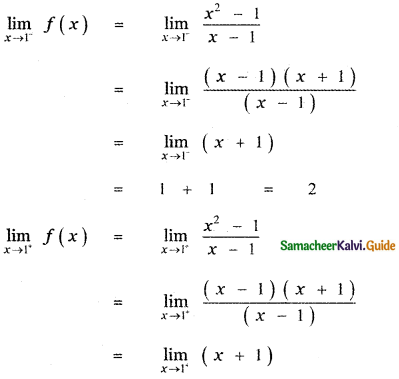
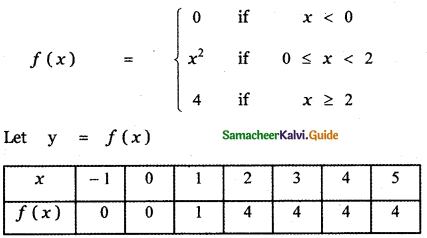
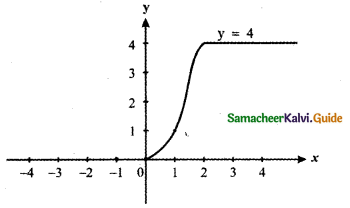
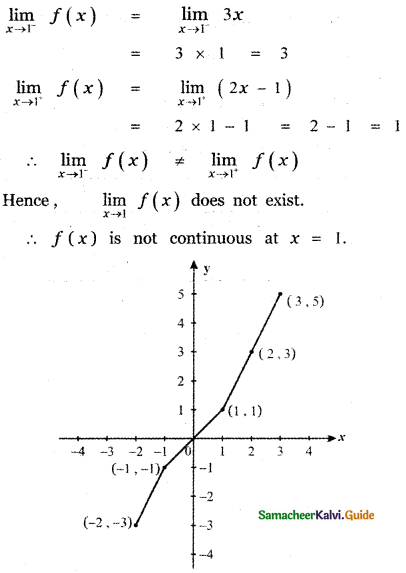
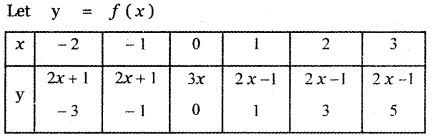
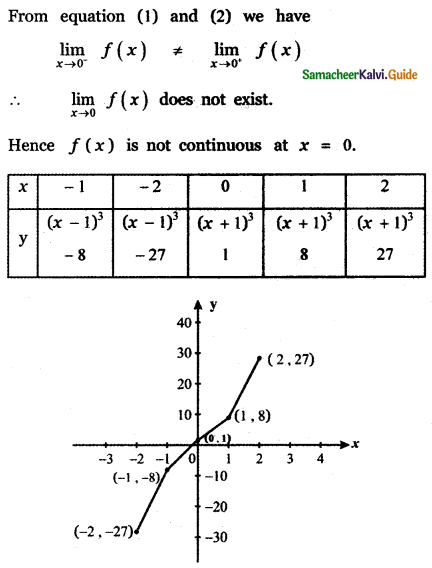
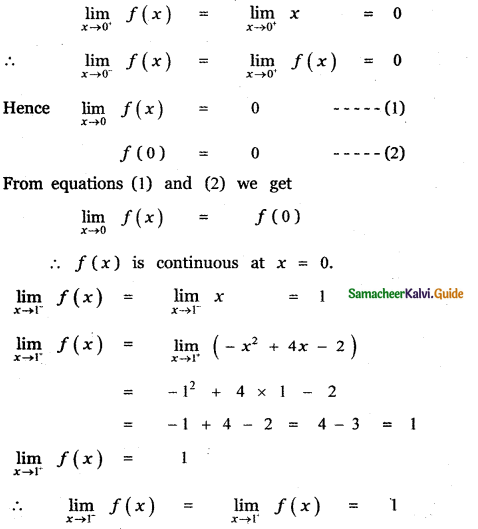
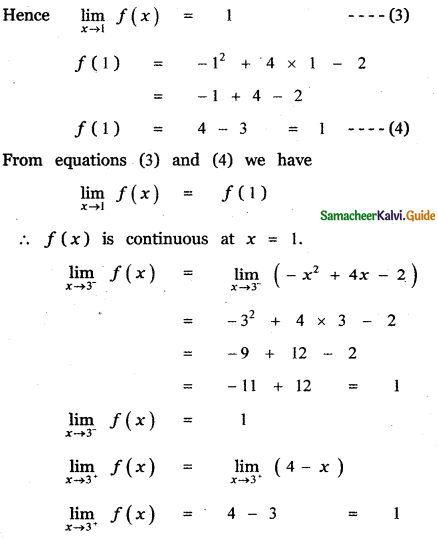
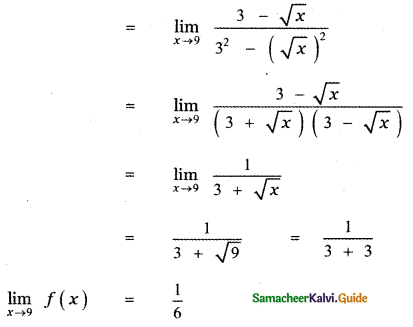
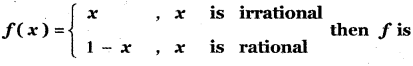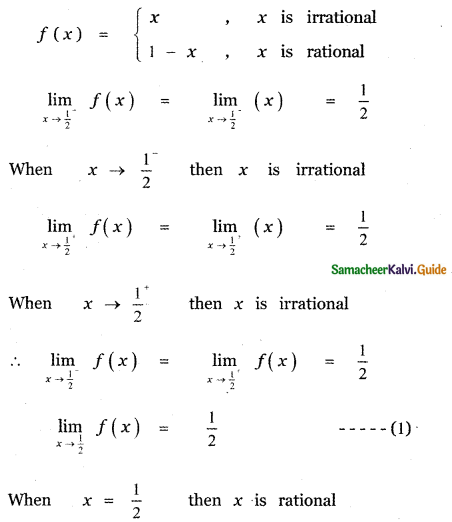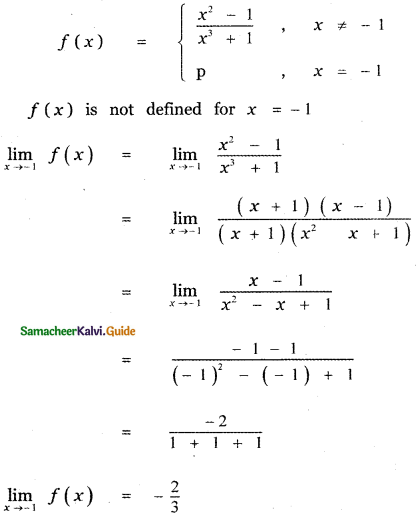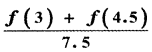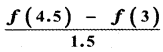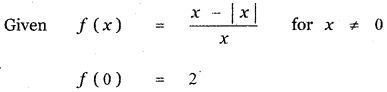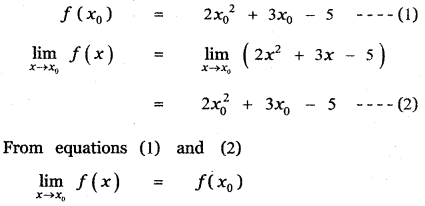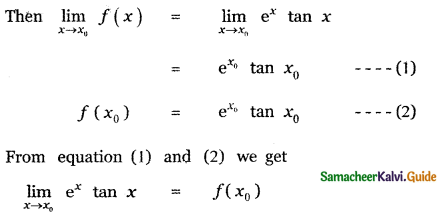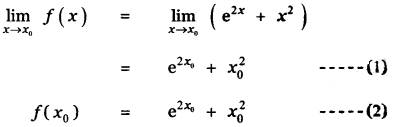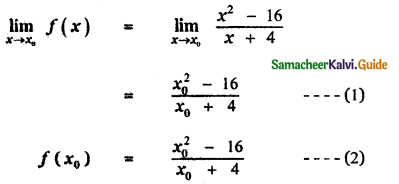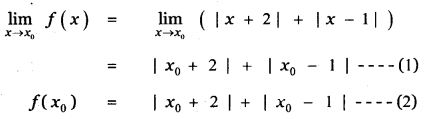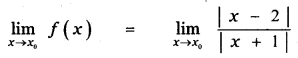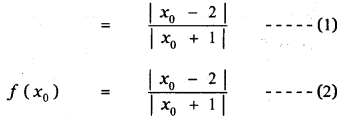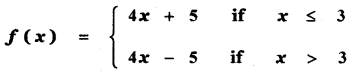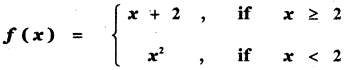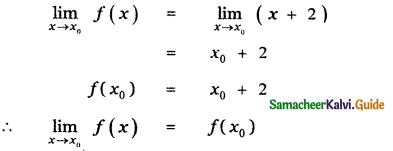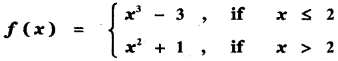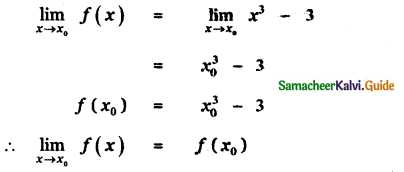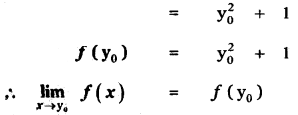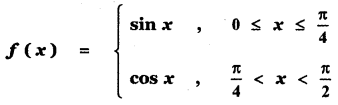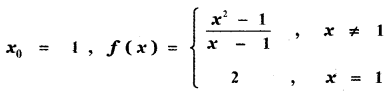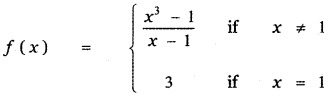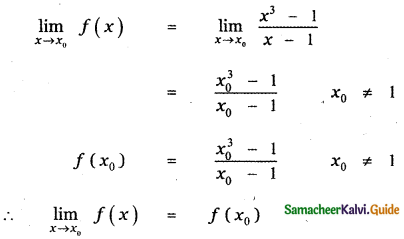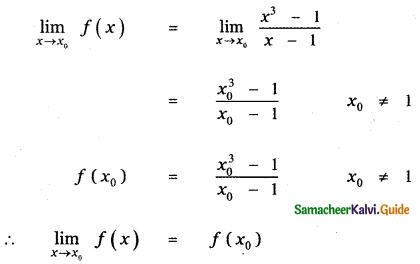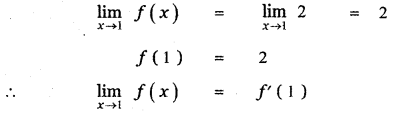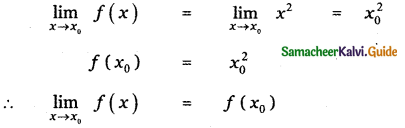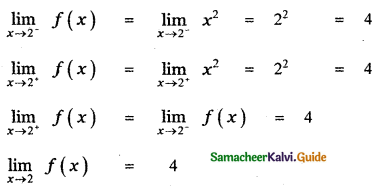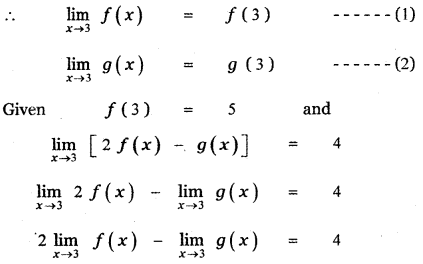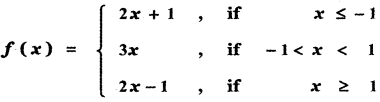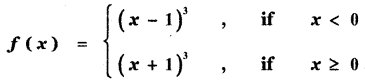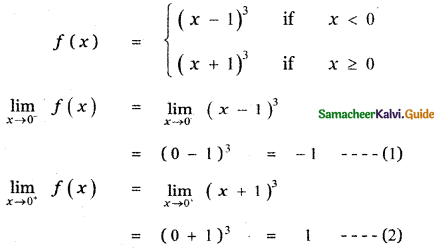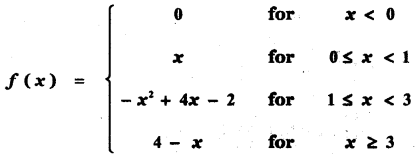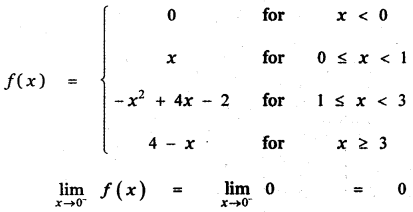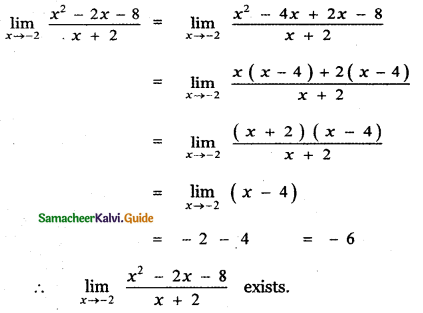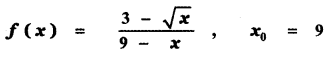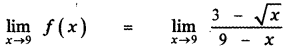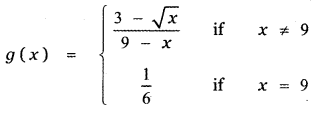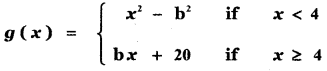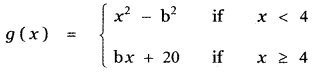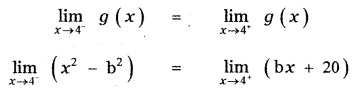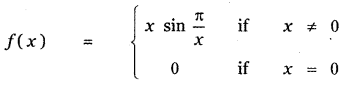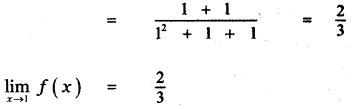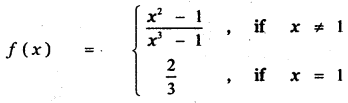Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 11 Integral Calculus Ex 11.3 Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Maths Solutions Chapter 11 Integral Calculus Ex 11.3
Integrate the following with respect to x:
Question 1.
