Students can Download Tamil Nadu 11th Accountancy Model Question Paper 4 English Medium Pdf, Tamil Nadu 11th Accountancy Model Question Papers helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
TN State Board 11th Accountancy Model Question Paper 4 English Medium
General Instructions:
- The question paper comprises of four parts.
- You are to attempt all the parts. An internal choice of questions is provided wherever applicable.
- All questions of Part I, II, III and IV are to be attempted separately.
- Question numbers 1 to 20 in Part I are Multiple Choice Questions of one mark each.
These are to be answered by choosing the most suitable answer from the given four alternatives and writing the option code and the corresponding answer - Question numbers 21 to 30 in Part II are two-mark questions. These are to be answered in about one or two sentences.
- Question numbers 31 to 40 in Part III are three-mark questions. These are to be answered in above three to five short sentences.
- Question numbers 41 to 47 in Part IV are five-mark questions. These are to be answered in detail Draw diagrams wherever necessary.
Time: 3:00 Hours
Maximum Marks: 90
PART – I
Answer all the questions. Choose the correct answer: [20 × 1 = 20]
Question 1.
On the basis of ledger balances the …………………….. are prepared.
(a) Trading A/c
(b) Financial statement
(c) Profit and loss A/c
(d) Balance sheet
Answer:
(b) Financial statement
![]()
Question 2.
Accounting is a basic necessity for all ……………………
(a) Human being
(b) Governments
(c) Enterprises
(d) Customers
Answer:
(c) Enterprises
Question 3.
What is GAAP?
(a) Generally Accepted Accounting Principles
(b) Government Accepted Accounting Principles
(c) Generally Accounting and Accountancy Principles
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Generally Accepted Accounting Principles
![]()
Question 4.
……………………… concept assumes that business enterprise and its owners are two separate independent entities.
(a) Business concern
(b) Business entity concepts
(c) Going Concern concept
(d) Matching concept
Answer:
(b) Business entity concepts
Question 5.
Which of the following is a personal account?
(a) Debtors
(b) Stationary
(c) Cash
(d) Sales
Answer:
(a) Debtors
Question 6.
Which of the following is a real account?
(a) Wages
(b) Salaries
(c) Bank account
(d) Shares and debentures of companies
Answer:
(d) Shares and debentures of companies\
![]()
Question 7.
Which of the following accounts is expected to have a debit balance?
(a) Assets
(b) Loss
(c) Expense
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 8.
A collection or group of all accounts of a business enterprises is known as …………………………
(a) Balance sheet
(b) Trial balance
(c) Ledger
(d) Journal
Answer:
(c) Ledger
![]()
Question 9.
Which account usually has debit balance?
(a) Discount received
(b) Purchase returns
(c) Purchases
(d) Owner equity
Answer:
(c) Purchases
Question 10.
A trial balance is a …………………… ?
(a) Nominal account
(b) Personal account
(c) Real account
(d) None
Answer:
(d) None
Question 11.
Which of the following is not only a subsidiary books of account?
(a) Purchase book
(b) Sales book
(c) Purchase return book
(d) Cash book
Answer:
(d) Cash book
![]()
Question 12.
If a cheque issued by us is dishonoured the credit is given to ……………………..
(a) Customer’s A/c
(b) Bank A/c
(c) Supplier’s A/c
(d) None
Answer:
(c) Supplier’s A/c
Question 13.
Cheques issued but not presented to bank …………………….
(a) Cash book – Add
(b) Cash book (Cr) – Add
(c) Bank statement (Cr) – Add
(d) Bank statement (Dr) subtract
Answer:
(a) Cash book – Add
Question 14.
Generally, one – sided errors are revealed by ……………………..
(a) Credit balance
(b) Debit balance
(c) Balance sheet
(d) Trial balance
Answer:
(d) Trial balance
![]()
Question 15.
Two – sided errors are not revealed by ……………………..
(a) Debit balance
(b) Trial balance
(c) Credit balance
(d) Balance sheet
Answer:
(b) Trial balance
Question 16.
The amount which is expected to be realised at the end of the estimated useful life of an asset is known as ………………………….
(a) Life of an asset
(b) Actual cost of asset
(c) Other factors
(d) Scrap value of an asset
Answer:
(d) Scrap value of an asset
![]()
Question 17.
There are various methods used for providing depreciation on …………………………
(a) Life of an asset
(b) Actual cost of asset
(c) Fixed asset
(d) Other factors
Answer:
(c) Fixed asset
Question 18.
Revenue receipts are ……………………. in the business.
(a) Non – recurring
(b) Recurring
(c) Neither of the above
(d) All the above
Answer:
(b) Recurring
![]()
Question 19.
Income statement is divided into …………………….. parts.
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Four
Answer:
(b) Two
Question 20.
Components of CAS can be classified into ………………………. categories.
