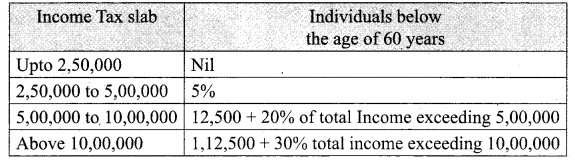
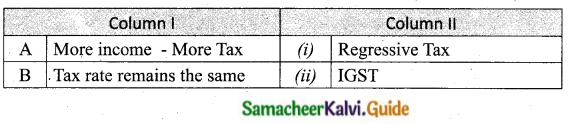
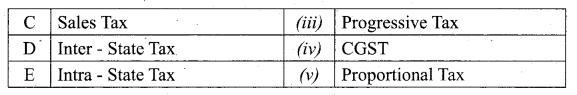
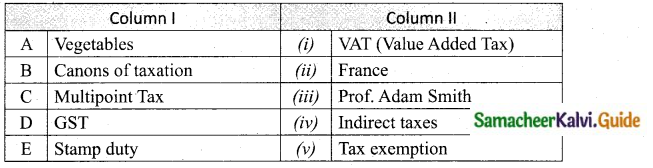
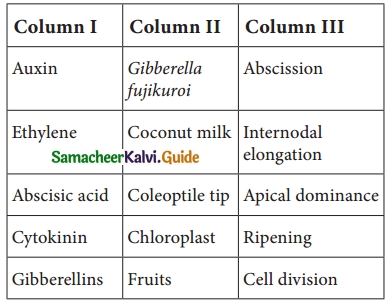
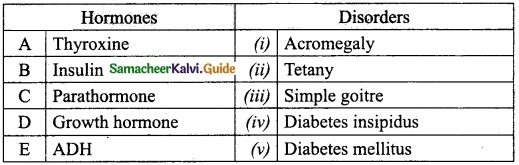
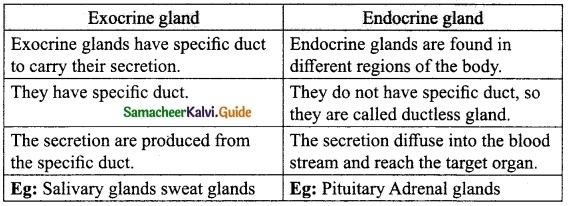
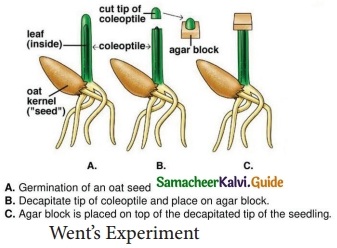
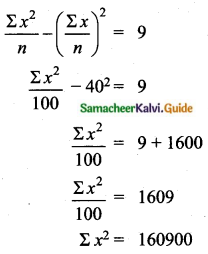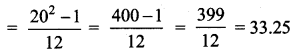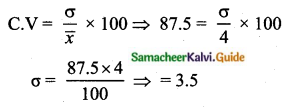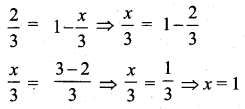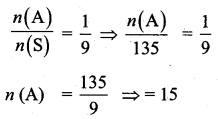Students can download Maths Chapter 8 Statistics and Probability Unit Exercise 8 Questions and Answers, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 10th Maths Solutions Chapter 8 Statistics and Probability Unit Exercise 8
Question 1.
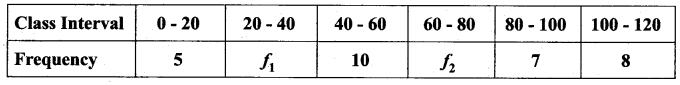
The mean of the following frequency distribution is 62.8 and the sum of all frequencies is 50. Compute the missing frequencies f1 and f2.