(x + 4)5 + \(\) – cosec2 (3x – 1)
Answer:
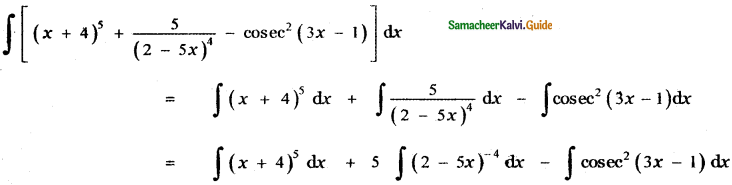
![]()
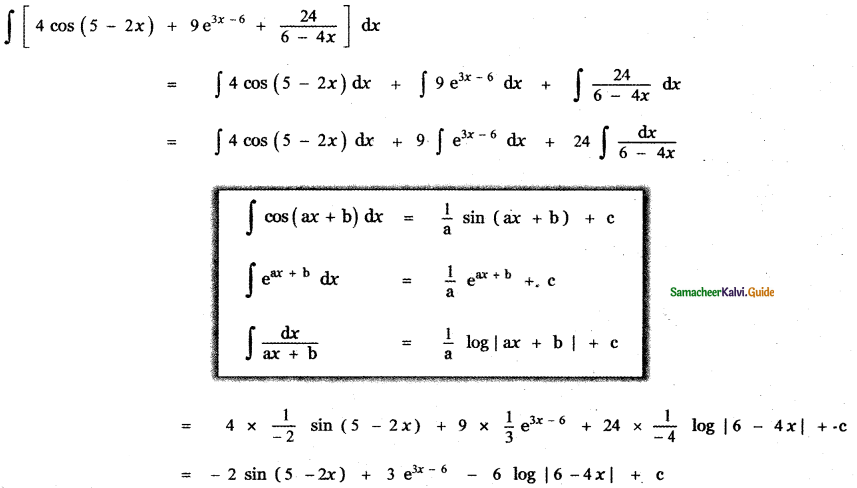
Question 2.
4 cos (5 – 2x) + 9 e3x – 6 + \(\frac{24}{6-4 x}\)
Answer:
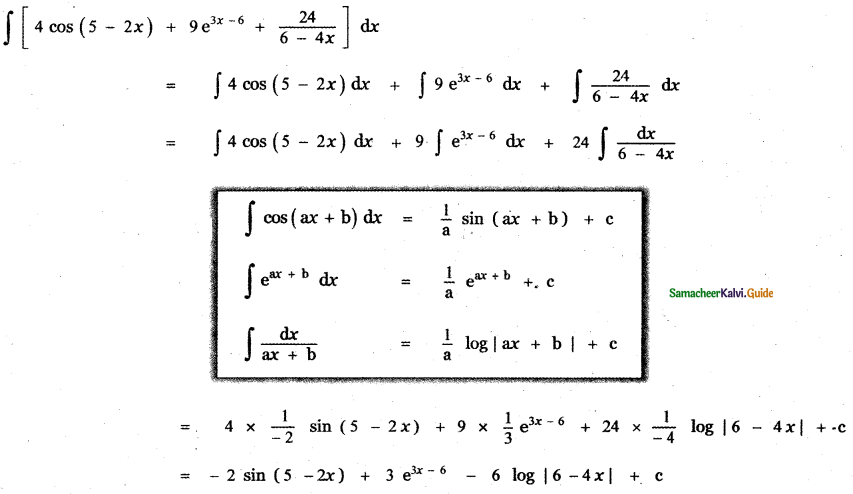
![]()
Question 3.
sec2 \(\frac{x}{5}\) + 18 cos 2x + 10 sec (5x + 3) tan (5x + 3)
Answer:
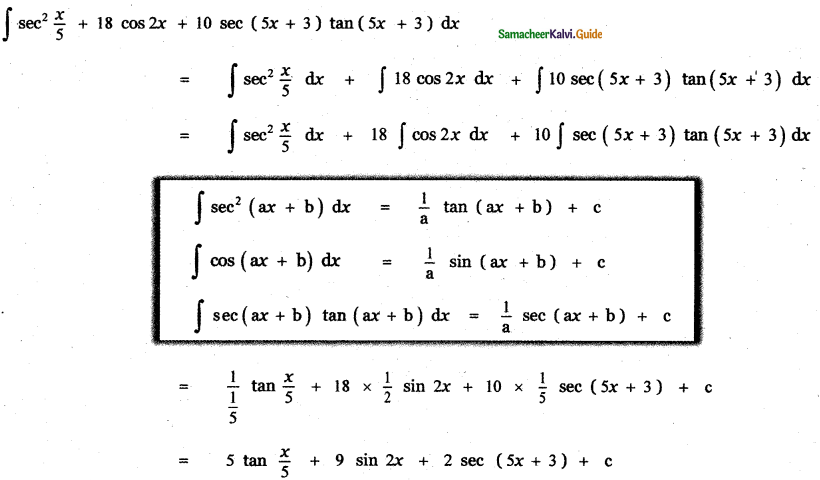
![]()
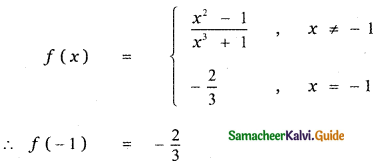
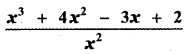
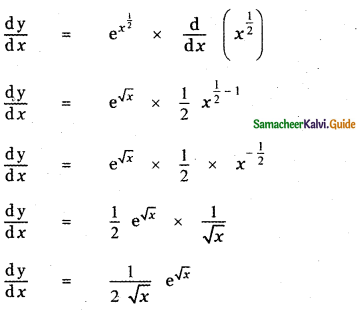
Question 4.
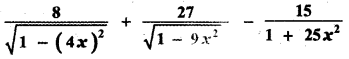
Answer:
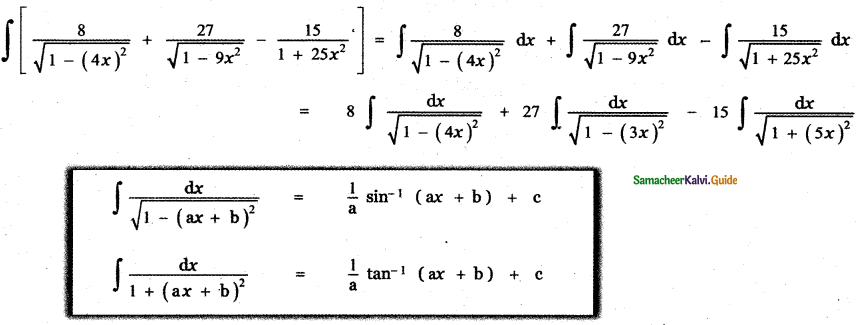
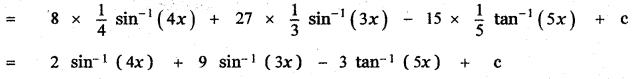
![]()
Question 5.

Answer:
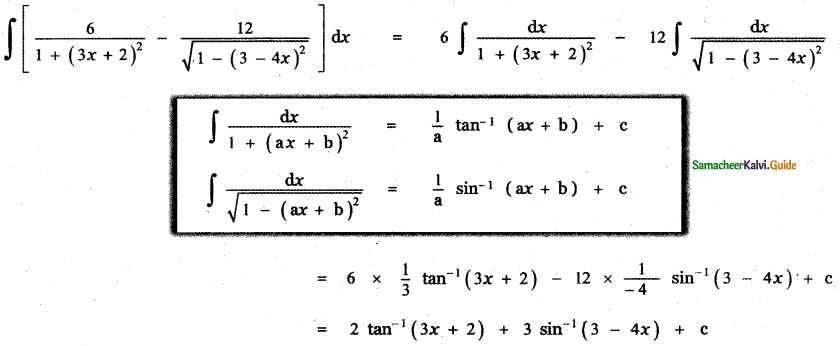
![]()
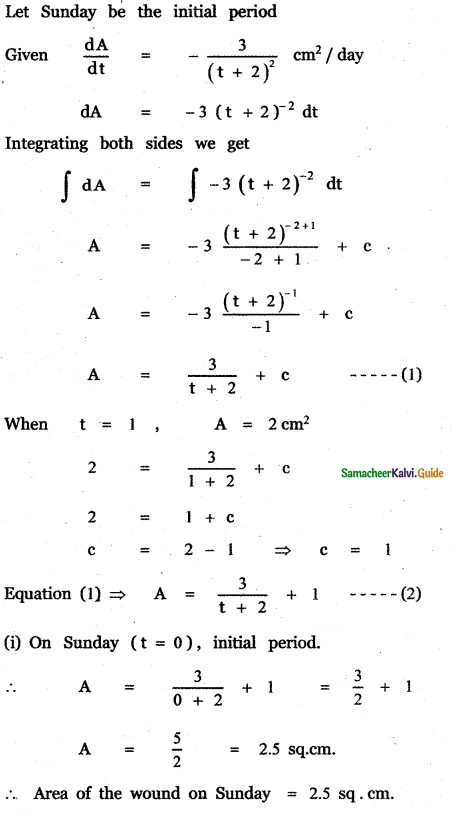
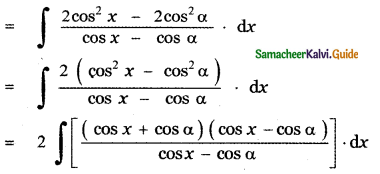
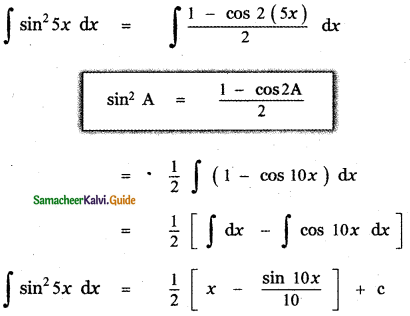
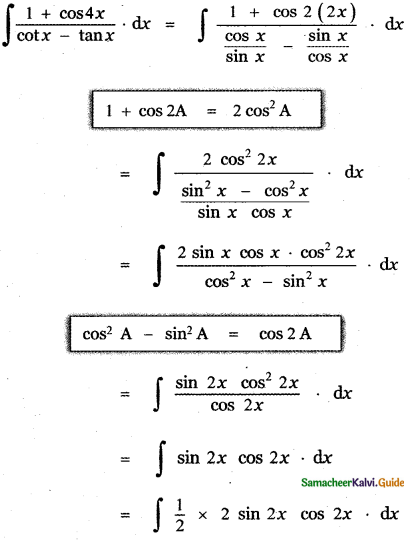
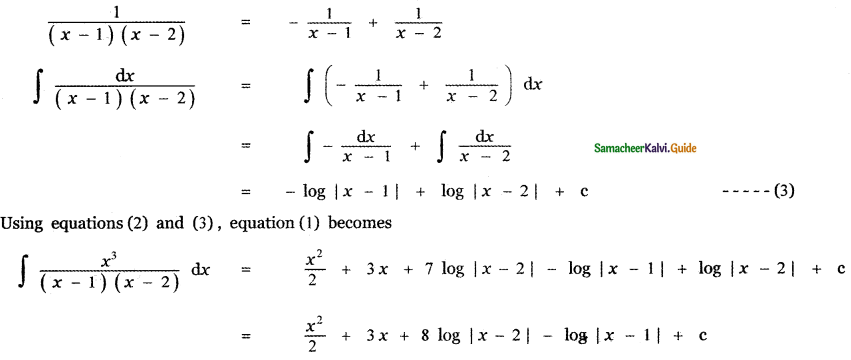
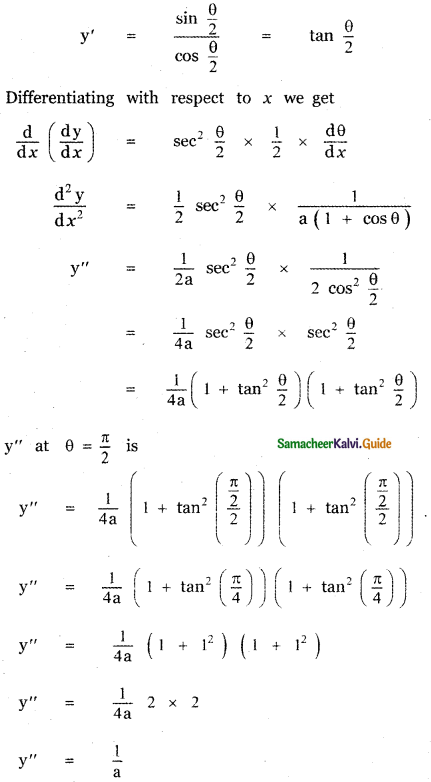
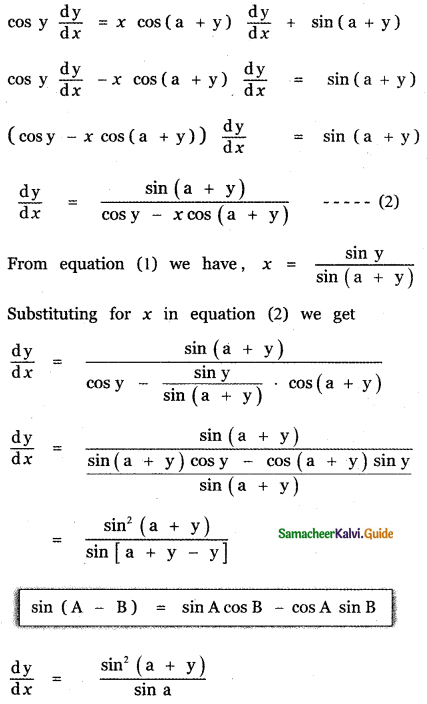
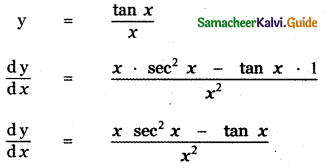
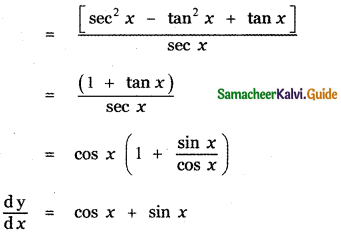
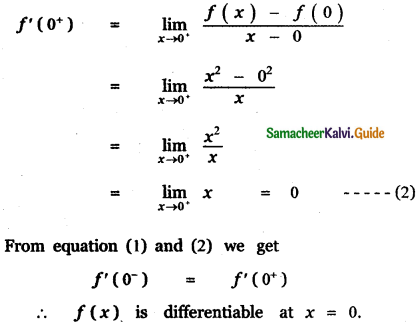
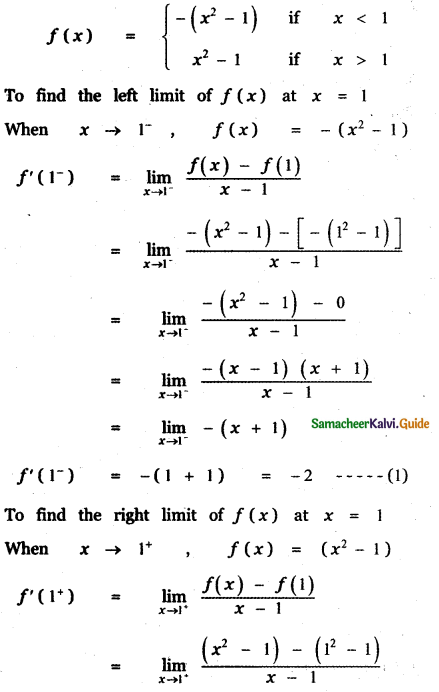
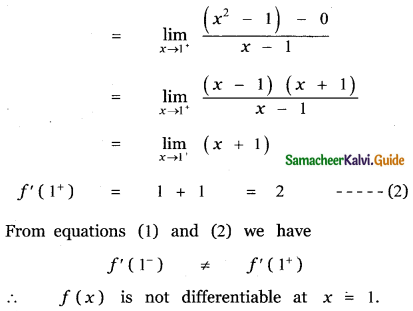
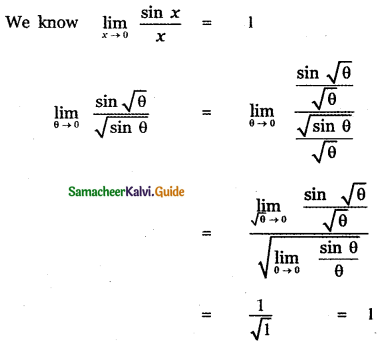
