Students can download 11th Economics Chapter 11 Tamil Nadu Economy Questions and Answers, Notes, Samcheer Kalvi 11th Economics Guide Pdf helps you to revise the complete Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus, helps students complete homework assignments and to score high marks in board exams.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Solutions Chapter 11 Tamil Nadu Economy
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Tamil Nadu Economy Text Book Back Questions and Answers
PART – A
Multiple Choice Questions:
Question 1.
In health index, Tamil Nadu is ahead of ……………………
(a) Kerala
(b) Punjab
(c) Gujarat
(d) All the above
Answer:
(c) Gujarat
![]()
Question 2.
In sex ratio, Tamil Nadu ranks …………………….
(a) First
(b) Second
(c) Third
(d) Fourth
Answer:
(c) Third
Question 3.
Tamil Nadu is rich in ………………………
(a) Forest resource
(b) Human resource
(c) Mineral resource
(d) All the above
Answer:
(b) Human resource
Question 4.
The main source of irrigation in Tamil Nadu is ………………………..
(a) River
(b) Tank
(c) Well
(d) Canals
Answer:
(c) Well
![]()
Question 5.
Knitted gannent production is concentrated in ………………………..
(a) Coimbatore
(b) Tiruppur
(c) Erode
(d) Karur
Answer:
(b) Tiruppur
Question 6.
Which of the following is wrongly matched?
(a) Gateway of Tamil Nadu – Thoothukudi
(b) Home textile city – Erode
(c) Steel city – Salem
(d) Pump city – Coimbatore
Answer:
(b) Home textile city – Erode
![]()
Question 7.
Which of the following cities does not have international airport?
(a) Madurai
(b) Tiruchirappalli
(c) Paramakudi
(d) Coimbatore
Answer:
(c) Paramakudi
Question 8.
TN tops in the production of the following crops except ……………………..
(a) Banana
(b) Coconut
(c) Plantation crops
(d) Cardamom
Answer:
(d) Cardamom
Question 9.
Largest area of land is used in the cultivation of …………………….
(a) Paddy
(b) Sugarcane
(c) Groundnut
(d) Coconut
Answer:
(a) Paddy
![]()
Question 10.
In literacy rate, TN ranks …………………………..
(a) Second
(b) Fourth
(c) Sixth
(d) Eighth
Answer:
(d) Eighth
Question 11.
In investment proposals filed by MSMEs, TN ranks …………………………
(a) I
(b) II
(c) III
(d) IV
Answer:
(a) I
![]()
Question 12.
Which district in TN has the highest sex ratio?
(a) Nagapattinam
(b) Nilgiris
(c) Tiruchirappalli
(d) Thanjavur
Answer:
(b) Nilgiris
Question 13.
Which district has the lowest child sex ratio?
(a) Madurai
(b) Theni
(c) Ariyalur
(d) Cuddalore
Answer:
(c) Ariyalur
![]()
Question 14.
Which Union Territory has the highest sex ratio?
(a) Chandigarh
(b) Pondicherry
(c) Lakshadeep
(d) Andaman Nicobar
Answer:
(b) Pondicherry
Question 15.
The largest contribution to GSDP in Tamil Nadu comes from …………………………
(a) Agriculture
(b) Industry
(c) Mining
(d) Services
Answer:
(d) Services
Question 16.
In human development index, TN is ranked …………………………
(a) Second
(b) Fourth
(c) Sixth
(d) Seventh
Answer:
(d) Seventh
![]()
Question 17.
SPIC is located in ……………………
(a) Chennai
(b) Madurai
(c) Tuticorin
(d) Pudukkottai
Answer:
(c) Tuticorin
Question 18.
The TICEL park is ……………………..
(a) Rubber Park
(b) Textile park
(c) Food park
(d) Bio park
Answer:
(d) Bio park
Question 19.
In India’s total cement production, Tamil Nadu ranks ………………………..
(a) Third
(b) Fourth
(c) First
(d) Second
Answer:
(a) Third
![]()
Question 20.
