Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Guide Pdf Chapter 2 Motion Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Solutions Chapter 2 Motion
9th Science Guide Motion Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
The area under velocity – time graph represents the
(a) velocity of the moving object.
(b) displacement covered by the moving object,
(c) speed of the moving object.
(d) acceleration of the moving object.
Answer:
(b) displacement covered by the moving object
![]()
Question 2.
Which one of the following is most likely not a case of uniform circular motion?
(a) Motion of the Earth around the Sim.
(b) Motion of a toy train on a circular track.
(c) Motion of a racing car on a circular track.
(d) Motion of hours’ hand on the dial of the clock.
Answer:
(c) Motion of a racing car on a circular track
Question 3.
Which of the following graph represents uniform motion of a moving particle?
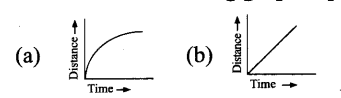

Answer:
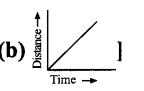
![]()
Question 4.
The centrifugal force is
(a) a real force.
(b) the force of reaction of centripetal force.
(c) a virtual force.
(d) directed towards the centre of the circular path.
Answer:
(c) a virtual force
II. Fill in the blanks :
1. Speed is a …………………….quantity whereas velocity is a …………….quantity.
Answer:
Scalar, Vector
2. The slope of the distance – time graph at any point gives ………………
Answer:
Speed
![]()
3. Negative acceleration is called ……………………
Answer:
retardation (or) deceleration
4. Area under velocity – time graph shows ……………………………….
Answer:
displacement
III. State whether true or false. If false, correct the statement:
1. The motion of a city bus in a heavy traffic road is an example for uniform motion.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: The motion of a city bus in a heavy traffic road is an example for non-uniform motion.
2. Acceleration can get negative value also.
Answer:
True.
![]()
3. Distance covered by a particle never becomes zero but displacement becomes zero.
Answer:
True.
4. The velocity – time graph of a particle falling freely under gravity would be a straight line parallel to the x axis. .
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: The velocity – time graph of aparticle moving at uniform do dry. would be straight line parallel to the x axis.
5. If the velocity – time graph of a particle is a straight line inclined to X-axis then its displacement – time graph will be a straight line.
Answer:
True.
IV. Assertion and Reason Type Questions :
Mark the correct choice as:
(a) If both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If assertion is false but reason is true.
![]()
Question 1.
Assertion : The accelerated motion of an object may be due to change in magnitude of velocity or direction or both of them..
Reason : Acceleration can be produced only by change in magnitude of the velocity. It does not depend the direction.
Answer:
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
Question 2.
Assertion : The Speedometer of a car or a motor-cycle measures its average speed.
Reason : Average velocity is equal to total displacement divided by total time taken.
Answer:
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true
Question 3.
Assertion : Displacement of a body may be zero when distance travelled by it is not zero.
Reason : The displacement is the shortest distance between initial and final position.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion and reason are true and reason is the correct explanation of assertion
![]()
V. Match the Following :
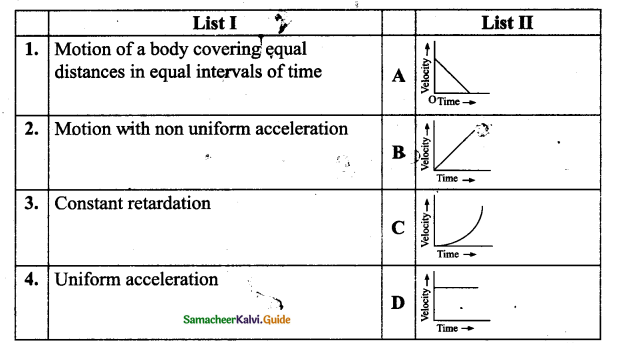
Answer:
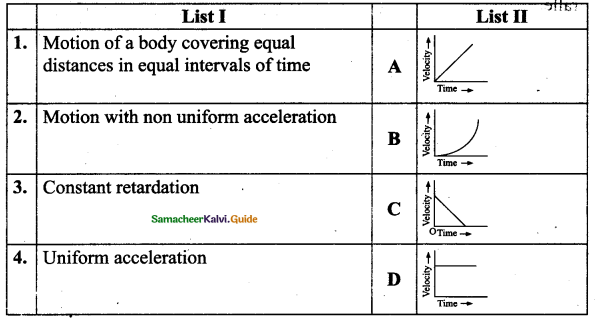
![]()
VI. Answer briefly :
Question 1.
Define velocity.
Answer:
Velocity is the rate of change of displacement. It. is the displacement in unit time.
Question 2.
Distinguish distance and displacement.
Answer:
Table
Distance
- The actual length of the path travelled by a moving body irrespective of the direction
- It is a Scalar quantity
Displacement:
- The change in position of a moving body in a particular direction
- It is a Vector quantity
Question 3.
What do you mean by uniform-motion?
Answer:
An object is said to be in uniform motion if it covers equal distances in equal intervals of time how so ever big or small these time intervals may be.
![]()
Question 4.
Compare speed and velocity.
Answer:
| Speed | Velocity |
| 1. It is the rate of change of distance with respect to time | It is the rate of change of displacement with respect to time |
| 2. It is a scalar quantity having magnitude only | It is a vector quantity having both magnitude and direction |
| 3. Speed is velocity without a particular direction | Velocity is speed in a particular direction |
| 4. It is measured in ms-1 in SI system | It is also measured in ms-1 in a particular direction in SI system |
| 5. Speed in any direction would be a positive quantify, since the distance in any direction is a positive quantity. | Velocity can get both positive and negative values. If velocity in one direction is assumed to be positive then the velocity in the opposite direction would be a negative quantity. Velocity can get zero value also. |
Question 5.
