Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 5th English Guide Pdf Term 1 Prose Chapter 3 The Guardians of the Nation Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Summary, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 5th English Solutions Term 1 Prose Chapter 3 The Guardians of the Nation
5th English Guide The Guardians of the Nation Text Book Back Questions and Answers
In-Text Question (Think):
Question 1.
Why do the soldiers (people) die? When will it be stopped?
Answer:
Soldiers are the persons who vigorously support their countries and are prepared to defend it against enemies or detractors. They have true patriotism. So, when a war breaks out, due to conflicts between two countries on the border issue, soldiers fight for their respective countries. Ultimately a quite number of soldiers die.
It will be stopped only when peace prevails in all the countries in the world.
![]()
Let us understand:
A. Choose the best answer:
Question 1.
Karmugilan went to ______ for higher studies.
(a) London
(b) Australia
(c) USA
(d) New Zealand
Answer:
(c) USA
Question 2.
______ broke out in the near by villages.
(a) malaria
(b) cholera
(c) dengue
(d) flu
Answer:
(c) Dengue
Question 3.
He got _______ the disease.
(a) infected by
(b) cured off
(c) upset
(d) remedy for
Answer:
(a) Infected by
Question 4.
The villagers, built a ______ on his memory.
(a) statue
(b) memorial
(c) library
(d) hospital
Answer:
(d) Hospital
![]()
B. Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
They ate a bowl of ______.
Answer:
chickpea sundal
Question 2.
______ is the memorial for the soldiers.
Answer:
Amar Jawan Jyoti
Question 3.
Flag day is observed on the ______.
Answer:
7th December
Question 4.
A ______ dies for the nation.
Answer:
Soldier
Question 5.
______ was a young talented doctor.
Answer:
Karmugilan
![]()
Answer the following questions:
Question 1.
What were Anandhan and Yazhini watching in the television?
Answer:
Anandhan and Yazhini were watching a ceremony at Amar Jawan Jyoti, where people were paying respect to a helmet on top of a gun.
Question 2.
What is Amar Jawan Jyoti?
Answer:
Amar Jawan Jyoti is a memorial for the soldiers who died for our country.
Question 3.
What did Anandhan want to become?
Answer:
Anandhan wanted to become a doctor.
Question 4.
Why did Yazhini want to join the military?
Answer:
Yazhini wanted to serve the nation. So she wanted to join the military
Question 5.
What happened to Dr. Karmugilan in the story?
Answer:
Dr. Karumugilan served the people who were infected with dengue. Finally he was also affected by the disease and died.
Question 6.
What was the epidemic that broke out in the story?
Answer:
Dengue was the epidemic that broke out in the story.
![]()
Let us Build:
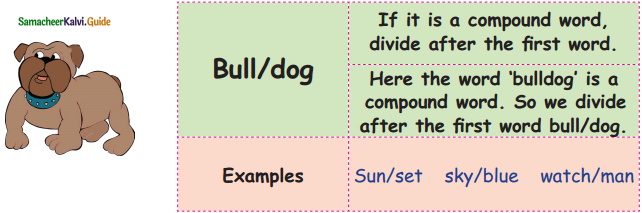
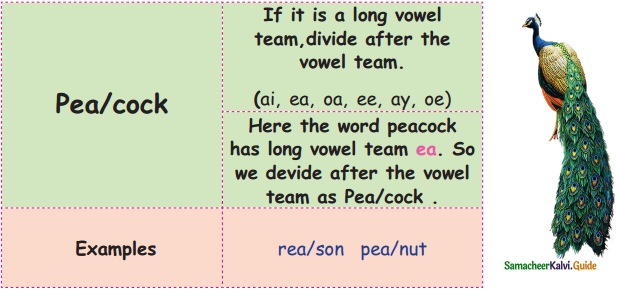
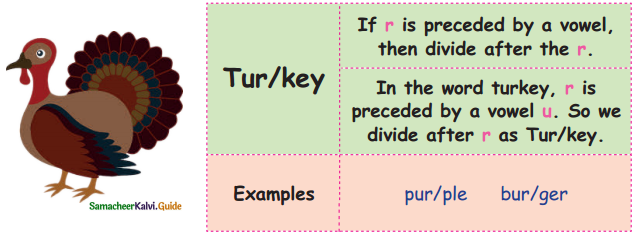
We divide the words to pronounce them easier. Here are some tips to divide.
உச்சரிப்பதற்கு வசதியாக நாம் வார்த்தைகளைப்பிரிக்கிறோம். எவ்வாறுவார்த்தைளைப் பிரிப்பது என்பதற்கான குறிப்புகளை இங்கு காண்போம்.
![]()
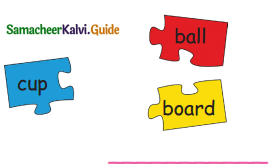
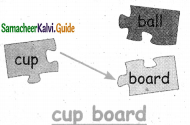
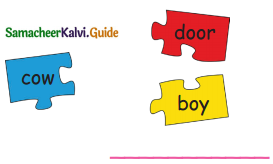
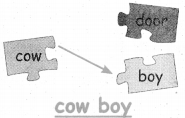
A. Circle and divide the bulldog pattern words:
Question 1.