The Headquarters of Southern Railway is a ………………………
(a) Tiruchirappalli
(b) Chennai
(c) Madurai
(d) Coimbatore
Answer:
(b) Chennai
PART – B
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences.
Question 21.
State any two districts with favourable sex ratio. Indicate the ratios?
Answer:
Population Growth in Tamil Nadu: At a glance (2011 census)
1. Sex Ratio (per 1000 males) District with highest:
The Nilgiris (1041 females) Thanjavur (1031 females) Nagapattinam (1025 females)
2. Sex Ratio (per 1000 males) District with Lowest:
Theni (900 females) Dharmapuri (946 females)
![]()
Question 22.
Define GSDP?
Answer:
- The Gross State Domestic Product refers to the total money value of all the goods and services produced annually in the state.
- Tamil Nadu is the second-largest economy in India with a GSDP of $ 207.8 billion in 2016 – 2017 according to the Directorate of Economics and Statistics, Tamil Nadu.
Question 23.
Mention any four food crops which are favourable to Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
- Rice: Tamil Nadu is India’s second-biggest producer of rice.
- Banana and Coconut: Tamil Nadu ranks first in the production of Banana and coconut.
- Cashewnut: Tamil Nadu ranks second in the production of cashew nut.
- Pepper: Tamil Nadu ranks third in the production of pepper.
- Sugarcane: Tamil Nadu ranks fourth in the production of Sugarcane.
![]()
Question 24.
What are the major ports in Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
- Tamil Nadu has three major ports; one each at Chennai, Ennore, and Tuticorin as well as one intermediate port in Nagapattinam, and 23 minor ports.
- All the minor ports are managed by the Tamil Nadu Maritime Board, Chennai Port.
- Ennore port was recently converted from an intermediate port to a major port and handles all the coal and ore traffic in Tamil Nadu.
Question 25.
What is heritage tourism?
Answer:
Heritage tourism is travelling to experience the places and activities that authentically represent the stories and people of the past.
![]()
Question 26.
What are the nuclear power plants in Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
The Kalpakkam Nuclear Power Plant and the Koodankulam Nuclear Power Plant are the major nuclear energy plants for the energy grid.
Question 27.
Define Micro industry?
Answer:
The enterprises with a capital investment not exceeding 25 lakhs.
PART – C
Answer the following questions in one paragraph.
Question 28.
Write a note on mineral resources in Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
Mineral Resources in Tamil Nadu:
- Tamil Nadu has a few mining projects based on Titanium, Lignite, Magnesite, Graphite, Limestone, Granite, and Bauxite.
- The first one is the Neyveli Lignite Corporation that has led the development of large industrial complex around Neyveli in the Cuddalore district with Thermal Power Plants, fertilizers, and Carbonisation plants.
- Magnesite mining is at Salem from which mining of Bauxite ores are carried out at Yercaud, and this region is also rich in Iron Ore at Kanjamalai.
- Molybdenum is found in Dharmapuri and is the only source in the country.
![]()
Question 29.
Explain GSDP in Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
GSDP in Tamil Nadu:
- GSDP refers to the total money value of all the goods and services produced annually in the state.
- According to Tamil Nadu’s Directorate of Economics and Statistics, Tamil Nadu is the second-largest economy in India with a GSDP of $207.8 billion in 2016 -17
- The GSDP of Tamil Nadu is equal to the GDP of Kuwait on nominal terms and the GDP of UAE on PPP terms.
- Sectoral contribution of GSDP of Tamil Nadu
- Tertiary sector – 63. 70%
- Secondary sector – 28.5%
- Primary sector – 7.76%
Question 30.
Describe the development of the textile industry in Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
Textile industry in Tamil Nadu:
- Tamil Nadu is the largest textile hub of India.
- Tamil Nadu is known as the “Yam Bowl” of the country accounting for 41% of India’s cotton yam production.
- The textile industry plays a significant role in the Indian economy by providing direct employment to an estimated 35 million people and thereby contributing 4% of GDP and. 35% of gross export earnings.