What do you understand about negative acceleration?
Answer:
If v < u, i.e. if final velocity is less than initial velocity, the velocity decreases with time and the value of acceleration is negative. It is called negative acceleration. It is also called as retardation (or) deceleration.
Question 6.
Is the uniform circular motion accelerated? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer: When an object is moving with a constant speed along a circular path, the change in velocity is only due to the change in direction. Hence it is accelerated motion.
![]()
Question 7.
What is meant by uniform circular motion? Give two examples of uniform circular motion.
Answer:
When an object moves with constant speed along a circular path, the motion is called uniform circular motion.
Example :
- The earth moves around the sun in the uniform circular motion.
- The moon moves in uniform circular motion around the earth.
VII. Answer in detail :
Question 1.
Derive the equations of motion by graphical method.
Answer:
Equations of motion from velocity-time graph:
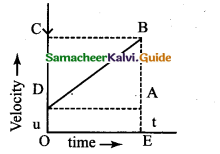
Graph shows the change in velocity with time of a uniformly accelerated object. The object starts from the point D in the graph with velocity u. Its velocity keeps increasing and after time t it reaches the point B on the graph.
The initial velocity of the object = u = OD = EA
The final velocity of the object = v = OC = EB
Time = t = OE = DA
Also from the graph we know that, AB = DC
![]()
1. First equation of motion :
By definition, acceleration = change in velocity / time
= (final velocity – initial velocity)/time
= (OC – OD) / OE
= DC / OE
a = DC /t
DC = AB = at
From the graph EB = EA + AB
v = u + at…………..(1)
This is first equation of motion. .
2. Second equation on of motion :
From the graph the distance covered by the object during time t is given by the area of quadrangle DOEB
s = area of the quadrangle DOEB
= area of the rectangle DOEA + area of the triangle DAB
= (AE x OE) + (1/2 × AB × DA) .
s = ut + 1/2 (at2) …………(2)
This is the second equation of motion.
![]()
3. Third equation of motion :
From the graph the distance covered by the object during time, t is given by the area of the quadrangle DOEB. Here DOEB is a trapezium. Then,
s = area of trapezium DOEB
= 1/2 × sum of length of parallel side × distance between parallel sides
= 1/2 × (OD + BE) × OE
S = 1/2 ×× (u + v) × t
since a = (v – u) /1 or t = (v – u) / a
Therefore s = 1/2 × (v + u) x (v – u) / a
2as = v2 – u2
v2 = u2 + 2 as …………….. (3)
This is the third equation of motion.
Question 2.
Explain different types of motion.
Answer:
In physics, motion can be classified as below.
1. Linear motion: Motion along a straight line.
2. Circular motion: Motion along a circular path.
3. Oscillatory motion: Repetitive to and fro motion of an object at regular intervals of time. Random motion: Motion of the object which does not fall in any of the above categories.
Uniform and Non-uniform motion:
Uniform motion: Consider a car that covers 60 km in the first hour, 60 km in the second horn-, and another 60 km in the third hour, and so on. The car covers equal distance at equal intervals of time. We can say that the motion of the car is uniform. An object is said to be in uniform motion if it covers equal distances in equal intervals of time howsoever big or small these time intervals may be.
Non-uniform motion: Now, consider a bus starting from one stop. It proceeds slowly when it passes through a crowded area of the road. Suppose, it manages to travel merely 100 m in 5 minutes due to heavy traffic and is able to travel about 2 km in 5 minutes when the road is clear. Hence, the motion of the bus is non-uniform i.e. it travels unequal distances in equal intervals of time.
VIII. Exercise Problems:
Question 1.
A ball is gently dropped from a height of 20 m. If its velocity increases uniformly at the rate of 10ms-2, with what velocity will it strike the ground? After what time will it strike the ground?
Answer:
Here we have
Initial velocity, u = 0
Distance, s = 20 m
Acceleration, a = 10 m/s2
Final velocity, v = ?
Time, t = ?
a) Calculation of final velocity, v
We know that, v2 = u2 + 2as
v2 = 0 + 2 × 10m/s2 × 20m
v2 = 400m2/s2
\(=\sqrt{400 m^{2} / s^{2}}\)
v = 20m/s
b) Calculation of time, t
We know that, v = u + at
20 m/s = 0 + 10m/s2 × t
t = \(\frac{20 m / s^{2}}{20 m / s}=2 s\)
∴ Ball will strike the ground at a velocity of 20 ms-1
Time taken to reach the ground = 2s.
![]()
Question 2.
An athlete completes one round of a circular track of diameter 200 m in 40 s. What will be the distance covered and the displacement at the end of 2 m and 20 s?
Answer:
Here we have
Diameter = 200. m
∴ Radius = 200 m/2 = 100 m
Time of one rotation = 40 s
Time after 2m 20 s = 2 × 60 s +20 s = 140 s
Distance after 140 s = ?
Displacement after 140 s = ?
