Students get through the TN Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 14 Transportation which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 14 Transportation
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by land transport?
Answer:
Transport of people and goods by land vehicles is known as Surface transport. It is also called ‘Land Transport’.
Question 2.
What are the types of transport?
Answer:
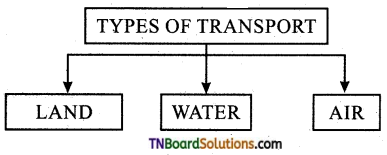
Question 3.
What are tramways?
Answer:
Tramways were initially horse-drawn later steam-powered and now electrically operated. Its carrying capacity is large. They are able to cope up with the peak hour traffic in big cities.
![]()
Question 4.
What are Inland waterways?
Answer:
Inland Waterways comprise rivers, canals, and lakes. It is also known as internal water transport. Rivers that are naturally navigable are called natural waterways. Canals and canalized rivers belong to the category of ‘Artificial Waterways’.
Question 5.
What is a common carrier?
Answer:
A common carrier is a person who is engaged in the business of carrying goods for hire indiscriminately for all persons.
Question 6.
What are the liners types?
Answer:
There are two types of liners namely (i) Passenger liners, (ii) Cargo liners.
Question 7.
What are the types of commercial ships?
Answer:
The following is the major types of commercial ships –
- The general cargo ship,
- Bulk carriers,
- Container ships,
- Auto carrier,
- Tankers,
- Fishing vessels,
- Oil vessels,
- Passengers ships,
- Ferryboats,
- Tow and tug boats,
- Specialized ships.
![]()
Question 8.
What are bullock carts?
Answer:
It constitutes the predominant form of rural road transport in India for goods traffic and to some extent for passengers’ traffic. It links up the villages with the nearby markets and railway stations. It carries the produce for sale to the market and consumer goods to the villages.
Question 9.
What is a private carrier?
Answer:
A private carrier is engaged in casual occupation and carries goods on occasions or under a special contract.
Short answer questions
Question 1.
What are the demerits of Air transport?
Answer:
- It is a very costly mode of transport. The rates and fares charged by which are beyond the reach of common people.
- Aircraft are not quite suitable for carrying heavy loads and weights.
- It is not dependable because of unfavorable weather which may disturb the air service suddenly.
- The construction and maintenance of aerodromes involve huge capital expenditure.
- Every country controls the air space above its territory. Therefore, an airplane cannot fly over another country without obtaining prior permission from the concerned authority.
Question 2.
What is sea transport?
Answer:
Ocean transport has been playing a significant role in the development of economic, social, and cultural relations among countries of the world. International trade owes its growth to ocean transport. Ocean transport enjoys a pride of place in aiding international trade. Cheapness is its great virtue. In the transportation of low-grade, bulky goods among the countries, the role of ocean transport is commendable.
![]()
Question 3.
What is Monorail?
Answer:
A monorail is like a train, but instead of having two sets of wheels that balances on a railway track, the monorail is balanced on top of one rail. Monorails are often used to transport people around large cities. Some monorails utilize magnets to hover on their rails, reducing friction between the train and the rail. The first monorail was invented in the 19th century.
Question 4.
What is conveyor transport?
Answer:
It is the broad category of transport mode that includes modes developed from the idea of a conveyor belt. Examples include a Conveyor belt, two or more Pulleys with a continuous loop of material that rotates about them, an Escalator, an Elevator which is used to carry people among floors of the building, etc.
Question 5.
What is Railway Receipt?
Answer:
A railway Receipt is an acknowledgment of receipt of goods by the railway for transporting. It serves as a document of title of goods, viz., it shows the title of its holders of the goods. It may be issued in the name of the consignor or consignee. Only on presentation of the railway receipt, the railways will deliver the goods.
Question 6.
What are the types of Ocean transport?
Answer:
Ocean transport may be divided into two broad categories.
- Coastal shipping: Coastal shipping
constitutes an important means of transport in all countries having a long coastline. It is a cheap means of transport for the movement of bulky cargoes like coal, iron ore, etc. to domestic ports of the country. Usually, the coastal shipping trade of a country is reserved for national shipping. In India, the Coastal shipping trade is now exclusively reserved for Indian ships. - Overseas shipping: It means the passengers and goods have to cross an ocean. For Example India export goods to America.
![]()
Question 7.
What are the demerits of inland waterways?
Answer:
- It is the slowest means of transport. As compared to this, railways are quicker, safer, and cheaper means of transport.
- Floods caused during the rainy season, lack of flow of water during summer season affect to ply boats and steamers.