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Six
(d) Three
Answer:
(c) Six
PART – II
Answer any seven questions in which question No. 21 is compulsory: [7 × 2 = 14]
Question 21.
Discuss briefly the branches of accounting?
Answer:
The various branches of accounting are:
1. Financial Accounting:
It involves recording of financial transactions and events.
2. Cost Accounting:
It involves the collection, recording, classification and appropriate allocation of expenditure for the determination of the costs of products or services and for the presentation of data for the purposes of cost control and managerial decision making.
3. Management Accounting:
It is concerned with the presentation of accounting information in such a way as to assist management in decision making and in the day-to-day operations of an enterprise.
4. Social Responsibility Accounting:
It is concerned with presentation of accounting information by business entities and other organizations from the view point of the society by showing the social costs incurred such as environmental pollution by the enterprise and social benefits such as infrastructure development and employment opportunities created by them.
5. Human Resources Accounting:
It is concerned with identification, qualification and reporting of investments made in human resources of an enterprise.
![]()
Question 22.
State the principles of double entry system of book – keeping?
Answer:
- In every business transaction, there are two aspects.
- The two aspects involved are the benefit or value receiving aspect and benefit or value giving aspect.
- These two aspects involve minimum two accounts; atleast one debit and atleast one credit.
- For every debit, there is a corresponding and equivalent credit. If one account is debited . the other account must be credited.
Question 23.
Journalise the following transactions?

Answer:
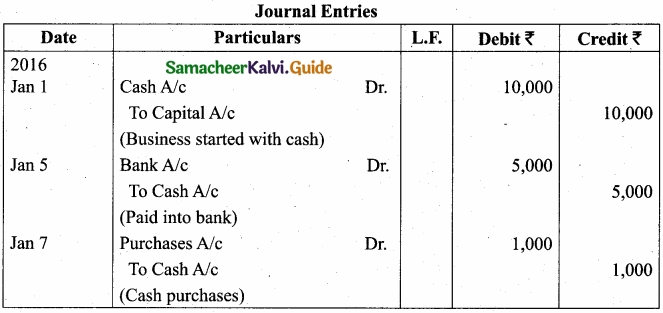
![]()
Question 24.
What are the objectives of preparing trial balance (any two)?
Answer:
- Test of arithmetical accuracy: Trial balance is the means by which the arithmetical accuracy of the book-keeping work is checked.
- Basis for preparing final accounts: Financial statements, namely, trading and profit and loss account and balance sheet are prepared on the basis of summary of ledger balances obtained from the trial balance.
Question 25.
What is Journal proper?
Answer:
Journal proper is a residuary book which contains records of transactions, which do not find a place in the subsidiary »books such as cash book, purchases book, sales book, purchases returns book, sales returns book, bills receivable books and bills payable book.
Question 26.
What is Cash Book?
Answer:
Cash book is the book in which only cash transactions are recorded in the chronological order. The cash book is the book of original entry or prime entry as cash transactions are recorded for the first time in it. Cash transactions here may include bank transactions also.
![]()
Question 27.
Give any two expenses which may be paid by the banker as per standing instruction?
Answer:
- Insurance premium paid by the bank as per the standing instruction.
- Loan instalment, paid by the bank as per the instruction.
Question 28.
What is meant by error of partial omission?
Answer:
When the accountant has failed to record a part of the transaction, it is known as error of partial omission. This error usually occurs in posting. This error affects only one account.
Question 29.
What is Sinking Fund method?
Answer:
This method is adopted especially when it is desired not merely to write off an asset but also to provide enough funds to replace an asset at the end of its working life.
![]()
Question 30.
What is capital expenditure?
Answer:
It is an expenditure incurred during an accounting period, the benefits of which will be available for more than one accounting period.
PART – III
Answer any seven questions in which question No. 31 is compulsory: [7 × 3 = 21]
Question 31.
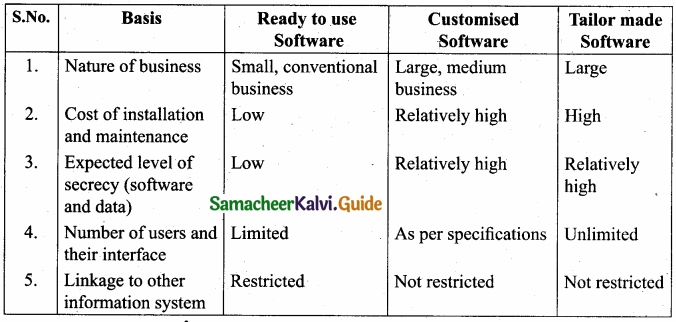
Write any three differences among the readymade software, customised software and tailor made software?
Answer:
|
Basis |
Readymade Software | Customised Software |
Tailor made Software |
| 1. Nature of business | Small, conventional business | Large, medium business | Large |
| 2. Cost of installation and maintenance | Low | Relatively high | High |
| 3. Expected level of secrecy (software and data) | Low | Relatively high | Relatively high |
![]()
Question 32.