Circular track with a diameter of 200m
We know that, velocity
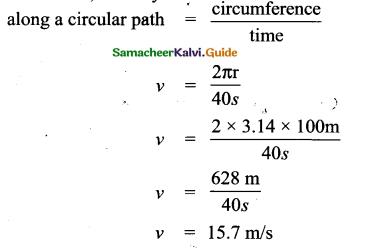
a) Distance after 140 s
We know that, distance = velocity × time
= Distance 15.7 rn/s × 140 s
= 2198m
![]()
b) Displacement after 2 min 20 s i.e, in 140 s
We know that, distance = velocity × time
Since, rotation in 40 s = 1
∴ Rotation in 1 s = \(\frac{1}{40}\)
∴ Rotation in 140 s = \(\frac{1}{40} \times 140=3.5\)
∴ In 3.5 rotation athlete will be just at the opposite side of the circular track,
i.e. at a distance equal to the diameter of the circular track which is equal to 200m
∴ Distance covered in 2min 20 s = 2198 m
Displacement after 2min 20 5 = 200 m.
Question 3.
A racing car has a uniform acceleration of 4ms-2. What distance it covers in 10s after the start?
Answer:
Here we have
Acceleration, a = 4 m/s2.
Initial velocity u = 0
Time t = 10 s
Distance (s) covered =?
We know that, s = ut + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) at2
s = (0 × 10s) + [\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 4 m/s2 × (10 s)2]
= \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 4 m/s2 × 100 s2
= 2 × 100 m = 200 m
Thus, racing car will cover a distance of 200 m after start in 10s with given acceleration.
![]()
Intex Activities
ACTIVITY – 1
Look around you. You can see many things: a row of houses, large trees, small plants, flying birds, running cars and many more. List the objects which remain fixed at their position and the objects which keep on changing their position.
Solution:
- Row of houses, large trees, small plants are the examples, of immovable objects.
- Flying birds, running cars and buses are the examples of movable objects.
Activity to be done by the students themselves
ACTIVITY – 2
Tabulate the distance covered by a bus in a heavy traffic road in equal intervals of time and do the same for a train which is not in an accelerated motion. From your table what do you understand?
The bus covers unequal distance in equal intervals of time but the train covers equal distances in equal intervals of time.
Solution:
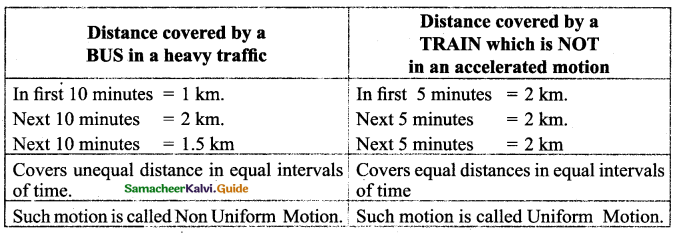
![]()
ACTIVITY – 3
Observe the motion of a car as shown in the figure and answer the following questions:
Compare the distance covered by the car through the path ABC and AC. What do you observe? Which path gives the shortest distance to reach D from A? Is it the path ABCD or the path ACD or the path AD?
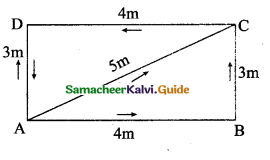
Solution:
- Distance covered by the car through the path ABC = 4m + 3m = 7 m. and AC = 5 m. The distance covered by the car through the path ABC is large compared to AC.
- The shortest distance to resell D from A is path AD = 3m.
- The total distance covered by the car ABCD A = 14 m. It finally reaches to A.
![]()
ACTIVITY – 4
Take a large stone and a small eraser. Stand on the top fit a table and drop them simultaneously from the same height? What do you observe? Now, take a small eraser and a sheet of paper. Drop them simultaneously from the same height. What do you observe? This time, take two sheets of paper having same mass and crumple one of the sheets into a ball. Now, drop the sheet and the ball from the same height. What do you observe?
Solution :
Both the stone and the eraser have reached the surface of the earth almost at the same time.
The eraser reaches first and the sheet of paper reaches later.
The paper crumpled into a ball reaches ground first and plain sheet of paper reaches later, although they have equal mass. It is because of air resistance. The magnitude of air resistance despends on the area of object exposed to air. So the sheet of paper reaches later.
![]()
9th Science Guide Motion Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
A particle is moving in a circular pattern of radius r. The displacement after half a circle would be
(a) zero
(b) πr
(c) 2r
(d) 2πr
Answer:
(c) 2r
Question 2.
In which of the following cases of motions, the distance moved and the magnitude of displacement are equal?
(a) If the car is moving in the straight road.
(b) If the car is moving in a circular road.
(c) The earth is revolving around the sun.
(d) The pendulum is moving to and fro
Answer:
(a) If the car is moving in the straight road
![]()
Question 3.
A body is thrown vertically upward with velocity, the greatest height h to which it will rise is
(a) u2/2g
(b) u2/g
(c) u/g
(d) u/2g
Answer:
(a) u2/2g
Question 4.
If the displacement of an object is proportional to square of time, then the object moves with
(a) uniform velocity
(b) uniform acceleration
(c) increasing acceleration
(d) decreasing acceleration
Answer:
(b) uniform acceleration
![]()
Question 5.
From the given v-t graph, u can be inferred that the object is
(a) in uniform motion
(b) at rest
(c) in non-uniform motion
(d) moving with uniform acceleration
Answer:
(a) in uniform motion
Question 6.
The area under v-t graph represents a physical quantity which has the unit.
(a) m2
(b) m
(c) m3
(d) ms-1
Answer:
(b) m
Question 7.
m/s2 is the unit of
(a) distance
(b) displacement
(c) velocity
(d) acceleration
Answer:
(d) acceleration
![]()
Question 8.
The rate of change of displacement
(a) speed
(b) velocity
(c) acceleration
(d) retardation
Answer:
(b) velocity
Question 9.
A scalar quantity has T
(a) magnitude only
(b) direction only
(c) both
(d) none
Answer:
(a) magnitude only
![]()
Question 10.