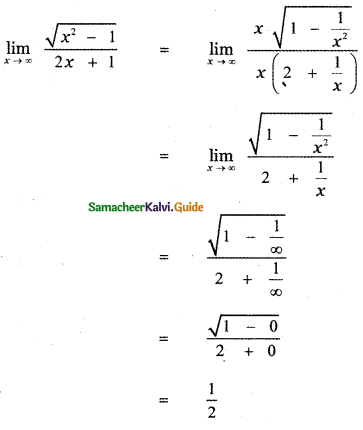
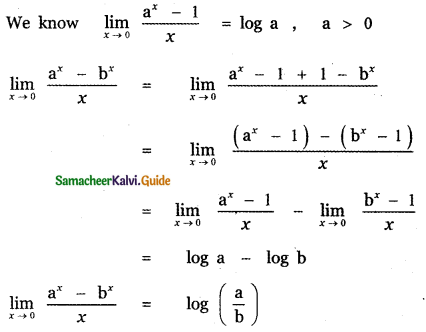
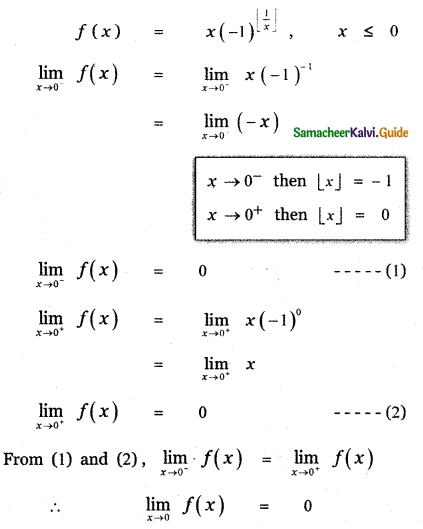
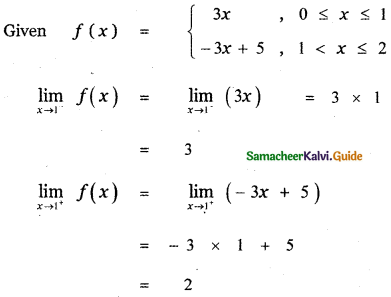
Question 6.
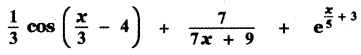
Answer:
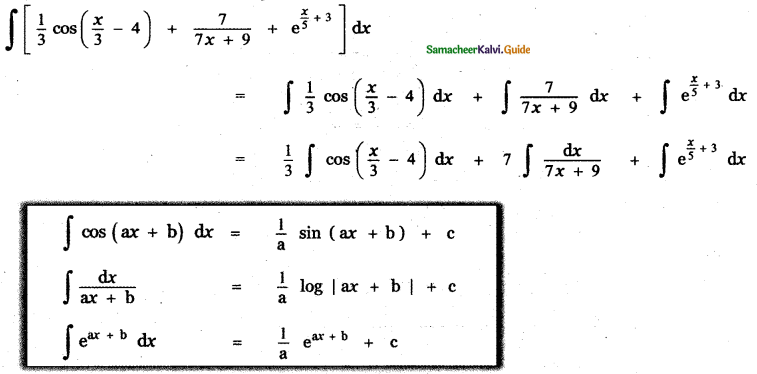
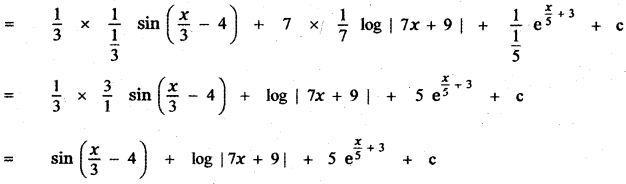
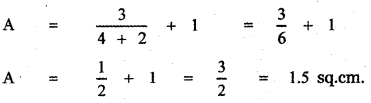
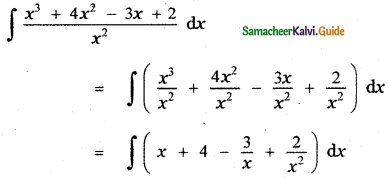
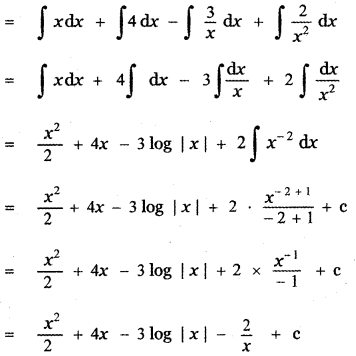
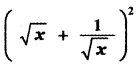
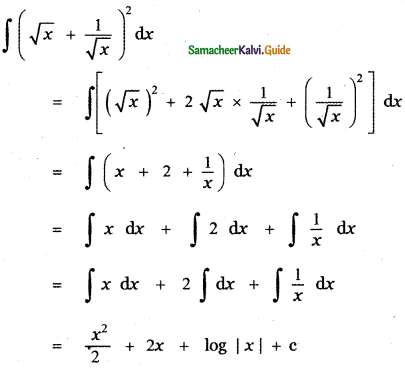
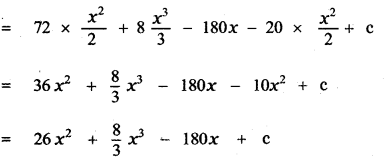
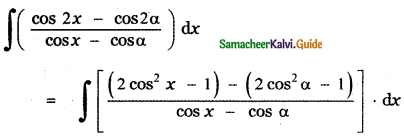
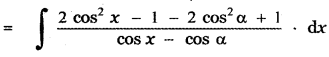
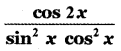
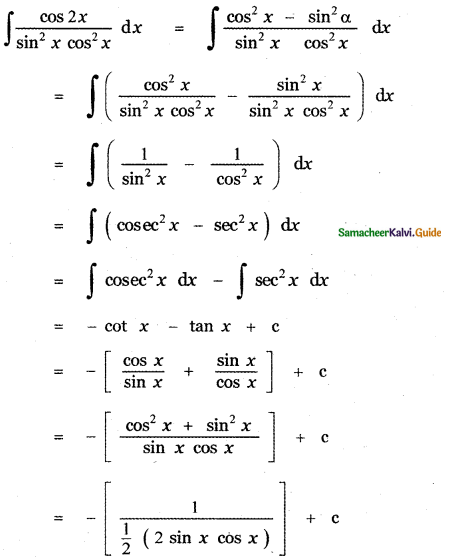
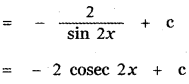
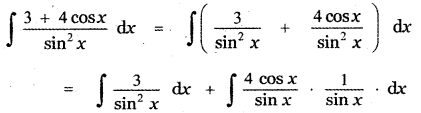
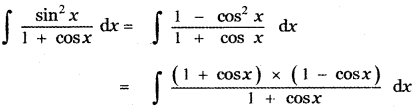
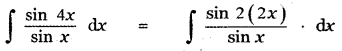
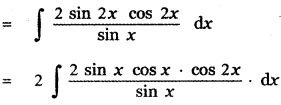
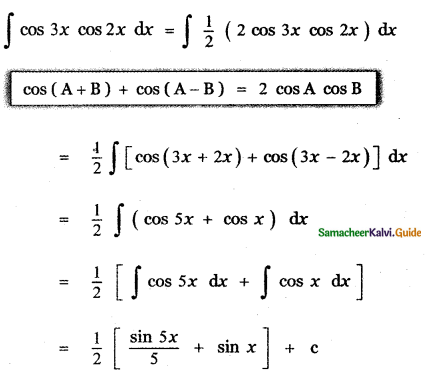
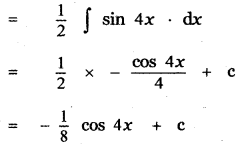
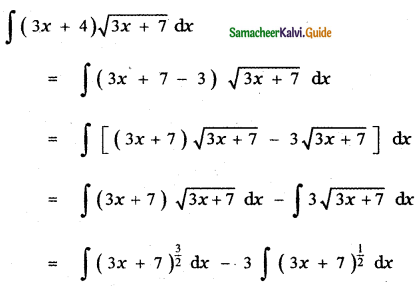
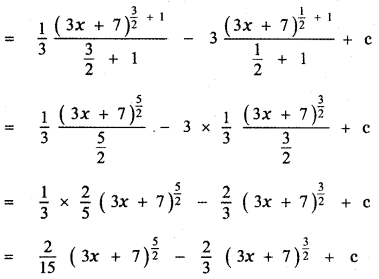
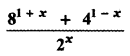
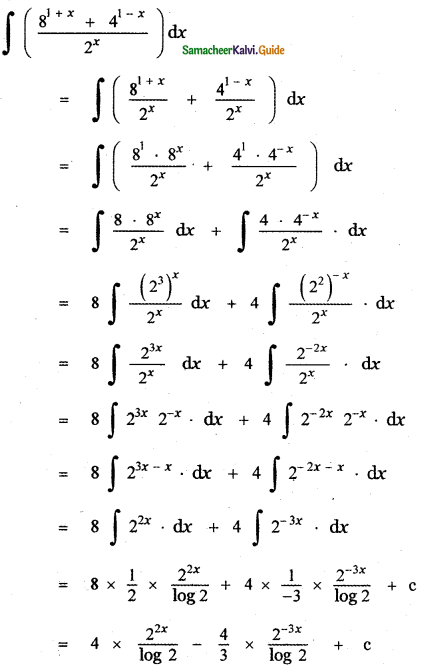
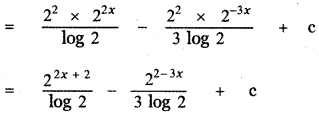