Answer:
Arithmetic Mean (\(\bar{x}\)) = 62.8
Sum of all the frequencies (Σfi) = 50
Let the missing frequencies be f1 and f2
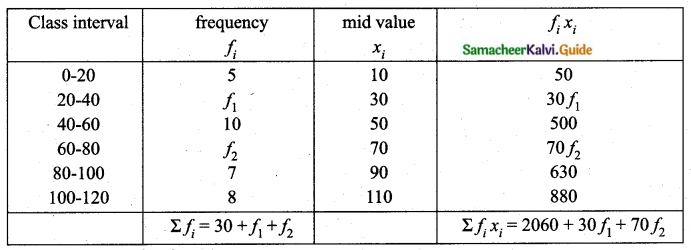
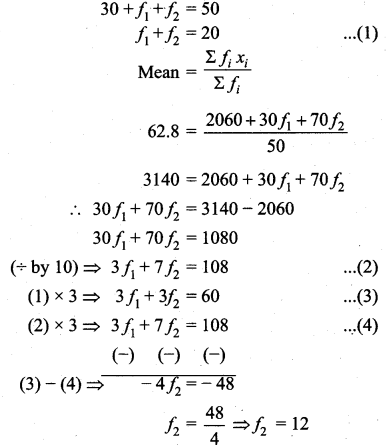
Substitute of the value of f2 in (1)
f1 + 12 = 20
⇒ f1 = 20 – 12 = 8
The Missing frequency is 8 and 12.
![]()
Question 2.
The diameter of circles (in mm) drawn in the design are given below.
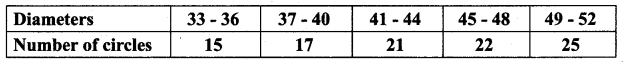
Calculate the standard deviation.
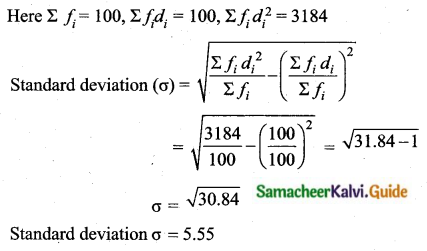
Answer:
Assumed mean = 42. 5
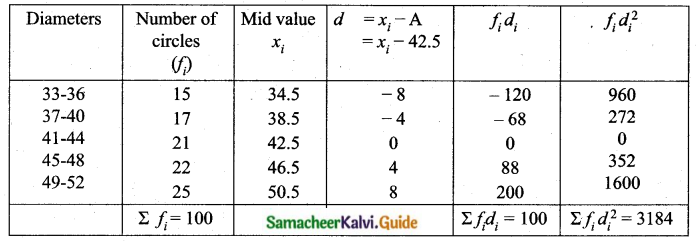
Question 3.
The frequency distribution is given below
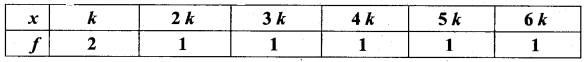
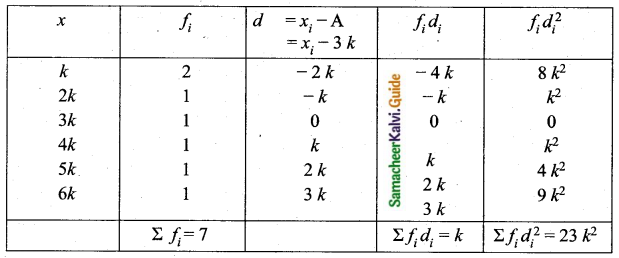
In table k is a positive integer, has a variance of 160. Determine the value of k.
Answer:
Assumed mean = 3k
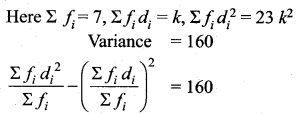
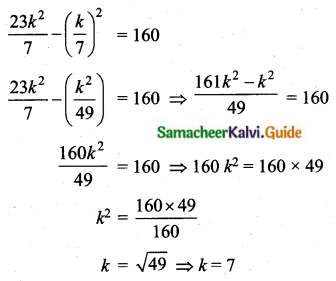
The value of k = 7
![]()
Question 4.
The standard deviation of some temperature data in degree Celsius (°C) is 5. If the data were converted into degree Fahrenheit (°F) then what is the variance?
Solution:
F° = (C° × 1.8) + 32
\(\begin{array}{l}{\sigma_{c}=5^{\circ} \mathrm{C}} \\ {\sigma_{\mathrm{F}}=\left(1.8 \times 5^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\right) \cdot 9^{\circ} \mathrm{F}}\end{array}\)
Adding value to data doesn’t affect standard deviation.
New variance = \(\sigma_{\mathrm{F}}^{2}=81^{\circ} \mathrm{F}\)
Question 5.
If for a distribution, Σ (x – 5) = 3, Σ (x – 5)2 = 43, and total number of observations is 18, find the mean and standard deviation.
Answer:
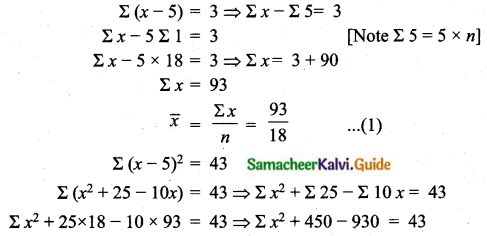
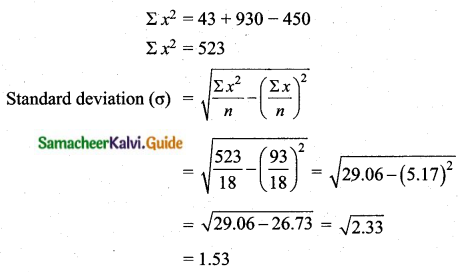
(i) Arithmetic mean (\(\bar{x}\)) = 5.17
(ii) Standard deviation (σ) = 1.53
Question 6.
Prices of peanut packets in various places of two cities are given below. In which city, prices were more stable?
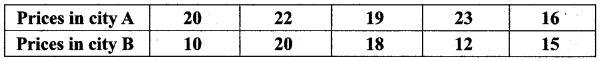
Answer:
Coefficients of variation of prices in city A.
Arrange in ascending order we get, 16, 19, 20, 22, 23
Assumed mean = 20
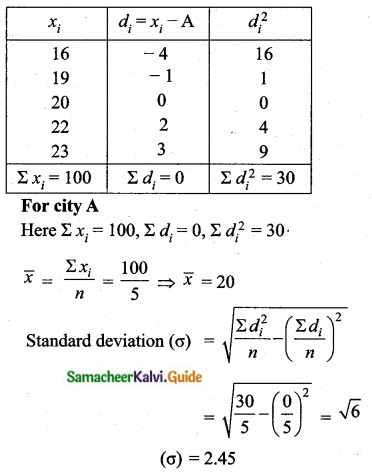
Coefficient of variation = \(\frac{\sigma}{\bar{x}} \times 100\)
= \(\frac{2.45}{20} \times 100\)
= 12. 25%
Coefficient of variation = 12.25%
Coefficients of variation of prices in city B.
Arrange in ascending order we get, 10, 12, 15, 18, 20
Assumed mean = 15
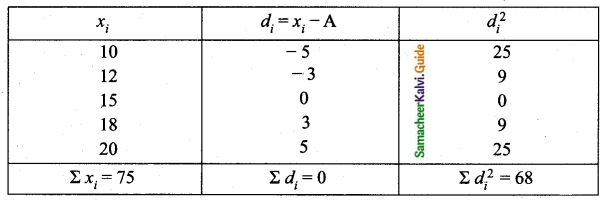
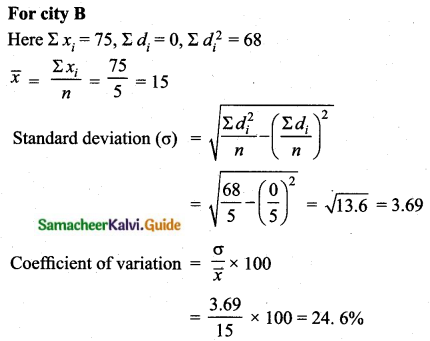
Prices in city A is more stable (since 12.25 < 24.6 %)
![]()
Question 7.
If the range and coefficient of range of the data are 20 and 0.2 respectively, then find the largest and smallest values of the data.
Answer:
Range of the data (R) = 20
L – S = 20 ……(1)
Coefficient of range = 0.2
Coefficient of range = \(\frac{L-S}{L+S}\)
0.2 = \(\frac{20}{L+S}\)

substituting the value of L = 60 in (2)
60 + S = 100
S = 100 – 60 = 40
Largest value = 60
Smallest value = 40
Question 8.
If two dice are rolled, then find the probability of getting the product of face value 6 or the difference of face values 5.
Answer:
Sample space = {(1, 1),(1, 2),(1, 3),(1, 4),(1, 5),(1, 6),(2, 1),(2, 2),(2, 3),(2, 4),(2, 5),(2, 6), (3, 1), (3, 2), (3, 3),(3, 4), (3, 5), (3, 6), (4, 1), (4, 2), (4, 3), (4, 4), (4, 5), (4, 6), (5, 1), (5, 2), (5, 3), (5, 4), (5, 5), (5, 6), (6, 1),(6, 2), (6, 3), (6, 4),(6, 5), (6, 6)}
n(S) = 36
(i) Let A be the event of getting product of face value 6.
A = {(1, 6), (2, 3), (3, 2) (6, 1)}
n(A) = 4
P (A) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{A})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{4}{36}\)
(ii) Let B be the event of getting difference of face value is 5.
B = {(6, 1)}
n(B) = 1
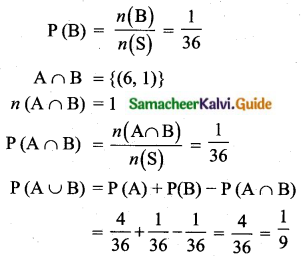
The probability is \(\frac{1}{9}\)
![]()
Question 9.
In a two children family, find the probability that there is at least one girl in a family.
Answer:
Sample space (S) = {(Boy, Boy) (Boy, Girl) (Girl, Boy) (Girl, Girl)}
n(S) = 4
Let A be the event of getting atleast one Girl
A = {(Boy, Girl) (Girl, Boy) (Girl, Girl)}
n(A) = 3
P(A) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{A})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{3}{4}\)
Probability of atleast one girl in a family is \(\frac{3}{4}\)
Question 10.
A bag contains 5 white and some black balls. If the probability of drawing a black ball from the bag is twice the probability of drawing a white ball then find the number of black balls.
Answer:
Let the number of black balls be “x”
Sample space (S) = x + 5
n(S) = x + 5
Let A be the event of drawing a black ball
n (A) = x
P(A) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{A})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{x}{x+5}\)
Let B be the event of getting a white ball
n(B) = 5
P(B) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{B})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{5}{x+5}\)
By the given condition,
\(\frac{x}{x+5}=2 \times\left(\frac{5}{x+5}\right)\)
⇒ \(\frac{x}{x+5}=\left(\frac{10}{x+5}\right)\)
⇒ 10x + 50 = x2 + 5x
⇒ x2 + 5x – 10x – 50 = 0
⇒ x2 – 5x – 50 = 0
⇒ (x – 10)(x + 5) = 0
⇒ x = 10 or x = -5
Number of balls will not be negative.
Number of black balls = 10
![]()
Question 11.
The probability that a student will pass the final examination in both English and Tamil is 0.5 and the probability of passing neither is 0.1. If the probability of passing the English examination is 0.75, what is the probability of passing the Tamil examination?
Answer:
Let A be the event of getting student pass in English
Let B be the event of getting student pass in Tamil
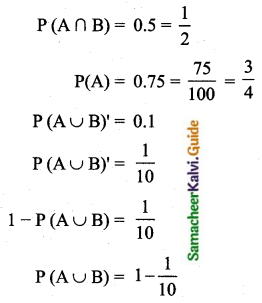
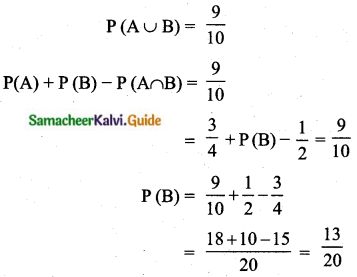
Probability of passing the tamil examination is \(\frac{13}{20}\)
![]()
Question 12.
The King, Queen and Jack of the suit spade are removed from a deck of 52 cards. One card is selected from the remaining cards. Find the probability of getting
(i) a diamond
(ii) a queen
(iii) a spade
(iv) a heart card bearing the number 5.
Answer:
Total number of cards = 52
3 cards are removed
Remaining number of cards = 52 – 3 = 49
n(S) = 49
(i) Let A be the event of getting a diamond card.
n(A) = 13
P(A) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{A})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{13}{49}\)
(ii) Let B be the event of getting a queen card.
n(B) = (4 – 1) = 3
P(B) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{B})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{3}{49}\)
(iii) Let C be the event of getting a spade card.
n(C) = (13 – 3) = 10
P(C) = \(\frac{n(C)}{n(S)}=\frac{10}{49}\)
(iv) Let D be the event of getting a 5 of heart card.
n(D) = 1
P(D) = \(\frac{n(\mathrm{D})}{n(\mathrm{S})}=\frac{1}{49}\)