- The textile sector contributes to 14% of the manufacturing sector.
- From spinning to garment manufacturing, entire textile production chain facilities are in Tamil Nadu.
- About half of India’s total spinning mill capacity is in Tamil Nadu.
- The western part of Tamil Nadu comprising Coimbatore, Tirupur, Erode, Dindigul, and Karur has the majority of spinning mills manufacturing cotton, polyester, blended yam, and silk yam used by garment units in Tamil Nadu, Maharashtra, etc.,
- Yam is also exported to China, Bangladesh, etc.
- Tirupur is known as “knitting city” is the exporter of garments worth USD (United States Dollar) 3 billion.
- Karur is the major home for textile manufacturing (curtain cloth, bed linens, kitchen linens, toilet linens, table linens, wall hangings, etc.,) and export hub in India.
- Erode is the main cloth market in South India for both retail and wholesale ready-mades.
![]()
Question 31.
Compare productivity of any two food crops between Tamil Nadu and India?
Answer:
Productivity position of Tamil Nadu and India:
- The Government of Tamil Nadu lays emphasis on agricultural production and productivity.
- Tamil Nadu tops in productivity, in food crops as well as non-food crops among the States in India.
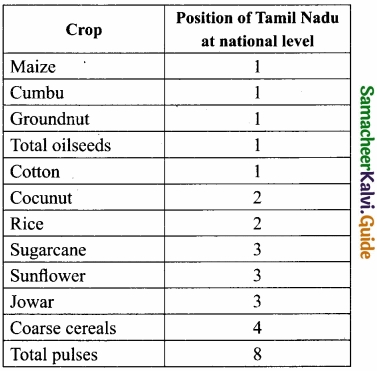
Productivity position of Tamil Nadu:
- Tamil Nadu ranks first in maize, cumbu, groundnut, oilseeds, and cotton.
- Tamil Nadu ranks second in rice and coconut.
- Tamil Nadu ranks third in sugarcane, sunflower, and jowar.
![]()
Question 32.
Explain the prospect for the development of Tourism?
Answer:
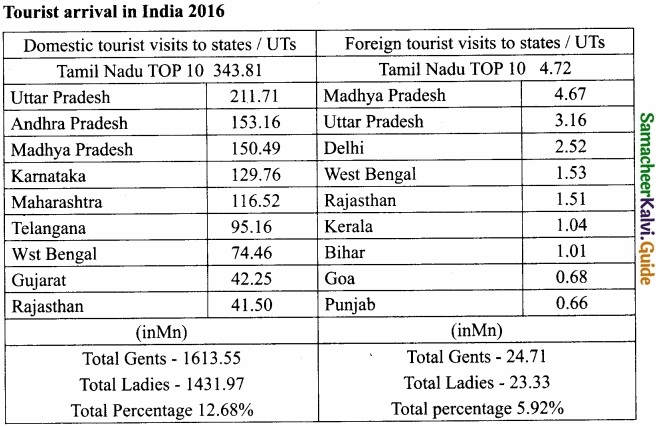
Prospect for development of tourism:
- Tamil Nadu has emerged as one of the leading tourist destinations for both domestic and foreign tourists.
- Tourism in Tamil Nadu is promoted by Tamil Nadu Tourism Development Corporation (TTDC), a Government of Tamil Nadu undertaking.
- The state currently ranks the highest among Indian states with about 25 crore arrivals.
- The annual growth rate of this industry stood at 16 percent.
- Approximately 28 lakh foreign and 11 crore domestic tourists visit the state.
![]()
Question 33.
What are the renewable sources of power in Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
Energy:
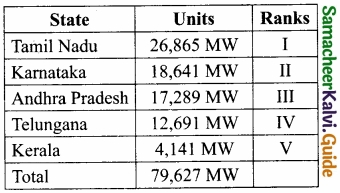
- Tamil Nadu tops in power generation among the southern States as seen in the following table.
- Installed capacity of power utilities in States in the southern region.