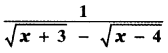
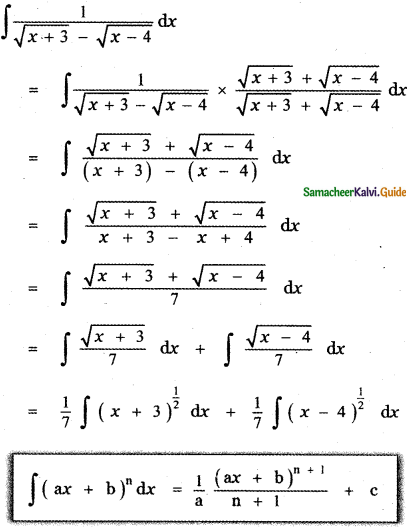
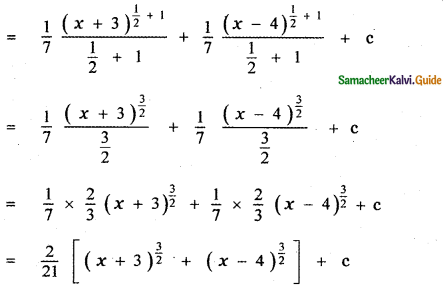
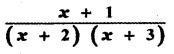
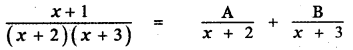
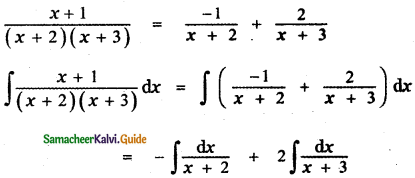
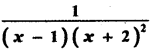
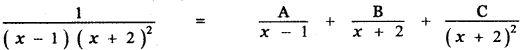
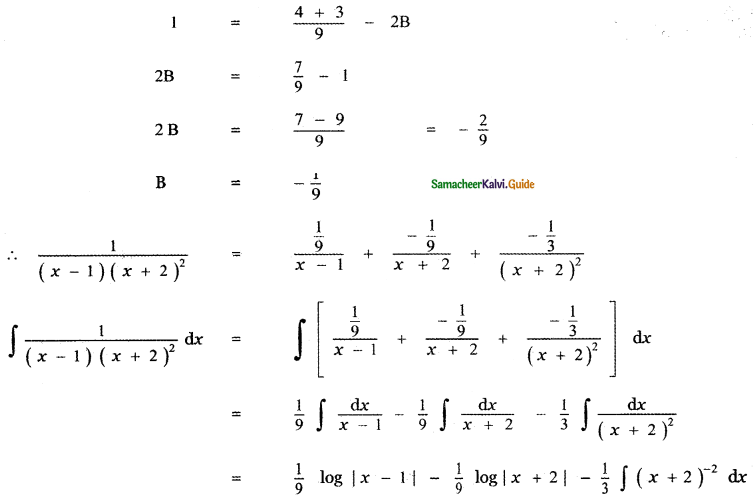
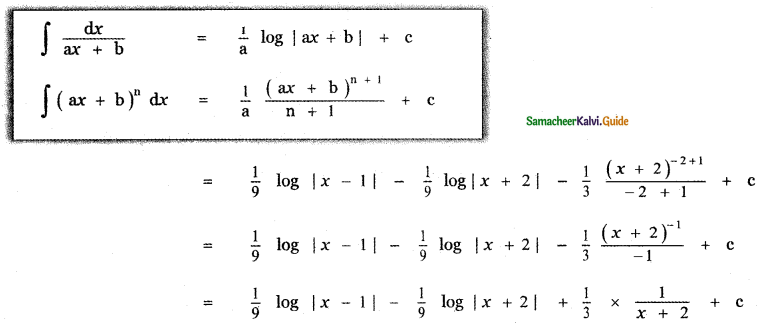
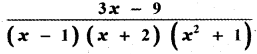
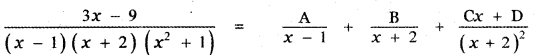
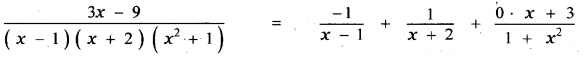
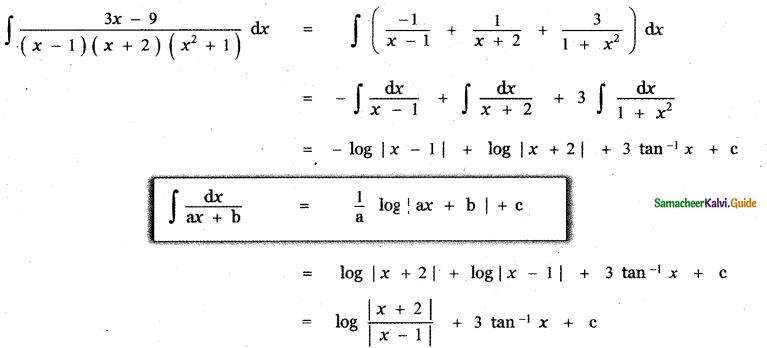
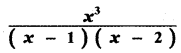
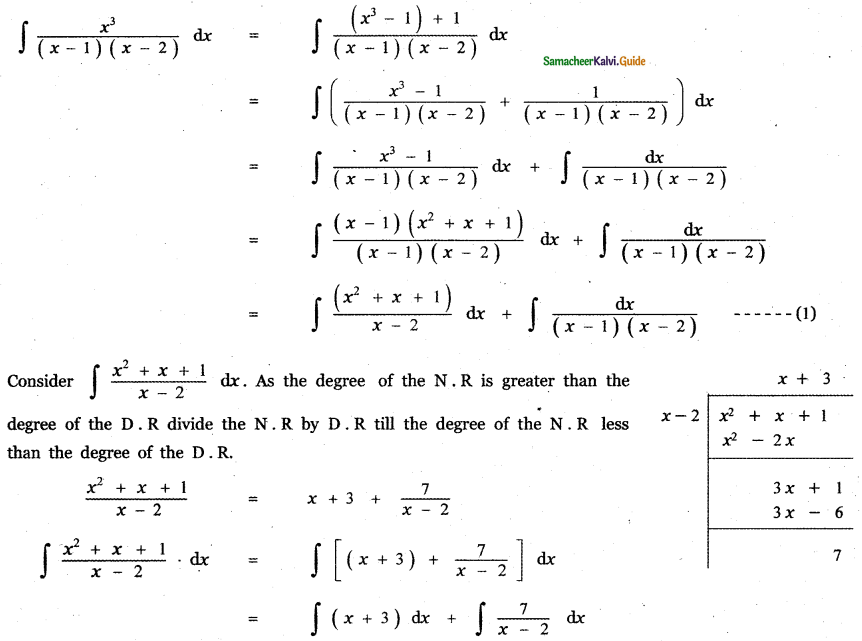
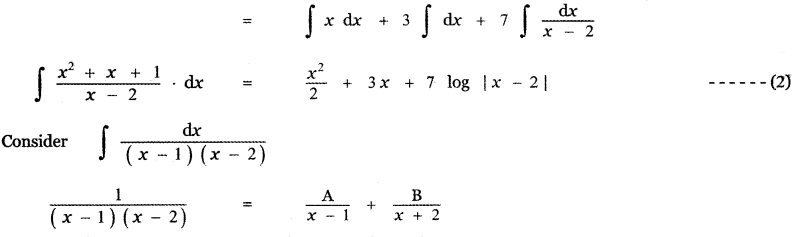
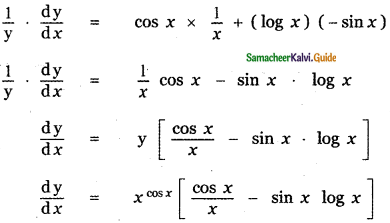
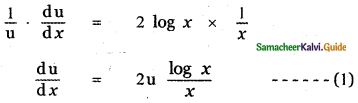
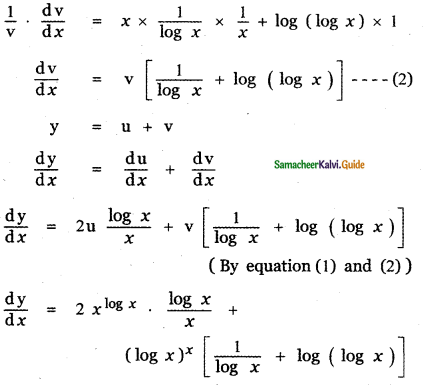
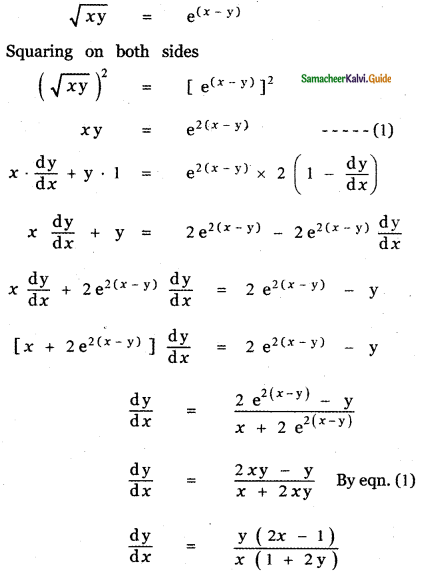
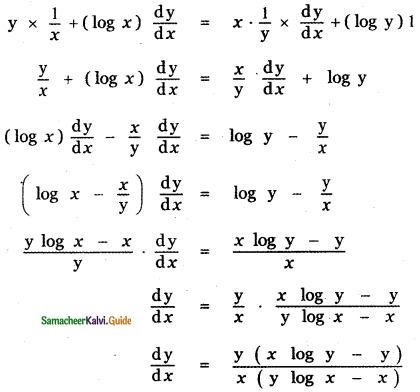
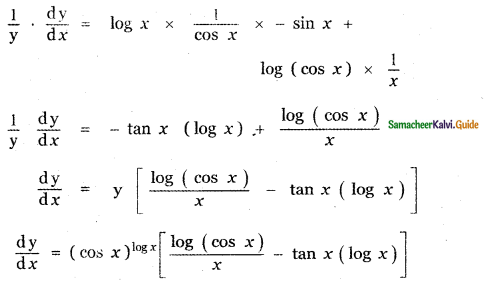
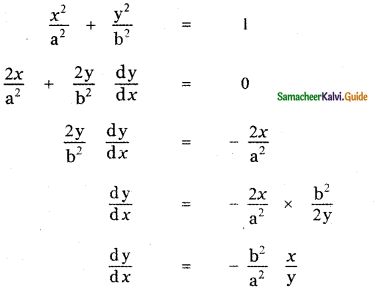
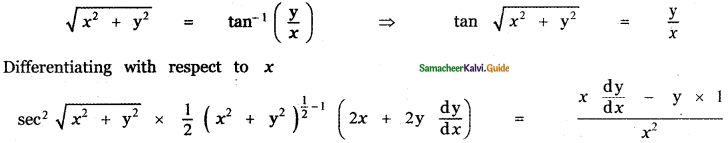
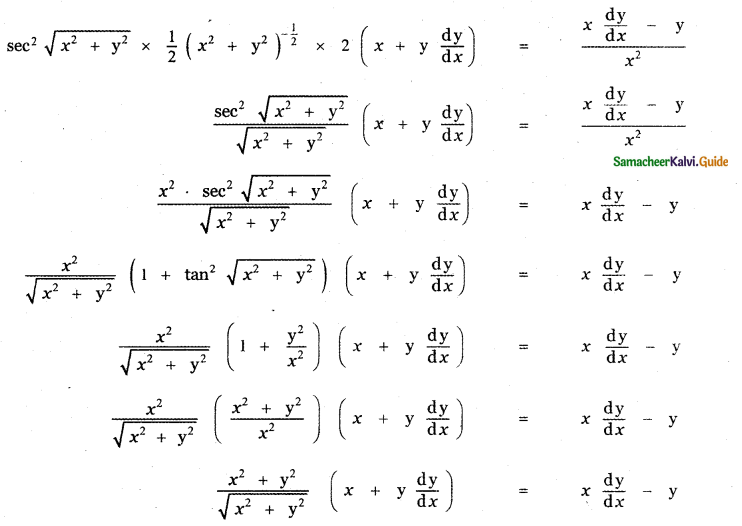
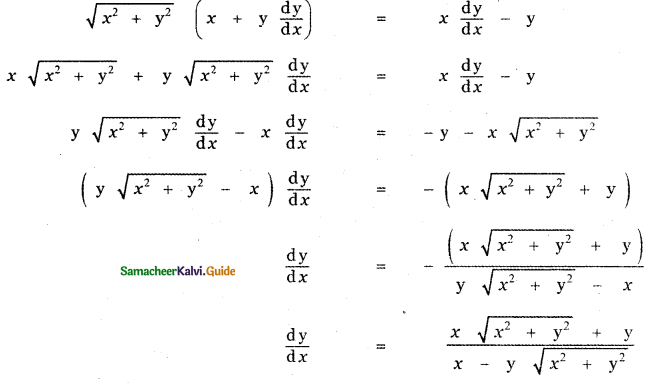
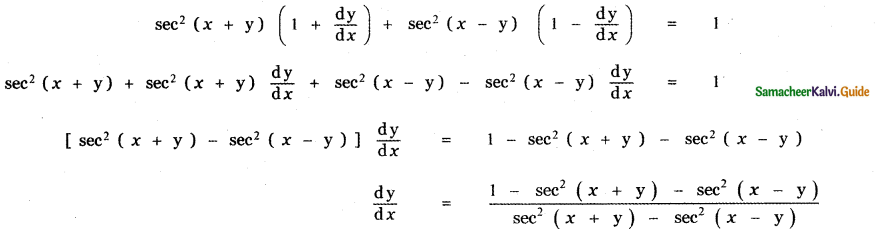
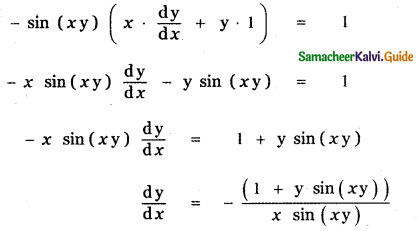
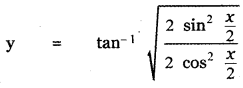