- Sometimes rivers also change their way. It leads to stoppage and uncertainty in the usage of this means of transport.
Question 8.
What are the economic benefits of transport?
Answer:
- It increases the efficiency of production.
- It stimulates wants by increasing the quantity and variety of consumer goods.
- It develops and expands the market.
- It helps in price stability by distributing goods all over the country.
- It aids in economic growth.
- It helps in specialization and mass production.
- It encourages innovations in product production and design.
![]()
Long answer questions
Question 1.
What are the services of transport to business?
Answer:
- It increases the efficiency of production: The object of production is consumption. Effective transport system creates time and place utilities and thereby influences the demand for goods and the value of goods. Thus, transport makes production efficient and purposeful.
- It stimulates wants by increasing the quantity and variety of consumer goods: It helps in getting commodities, which cannot be had or produced in a region due to unsuitable natural conditions. Without adequate and effective transport, goods cannot be had either in the quantities or varieties required in a complex economy.
- It develops and expands the market: The primary function of transport is to enable the physical distribution of goods at the global level. The distribution of goods must take place easily, economically, and speedily. It provides the chance of expanding the national land international market.
- It helps in price stability by distributing goods all over the country.
- It aids to economic growth: The movement of raw materials, fuel, labor, and finished products and the mobility of capital and technical know-how, transport playing a remarkable role in the growth of all industries from agriculture to manufacturing.
- It helps, in specialization and mass production: Specialization means the division of a complex process of production into a number of separate processes so that each person or group specializes in each and every process. It has been extended to the international level too.
- It encourages innovations in product production and designing: It provides plenty of opportunities to the producers to produce their product in an innovative and creative way, to catch up with the wider market and reap more profit.
Question 2.
What are the documents used in transport?
Answer:
- Way Bill: The waybill is an acknowledgment of receipt of goods for transport by the carrier. The carrier, accepting goods for transport, issues waybills in the name of the consignors or consignees. It serves as evidence of the contract of transport. It is also a document of the title of goods. The ownership of goods represented by a waybill can be transferred, by endorsement and delivery of the waybill. If a waybill lost, the consignee will be allowed to clear the goods from the carrier after he executes an indemnity bond.
- Railway Receipt: Railway Receipt is an acknowledgment of receipt of goods by the railway for transporting. It serves as a document of title of goods, viz., it shows the title of its holders of the goods. It may be issued in the name of the consignor or consignee. Only on presentation of the railway receipt, the railways will deliver the goods. If railway receipt is lost, the consignees can obtain the goods from the railway by executing an indemnity bond. Ownership of the goods can be transferred by endorsement and delivery of the receipt.
- Charter Party: When goods are to be consigned in large quantity, it is advantageous to hire the whole or substantial part of the ship. The document through which this contract is made is known as ‘Charter Party may also be known as ‘Voyage Charter’ or ‘Time Charter’. The person who hires the ship is known as Charter The charter party brings the vessel and crew under the control of the charter. The charter becomes responsible to the third parties for the acts of the master and crew of the ship.
- Bill of Lading: Bill of Lading is a document containing the terms and conditions of the contract of the carriage! It is issued by the shipping company and signed by the captain of the ship. It acknowledges the receipt of the goods described in it on board the ship. It also serves as an official receipt of goods. It is a document of the title of goods. The main contents are Name of Exporter, name of the ship, place of loading, particulars of goods shipped, port of destination, freight paid or to be paid, person to whom delivery of goods is to be made, date, etc. If the condition of the packages is good, a clean bill of lading is issued. If some of the packages are found damaged, a foul or clause bill of lading is issued.
- Air Consignment Note or Airway Note: It is a document prepared by the consignor, which is handed over to the carrier of goods while transporting goods through Airways. Air Consignment Note is made out of three original parts. One is signed by the consignor and marked for the carrier. The second is signed by both the consignor and the carrier and marked for the consignee (intended to accompany the goods) and the third is signed by the carrier and handed back to the consignor after the goods have been accepted.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the recent trends in transportation?
Answer:
- Metro Rail: Metro Rail is a Mass Rapid Transport System (MRTS). It is a convenient, fast, efficient, reliable, comfortable mode of urban transport. Rapid transit is also known as heavy rail, metro, subway, tube, or underground is a type of high capacity, public transport generally found in urban areas.
- Monorail: A monorail is like a train, but instead of having two sets of wheels that balances on a railway track, the monorail is balanced on top of one rail. Monorails are often used to transport people around large cities. Some monorails utilize magnets to hover on their rails, reducing friction between the train and the rail. The first monorail was invented in the 19th century.