When an object undergoes acceleration
(a) there is always an increase in its velocity
(b) there is always an increase in its speed
(c) a force always acting on it.
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(c) a force always acting on it
Question 11.
A body is projected up with an initial velocity u m/s. It goes up to a height, ‘h’ metres in seconds time. Then it comes back at the point of projection. Considering negligible air resistance, which of the following statement is true?
(a) the acceleration is zero
(b) the displacement is zero
(c) the average velocity is 2hit
(d) the final velocity is 2u when body reaches projection point
Answer:
(b) the displacement is zero
![]()
Question 12.
A car accelerates at 1.5m/s2in a straight road. How much is the increase in velocity in 4s.
(a) 6 m/s
(b) 4 m/s
(c) 3 m/s
(d) 2.66 m/s
Answer:
(a) 6 m/s
Question 13.
The slope of the distance-time curve is steeper / greater is the
(a) velocity
(b) acceleration
(c) displacement
(d) speed
Answer:
(d) speed
Question 14.
The given graph represents motion with …………….speed.
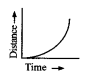
(a) uniform
(b) non-uniform
(c) constant
(d) none
Answer:
(b) non-uniform
![]()
Question 15.
The relation between displacemeñt and time is given by the equation of
(a) v2 = ut + at
(b) s = ut + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) at2
(e) c = s/t
(d) v2 = u2 + 2as
Answer:
(b) s = ut + \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) at2
Question 16.
A body moves in a uniform circular motion
(a) It is moving with constant velocity
(b) its acceleration is zero
(c) the body has an acceleration y
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(a) It is moving with constant velocity
Question 17.
Speed of the body in particular direction can be called
(a) acceleration
(b) displacement
(c) velocity
(d) distance
Answer:
(c) velocity
![]()
Question 18.
Statement A: Uniform circular motion is a case of accelerated motion
Statement B: In third equation of motion we do not have the term time
(a) Statement B is true, A is false
(b) Statement A is true, B is false
(c) neither statement A nor B is true
(d) both are true
Answer:
(d) both are true
Question 19.
Which of the following is correct about uniform circular motion
(i) direction of motion is continuously changed
(ii) direction of motion is not changed
(iii) speed and direction both remain constant
(iv) speed is constant but direction is changing
(a) ii & iii are correct
(b) i, ii & iii are correct
(c) i & iv are correct
(d) all of these
Answer:
(c) i & iv are correct
Question 20.
Which of the quantities have the same SI unit?
(a) speed, velocity
(b) acceleration, time
(c) velocity, time
(d) velocity, acceleration
Answer:
(a) speed, velocity
![]()
Question 21.
Rest and motion of body are
(a) non-relative
(b) not related
(c) relative
(d) none
Answer:
(c) relative
Question 22.
An ant moves from one corner of a room diagonally to the opposite corner. If the dimensions of the hall are 8m x 6m, the displacement of the ant is
(a) 10m
(b) 14m
(c) 28m
(d) 2m
Answer:
(a) 10m
![]()
Question 23.
The displacement covered by a second hand of radius V in a clock after one revolution is
(a) 360°
(b) 0
(c) 3r
(d) 2r
Answer:
(b) 0
Question 24.
A man leaves his house at 6.30 a.m. for a morning walk and returns back at 7.30 a.m. after covering 4 km. Displacement covered by him is …………….
(a) 2 km
(b) zero
(c) 8 km
(d) 4 km
Answer:
(b) zero
Question 25.
A body is said to be in non uniform motion if it travels
(a) equal distance in unequal interval of time
(b) equal distance in equal interval of time
(c) unequal distance in unequal interval of time
(d) unequal distance in equal interval of time.
Answer:
(d) unequal distance in equal interval of time
Question 26.
A quantity which has both magnitude and direction is
(a) scalar
(b) distant
(c) vector
(d) moving body
Answer:
(c) vector
Question 27.
A bus accelerating with 4ms-2 changes its speed from 60ms_1 to a certain value in 5s. The final speed is
(a) 40 m/s
(b) 25 ms-1
(c) 60 ms-1
(d) 30 ms-1
Answer:
(a) 40 m/s
![]()
Question 28.
A quantity has a value of 16ms-2. It is the
(a) acceleration of an object
(b) velocity of an object
(c) retardation of an object
(d) speed of an object
Answer:
(c) retardation of an object
Question 29.
A boy throws a ball up and catches it when the ball falls back. In which part of the motion the ball is accelerating?
(a) during downward motion
(b) when the ball comes to rest
(c) during upward motion
(d) when the boy catches the ball.
Answer:
(a) during downward motion]
Question 30.
Choose the correct option.
(a) distance is a scalar, velocity is a vector, acceleration is a vector
(b) distance is a vector, velocity is a scalar, acceleration is a vector
(c) distance is a vector, velocity is a vector, acceleration is a vector
(d) distance is a scalar, velocity is a vector, acceleration is scalar
Answer:
(a) distance is a scalar, velocity is a vector, acceleration is a vector
Question 31.
If a moving body comes to rest, then its acceleration is
(a) positive
(b) negative
(c) zero
(d) all of these depending upon initial velocity.
Answer:
(b) negative
![]()
Question 32.
If the velocity of a body changes uniformly from u to v in time t, the sum of average velocity and acceleration is
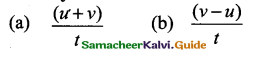

Answer:
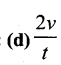
Question 33.
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of
(a) distance
(b) velocity
(c) speed
(d) displacement
Answer:
(b) velocity
![]()
Question 34.