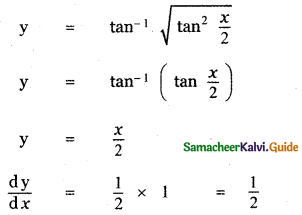
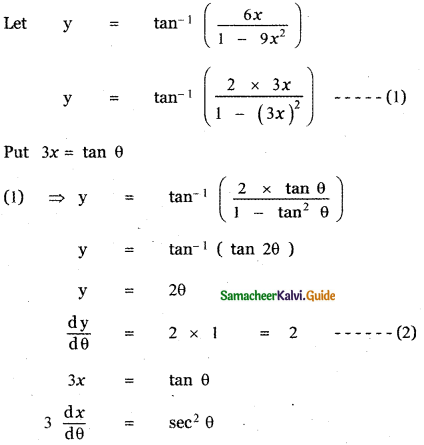
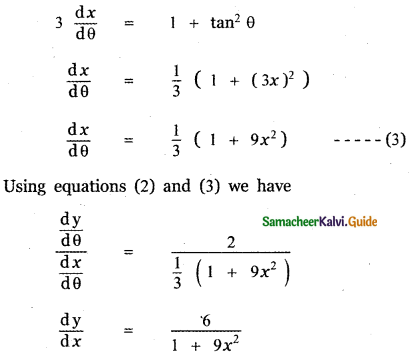
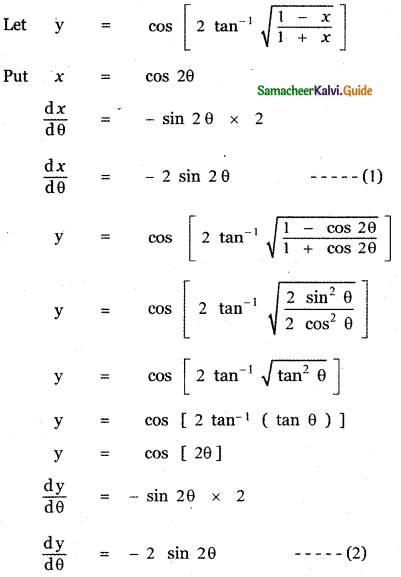
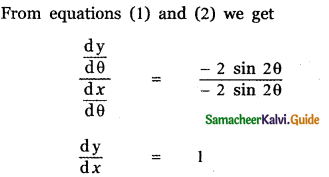
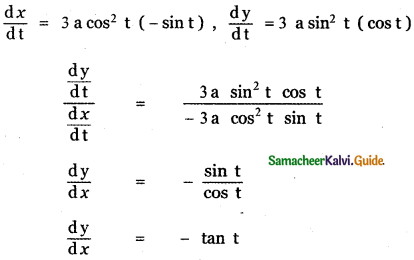
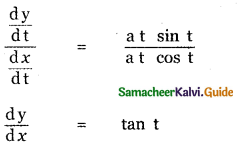
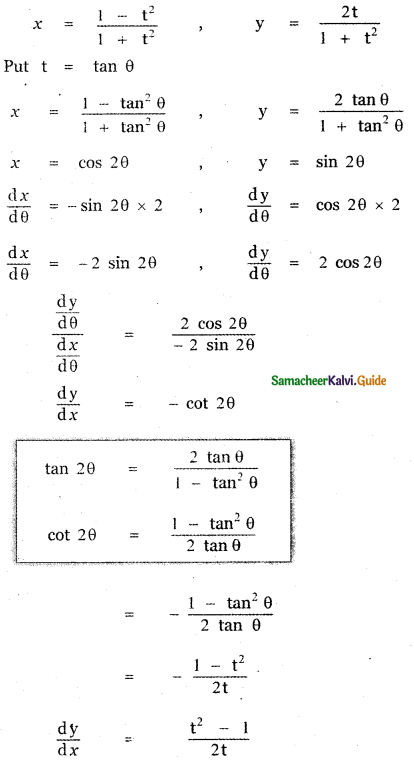
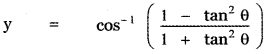
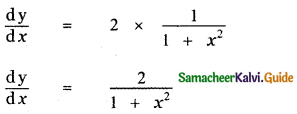
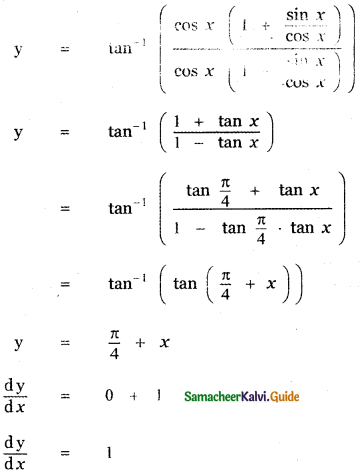
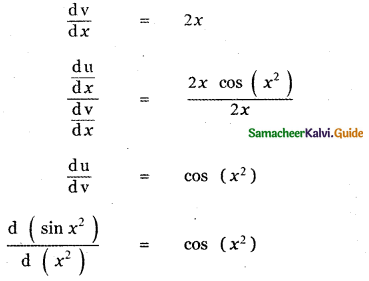
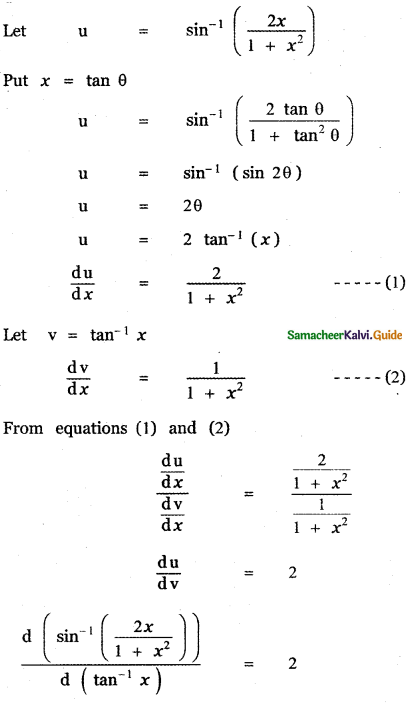
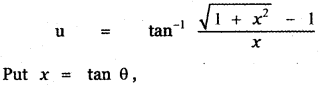
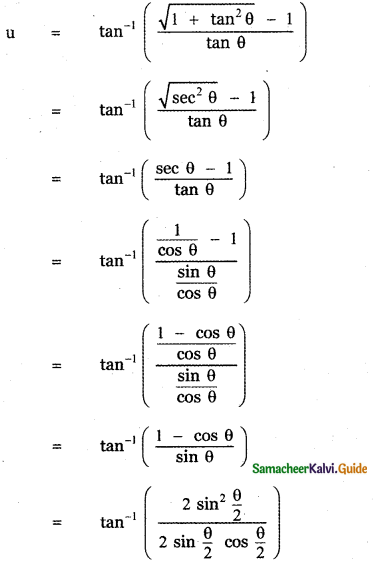
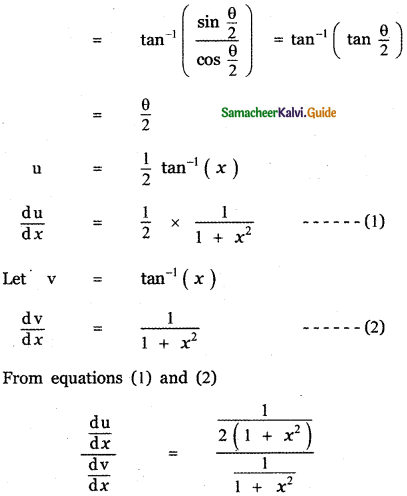
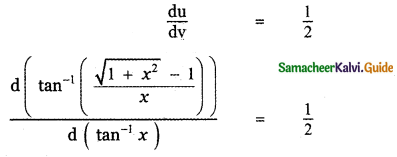
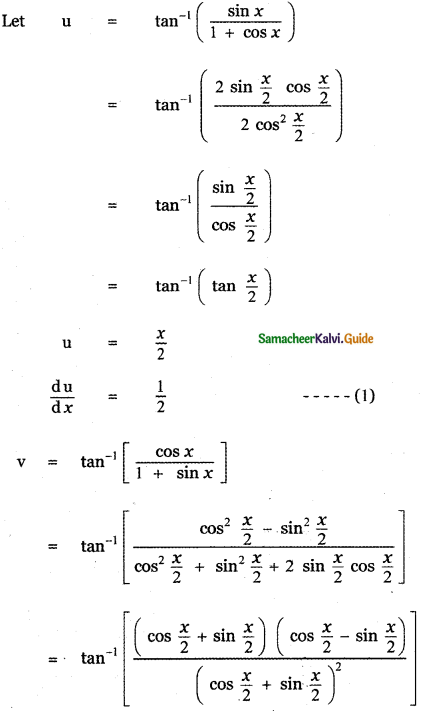
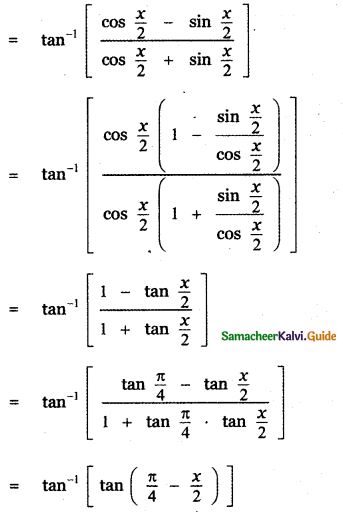
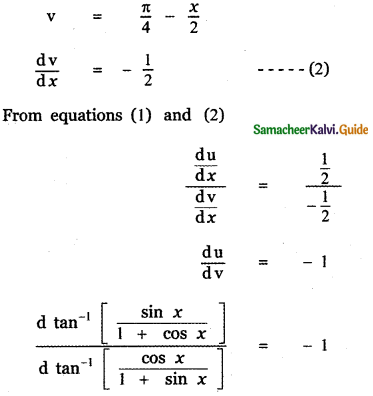
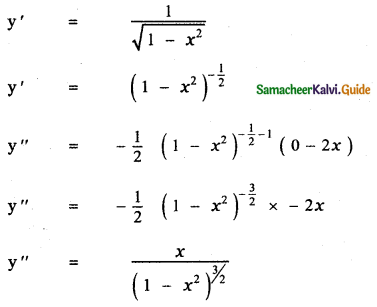
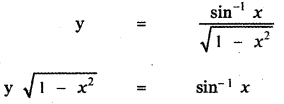

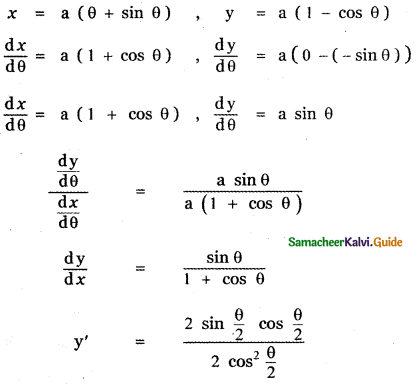
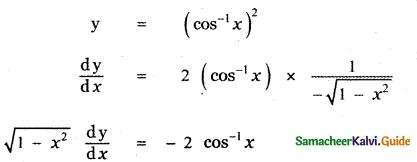
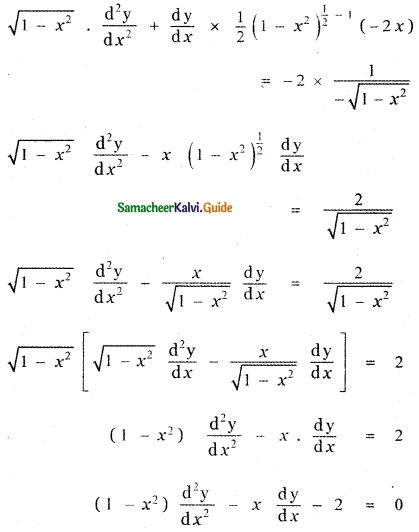
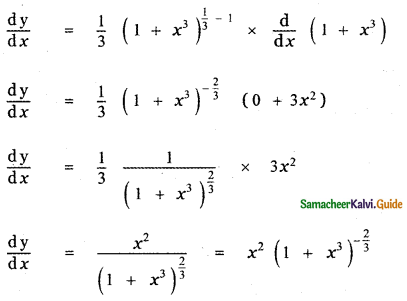
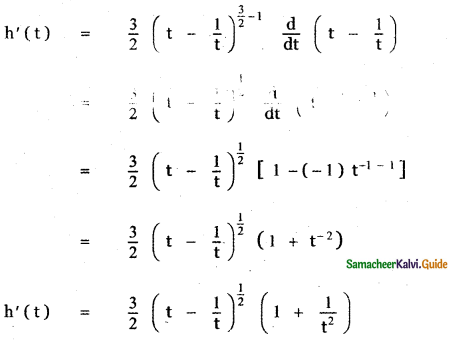
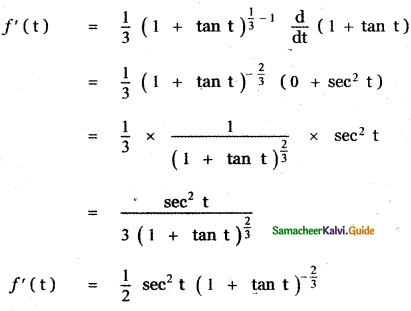
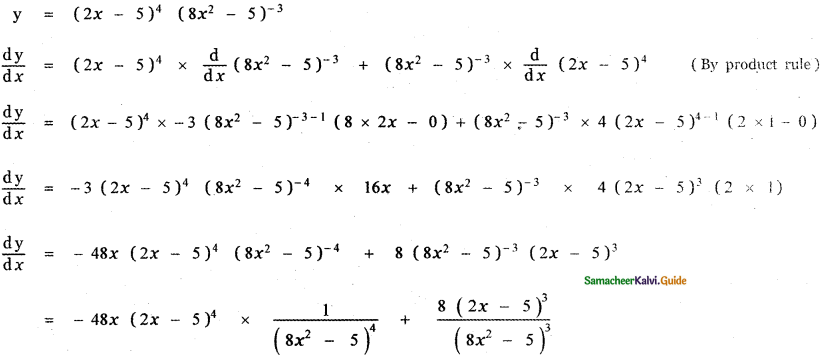
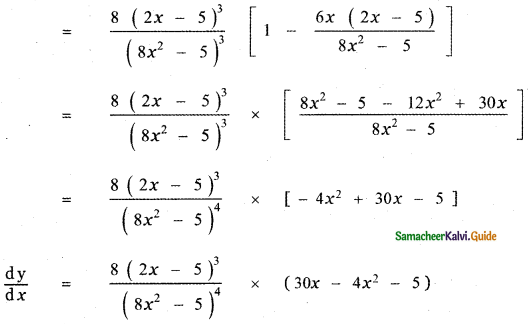