Abstracts from the trial balance as on 31st March, 2016?
Answer:

Adjustments:
- Additional bad debts ₹2,000.
- Create 5% provision for bad and doubtful debts. You are required to pass adjusting entries.
Answer:
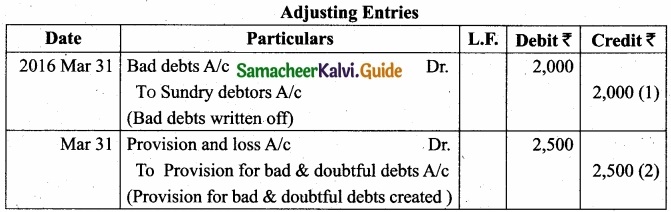

![]()
Question 33.
A firm purchased a plant for ₹40,000. Erection charges amounted to ₹2,000. Effective life of the plant is 5 years. Calculate the amount of depreciation per year under straight line method?
Answer:
Caluculation of amount of depreciation:
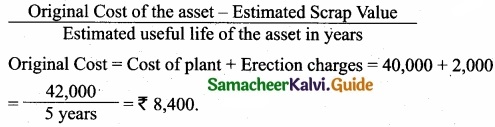
Question 34.
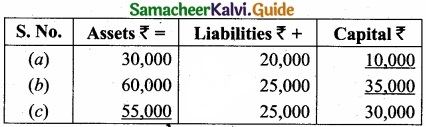
Complete the missing items:
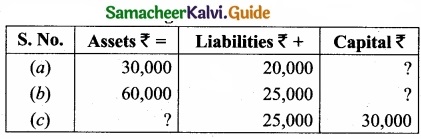
Answer:
![]()
Question 35.
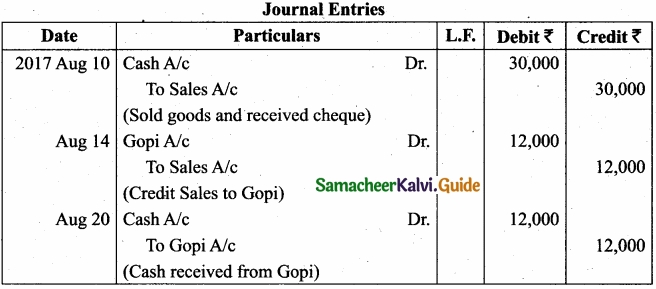
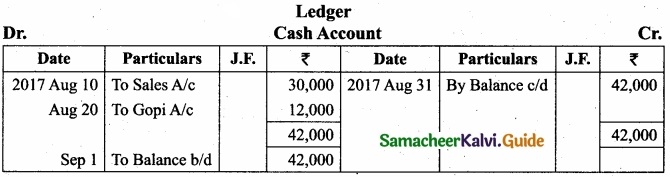
Give journal entries for the following transactions and post them to cash A/c and sales A/c?

Answer:
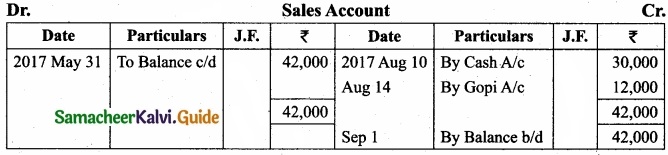
Question 36.
The following balances are extracted from the books of Murali, as on 31st March, 2017. Prepare Trial balance?
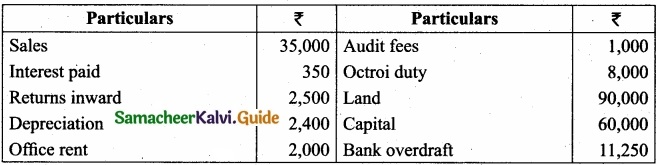
Answer:
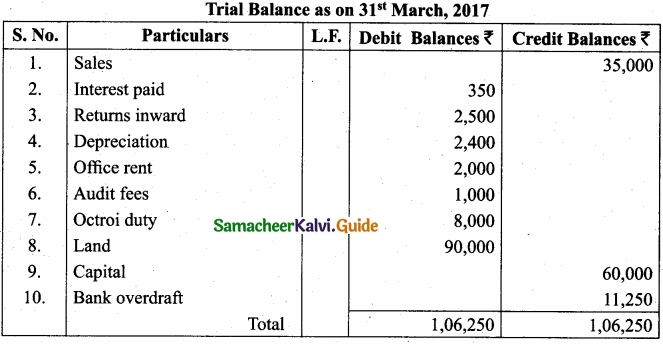
![]()
Question 37.
Enter the following transactions in the purchase book of M/s. Subhashree Electric Co., which deals in electric goods?