When an object undergoes acceleration
(a) there is always an increase in its velocity ‘
(b) there is always an increase in its speed
(c) a force always acting on it.
(d) all the above
Answer:
(c) a force always acting on it
Question 35.
The equation v = u + at gives information as
(a) velocity is a function of time
(b) velocity is a function of position
(c) position is a function of time
(d) position is a function of time and velocity
Answer:
(a) velocity is a function of time
Question 36.
Which of the following can determine the acceleration of a moving object.
(a) area of the velocity-time graph
(b) the slope of the velocity-time graph
(c) area of a distance-time graph
(d) the slope of a distance-time graph
Answer:
(b) slope of the velocity-time graph
![]()
Question 37.
What is the slope of the body when it moves with uniform velocity?
(a) positive
(b) negative
(c) zero
(d) may be positive or negative
Answer:
(c) zero]
Question 38.
If a body starts from rest, what can be said about the acceleration of the body?
(a) positively accelerated
(b) negative accelerated
(c) uniform accelerated
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(a) positively accelerated
Question 39.
When a body moves uniformly along the circle then
(a) its velocity changes but speed remain the same
(b) its speed changes but velocity remains the same
(c) both speed and velocity changes
(d) both speed and velocity remains same
Answer:
(a) its velocity changes but speed remains the same
![]()
Question 40.
Distance travelled by a freely falling body is proportional to
(a) mass of the body
(b) square of the acceleration due to gravity
(c) square of the time of fall
(d) time of fall
Answer:
(c) square of the time of fall
Question 41.
If the displacement-time graph of a particle is parallel to the time axis, then velocity of the particle is.
(a) infinity
(b) unity
(c) equal to acceleration
(d) zero
Answer:
(d) zero
Question 42.
In the velocity-time graph, AB shows that the body has
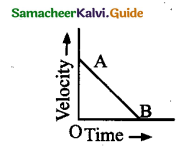
(a) uniform acceleration
(b) non-uniform retardation
(c) uniform speed
(d) initial velocity OA & is moving with uniform retardation.
Answer:
(d) initial velocity OA & is moving with uniform retardation
![]()
Question 43.
The magnitude of the centripetal force is given by (F= ….)


Answer:
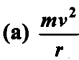
Question 44.
A body moving with an initial velocity 5ms-1 and accelerates at 2ms -2. Its velocity after 10s is
(a) 20ms-1
(b) 25ms-1
(c) 5ms-1
(d) 22.55ms-1
Answer:
(b) 25ms-1
![]()
Question 45.
In a 100m race, the winner takes 10s to reach the finishing point. The average speed of the winner is
(a) 5ms-1
b) 20ms-1
c) 40ms-1
d) 10ms-1
Answer:
(d) 10ms-2
Question 46.
The area under the velocity-time graph represents
(a) the velocity of the moving object
(b) displacement covered by the moving object
(c) speed of the moving object.
(d) acceleration of the moving object
Answer:
(b) displacement covered by the moving object
Question 47.
A car is being driven at a speed of 20ms-1 when brakes are applied to bring it to rest in 5 s. The deceleration produced in this case will be
(a) +4ms-2
(b) -4ms-2
(c) -0.25ms-2
(d) +0.25ms-2
Answer:
(b) -4ms-2
![]()
Question 48.
Unit of acceleration is
(a) ms-1
(b) ms-2
(c) ms
(d) ms2
Answer:
(b) ms-2
Question 49.
The force responsible for drying clothes in a washing machine is …………….
(a) Centripetal force
(b) Centrifugal force
(c) Gravitational force
(d) Electro static force
Answer:
(b) Centrifugal force
II. Fill in the blanks:
1. If a body does not change its position, then it is said to be at …………………
Answer:
rest
2. The back and forth motion of a swing is an ………………… motion.
Answer:
Oscillatory
3. In uniform motion an object travels equal ………………… in ………………… interval of time.
Answer:
distances, equal
![]()
4. The actual path covered by a body is called …………………
Answer:
distance
5. Displacement is the ………………… distance covered by a body.
Answer:
shortest
6. The motion of the bus is ………………… motion.
Answer:
non-uniform
7. Rate of change of displacement is …………………
Answer:
velocity
8. Speed is a ………………… quantity whereas velocity is a …………………
Answer:
scalar, vector
9. If final velocity is less than initial velocity the acceleration is ………………….
Answer:
negative
![]()
10. If final velocity is equal to initial velocity the value of acceleration is ………………….
Answer:
zero
11. The slope of the distance-time graph becomes steeper & steeper the speed ………………….
Answer:
increases
12. A straight line parallel to the x-axis in the velocity-time graph, represents the object moves in…………………
Answer:
uniform velocity
![]()
13. From v-t graph ………………… can be calculated.
Answer:
displacement
14. ………………… measures the instantaneous speed of the automobile.
Answer:
Speedometer
15. Slope of the velocity-time graph gives…………………
Answer:
acceleration
16. The value of acceleration for a body at rest is…………………
Answer:
zero
17. At the highest point, when a body is thrown vertically upwards, the velocity is ………………….
Answer:
zero
![]()
18. A body moves in a circular pattern the ………………… of velocity does not change but changes.
Answer:
magnitude, direction
19. When a body moves in a circular pattern ………………… acceleration is directed radially towards the centre of the circle.
Answer:
centripetal
20. The separation of cream from milk-hn example for the application of ………………….
Answer:
centrifugal
21. Consider an object is rest at position x = 20m. Then its displacement – time graph will be straight-line ………………… to the time axis.
Answer:
Parallel
![]()
III. State whether true or false. If false, correct the statement:
1. Displacement can be zero but distance never.
Answer:
True.