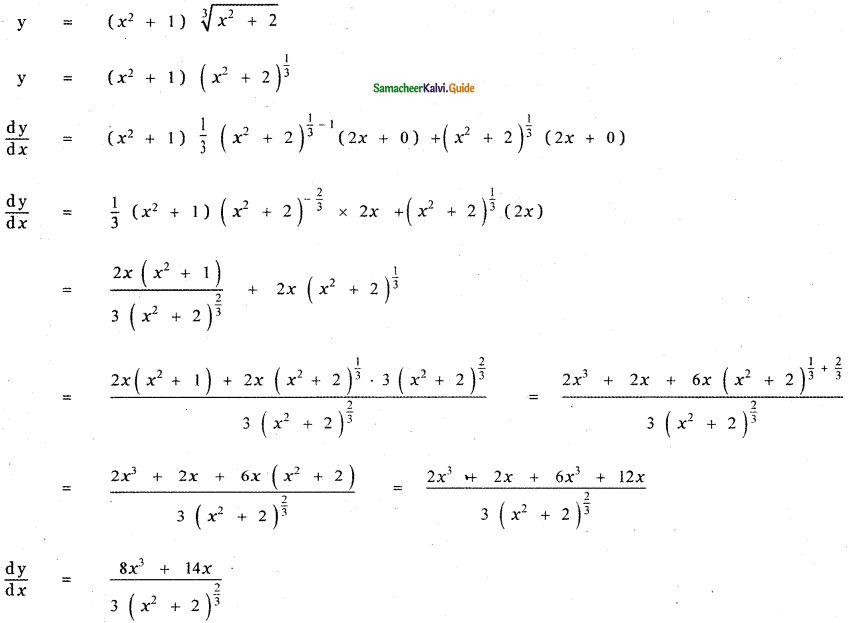
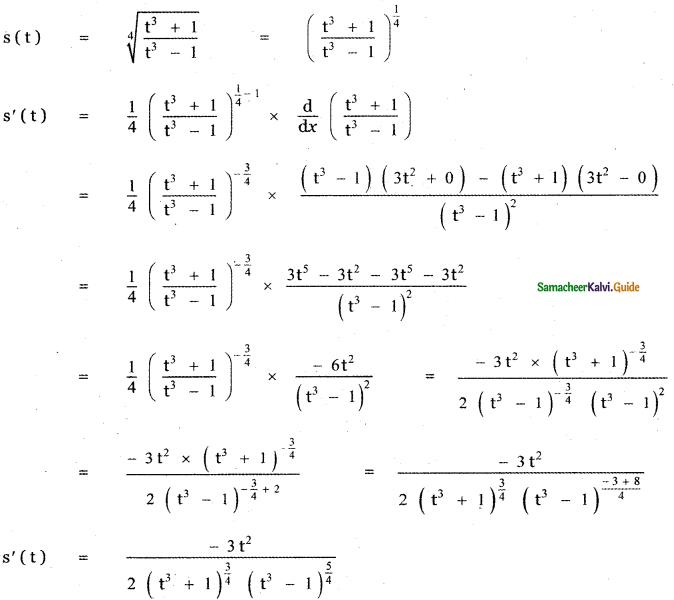
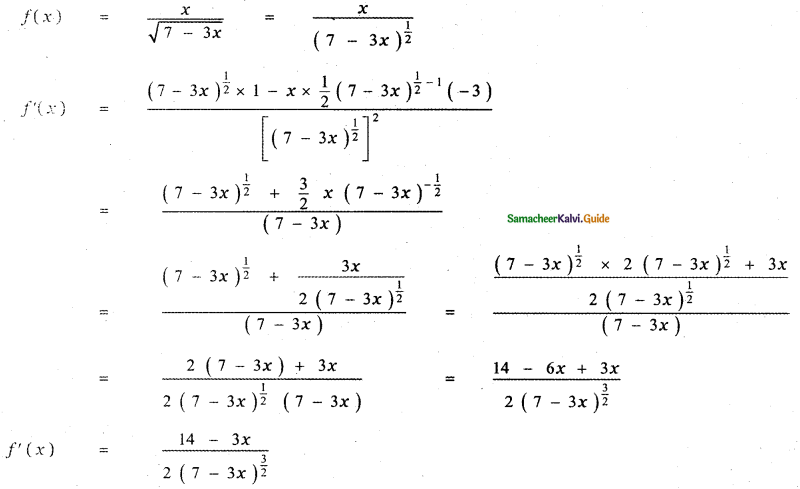
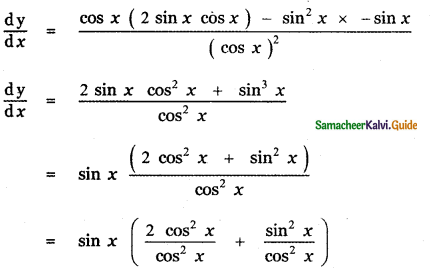
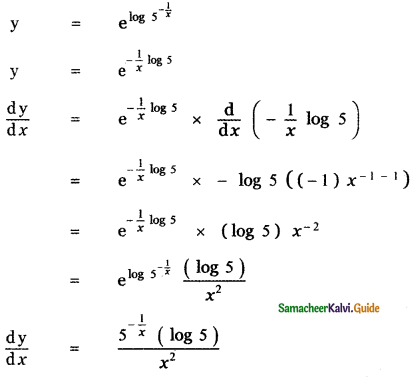
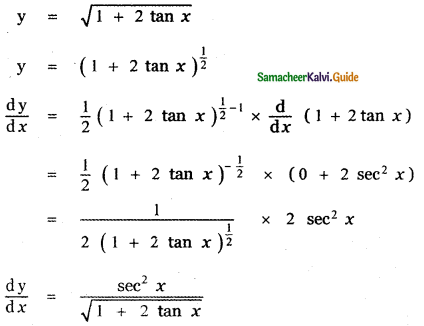
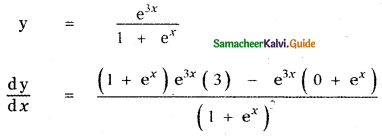
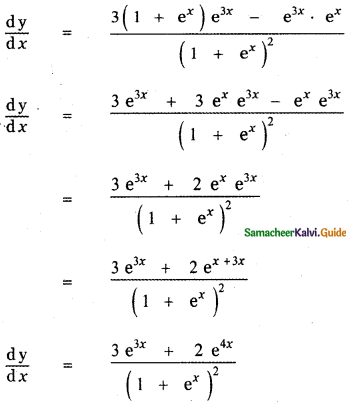
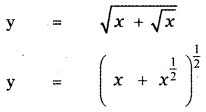
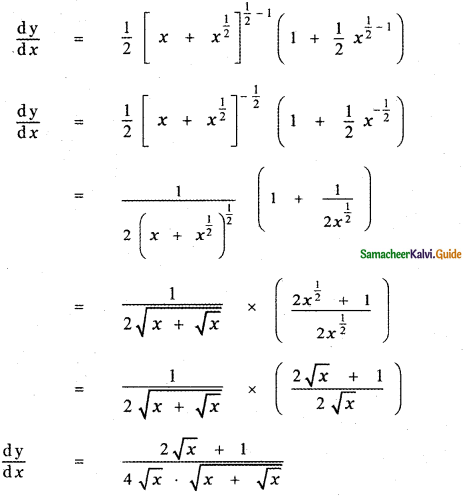
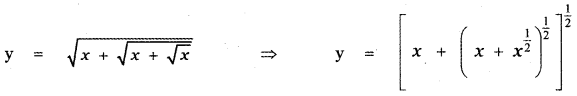
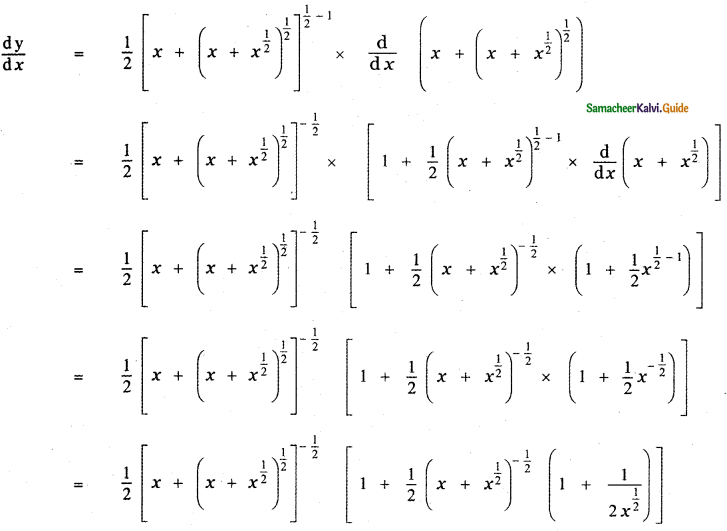
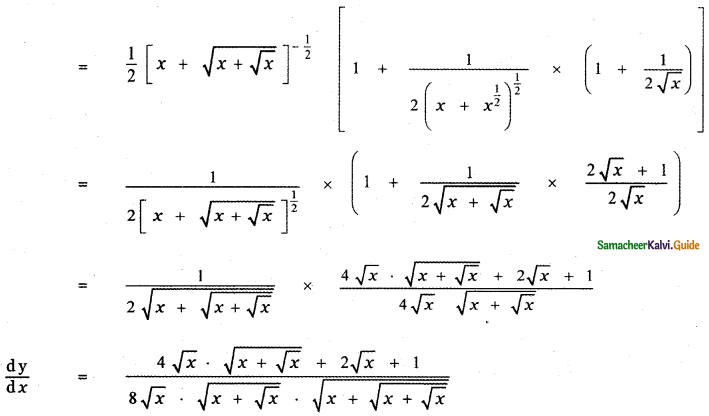
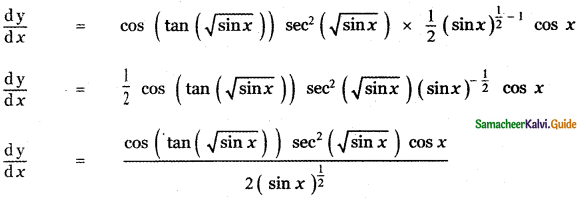
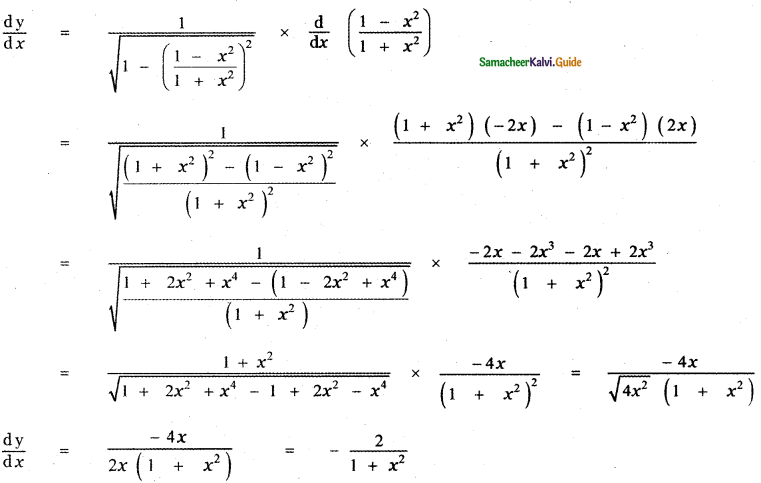
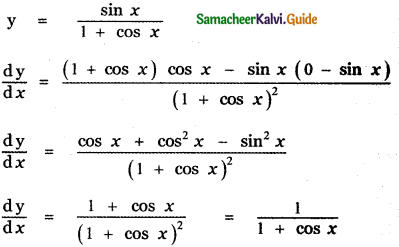
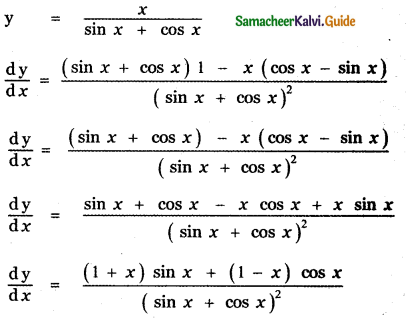
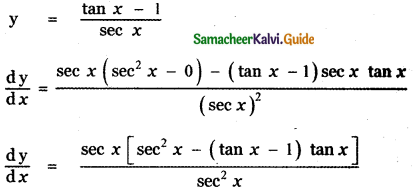
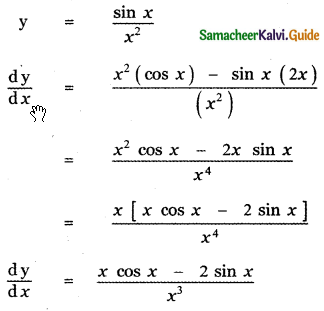
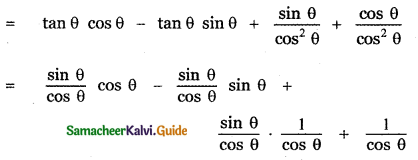
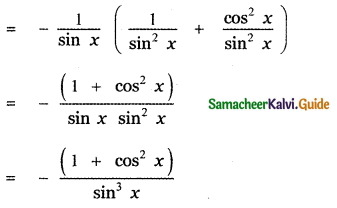

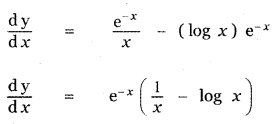
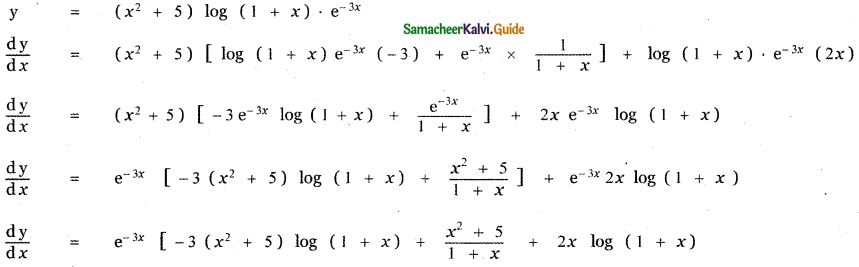
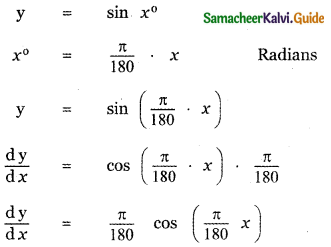
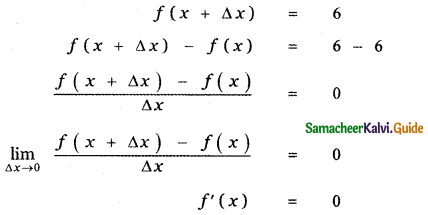
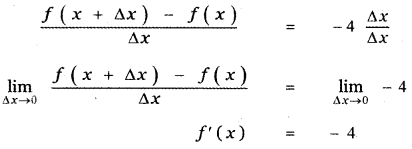
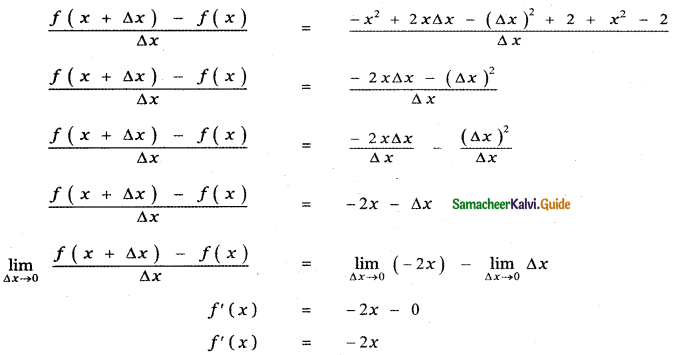
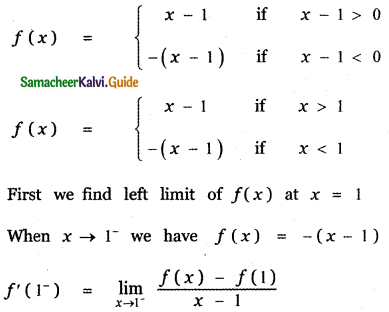
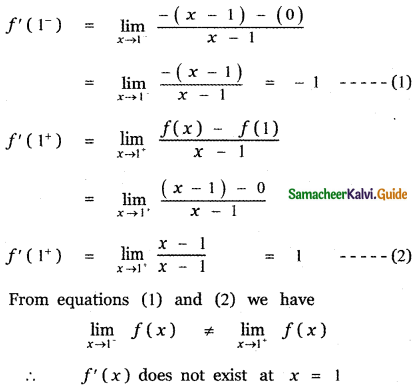
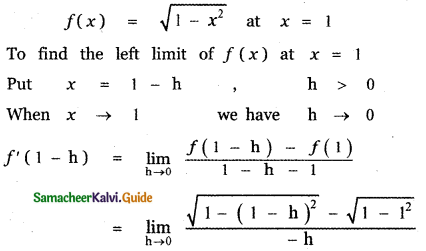