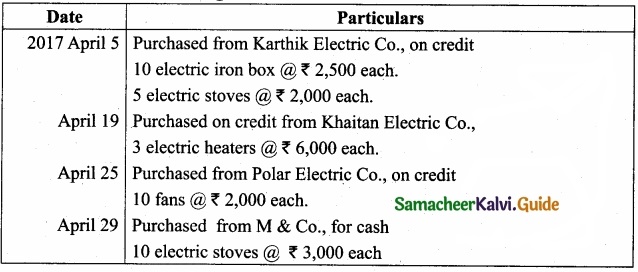
Answer:
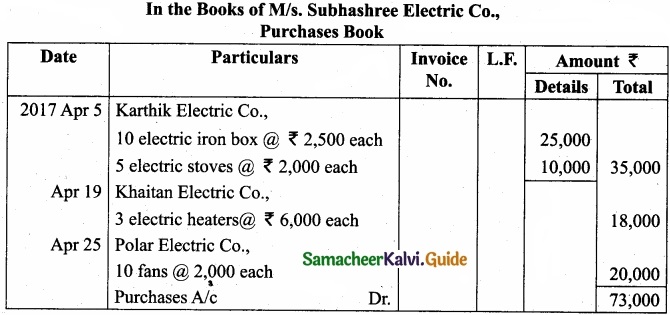
Question 38.
Briefly explain about contra entry with examples?
Answer:
When the two accounts involved in a transactions are cash account and bank account, then both the aspects are entered in cash book itself. As both the debit and credit aspect of a transaction are recorded in the cash book, such entries are called contra entries.
Example: When cash is paid into bank, it is recorded in the bank column on the debit side and in the cash column on the credit side of the cash book.
![]()
Question 39.
Rectify the following errors:
- Sales returns book is overcast by ₹1,000.
- Purchases book is undercast by ₹2,000.
- Purchase returns book is overcast by ₹500.
Answer:
- Sales returns account should be credited with ₹1,000.
- Purchases account should be debited with ₹2,000.
- Purchase returns account should be debited with ₹500.
![]()
Question 40.
Classify the following receipts into capital and revenue:
- Sale proceeds of goods ₹75,000.
- Loan borrowed from bank ₹2,50,000.
- Sale of investment ₹1,20,000.
Answer:
- Revenue
- Capital
- Capital
PART – IV
Answer all the questions: [7 × 5 = 35]
Question 41(a).
Jayaseeli is a sole proprietor having a provisions store. Following are the transactions?
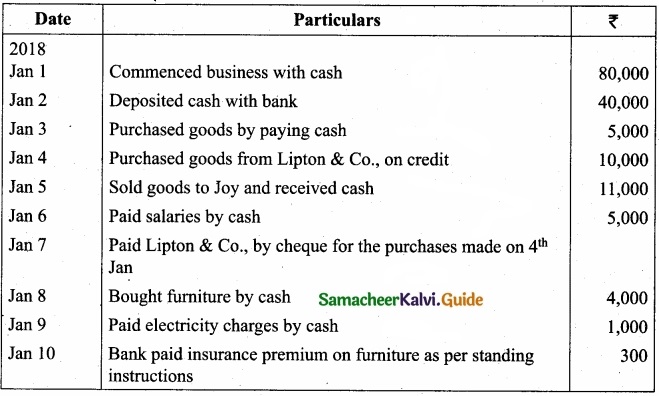
Answer:
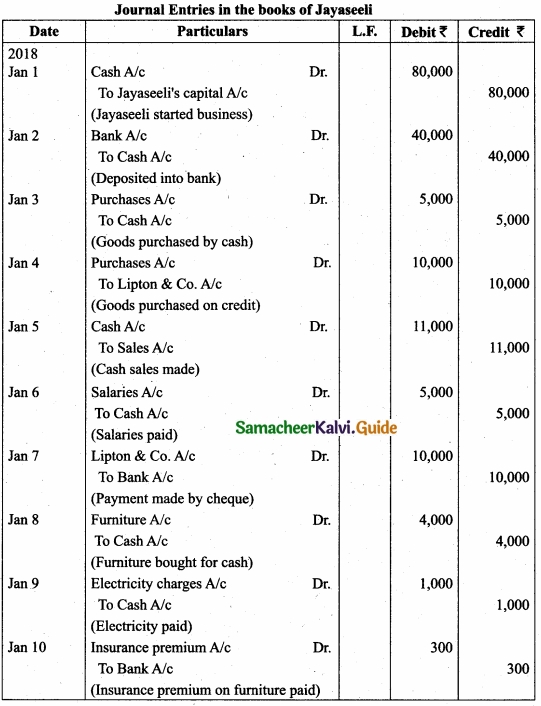
[OR]
(b) Show the accounting equation on the basis of the following:
- Started business with cash ₹60,000
- Purchased goods fof cash ₹20,000
- Sold goods for cash (costing ₹10,000) for ₹15,000
- Paid rent by cash ₹500
- Cash withdrawn for personal use ₹5,000
Answer:
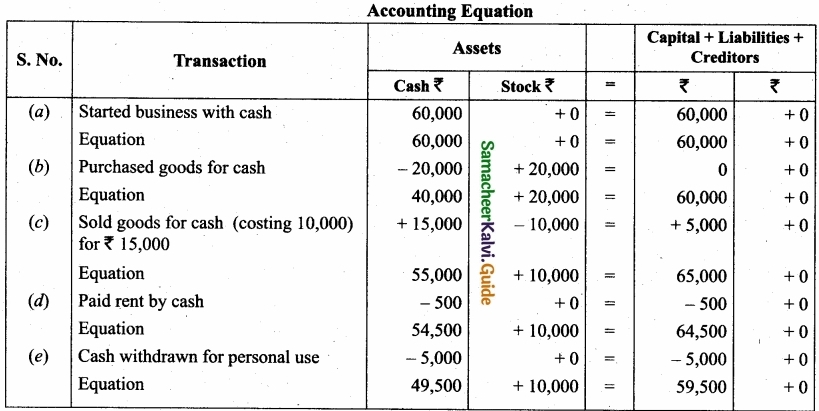
![]()
Question 42 (a).