- Tamil Nadu is at the forefront of all other Indian States in installed capacity.
- Muppandal wind farm is a renewable energy source, supplying the villagers with electricity for work.
- Wind farms were built in Nagercoil and Tuticorin apart from already existing ones around Coimbatore, Pollachi, Dharapuram, and Udumalaipettai.
- These areas generate about half of India’s 2,000 megawatts of wind energy or two percent of the total power output of India.
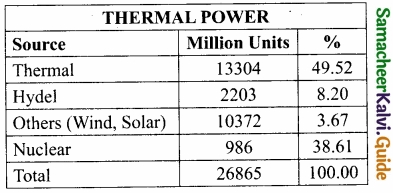
Thermal Power:
- In Tamil Nadu, the share of thermal power in total energy sources is very high and the thermal power plants are at Athippattu [North Chennai] Ennore, Mettur, Neyveli, and Thoothukudi.
- The generation of power under various sources is given below.
Hydel Energy:
- There are about 20 hydro-electric units in Tamil Nadu.
- The prominent units are Hundah, Mettur, Periyar, Maravakandy, Parson Valley, etc.
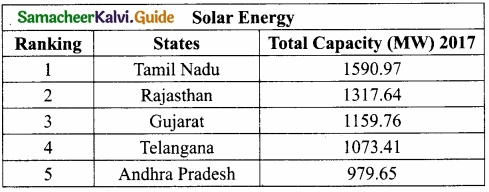
Solar Energy:
- Tamil Nadu tops in solar power generation in India as seen in the following table:
- Southern Tamil Nadu is considered as one of the most suitable regions in the country for developing solar power projects.

Wind Energy:
- Tamil Nadu has the highest installed wind energy capacity in India.
- The State has a very high quality offshore wind energy potential of the Tirunelveli coast and southern Thoothukudi and Rameswaram coast.
![]()
Question 34.
Describe the performance of Tamil Nadu Economy in health?
Answer:
Health:
- Tamil Nadu has a three-tier health infrastructure comprising hospitals, primary health centres, health units, community health centres, and sub-centers.
- As of March 2015, the State had 34 district hospitals, 229 sub-divisional hospitals, 1,254 primary health centres, 7,555 sub-centers, and 313 community health centres.
PART – D
Answer the following questions in about a page.
Question 35.
Describe the qualitative aspects of the population?
Answer:
- Population: Tamil Nadu stands sixth in population with 7.21 crore.
- Density: Tamil Nadu ranks 12th in density with 555 people per sq. km.
- Urban population: Tamil Nadu is one of the most urbanized states with 48.4% of the urban population.
- Sex ratio: Balanced sex ratio implies improvement in the quality of life of the female population. The sex ratio of Tamil Nadu is nearing balance with 995 which stands third next to Kerala and Puducherry.
- Infant mortality rate: According to NITI AAYOG, the IMR is 17 for Tamil Nadu which is just half of the national average of 34 as of 2016.
- Maternal mortality rate: Tamil Nadu has a good record of controlling MMR, ranking third with 79 against the national average of 159.
- Literacy:
- The literacy rate of Tamil Nadu is higher than in many states.
- Tamil Nadu has the highest Gross Enrollment Ratio in higher education.
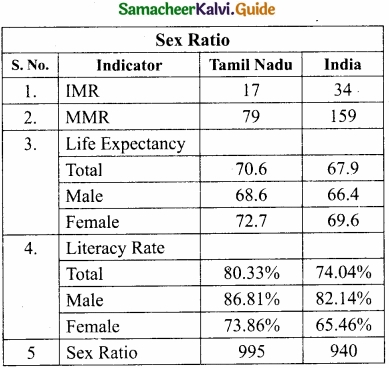
![]()
Question 36.
Explain the various sources of energy in Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
Tamil Nadu tops in power generation among the Southern States as seen in the table.
Tamil Nadu 26,865 MW is the 1st Rank in the energy level. Tamil Nadu is at the forefront of all other Indian States in installed capacity. Muppandal wind farm is a renewable energy source, supplying the villagers with electricity for work.