Answer:
Out of six given words, the bulldog pattern words are – Sunset, Skyblue, Goldfish

- sun/set
- sky/blue
- gold/fish.
![]()
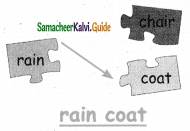
B. Divide and list out the word under each pattern:


Answer:

![]()
C. Write some  pattern words and divide them:
pattern words and divide them:
Answer:
- airport – air/port
- headlight – head/light
- breakfast – break/fast
- landmark – land/mark
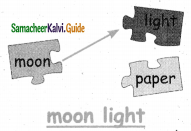
- moonlight – moon/light
- wheelchair – wheel/chair
![]()
5th English Guide The Guardians of the Nation Additional Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Write some  pattern words and divide them.
pattern words and divide them.
Answer:
- reach – rea/ch
- board – boa/rd
- deal – dea/l
- oap – soa/p
- ecise – plea/se
- roast – roa/st
Question 2.
Write some  pattern words and divide them.
pattern words and divide them.
Answer:
- march – mar/ch
- nurse – nur/se
- target – tar/get
- purse – pur/se
- interest inter/est
- church – chur/ch
![]()
Answer the following Questions:
Question 1.
What was Anand’s father doing when Anand came from school?
Answer:
Anand’s father was watching the news on the television.
Question 2.
What is the importance of 7th December?
Answer:
Armed Forces Flag Day is observed on 7th December every year.
Question 3.
Why did Karmugilan go to the USA?
Answer:
Karmugilan went to the USA for studying.
Question 4.
What did Karmugilan’s parents think of him?
Answer:
Karmugilan’s parents thought that he would live in the USA and continue his practice.
Question 5.
Why did Karmugilan come back to India?
Answer:
Karmugilan came back to India to treat the poor people at free of cost.
Question 6.
What is the real service to the nation?
Answer:
We should treat everyone around us with love and respect. That is the real service to the nation.
![]()
The Guardians of the Nation Summary in English and Tamil
Anand and Yazhini came home from school. After washing their face, hands, and legs, they sat down next to their Father Their Father was watching the news on the television. There were two bowls of chickpea sundal. They ate and watched a ceremony where people were paying respect to a helmet on top of a gun. “Dad, what is this place? What are they doing?” asked Anandhan. Dad replied, “This is Amar Jawan Jyoti, a memorial for the soldiers who died for our country.
ஆனந்தும், யாழினியும் பள்ளியிலிருந்து வீட்டிற்கு வந்தார்கள். முகம், கை, கால்களைக் கழுவிய பிறகு, அவர்களது தந்தைக்கு அருகே வந்து அமர்ந்த னர். அவர்களது தந்தை தொலைகாட்சியில் செய்திகளை பார்த்துக் கொண்டிருந்தார். அங்கு இரு கிண்ணங்களில் சுண்டல் இருந்தது. அவர்கள் சாப்பிட்டுக் கொண்டே தொலைகாட்சியில் ஒரு நிகழ்ச்சியைப் பார்த்தார்கள். ஒரு துப்பாக்கியின் மீது வைக்கப்பட் வைக்கப்பட்டிருந்த ஒரு தலைக்கவசத்திற்கு மக்கள் மரியாதை செய்து கொண்டிருந்த காட்சி அது. “அப்பா, இது என்ன இடம்? அவர்கள் என்ன செய்கிறார்கள்?”, என்று ஆனந்தன் கேட்டான். “இதுதான் அமர் ஜவான் ஜோதி. நமது நாட்டிற்காக உயிரிழந்த படைவீரர்களின் நினைவுச்சின்னம்.