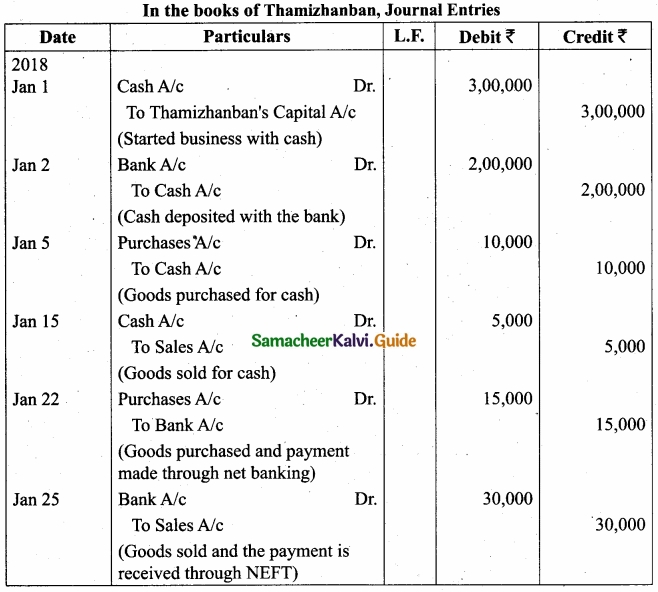
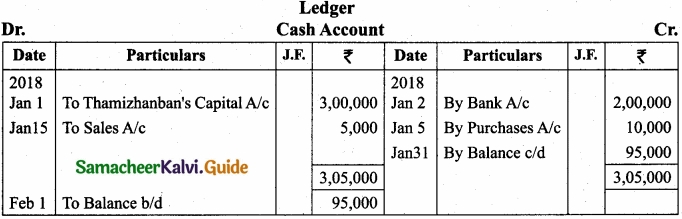
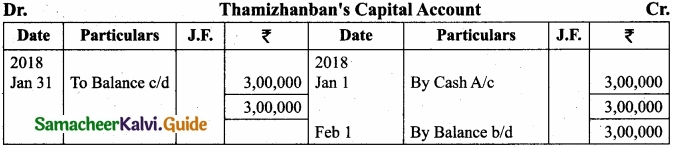
Pass journal entries and prepare ledger accounts in the books of Thamizhanban?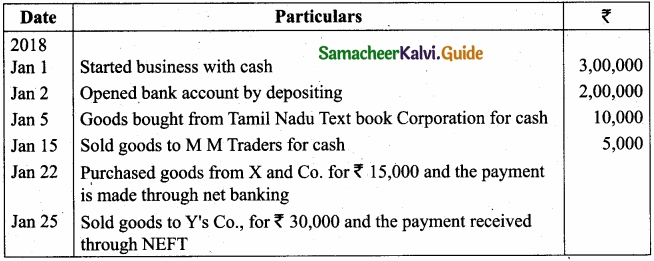
Answer:
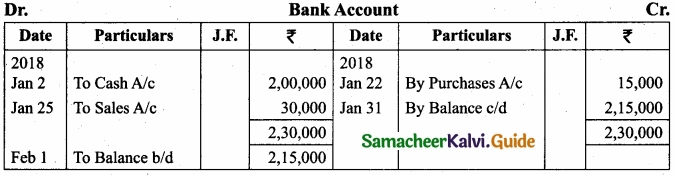 `
`
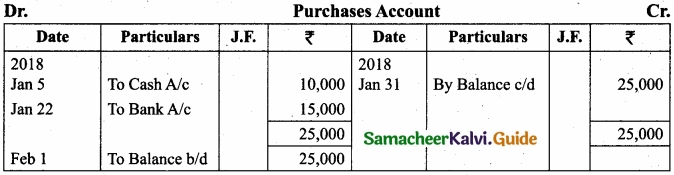
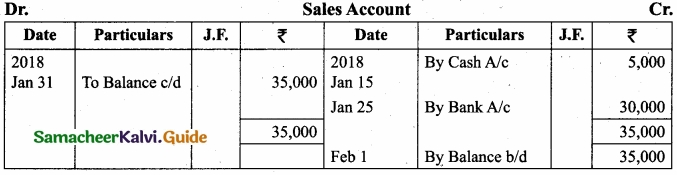
[OR]