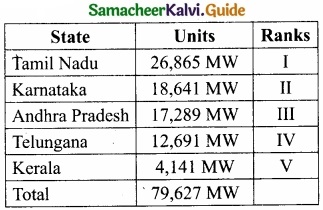
Wind farms were built in Nagercoil and Tuticorin apart from already existing ones around Coimbatore, Pollachi, Dharapuram, and Udumalaipettai. These areas generate about half of India’s 2,000 megawatts of wind energy or two percent of the total power output of India.
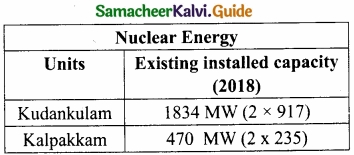
Nuclear Energy:
The Kalpakkam Nuclear Power Plant and the Koodankulam Nuclear Power Plant are the major nuclear energy plants for the energy grid.
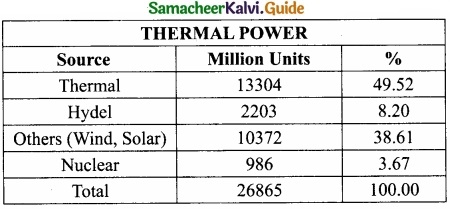
Thermal power:
- In Tamil Nadu, the share of thermal power in total energy sources is very high and the thermal power plants are at Athippattu (North Chennai) Ennore, Mettur, Neyveli, and Thoothukudi.
- The generation of power under various sources is given below.
Hydel Energy:
- There are about 20 hydro-electric units in Tamil Nadu.
- The prominent units are Hundah, Mettur, Periyar, Maravakandy, Parson Valley, etc.,
Solar Energy:
- Tamil Nadu tops in solar power generation in India as seen in the following table
- Southern Tamil Nadu is considered one of the most suitable regions in the country for developing solar power projects.
Wind Energy:
- Tamil Nadu has the highest installed wind energy capacity in India.
- The State has a very high-quality offshore wind energy potential off the Tirunelveli coast and southern Thoothukudi and Rameswaram coast.
![]()
Question 37.
Explain the public transport system in Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
Tamil Nadu has a well-established transportation system that connects all parts of the state. This is partly responsible for the investment in the state.
Road transport:
- There are 28 national highways in the state, covering a total distance of 5,036 km.
- The state has a total road length of 1,67,000 km.
- It ranks second in India with a share of over 20% in total road projects.
Rail transport:
- Tamil Nadu has a well-developed rail network as part of Southern Railway, headquartered in Chennai.
- Tamil Nadu has a total railway track length of 6,693 KM and there are 690 railway stations in the state.
- The system connects it with most major cities in India.
- Chennai developed a metro system, which came into operation in May 2017.
Air transport:
- Tamil Nadu has four major international airports.
- Chennai, Coimbatore, Tiruchirapalli, and Madurai International airports.
- It also has domestic airports at Tuticorin, Salem, and Madurai.
Samacheer Kalvi 11th Economics Tamil Nadu Economy Additional Important Questions and Answers
PART – A
Multiple Choice Questions.
Question 1.
Tamil Nadu is the geographically largest state of India.
(a) 5th
(b) 7th
(c) 9th
(d) 11th
Answer:
(d) 11th
![]()
Question 2.
Tamil Nadu lies in the part of India.
(a) North East
(b) South West
(c) South East
(d) northwest
Answer:
(c) South East
Question 3.
TNPL is the ……………………. largest eco-friendly paper mill.
(a) Asia’s
(b) America’s
(c) Europe’s
(d) Australia’s
Answer:
(a) Asia’s
Question 4.
………………………. known as “knitting city” is the exporter of garments.
(a) Tiruppur
(b) Thirunelveli
(c) Erode
(d) Karur
Answer:
(a) Tiruppur
![]()
Question 5.
……………………….. nicknamed as “The Detroit of Asia” is home to a large number of auto component industries.
(a) Thiruvallur
(b) Kancheepuram
(c) Thoothukudi
(d) Chennai
Answer:
(d) Chennai
Question 6.
SAIL has a steel plant in ……………………
(a) Salem
(b) Karur
(c) Ariyalur
(d) Coimbatore
Answer:
(a) Salem
Question 7.
The Kalpakkam nuclear power plant and the Kudankulam nuclear power plant are the major …………………. plants for the energy grid.
(a) Nuclear energy
(b) Hydel energy
(c) Solar energy
(d) Wind energy
Answer:
(a) Nuclear energy
![]()
Question 8.
The district which has the lowest density of population is ……………………….
(a) Sivagangai
(b) Nilgiris
(c) Kanyakumari
(d) Thiruvallur
Answer:
(a) Sivagangai
Question 9.
Tamil Nadu Newsprint Paper Limited (TNPL) is a ……………………….. Industry in Tamil Nadu
(a) Joint sector
(b) Private sector
(c) Public sector
(d) Co-operative sector
Answer:
(c) Public sector
![]()
Question 10.
SPIC is the largest producer of …………………….. in India.
(a) Chemical
(b) Fertilizers
(c) Petrol
(d) Fisheries
Answer:
(b) Fertilizers
PART – B
Answer the following questions in one or two sentences.
Question 1.
Write a note on “water resources”?
Answer:
- There are 17 river basins in Tamil Nadu.
- The main rivers are Palar, Cheyyar, Ponnaiyar, Cauvery, Bhavani, Vaigai, Chittar, Tamiraparani, Vellar, Noyyal, Siruvani, Gundar, Vaipar, Valparai, etc.
- North-East monsoon is the major source of rainfall followed by the southwest monsoon.
- Wells are the largest source of irrigation in Tamil Nadu (56%).
![]()
Question 2.
Write a note on “Urbanisation in Tamil Nadu”?
Answer:
Tamil Nadu is the most urbanized state with 48.4% of the urban population against 31.5% for India as a whole. The State accounts for 9.61% of total urbanites in India against a 6% share of the total population.
Question 3.
Explain Per capita income in Tamil Nadu?
Answer:
- The Per capita GSDP (Gross State Domestic Product) of Tamil Nadu also ($ 2,200) which is higher than that of many other States in India.
- Per capita, the GSDP of Tamil Nadu is nearly 1.75 times higher than the national average, as per 2018 data.
- In terms of rupees, the per capita income in Tamil Nadu was ₹1,03,600 in 2010 – 2011 and it has increased to ₹1,88, 492 in 2017 – 2018 as per the Budget.
PART – C
Answer the following questions in one paragraph.
Question 1.
Write a note on “Educational Loans”?
Answer:
- Educational loans disbursed by Public Sector Banks under priority sector are concerned, 20.8% of the total amount was disbursed in Tamil Nadu between 2013-14 and 2015-16.
- Andhra Pradesh was second with 11.2% of the total loan amount followed by Maharashtra [10.2%]
- The total amount of educational loans disbursed by Private Banks during the same period, Kerala accounted for 37.8% followed by Tamil Nadu with 24.8%.
![]()
Question 2.
Describe the “Unemployment and Poverty”?
Answer:
- The national average unemployment rate stands at 50 and Tamil Nadu ranks 22nd with an unemployment rate of 42 per 1000.
- There are different kinds of unemployment with different economic implications.
- All those aspects need to be studied to fully understand the employment situation.
- Tamil Nadu is one of India’s richest states since 1994, the state has seen a steady decline in poverty.
- Tamil Nadu has lower levels of poverty than most other states in the country.
- After 2005, Tamil Nadu was among India’s fastest-growing states, with growth being driven mainly by services.
PART – D
Answer the following questions in about a page.
Question 1.
Explain the highlights of the Tamil Nadu Economy?
Answer:
Highlights of Tamil Nadu Economy:
- The growth of SGDP in Tamil Nadu has been among the fastest in India since 2005.