Every year, 7th December is observed as Armed Forces Flag Day. On that day, we remember the sacrifices of our soldiers for guarding our nation. It is a great honour to serve the nation by joining the army.”
ஒவ்வொரு ஆண்டும் டிசம்பர் 7-ஆம் தேதி இராணுவக் கொடிநாளாக அனுசரிக்கப்படுகிறது.அன்றைய நாளில், நம் தேசத்தைக் காத்த வீரர்களின் தியாகங்களை நாம் நினைவு கூர்கிறோம். இராணுவத்தில் சேர்ந்து தேசத்திற்கு சேவை செய்வது ஒரு பெரிய கௌரவமாகும்”, என அவனது தந்தை பதிலளித்தார்.
Yazhini proudly declared, “When I grow up, I will join the army and serve the nation.” Anandhan said,”I will become a doctor, and treat the people.” Yazhini asked, “Why don’t you join the army and serve the nation like me?”
யாழினி பெருமையுடன், “நான் வளர்ந்த பிறகு இராணுவத்தில் சேர்ந்து தேசத்திற்கு பணியாற்றுவேன்”, என அறிவித்தாள். “நான் ஒரு மருத்துவராகி, மக்களுக்கு சிகிச்சையளிப்பேன்”, என்றான் ஆனந்தன். “நான் சொன்ன மாதிரி, நீயும் ஏன் இராணுவத்தில் சேர்ந்து தேசத்திற்கு பணியாற்றக்கூடாது?”, என யாழினி கேட்டாள்.
Father intervened her and said, “Joining the army is not the only way to serve the nation. Each one of us can serve the nation in our own way.” Yazhini asked, “Really dad? How can we serve the .nation?” Father said, “Serving in the army is a grace, but not everyone gets a chance to serve. But, each of us has a role in our society and, by doing that role we are serving our nation.”
![]()
அப்போது அவளது தந்தை குறுக்கிட்டு, “இராணுவத்தில் சேர்வது மட்டுமே தேசத்திற்கு சேவை செய்யும் ஒரே வழி என்று நினைக்கக் கூடாது”, என்று கூறினார். “உண்மையாகவா அப்பா? தேசத்திற்கு நாம் எப்படி சேவை புரியலாம்?”, என்று யாழினி கேட்டாள். “இராணுவத்தில் சேவை புரிவது என்பது ஒரு வரம். ஆனால் ஒவ்வொருவரும் அந்த வாய்ப்பை பெறுவதில்லை ஆனால் சமூகத்தில் நம் ஒவ்வொருவருக்கும் ஒரு பொறுப்பு இருக்கிறது. அதைச் செய்தாலே நமது தேசத்திற்கு சேவை செய்த மாதிரி தான்”, என்றார் அவள் தந்தை.
Father continued, “I will tell you the story of Karmugilan. He was a doctor. who died, serving the people. He was young and talented. He went to the USA for studying. His parents were very proud of him. They thought that he would live in the USA and continue his practice. But to everyone’s surprise, he came back to India and started treating poor people free of cost.”
“நான் உங்களிருவருக்கும் கார்முகிலனின் கதையைச் சொல்கிறேன். அவர் ஒரு மருத்துவர். மக்களுக்காவே சேவை செய்து இறந்துபோனார். அவர் இளமையானவர், மற்றும் திறமைசாலி. படிப்பதற்காக அமெரிக்கா போனார். அவரது பெற்றோர் அவரை நினைத்து பெருமை பட்டனர். அவர் அமெரிக்காவிலேயே வாழ்ந்து, அங்கேயே மருத்துவத்தைத் தொடருவார் என
அவர்கள் நினைத்தனர். ஆனால் எல்லோரும் ஆச்சர்யப்படும் வகையில் அவர் இந்தியாவுக்கு திரும்பிவந்து ஏழை மக்களுக்கு இலவசமாக மருத்துவம் பார்க்கத் தொடங்கினார்”, என்றார் யாழினியின் தந்தை.
Yazhini asked, “Were his parents not angry with him?” Dad said, “They were anary. But, they knew he was happy.”
அப்போது யாழினி கேட்டாள்: “அவரது பெற்றோர்கள் அவர் மீது கோபப்பட வில்லையா?” தந்தை சொன்னார் : “ஆம், அவர்களுக்கு கோபம் வந்தது. ஆனால் கார்முகிலன் மகிழ்ச்சியாக இருந்ததை அவர்கள் அறிந்தனர்”.