(b) Prepare Trial balance from the following ledger abstract of Rathna Kumar?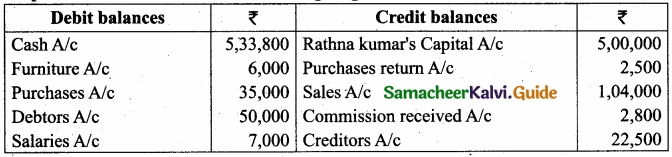
Answer:
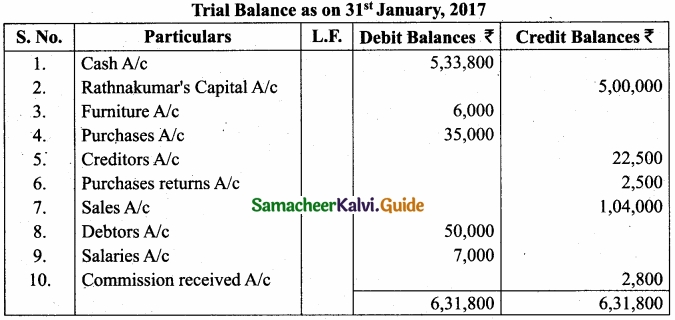
![]()
Question 43 (a).
Record the following transactions in the purchases book of Shanthi furniture mart: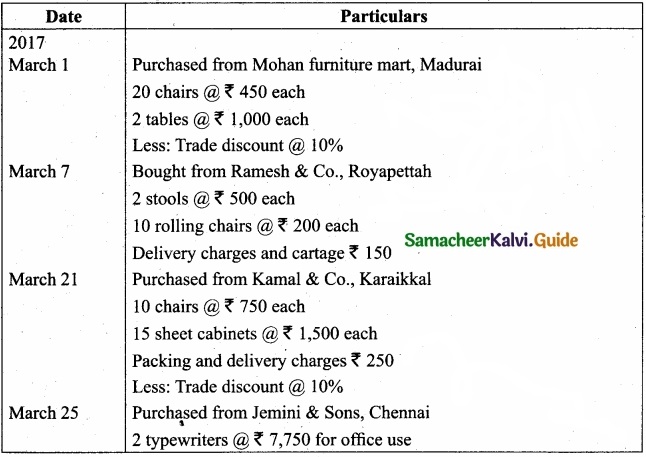
Answer:
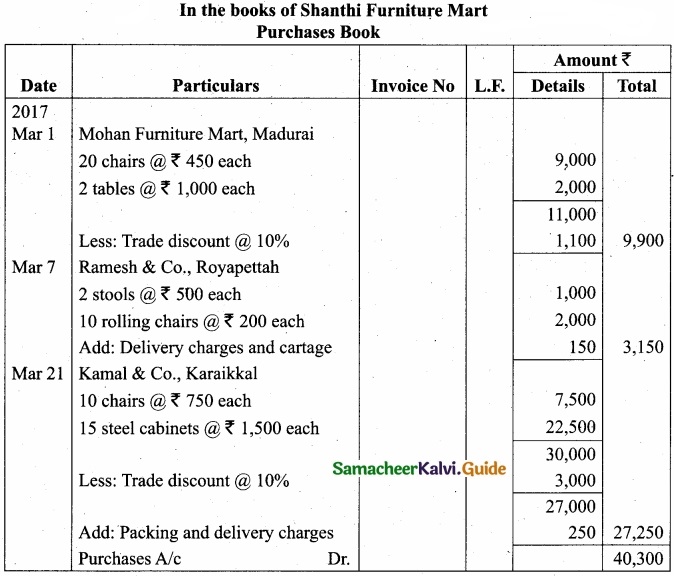
[OR]
(b) Enter the following transactions of Fathima in the cash book with cash, bank and discount columns for the month of May, 2017?