- Bullet train: High-speed rail is a type of rail transport that operates significantly faster than traditional rail traffic, using an integrated system of specialized rolling stock and dedicated tracks. The first such system began operations in Japan in 1964 and was widely known as the bullet train. High-speed trains normally operate on standard gauge tracks of continuously welded rail.
- Pipeline Transport: It is the mode of transportation of goods or materials through the pipe. Liquids and gases are transported in pipelines. Pipeline exist for the transport of crude and refined petroleum, fuels such as Oil, Natural gas and Biofuel, etc., and other fluids including sewage, slurry, and water. It requires heavy investment to install.
- Conveyor Transport: It is the broad category of transport mode that includes modes developed from the idea of a conveyor belt. Examples include a Conveyor belt, two or more Pulleys with a continuous loop of material that rotates about them, an Escalator, an Elevator which is used to carry people among floors of buildings etc.
- Ropeway Transport: A Ropeway is another means of transport in naval lifting device.
It can be operated in a place where road construction is impractical and costly. Certain limit of goods of people can be transported with the help of (naval lifting device) electricity. In the hilly remote areas ropeway system of transport may be suitable means of transport. - Hyperloop Transport: Hyperloop is a proposed system of transport that would see pods or containers travel at high-level speed through a tube that has been pumped into a near-vacuum. The train pods would either float using magnetic levitation technology or float using air caster “Skis”, similar to how pucks travel across an air hockey table. With so little friction in the tunnel, the pod would be able to travel at immense speed with projected top speeds of 760 mph. Hyperloop is a futuristic transport system. Tunnels for the Hyperloop would be built either above or below ground, at only around 3 meters in diameter, lacking up a smaller ground footprint than traditional rail or road. Elon Musk an entrepreneur had proposed this mode of transport as a “fifth mode of transport” in 2012.
Question 4.
What is Railway Transport? Explain advantages and disadvantages.
Answer:
The invention of the steam engine by James Watt revolutionized the mode of transport all over the world. Railway, as a mode of transport, is the most organized transport undertaking all over the world. Railways are the cheapest and quickest means of transport for carrying heavy goods over long distances.
Advantages of Railway Transport:
- Railways are well suited for carrying heavy and bulky goods over long distances.
- It can provide long-distance travel throughout the day and night with unbroken services.
- It can provide better production and safety to the goods than motor transport. The goods generally carried in closed wagons are not exposed to sun, rain, etc.
- Though the initial investment is large, in the long run, the operating expenses will be very low in railways and it will prove a cheaper mode of transport. It requires less time than motor transport for carrying goods over long distance with greater speed
- It has a regular schedule of timing and is available throughout the year.
- It provides unaffected services whether rainy or shinny weather conditions.
Disadvantages of Railway Transport:
- Railway rates are relatively higher than motor transport for transporting lightweight articles over short distances.
- It is inflexible, as it is operated to a particular track that cannot deviate from the set routes.
- In rural areas, it cannot offer adequate traffic because of uneconomical operating costs.
- It requires heavy investment for the installation of tracks and maintenance that increases its fare on the users.
- If railways are not fully utilized and if wagons and coaches are too half-empty to their capacity, a heavy financial burden will be cast on the railway.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the advantages of motor transport.
Answer:
Roads connect the interior parts of a country with railway stations and markets. They help in the exploitation of villages that are the rich sources of raw materials and valuable markets for finished products. Motor transport, as the dominant form of road transport, offers many advantages. They are:
- Flexibility: The greatest merit of motor transport is its flexibility. It can reach the interior and remote villages. Unlike railways, it is not wedded to any particular track. It can change its route, timing, and areas of operation. It can pick up as well as deliver goods almost anywhere.
- Complete service: It provides a complete service to businessmen. It leads the goods from the factory or the firm and delivers them at the door of buyers. It thus avoids much handling and the resultant damage. But in the case of railways, goods have to be taken to the railway station, unloaded from the carriers, and then loaded in the railway wagons; at the destination, they have to be again unloaded from them before being delivered to consignees. Besides adding to the cost of goods, this intermediate loading and handling causes damage to goods and delays their delivery.
- Suitability: Motor transport is very well suited for short-distance traffic. It is also suitable for the delivery of small loads to many consignees on the way. As the capacity of lorries is less than that of railway wagons, small traders who have to transport limited loads can conveniently make use of this transport. It is more suitable for goods like perishable articles which are to be delivered quickly and for meeting sudden demand.