![]()
One day, dengue broke out in the nearby villages. He left to those villages to treat the people. He saved the lives of many. He was soon well known in the village, and people poured known in the village and people poured in to get treated.
ஒரு நாள், பக்கத்து கிராமங்களில் டெங்கு காய்ச்சல் பரவத்தொடங்கியது. அந்த மக்களுக்கு சிகிச்சை அளிக்க கார்முகிலன் அந்த கிராமங்களுக்குச் சென்றார். பலருடைய உயிரை அவர் காப்பாற்றினார். அந்த கிராமத்தில் அவர் மிகவும் பிரபலமடைந்து விட்டார். அவரிடம் சிகிச்சை பெறுவதற்காக மக்கள் வந்து குவிந்தனர்.
But, one day he got infected by the disease and was taken to the city hospital. He was in critical condition. His parents were upset and worried. He told his parents that he had done his duty to the country and, was happy. In a couple of days, he died. In his memory, the people of the village have built a hospital and treat people at free of cost.”
ஆனால் ஒரு நாள் அவரையும் அந்த நோய் தாக்கியது. அவர் நகர மருத்துவமனைக்கு எடுத்துச்செல்லப்பட்டார். அவர் மிக ஆபத்தான நிலையில் இருந்தார். அவரது பெற்றோர் வருத்தப்பட்டனர். தான் இந்த நாட்டிற்கு தன் கடமையை செய்துவிட்டதாகவும், அதனால் மகிழ்ச்சியுடன் இருப்பதாகவும் கார்முகிலன் தன் பெற்றோரிடம் கூறினார். அடுத்த சில நாட்களில் அவர் இறந்துவிட்டார். அவரது நினைவாக அந்த கிராமத்து மக்கள் ஒரு மருத்துவமனையைக் கட்டினார். அங்கு மக்களுக்கு இலவச வைத்தியம் கிடைக்கிறது”.
“That’s really great, dad. He is a real hero.”, said Yazhini.
“அது உண்மையிலேயே சிறப்பான ஒன்று தான், அப்பா. அவர்தான் உண்மையான நாயகன்”, என்றாள் யாழினி.
Father replied, “Each one of us should love and respect our country.” we should treat everyone around us with love and respect. That’s the real service to the nation.”
நாம் ஒவ்வொருவரும் நம் நாட்டை நேசித்து மதிக்க வேண்டும். நம்மை சுற்றியுள்ள ஒவ்வொருவரையும் அன்போடும், மரியாதையுடனும் | நடத்த வேண்டும். அதுவே தேசத்திற்கு செய்யும் உண்மையான சேவை”, என்றார் அவளது தந்தை.
![]()
The Guardians of the Nation Glossary:
Ceremony – A formal event to celebrate an anniversary (ஆண்டுவிழா )
Critical – Serious/dangerous (ஆபத்தான நிலை)
Declared – Said / stated (அறிவித்த ல்)
Grace – Blessing (வரம்)
Guarding – To watch over to protect or control (பாதுகாத்தல்)
Honour – Respect (மரியாதை)
Infected – Contaminated with harmful things (கேடுகளால் பாதிக்கப்படுதல்)
Intervened – Interrupt a conversation (குறுக்கிட்டு பேசுதல்)
Memorial – A structure established to remind of a person or event (நினைவுச் சின்னம்)
Munching – Eating something steadily (தொடர்ந்து கொறித்தல்)
Observed – Commemorated (அனுசரிக்கப்படுதல்)
Poured in – Came in great numbers (அதிக அளவில் வருவது)
Proudly – With pride (பெருமையுடன்)
Remember – Recall (நினைவுபடுத்துதல்)
Sacrifices – Giving up something more valuable (தியாகங்க ள்)
Serve – To work for (சேவை)
Talented – Skilled/expert (திறமையாளர்)
Upset – Unhappy (வருத்தப்படுதல்)
Worried – Distressed (கவலையடைதல்)
Wreath – Flowers arranged in a ring, for lying on a grave (கல்லறையில் வைக்கப்படும் மலர் வளையம் )