- Poverty reduction in Tamil Nadu has been faster than that in many other States.
- Tamil Nadu ranks 3rd in terms of invested capital (₹ 2.92 lakh crore) and the value of total industrial output (₹ 6.19 lakh crore).
- Tamil Nadu ranks first among the states in terms of the number of factories with 17% share and industrial workers (16% share) of the country.
- Tamil Nadu is placed third in the health index as per the NITIAAYOG report.
- Tamil Nadu has the highest Gross Enrolment Ratio in higher education.
- Tamil Nadu has the largest number of engineering colleges.
- Tamil Nadu has emerged as a major hub for renewable energy.
- Tamil Nadu has the highest credit Deposit Ratio in commercial and cooperative banks.
- Tamil Nadu has the highest ranks first on investment proposals filed by MSMEs.
![]()
Question 2.
Describe the “MSMEs”?
Answer:
- The Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises are defined under the MSMED Act 2006.
- The enterprises are classified as Manufacturing and Service enterprises based on the investment in plant and machinery and equipment (excluding land and building).
- Tamil Nadu accounts for 15.07% of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in the country (the highest among all States) with 6.89 lakhs registered MSMEs.
- Producing over 8000 varieties of products for a total investment of more than ₹32,008 crores.
- MSMEs produce a wide variety of products in almost all sectors.
- The prominent among them are the engineering, electrical, chemicals, plastics, steel paper, matches, textiles, hosiery, and garments sector.
- Around 15.61 lakh entrepreneurs have registered, providing employment opportunities to about 99.7 lakhs persons with a total investment of Rs. 1,68,331 crore.
ACTIVITY
Question 1.
Visit your nearby village and make an on-the-spot study about crops production, source of irrigation, and living conditions of farmers?
Answer:
Crop Production:
- Crop Production includes all the feed sources that are required to maintain the dairy herd and the resource inputs used to produce the crops.
- The type of feed depends on animal management. System – conventional or organic.
- Feeds may include mainly corn-silage, corn – grain, alfalfa – hay and alfalfa-silage, soybeans, soybean meal, wheat, oats, distiller’s grains solids, with grasses, forage, and hay and dietary supplements such as minerals.
- The inventory would include the production of all feed crops raised on the farm, purchased from a vendor or other farm, or sold to another farm.
- In the United States, larger farms purchase feed while smaller farms grow their own feed. [USDA ECONOMIC RESEARCH SERVICE, 2007] USDA – United States Development Association.
- A separate analysis would be conducted for the feed milling operations to account for its resource inputs such as fuel used in transportation and electricity.
- Inputs in crop production include fuel for tractors and other equipment, water, machinery, fertilizer, pesticides.
- Manure nutrients are a resource input if used in crop production.
Important sources of irrigation available in Indian villages are as follows:
There are three major sources of irrigation in India.
They are:-
- Canals
- Wells and Tube – wells
- Tanks
- Wells and Tube wells are the major sources of irrigation.
- Canals rank second.
- Tanks rank third.
Canal irrigation: Canal irrigation has its maximum development in the Great Plains and in the Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna deltas in the eastern coastal plains.
Wells and Tube – wells: Wells and Tube – wells are popular in the alluvial plains.
The living condition of farmers:
- Smallholder farmers already face numerous risks to agricultural production.
- Climate change is expected to disproportionately affect smallholder farmers and make their livelihoods even more precarious.
- Farmers crop with risks and explore what strategies are needed to help them adapt to climate change.
- Agricultural system owing to their high dependence on agriculture for their livelihood, chronic food insecurity, physical, isolation and lack of access to formal safety nets.
- Farmers are frequently exposed to pest and disease outbreaks and extreme weather events particularly cyclones.
- Farmers use a variety of risk cropping strategies.
- To prevent them from remaining food insecure.
- Few farmers have adjusted their farming strategies in response to climate change, owing to limited resources and capacity.
- Technical, Financial, and Institutional support is needed to improve agricultural production and food security.
- Farmers and make their livelihoods resilient to climate change.