- Economy: Goods for lorry transport do not require elaborate packing. It is common for owners of goods to travel in lorries along with their goods in order to personally attend to loading and unloading. This practice reduces the risks of breakages and thefts. Further, freight rates in roadways are comparatively lower for short distances and small loads than that in railways. The absence of intermediate handling and loading also reduces the cost in the case of motor transport. Moreover, laying a road is cheaper than laying a railway track. The users of roads pay very little for their laying and maintenance.
- Speed: Motor transport is quicker than rail transport for transporting goods over short distances. Quick transport and prompt delivery help to increase the turnover of the business.
- Service: Motor transport renders a valuable service to interior rural areas by connecting them with railway stations, markets, and nearby towns. It serves as a feeder to other forms of transport, namely railways, waterways, and airways. It helps fruits, vegetables, dairy products, etc. reach nearby cities and towns in a state of freshness. Its service to hill areas deserves special mention because of its greater climbing capacity than rail transport. It earns huge revenue from the government and creates more employment opportunities.
![]()
For Own Thinking
Geographical separation between producer and consumer – Comment. Importing Crude oil from foreign countries to Petroleum refineries – transporting through Truck tankers or Pipelines – Suggest with reason.
Answer:
Goods are produced at a few places but are required for use at different places. Geographical distance separates producers and consumers. This difficulty is removed by transport, eg: Knitwear products of Tirupur are sold throughout the world, Nellore rice is widely consumed in Chennai and other places with the help of various means of transport.
Import crude oil from foreign countries to petroleum refineries transporting it through truck tankers is good. These tankers are specially designed to carry crude oil, petrol, and petroleum products, but pipelines sometimes suggested it is good because of lesser cost.
Multiple choice questions
1. Transport is an integral part of:
(a) trade
(b) commerce
(c) economics
(d) all the above
Answer:
(b) commerce
2. Transport help to reduce variation in:
(a) price of goods
(b) quality of goods
(c) quantity of goods
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) price of goods
3. …….. are used in deserts for similar purpose.
(a) Elephant
(b) Lion
(c) Camel
(d) Tiger
Answer:
(c) Camel
4. ……… connect the interior part of a country
(a) Roads
(b) Railways
(c) Tramways
(d) All the above
Answer:
(a) Roads
5. Tramways made their appearance in the ……… century.
(a) 18th century
(b) 16th century
(c) 17th century
(d) 19th century
Answer:
(d) 19th century
![]()
6. Motor transport complete service to:
(a) Businessmen
(b) Customers
(c) Bankers
(d) Wholesaler
Answer:
(a) Businessmen
7. ……….. is a free gift of nature.
(a) Air
(b) Water
(c) Land
(d) Animals
Answer:
(b) Water
8. Tramways are a ……….. form of transport.
(a) Very slow
(b) Very speed
(c) Slow
(d) Speed
Answer:
(a) Very slow
9. Which one of the following is covered under land transport:
(a) Liners
(b) Tankers
(c) Pack animals
(d) Tramps
Answer:
(c) Pack animals
![]()
10. Which one of the following not covered under transport:
(a) canal
(b) river
(c) Bullock carts
(d) bill of lading
Answer:
(d) bill of lading
11. Who is the Inventor of the steam engine?
(a) James watt
(b) Gopal
(c) R.Bhatt
(d) PK. Ghosh
Answer:
(a) James watt
12. In which year cycle and rickshaw were introduced in the world.
(a) 1850
(b) 1847
(c) 1972
(d) 1867
Answer:
(d) 1867
13. The first railway line in India was opened to traffic between:
(a) Mumbai – Chennai
(b) Chennai – Kolkata
(c) Mumbai and thane
(d) Delhi-Chennai
Answer:
(c) Mumbai and thane
14. Air consignment note is made out in original part:
(a) one
(b) two
(c) three
(d) four
Answer:
(c) three
![]()
15. Transport can be divided into types.
(a) three
(b) five
(c) four
(d) one
Answer:
(a) three
16. Cargo vessels are called:
(a) cargo liners
(b) Perrys
(c) liners
(d) tankers
Answer:
(a) cargo liners
17. Best way of transport for long distances:
(a) motor
(b) boats
(c) tramways
(d) railways
Answer:
(d) railways
18. The invention of the steam engine by James watt ……… modes of transport all over the world.
(a) revolutionized
(b) modernized
(c) industrialized
(d) economized
Answer:
(a) revolutionized
![]()
19. In the rural areas the most important mode of transport is:
(a) donkeys
(b) horses
(c) motor vehicles
(d) Bullock carts
Answer:
(d) Bullock carts
20. For carrying heavy logs in forests used.
(a) elephants
(b) horses
(c) camels
(d) donkeys
Answer:
(a) elephants