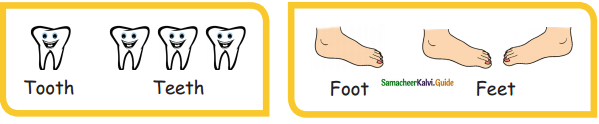
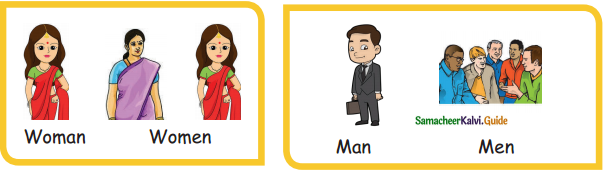

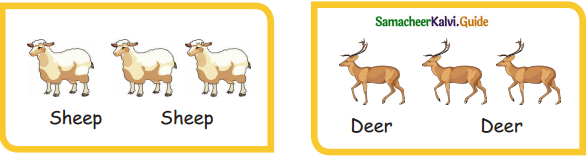

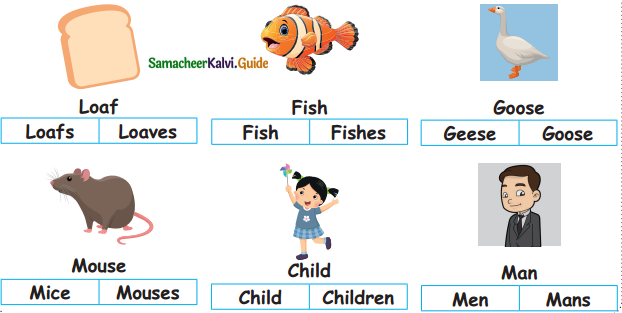
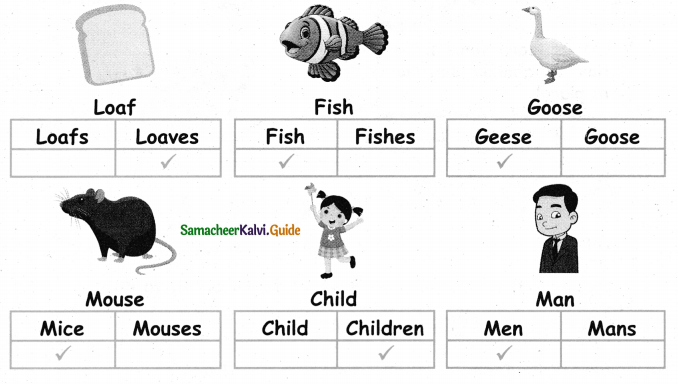


 = ________
= ________ = ________
= ________ = ________
= ________ = ________
= ________ = ________
= ________ = ________
= ________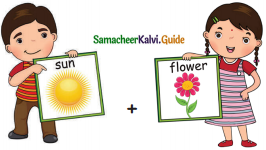 = ______
= ______
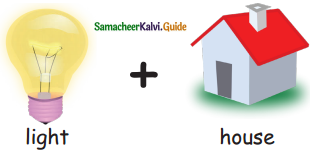 =________
=________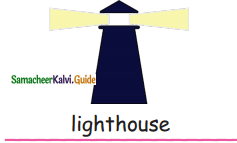
 = ________
= ________
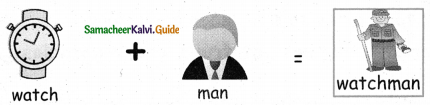

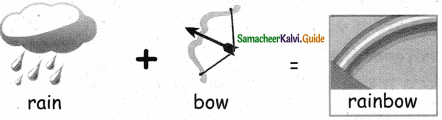

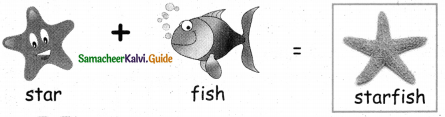

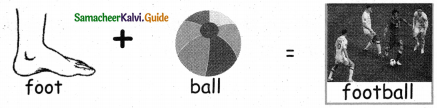
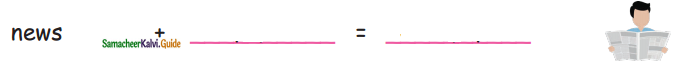

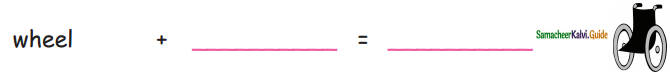
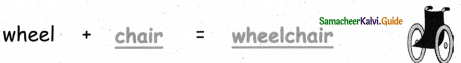
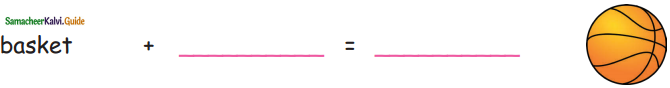


 = ______.
= ______.
 = ______.
= ______.
 = ______.
= ______.
 = ______.
= ______.
 = ______.
= ______.