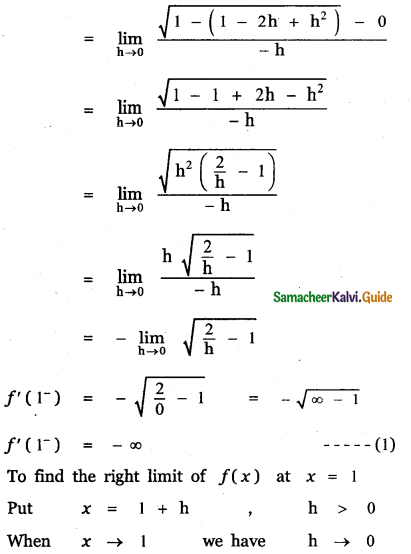
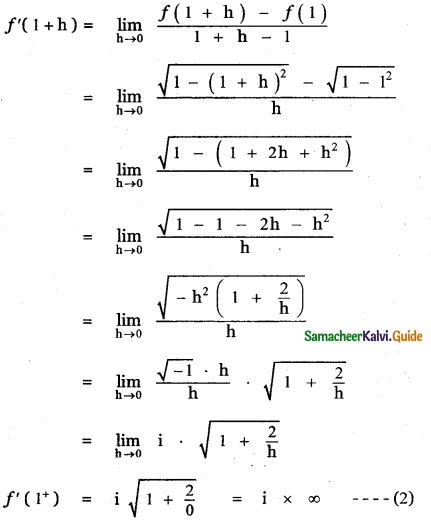
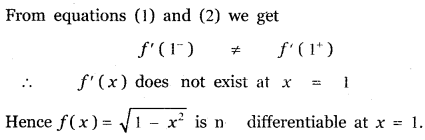
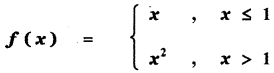

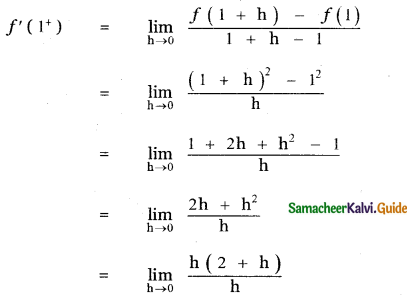
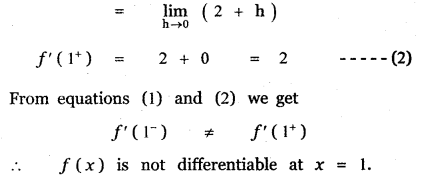
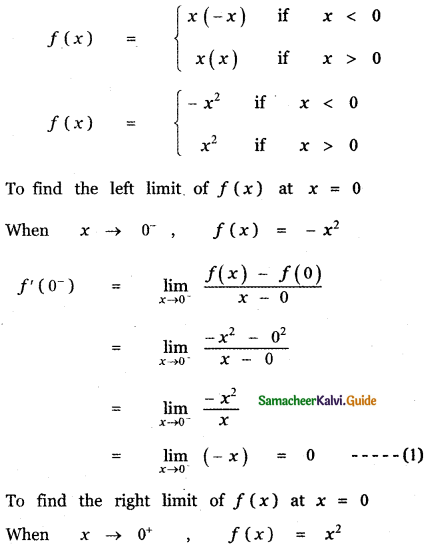
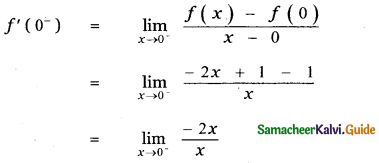
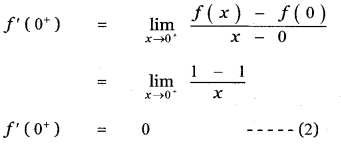
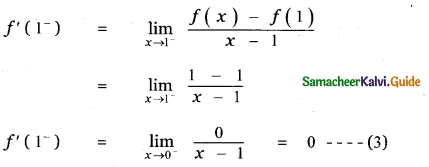
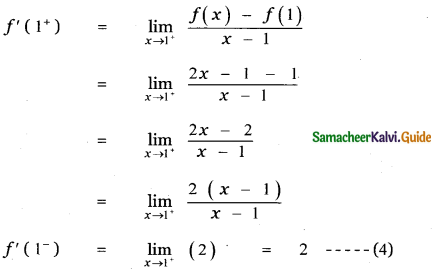
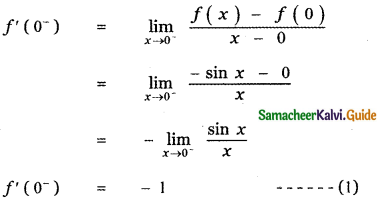
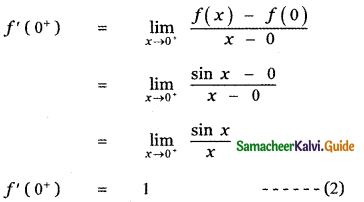
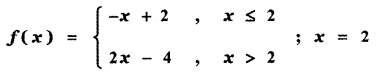
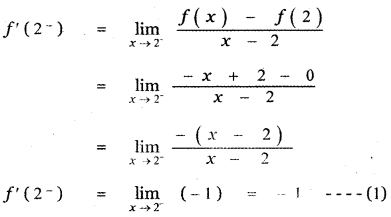
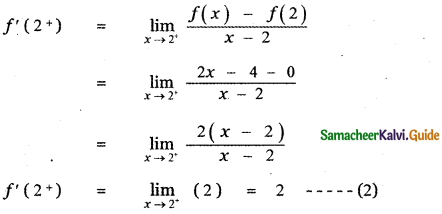
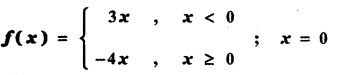
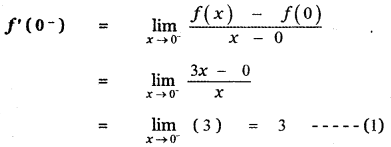
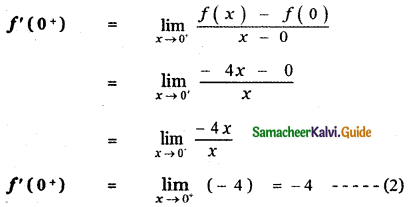
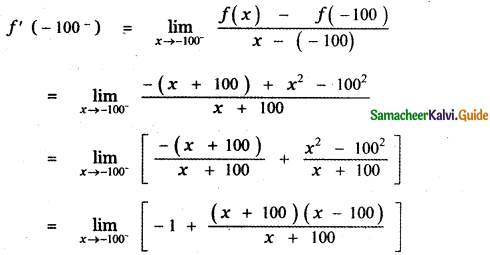
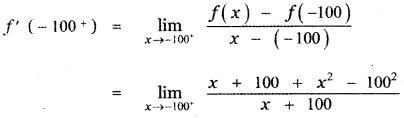
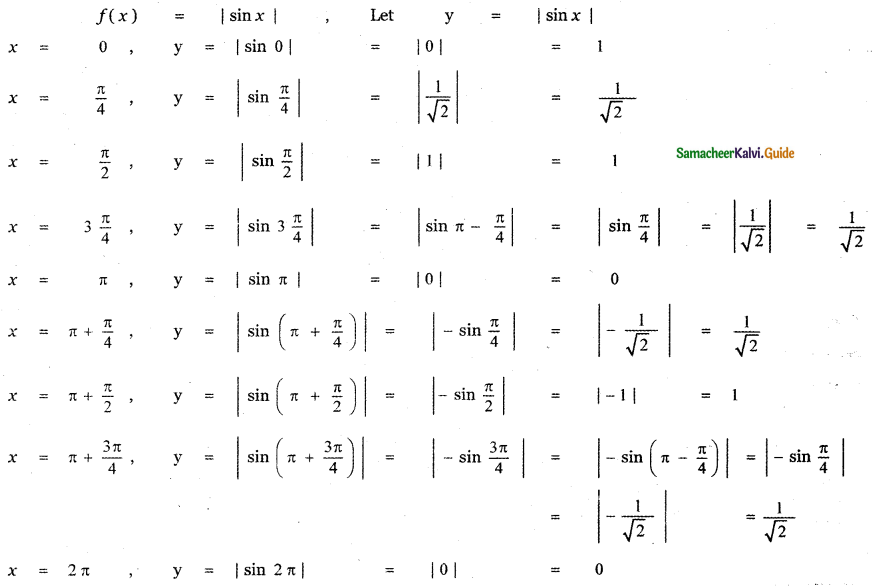
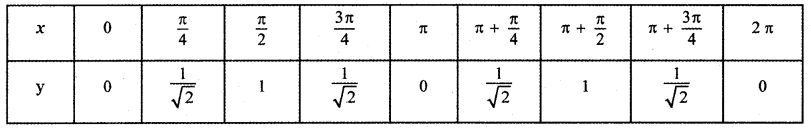
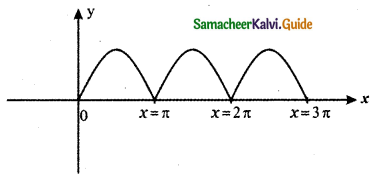
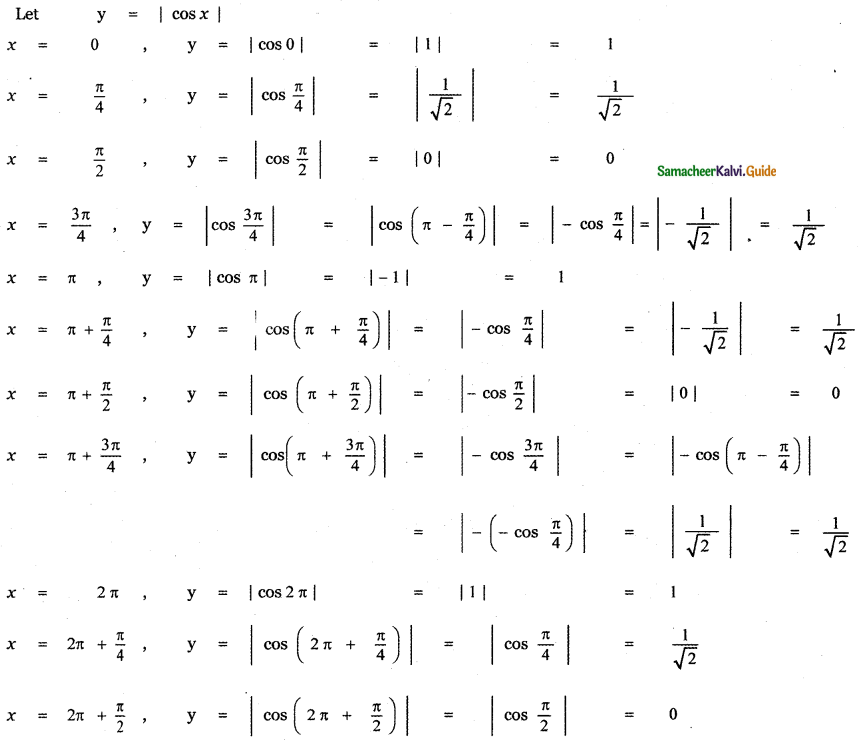
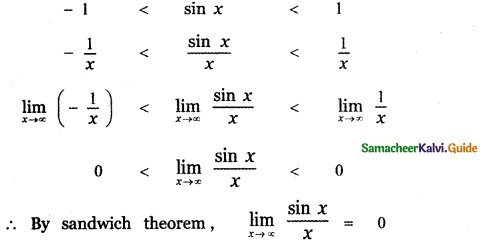
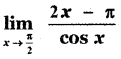
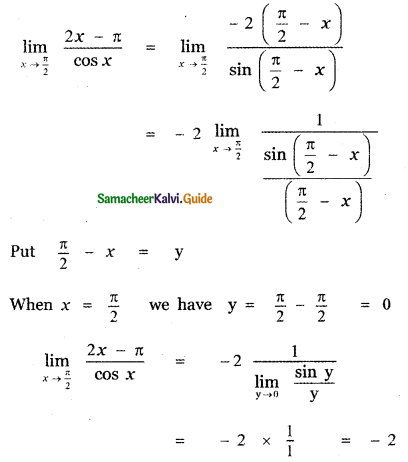
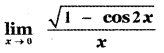
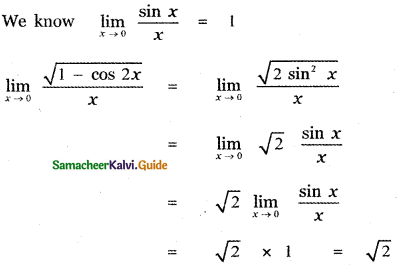