2. Time is a vector quantity.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Time is a scalar quantity.
3. Displacement magnitude can be greater than the distance travelled by the object.
Answer:
True.
4. If the velocity of the body decreases with time the acceleration is negative and the motion is called decelerated motion.
Answer:
True.
![]()
5. Acceleration is a scalar.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Acceleration is a vector.
6. The area of the velocity-time graph gives the displacement of the body.
Answer:
True.
7. Motion & rest are relative terms.
Answer:
True.
8. An object can be moving with uniform speed but variable acceleration.
Answer:
True.
9. Slope of the distance-time graph indicates the speed.
Answer:
True.
![]()
10. It is possible to have object moving with uniform velocity but non-uniform acceleration.
Answer:
True.
11. It is possible to have object moving with uniform speed but variable acceleration.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement : It is possible to have object moving with uniform speed but constant acceleration.
12. The force experienced by a boy in the merry-go-round is a centripetal force.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: The force experienced by a boy in the merry-go-round is a centrifugal force.
13. The initial velocity of a freely falling object is zero as it is released from rest.
Answer:
True.
![]()
IV. Assertion and Reason Type Questions :
(a) If both assertion & reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) If both assertion & reason are true but the reason is not correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) If the assertion is true but the reason is false.
(d) If assertion & reason both are false.
(e) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Question 1.
Assertion : A body can have acceleration even if its velocity is zero at a given instant of time.
Reason: A body is momentarily at rest when it reverses its direction of motion.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion & reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion
Question 2.
Assertion : If the displacement of the body is zero, the distance covered by it may not be zero.
Reason: Displacement is a vector & distance is a scalar quantity.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion & reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion
![]()
Question 3.
Assertion: An object can have constant speed but the variable velocity
Reason: Speed is a scalar but velocity is a vector.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion & reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion
Question 4.
Assertion: The speed of a body can be Negative.
Reason : If the body is moving in the opposite direction of positive motion, then its speed is Negative.
Answer:
(d) Assertion & reason both are false
Question 5.
Assertion : The position-time graph of a uniform motion in one dimension of a body can have Negative slope
Reason : When the speed of body decreases with time then, position-time graph of the moving body has Negative slope.
[Answer:
(c) Assertion is true but the reason is false
![]()
Question 6.
Assertion: A positive acceleration of a body can be associated with slowing down of the body.
Reason: Acceleration is a vector.
[Answer: (b) Both assertion & reason are true but the reason is not correct explanation of the assertion]
Question 7.
Assertion :A negative acceleration of a body can be associated with speeding up of the body.
Reason: Increase in speed of a moving body is independent of its direction of motion.
Answer:
(b) Both assertion & reason are true but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
Question 8.
Assertion When a body is subjected to a uniform acceleration, it is always moving in a straight line.
Reason: Motion may be straight-line motion or circular motion.
Answer:
(e) Assertion is false but the reason is true
Question 9.
Assertion : Position-time graph of a stationary object is a straight line parallel to time axis. ’
Reason : For a stationary object, position does not change with time.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion & reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion
![]()
Question 10.
Assertion : The slope of distance-time graph of a body moving with high speed is steeper than slope of distance-time graph of a body with low velocity.
Reason: Slope of distance-time graph = speed of the body.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion & reason are true and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion
V. Answer briefly :
Question 1.
What are centripetal acceleration and centripetal force?
Answer:
When a body moves in a circular pattern the acceleration is directed radially towards the centre of the circle.
The force causing this acceleration is also directed towards the centre of the circle and it is called centripetal force.
Question 2.
Find the magnitude of centripetal force.
Answer:
Consider an object of mass m, moving along a circular path of radius r, with a velocity v, its centripetal acceleration is given by a = v2 / r
Hence, the magnitude of centripetal force is given by,
F = mass x centripetal acceleration
F = mv2 / r
![]()
Question 3.
What is centrifugal force? Give examples.
Answer:
Force acting on a body away from the centre of circular path is called centrifugal force. Thus centrifugal force is in a direction opposite to the direction of centripetal force. Its magnitude is same as that of centripetal force.
Example : Spin dryer of a washing machine, ride on a merry-go-round.
Question 4.
When an object is thrown upwards, what is true of velocity and acceleration at the highest point of motion of the object?
Answer:
- Velocity becomes zero
- Acceleration remains same as g.
Question 5.
Name the two quantities, the slope of whose graph gives (i) speed (ii) acceleration.
Answer:
(i) Distance – Time
(ii) Speed – Time
Question 6.
Define Average speed.
Answer:
It is the total distance travelled divided by the total time taken to cover this distance.
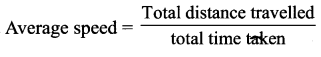
![]()
Question 7.
What do you infer if
(i) Distance – time graph is straight line.
(ii) Velocity time graph is curved.
(iii) Displacement time is zig zag.
Answer:
(i) Speed is constant.
(ii) Acceleration is not uniform.
(iii) Non uniform velocity.
Question 8.
Give the formula for each.
(i) Relation between initial, final velocity, acceleration and displacement in a uniformly accelerated straight line motion.
(ii) Relation between initial, final velocity, acceleration & time in a uniformly accelerated straight line motion.
(iii) Relation between initial velocity, acceleration, displacement and time.
Answer:
(i) Relation between initial, final Velocity, acceleration & displacement
in a uniformly accelerated straight line motion. v2 = u2 + 2as
(ii) Relation between initial, final velocity, acceleration & time
in a uniformly accelerated straight line motion. v = u + at
(iii) Relation between initial velocity, acceleration, displacement and time. s = ut+ 1/2 at2
![]()
Question 9.