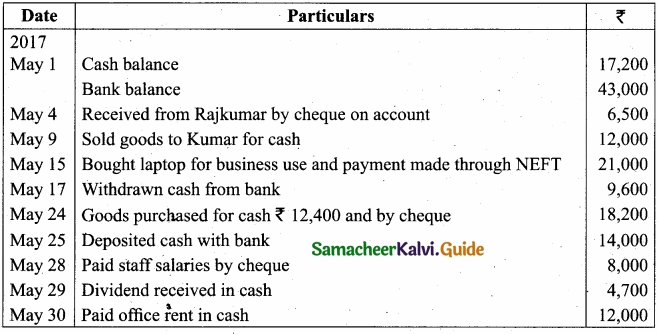
Answer:
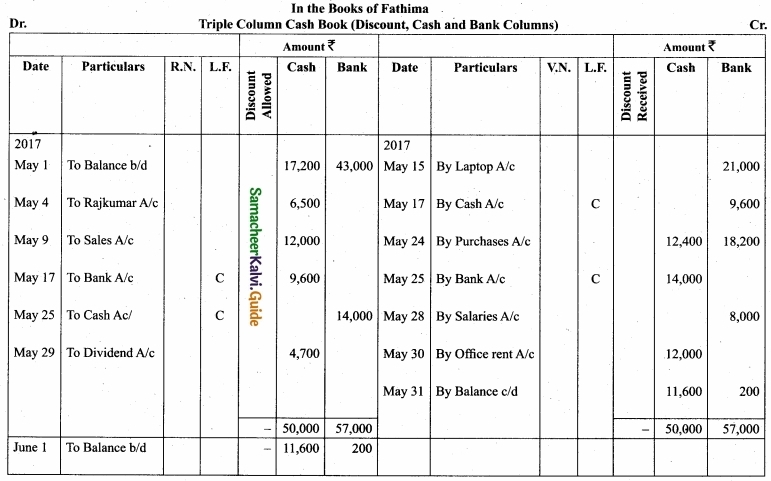
![]()
Question 44 (a).
From the following information, prepare bank reconciliation statement as on 31st December, 2017 to find out the balance as per bank statement?

Answer:

[OR]
(b) Rectify the following errors:
- Sales book is undercast by ₹100
- Sales book is overcast by ₹200
- Purchases book is undercast by ₹300
- Purchases book is overcast by ₹400
- Purchases returns book is undercast by ₹500
Answer:
- Sales account should be credited with ₹100
- Sales account should be debited with ₹200
- Purchases account should be debited with ₹300
- Purchases account should be credited with ₹400
- Purchases returns account should be credited with ₹500
![]()
Question 45 (a).
On 1st April 2015, Kumar purchased a machine for ₹80,000 and spent ₹20,000 on its installation. The residual value at the end of its expected useful life of 8 years is estimated at ₹4,000. On 30th September 2017, the machine is sold for v50,000. Depreciation is to be provided according to straight line method. Prepare machinery account. Accounts are closed on 31st December every year?
Answer:
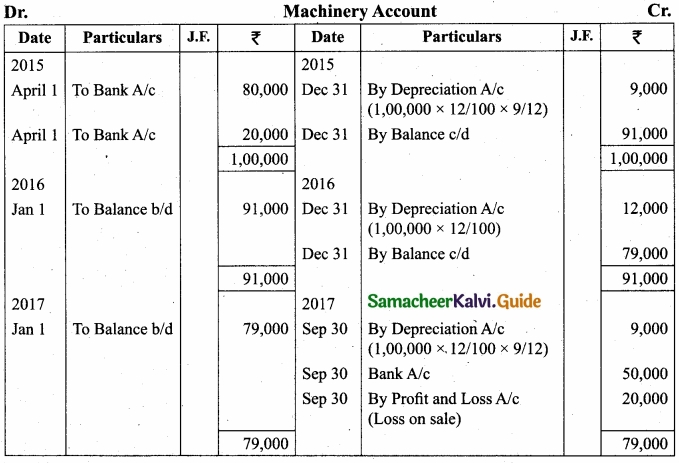
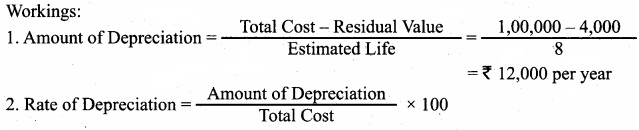
= Total cost = Cost price of machine + installation
= 80,000 + 20,000
= 1,00,000
= \(\frac{12,000}{1,00,000}\) × 100
= 12%
[OR]
(b) State whether the following are capital, revenue or deferred revenue?
- Legal fees paid to the lawyer after acquiring a land ₹20,000.
- Heavy advertising cost of ₹12,00,000 spent on introducing a new product.
- Renewal of factory licence ₹12,000.
- A sum of ₹4,000 was spent on painting the factory.
- Carriage paid on goods sold.
Answer:
- Capital
- Deferred revenue
- Revenue
- Revenue
- Revenue
![]()
Question 46 (a).
The following is the extract of a trial balance as on 31st December, 2017. Prepare Trading account: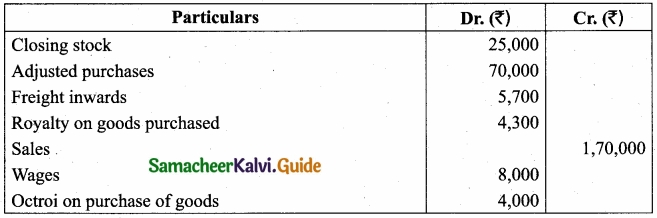
Answer:
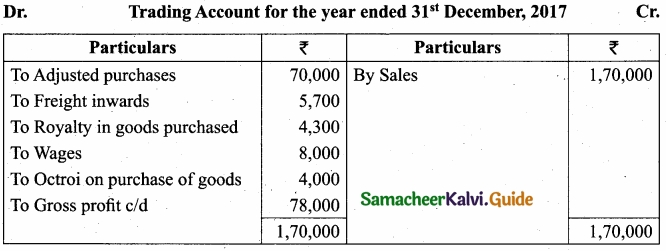
(b) From the following information, prepare profit and loss account for the year ended 31st December, 2017?
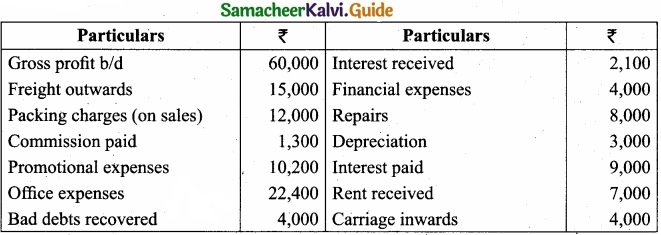
Answer:
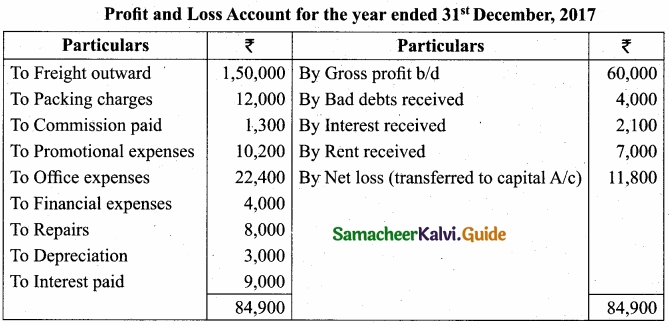
![]()
Question 47 (a).
From the following information, prepare final account of Mr. Jain for the year ended 31st December, 2016?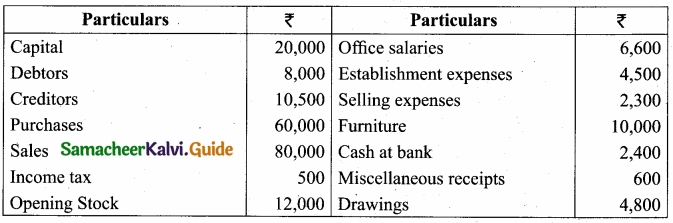
Adjustments:
- Salaries outstanding ₹600
- Depreciation on furniture ₹1,000
- Interest on capital₹1,000
- Closing Stock ₹14,000
Answer:
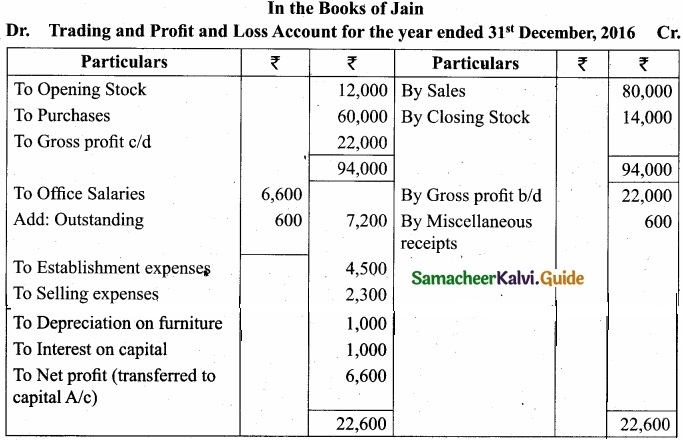
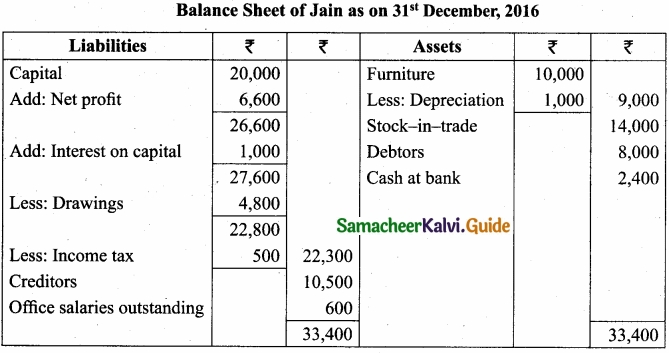
[OR]
(b) What are the differences among the three types of software? (Any five)
Answer: