Students can Download 9th Tamil Chapter 7.2 சீவக சிந்தாமணி Questions and Answers, Summary, Notes, Samacheer Kalvi 9th Tamil Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Tamil Solutions Chapter 7.2 சீவக சிந்தாமணி
கற்பவை கற்றபின்
![]()
Question 1.
அருகிலுள்ள இயற்கைக் காட்சிகளைக் குறிப்பெடுத்து ஓவியம் தீட்டுக.
Answer:

- நான் வசிக்கும் இடத்தின் அருகில், ஒரு குளம் இருக்கின்றது.
- குளத்தைச் சுற்றிலும் வயல் வெளிகள் உள்ளன.
- குளத்தின் கரையில் ஓர் ஆலமரம் உள்ளது.
- பறவைகளும், கிளிகளும் அதில் வசித்து மகிழ்கின்றன. பறவைகள் தன் குஞ்சுகளுக்கு உணவளிக்கும் காட்சி மனதை மயக்கும்.
- வயல் வெளிகளில் கூட்டமாய் உழவர்கள் வேலை செய்யும் போது ஆரவாரம் காணப்படும்.
- மாலை நேரத்தில் மயிலும் தோகை விரித்து ஆடும்.
Question 2.
உங்கள் பள்ளி வேரூன்றிய நாள் தொடங்கி வளர்ந்த வரலாற்றையும், அதன் சிறப்புகளையும் கட்டுரையாக்குக.
Answer:
எங்கள் பள்ளி
முன்னுரை : நான் பயிலும் பள்ளி. அரசு மேல்நிலைப் பள்ளி ஆகும். அன்ன சத்திரம் ஆயிரம், ஆலயங்கள் பல்லாயிரம் கட்டுவதைக் காட்டிலும் ஏழைக்கு எழுத்தறிவித்தலே கோடி புண்ணியங்களைக் கொண்டு வந்து சேர்க்கும் அல்லவா! எழுத்தறிவு கொடுத்துக் கொண்டிருக்கும் அறிவுத் திருக்கோவில் எம் பள்ளி.
தோற்றம் : எங்கள் பள்ளி அப்போதைய ஆங்கில அரசால் 1918 ம் ஆண்டு ஒன்று முதல் எட்டு வரை உள்ள நடுநிலைப் பள்ளியாகத் தோன்றி வேரூன்றி வளர ஆரம்பித்தது.
![]()
வளர்ச்சி : பின்னர் உயர்நிலைப் பள்ளியாக தரம் உயர்ந்தது. பின் 1978 இல் மேல்நிலைப்பள்ளியாக தரம் உயர்த்தப்பட்டு, இன்று கம்பீரமாக நகரின் மையத்தில் உள்ளது.
சாதனைகள்:
இந்த ஆண்டு எம் பள்ளி நூற்றாண்டு விழா காண இருக்கின்றது. பல அறிஞர்களை, விற்பனர்களை, சமூக சேவகர்களை, ஊருக்கு உழைக்கும் உத்தமர்களை, மருத்துவர்களை, பொறியாளர்களை, வழக்குரைஞர்களை, அறிஞர்களை, அரசியல்வாதிகளை உருவாக்கி நல்லறிவு புகட்டி, வரலாற்றுச் சிறப்பு மிக்க அறிவுக் கோயிலாகத் திகழ்கிறது.
![]()
முடிவுரை: பல்துறைகளிலும் முத்திரை பதிக்க பலருக்கும் வழிகாட்டிய அறிவுப் பெட்டகமாகவும், பலருடைய வாழ்வை உயரத்திற்குக் கொண்டு சென்ற ஏணியாகவும் இன்று வரை திகழ்கிறது. பல தலைமுறை கண்ட எம் பள்ளி, இன்னும் பல புதிய தலைமுறைகளை உருவாக்க வாழ்த்தி வணங்குகிறேன்.
பாடநூல் வினாக்கள்
பலவுள் தெரிக
Question 1.
வெறிகமழ் கழனியுள் உழுநர் வெள்ளமே – இவ்வடி உணர்த்தும் பொருள் யாது?
Answer:
அ) மணம் கமழும் வயலில் உழவர் வெள்ளமாய் உழுதிருந்தனர்.
ஆ) வறண்ட வயலில் உழவர் வெள்ளமாய் அமர்ந்திருந்தனர்.
இ) செறிவான வயலில் உழவர் வெள்ளமாய்க் கூடியிருந்தனர்.
ஈ) பசுமையான வயலில் உழவர் வெள்ளமாய் நிறைந்திருந்தனர்.
Answer:
அ) மணம் கமழும் வயலில் உழவர் வெள்ளமாய் உழுதிருந்தனர்.
குறுவினா
Question 1.
கருக்கொண்ட பச்சைப்பாம்பு, எதற்கு உவமையாக்கப்பட்டுள்ளது?
Answer:
கருக்கொண்ட பச்சைப்பாம்பு நெற்பயிர்கள் தோற்றத்திற்கு உவமையாக்கப்பட்டுள்ளது.
![]()
சிறுவினா
Question 1.
ஏமாங்கத நாட்டில் எவையெல்லாம் ஆயிரக்கணக்கில் இருப்பதாகத் திருத்தக்கதேவர் பாடியுள்ளார்?
Answer:
- வளம் நிறைந்த ஏமாங்கத நாட்டில் உள்ள ஊர்களில் நாள்தோறும் ஆயிரம் வகையான உணவுகள் இருக்கும்.
- பசி என்று வருவோருக்கும், நாடி வருவோருக்கும் அறச்சாலைகள் ஆயிரம் இருக்க்கின்றன.
- மகளிர் தம்மை ஒப்பனை செய்ய மணிமாடங்கள் ஆயிரம் இருக்கின்றன.
- செய்தொழிலில் சோம்பல் இல்லாத கம்மியர் ஆயிரமாயிரமாய் இருக்கின்றனர்.
- ஏமாங்கத நாட்டிலே இல்லாதவை இல்லை என்னும் வகையில் ஆயிரக்கணக்கான நிகழ்வுகள் குறைவின்றி நிகழ்கின்றன.
![]()
நெடுவினா
Question 1.
ஏமாங்கத நாட்டு வளம் குறித்த வருணனைகளை நும் ஊரின் வளங்களோடு ஒப்பிடுக.
Answer:
முன்னுரை:
சீவகசிந்தாமணியில் “நாமகள் இலம்பகத்தில்” நாட்டு வளம் என்னும் பகுதியில் ஏமாங்கத நாட்டின் வளம், திருத்தக்கதேவரால் நயம்பட உரைக்கப்பட்டுள்ளது. ஏமாங்கதநாட்டு வளம் போலவே எம் ஊரின் வளங்களும் உள்ளன எனில் மிகையாகாது.
வளம் மிக்க நெருங்கிய தோப்புகள்:
ஏமாங்கத நாட்டில் நிகழ்ந்த வளமான நிகழ்வு போலவே எம் ஊரிலும் அடர்ந்த தோப்புகளில் நிகழ்ந்த து.
![]()
தென்னை மரத்திலிருந்து முற்றிய தேங்காய் விழுகின்றது. அத்தேங்காய் நிலத்தை வந்தடையும்முன் விழும்வேகத்தில் அருகிருந்த பாக்கு மரத்தின் உச்சியின் உள்ள தேனடையைக் கிழித்து, தேனடையோடு பலாமரத்தில் உள்ள பலாப்பழத்தினை பிளந்து, தேங்காய், தேனடை, பலாச்சுளைகளோடு, வாழைப்பழங்களையும் உதிரச்செய்கிறது. இவ்வாறு ஏமாங்கத நாட்டை போலவே எம் ஊரும் முக்கனி வளமும், தென்னை மரங்களும், பாக்கு மரங்களும் நிறைந்தனவாய்க் காணப்படுகின்றது.
மண்வீசும் வயல்வளம்:
ஏமாங்கத நாட்டைப்போலவே, நீர்நிலைகள் சூழ்ந்த வயல் பகுதிகள் உள்ளன. அந்நீர்நிலைகளில் அழகான கொம்புகளையுடைய ஆண் எருமைகளும், வலிமையான நேரிய கொம்புகளை உடைய எருதுகளும் பேரொலி எழுப்பி நீந்துகின்றன. அவ்வொலியால் அந்நீர்நிலையில் உள்ள பொறிகளையுடைய வரால் மீன் இனங்கள் கலைந்து ஓடுகின்றன. இவ்வாறு எருமைகளும், எருதுகளும், நீரைக் கலக்குவதாலும், சேறுமணமும், நீந்தும் மீன் மணமும் கலந்த வயல்பகுதிகளில் வெள்ளமென உழவர்கள் உழுதிருந்தனர்.
இறைஞ்சி வணங்கும் நெற்பயிர்கள்:
கருக்கொண்ட பச்சைப்பாம்பைப்போல நெற்பயிர்கள் திரட்சியான தோற்றம் கொண்டுள்ளன. செல்வம் பெற்று பக்குவம் இல்லாது செருக்குடன் இருக்கும் மேல் அல்லார் போல, கதிர்விட்டு நிமிர்ந்துநிற்கின்றன நெற்பயிர்கள்.
அப்பயிர்களில் உள்ள நெற்கதிர்கள் முற்றியவுடன், தெளிந்த நூல் பல கற்றோரின் பணிவைப்போல பணிந்து, இறைஞ்சி தலைசாய்ந்து நிற்கும் கவின் மிகு காட்சியையும் எம் ஊரில் காணலாம்.
![]()
ஆயிரம் விழாக்கள்:
வளம்மிக்க எம் ஊரில் ஆயிரம் வகையான உணவு உண்டு. பசியுடன் நாடி வருவோருக்கு உணவு வழங்கும் அறச்சாலைகள் ஆயிரம் உண்டு. மகளிர் ஒப்பனை செய்துகொள்ளும் மணிமாடங்கள் ஆயிரம் உண்டு. சோம்பல் இன்றி தொழில் புரியும் கம்மியர்களும் ஆயிரக்கணக்கானோர் உண்டு. அதனால் திருமணங்களும், விழாக்களும் ஆயிரமாயிரமாய் நடைபெறுகின்றன.
முடிவுரை:
இவ்வாறு ஏமாங்கத நாட்டின் வளம் போலவே, வளமும்;, சிறப்பும் கொண்டனவாய் எம் ஊரும் உள்ளது என்பதில் பெருமிதமும் மகிழ்வும் கொள்கிறேன்.
கூடுதல் வினாக்கள்
பலவுள் தெரிக
Question 1.
இன்பங்களைத்துய்த்து துறவு பூண வேண்டும் என்னும் கருத்து அமைந்த காப்பியம் எது?
அ) சிலப்பதிகாரம்
ஆ) வளையாபதி
இ) குண்டலகேசி
ஈ) சீவகசிந்தாமணி
Answer:
ஈ) சீவகசிந்தாமணி
![]()
Question 2.
சீவகசிந்தாமணிக்குரிய மற்றொரு பெயர் யாது?
அ) மனநூல்
ஆ) மணநூல்
இ) மங்கல நூல்
ஈ) சமண நூல்
Answer:
ஆ) மணநூல்
Question 3.
சீவகசிந்தாமணியின் இலம்பகங்கள் எத்தனை?
அ) பதினான்கு
ஆ) பதினைந்து
இ) பதினாறு
ஈ) பதின்மூன்று
Answer:
ஈ) பதின்மூன்று
Question 4.
சீவகசிந்தாமணியை இயற்றியவர் யார்?
அ) இளங்கோவடிகள்
ஆ) சீத்தலைசாத்தனார்
இ) திருத்தக்கத்தேவர்
ஈ) கணிமேதாவியர்
Answer:
இ) திருத்தக்கத்தேவர்
![]()
Question 5.
சீவசிந்தாமணிக்கு முன்னோட்டமாக திருத்தக்கத்தேவர் பாடிய நூல் யாது?
அ) நரிவெண்பா
ஆ) நரிவிருத்தம்
இ) சிந்தாமணிமாலை
ஈ) காவடிச்சிந்து
Answer:
ஆ) நரிவிருத்தம்
Question 6.
“ஏமாங்கத நாட்டு வளம்” அமைந்த இலம்பகம் எது?
அ) விமலையார்
ஆ) சுரமஞ்சரி
இ) காந்தருவதத்தை
ஈ) நாமகள்
Answer:
ஈ) நாமகள்
Question 7.
திருத்தக்கத்தேவர் பின்பற்றிய சமயம் எது?
அ) பௌத்தம்
ஆ) சமணம்
இ) வைணவம்
ஈ) சைவம்
Answer:
ஆ) சமணம்
Question 8.
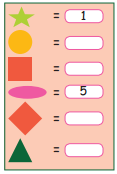
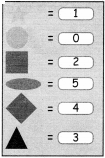
பொருத்துக. சொல்

Answer:

![]()
Question 9.
நெறி மருப்பு எருமை – வெறி கமழ் கழனி இத்தொடரின் கோடிட்ட சொற்களின் பொருள் யாது?
அ) கொம்பு, மணம்
ஆ) வயல், மலை
இ) தேங்காய், புகழ்
ஈ) சோறு, எல்லை
Answer:
அ) கொம்பு, மணம்
Question 10.
வள்ளல் கைத்தல மாந்தரின் மால்வரைக் கொள்ளை கொண்ட கொழுநிதிக் குப்பையை என்னும் அடிகளில் இடம் பெற்றுள்ள நயம் …………
அ) எதுகை
ஆ) மோனை
இ) இயைபு
ஈ) அந்தாதி
Answer:
அ) எதுகை
Question 11.
ஐம்பெருங்காப்பியத்தில் இடம் பெறாத நூல் …………….
அ) சிலப்பதிகாரம்
ஆ) மணிமேகலை
இ) சீவக சிந்தாமணி
ஈ) நீலகேசி
Answer:
ஈ) நீலகேசி
![]()
Question 12.
வளம் நிறைந்த ஏமாங்கத நாட்டிலுள்ள ஊர்களில் நாள்தோறும்……………… வகையான உணவுகள் கிடைக்கின்றன.
அ) பத்து
ஆ) நூறு
இ) பல
ஈ) ஆயிரம்
Answer:
ஈ) ஆயிரம்
Question 13.
ஏமராங்கத நாட்டிலுள்ள மணிமாடங்களின் எண்ணிக்கை………………..
அ) நூறு
ஆ) ஆயிரம்
இ) இரண்டாயிரம்
ஈ) இருநூறு
Answer:
ஆ) ஆயிரம்
![]()
Question 14.
சீவகசிந்தாமணியின் நாமகள் சிலம்பத்தில் ………….. என்னும் பகுதி நம் பாடப்பகுதியாக அமைந்துள்ளது.
அ) நாட்டு வளம்
ஆ) காட்டு வளம்
இ) ஆற்று வளம்
ஈ) இயற்கை வளம்
Answer:
அ) நாட்டு வளம்
Question 15.
திருத்தக்கத்தேவரின் காலம் ……………..
அ) எட்டாம் நூற்றாண்டு
ஆ) ஒன்பதாம் நூற்றாண்டு
இ) ஆறாம் நூற்றாண்டு
ஈ) ஏழாம் நூற்றாண்டு
Answer:
ஆ) ஒன்பதாம் நூற்றாண்டு
Question 16.
விருத்தப்பாக்களால் இயற்றப்பட்ட முதல் காப்பியம் ……………
அ) சிலப்பதிகாரம்
ஆ) கம்பராமாயணம்
இ) சீவகசிந்தாமணி
ஈ) வளையாபதி
Answer:
இ) சீவகசிந்தாமணி
![]()
குறுவினா
Question 1.
வரால் மீன்கள் கலைந்து ஓடுவதற்கான காரணம் யாது?
Answer:
அழகான கொம்புகளை உடைய ஆண் எருமைகளும் நேரான கொம்புகளையுடைய வலிமையான எருதுகளும் பேரொலி எழுப்புவதைக் கேட்டுப் புள்ளிகளும், வரிகளும் உடைய வரால் மீன்கள் கலைந்து ஓடுகின்றன.
Question 2.
நெற்பயிர்கள் கதிர்விட்டு நிமிர்ந்து நிற்பது எதனைப் போன்றது?
Answer:
நெற்பயிர்கள் கதிர்விட்டு நிமிர்ந்து நிற்பது, செல்வம் பெற்ற பக்குவம் இல்லாதவர் தலை நிமிர்ந்து நிற்பது போன்றதாகும்.
![]()
Question 3.
பயிர்கள் முற்றியவுடன் நெற்கதிர்கள் சாய்ந்திருப்பது எதனைப் போன்றது?
Answer:
தெளிந்த நூலைக் கற்ற நல்லவர்களின் பணிவைப் போன்றதாகும்.
Question 4.
ஏமாங்கத நாடு எவர்க்கெல்லாம் இனிய இடமாகத் திழக்கிறது?
Answer:
ஏமாங்கத நாடு, உண்மையான தவம் புரிவோர்க்கும் இல்லறம் நடத்துவோர்க்கும் இனிய இடமாகத் திகழ்கிறது.
Question 5.
எவற்றைத் தேடுவோர்க்கு உகந்த இடமாக ஏமாங்கத நாடு விளங்குகிறது?
Answer:
நிலையான பொருளைத் தேடுவோர்க்கும் நிலையில்லாத பொருட்செல்வத்தைத் தேடுவோர்க்கும் உகந்த இடமாக ஏமாங்கத நாடு விளங்குகிறது.
![]()
சிறுவினா
Question 1.
ஐம்பெருங்காப்பியங்கள் யாவை?
AnsweR:
- சிலப்பதிகாரம்
- மணிமேகலை
- சீவகசிந்தாமணி
- வளையாபதி
- குண்டலகேசி
Question 2.
சீவகசிந்தாமணி குறிப்பு வரைக.
Asnwer:
- சீவகசிந்தாமணி ஐம்பெருங்காப்பியங்களுள் ஒன்று.
- இது விருத்தப்பாக்களால் இயற்றப்பட்ட முதல் காப்பியம் ஆகும்
- இந்நூலில் இலம்பகம் என்னும் உட்பிரிவு காணப்படுகிறது.
- இந்நூல் மொத்தம் பதின்மூன்று இலம்பகங்களைக் கொண்டது.
- இதற்கு மணநூல் என்று மற்றொரு பெயரும் உண்டு.
- திருத்தக்கதேவரால் இயற்றப்பட்ட நூல்,