What is the difference between uniform acceleration and non – uniform acceleration?
Answer:
Uniform Acceleration
- It is the acceleration in which the object changes its velocity with equal intervals of time.
- eg. The motion of a ball rolling down.
Non – Uniform Acceleration
- It is the acceleration in which the object changes its velocity with unequal intervals of time.
- A car travels 2 km in 1st hour, 3 km in 2nd hour and 3.5 km in 3rd horn.
Question 11.
Define Acceleration.
Answer:
Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time or it is the rate of change of velocity in unit time. It is a vector quantity. The SI unit of acceleration is
VI. Paragraph Questions :
Question 1.
Define acceleration and state its SI unit for motion along a straight line, when do we consider the acceleration to be (i) positive (ii) negative? Give an example of a body in uniform acceleration.
Answer:
Answer: Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity with respect to time or it is the rate of change of velocity in unit time. It is a vector quantity. The SI unit of acceleration is ms-2
Acceleration = Change in velocity/time
= (Final velocity – initial velocity)/time
a = \(\frac{v-u}{t}\)
If v > u, then ‘a’ is positive. If final velocity is greater than initial velocity, the velocity increase with time, the value of acceleration is positive.
If v < u, then a is negative. If final velocity is less than initial velocity
Example : The motion of a freely falling body and vertically thrown up body are the examples of uniform acceleration.
The motion of ball rolling down on an inclined plane is another example.
![]()
Question 2.
Distinguish between uniform motion and non
Answer:
uniform motion.
- An object is said to be in uniform motion if it covers equkl distances in equal intervals of time.
- example of uniform motion ‘train’
non-uniform motion.
- If a body covers unequal distances in equal interval of time (or) equal distances in a different interval of time
- example of non – uniform motion ‘bus’
Question 3.
Define uniform circular motion and give an example of it. Why is it called accelerated motion?
Answer:
When an object is moving with a constant speed along a circular path, the change in velocity is only due to the change in direction. Hence it is accelerated motion. Example:
- The earth moves around the sun in a uniform circular motion.
- The moon moves in uniform circular motion around the earth.
Question 4.
When a body is said to be in (i) uniform acceleration (ii) non – uniform acceleration?
Answer:
(i) A body is said to be in uniform acceleration if it travels in a straight line and its velocity increases or decreases by equal amounts in equal time intervals.
(ii) A body is said to be in non-uniform acceleration if the rate of change of its velocity is not constant i.e. differs in different time intervals.
![]()
Question 5.
What remains constant in uniform circular motion? And what changes continuously in uniform circular motion?
Answer:
- Speed remains constant in a uniform circular motion.
- Velocity changes continuously in a uniform circular motion.
Problems
Question 1.
A bus speed decreases from 50 km/h to 40 km/h in 3s, find the acceleration of the bus.
Answer:
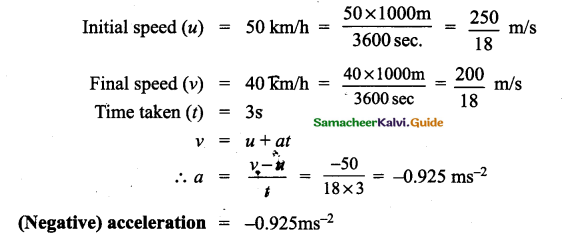
Question 2.
A car starting from rest moves with uniform acceleration of 0.2 ms-2 for 3 min. Fine the (a) speed acquired (b) the distance travelled.
Answer:
Initial speed (u) = 0 m/s
Acceleration (a) = 0.2 ms-2
Time taken (t) = 3 min = 3 × 60 = 180 s
Final velocity (v) = ?
Distance covered(s) = ?
v = u + at = 0 + 0.2 × 180 = 36 m/s
v = 36m/s
s = ut + 1/2 at2 = 0 + 1/2 × 0.2 × (180)2
= 0.1 × 32400 = 3240 m
s = 3240m
![]()
Question 3.
A train is travelling at a speed of 90 kmh-1. Brakes are applied so as to produce a uniform acceleration of-0.5 ms-2, find how far the train will go before it is brought to rest.
Answer:
Initial velocity of train (u) = 90 km/h = \(\frac{90,000 \mathrm{~m}}{3,600 \mathrm{sec}}=25 \mathrm{~ms}^{-1}\)
Final velocity (v) = 0 ms-1
Acceleration (a) = – 0.5 ms-2
v2 = u2+ 2as
s = (v2 – u2) / 2a = (02 – 252) / -(2 × 0.5)
s = -625/-1 = 625m
s = 625m
![]()
Question 4.
In a long-distance race the athletes were expected to take four rounds of the track such that the line of finish was same as the line of start. Suppose the length of the track was 300m,
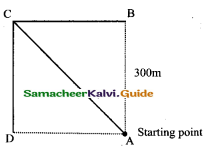
(i) What is the total distance to be covered by the athletes?
What is the total displacement of the athletes when they touch the finish line?
(iii) Is the motion of the athletes uniform or non- D .^starting point uniform?
(iv) Is the displacement & distance moved by an athlete at the end of the race equal?
Answer:
(i) Total distance covered = 4 × 300 = 1200 m
(ii) Displacement = 0 [final position – initial position]
(iii) Non – uniform.
∵ the direction of motion is changing while running on the track.
(iv) Both are not equal.
Question 5.
Ram swims in a 80m long swimming pool. He covers 160m in 1 min by swimming from one end to the other and back along the same straight pattern. Find the average speed and average velocity.