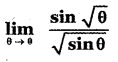
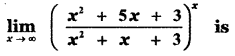
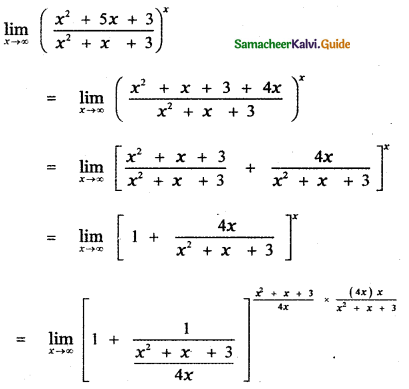
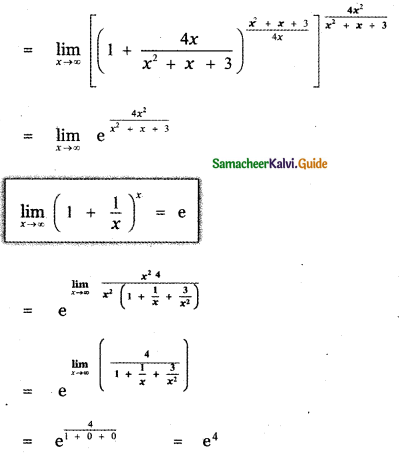
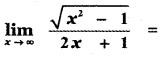
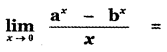
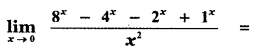
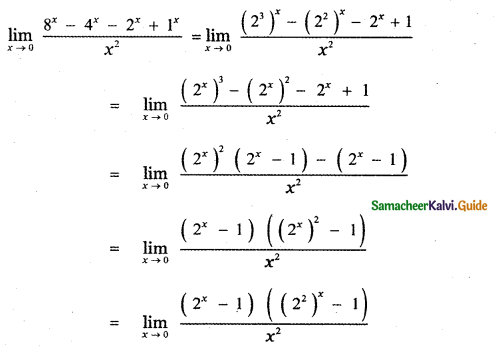
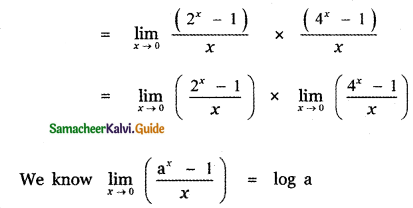
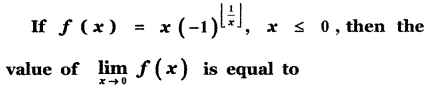
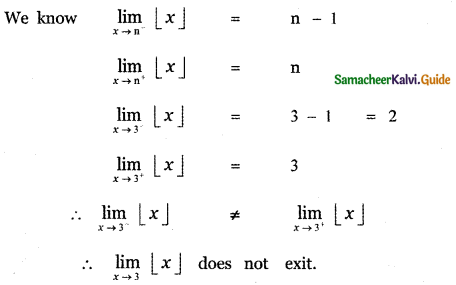
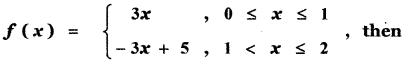
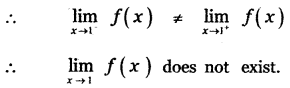
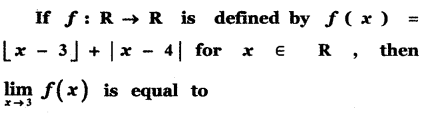
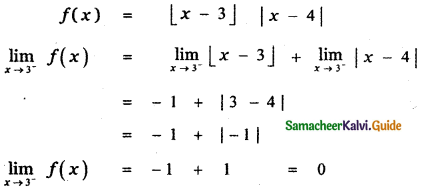
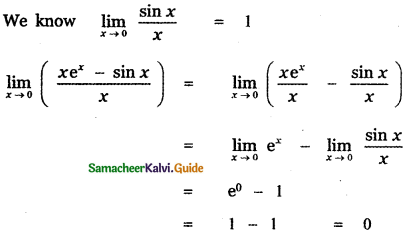
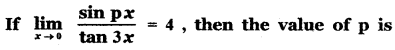
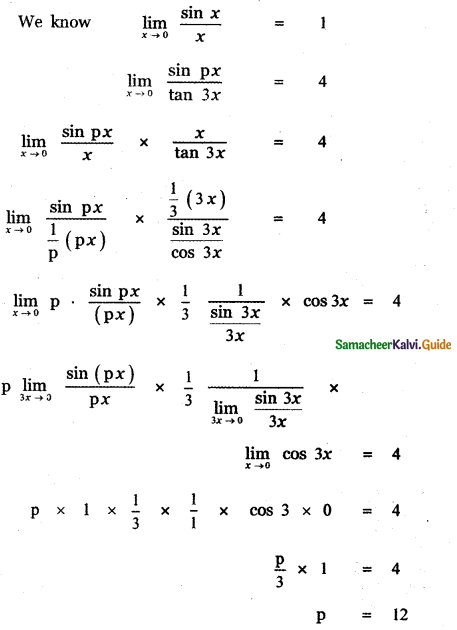
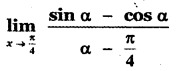
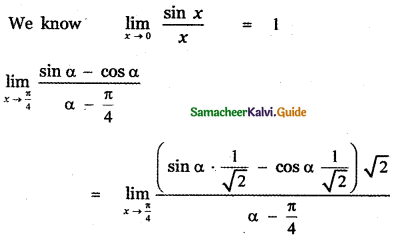
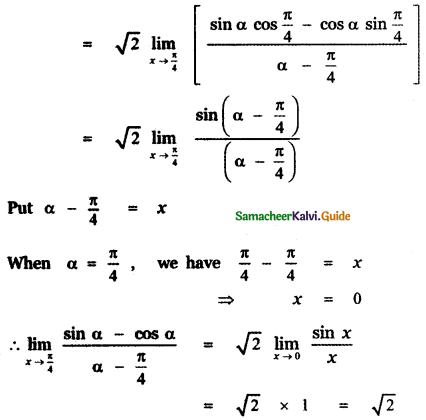
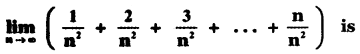
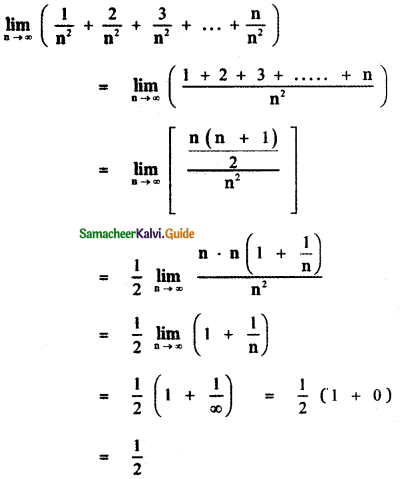
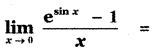
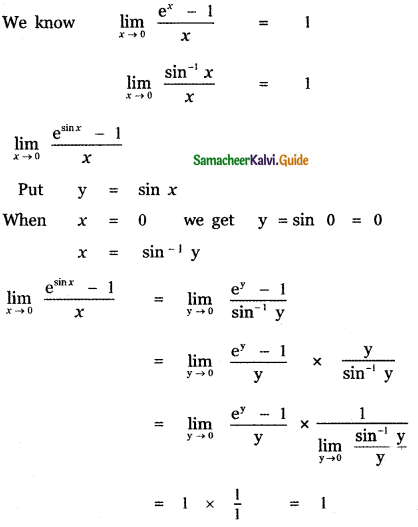
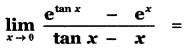
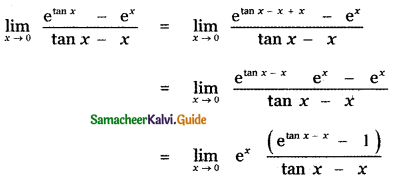
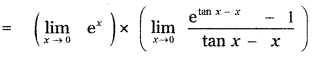
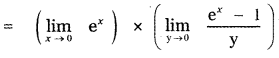
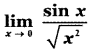 is
is