Answer:
Total distance = 160m
Total displacement = 0
Time taken (t) = 1 min = 60s

![]()
Question 6.
Abus from Chennai travels to Trichy passes loo km, 160 km at 10.15 am, 11.15 am respectively. Find the average speed of the bus during 10.15 – 11.15 am.
Answer:
The distance coveredbetween 10.l5am& 11.15 am = 160 – 100
= 60km
The time interval = 1 h
Average speed = 60/1
= 60km/h
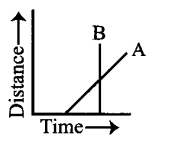
Question 7.
In a distance-time graph of two objects A & B, which object is moving with greater speed when both are moving?
Answer:
Object B makes a longer angle with the time – axis. Its slope is greater than the slope of object A. Thus the speed of B is greater than that of A.
Question 8.
Find the distance covered by a particle during the time interval which the speed-time graph is-shown in figure.
Answer:
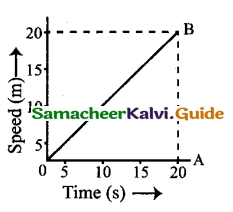
Distance covered in the. time interval 0 to 20s is equal to the area of the triangle OAB.
Area of A OAB. \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × base × height
\(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) × 20 x 20 = 200 ms-1
![]()
Question 9.
A car moves 30 km in 30 min and the next 30 km in 40 min. Calculate the average speed for the entire journey.
Answer:
Answer:
Total time taken = 30 + 40 = 70 min. = \(\frac { 70 }{ 60 }\) hour
Total distance = 30 + 30 = 60 km

Question 10.
A boy travels a distance of 3m due east and then 4m due north.
(a) How much is the total distance covered?
(b) What is the magnitude of the displacement?
Answer:
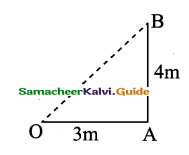
(a) Total distance covered = 3 + 4 = 7m
(b) Net displacement: OB2 = OA2 + AB2
= 32 + 42
OB2 = 25m2
∴OB = 5m 0 3m
Net displacement = 5m
![]()
Question 11.
During an experiment, a signal from a spaceship reached the ground station in five seconds. What was the distance of the spaceship from the ground station? The signal
travels at the speed of light that is 3 × 108 ms-1
Answer:
Time taken = 5 seconds.
Speed of signal u = 3 × 108 m/s ?
Distance = ?
Speed = Distance / Time
∴ Distance = Speed × Time
Distance = 3 × 108 × 5 = 15 × 108 m.
Question 12.
A train travelling at a speed of 90kmph. Brakes are applied so as to produce a uniform acceleration of -0.5 ms-2. Find how far the train will go before it is brought to rest?
Answer:
Here we have
Initial velocity , u = 90km/h
\(=\frac{90 \times 1000 \mathrm{~m}}{60 \times 60 \mathrm{~s}}=25 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}\)
Final velocity, v = 0
Acceleration, a = -0.5m/s2
Thus, distance travelled = ?
We know that, v2 = u2 + 2as
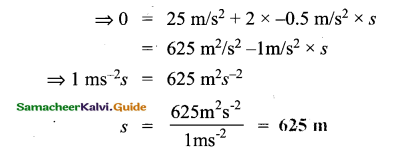
Question 13.
The adjacent diagram shows the velocity-time graph of the body.
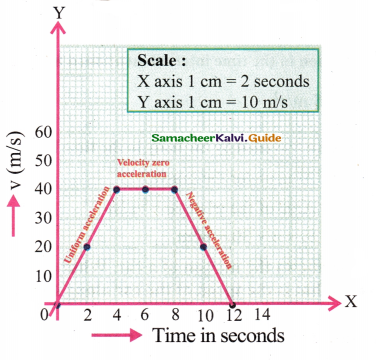
a) During what time interval is the motion of the body accelerated?
Answer:
At 0 to 4 second
![]()
b) Find the acceleration in the time Interval mentioned in part ‘a’.
Answer:
\(\mathrm{a}=\frac{v-u}{t}=\frac{30-0}{4}=7.5 \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{s}^{2}\)
c) What is the distance travelled by the body in the time interval mentioned ¡n part ‘a’?
Answer:Distance travelled Area under the graph
= Area of the triangle = 1/2 bh
= 1/2 × 4 × 30 = 60m
Question 14.
The following graph shows the motion of a car. What do you infer from the graph along with OA and AB? What is the speed of the car along with AB and what time it reached this speed?
a) What do you infer from the graph along OÄ and AB
Answer:
Graph along with OA: The car travels with uniform acceleration and uniform motion.
Graph along with AB : The car travels with constant speed and unaccelerated motion.
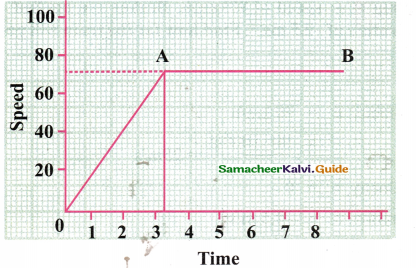
b) What is the speed of the car along AB?
Answer:
Along AB : The speed of the car is constant.
From the graph, it seems the speed along AB is 72 km/hr.
c) What time it reached this speed
Answer:
It reaches this speed after 3.2 hours, that is, 3 hours, 12 minutes.
![]()
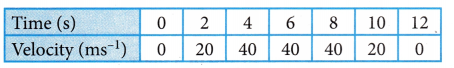
Question 15.
From the following table, check the shape of the graph.
Answer: