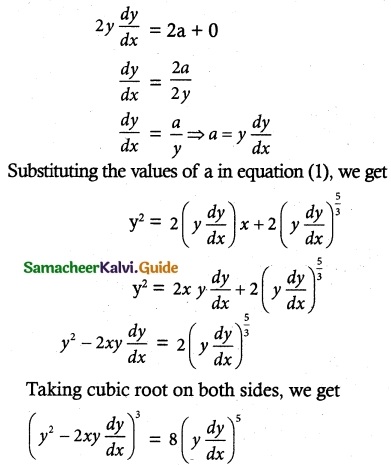
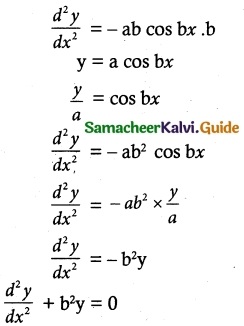
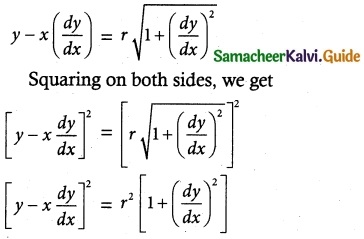
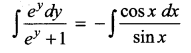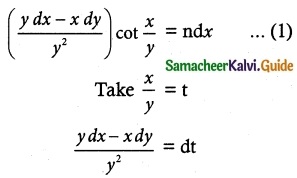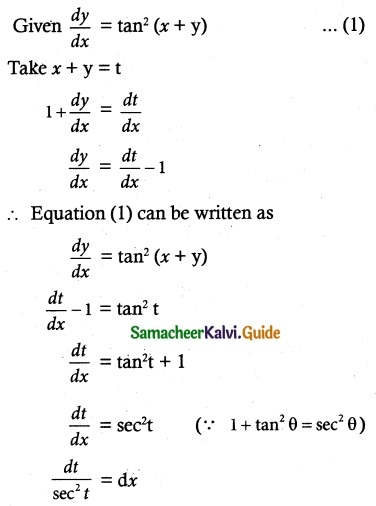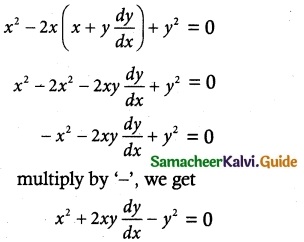Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Guide Pdf Chapter 10 Ordinary Differential Equations Ex 10.6 Textbook Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 12th Maths Solutions Chapter 10 Ordinary Differential Equations Ex 10.6
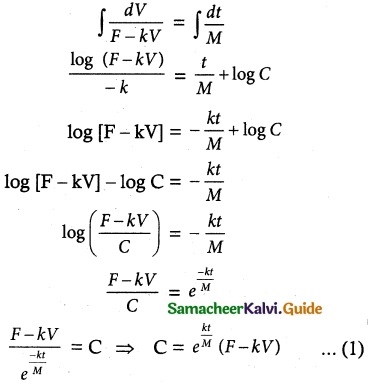
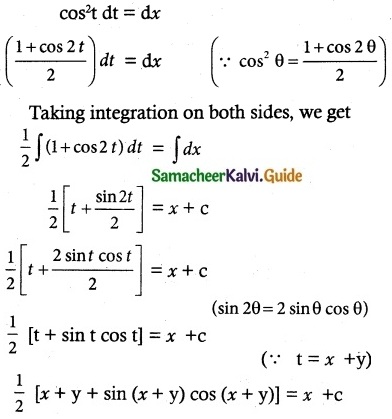
Question 1.
Solve the following differential equations.
[x + y cos(\(\frac { y }{ x }\))] dx = x cos (\(\frac { y }{ x }\)) dy
Solution:
The given equation can be written as
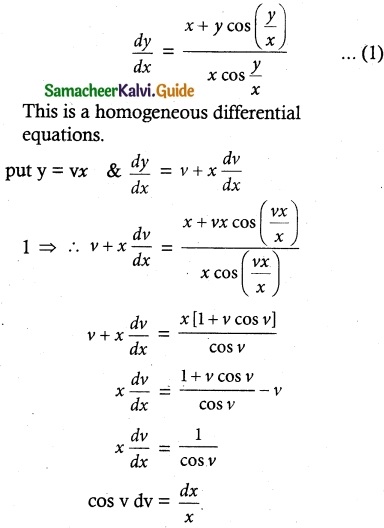
On integration we obtain
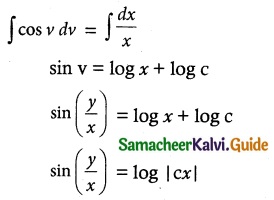
which gives the required solution.
![]()
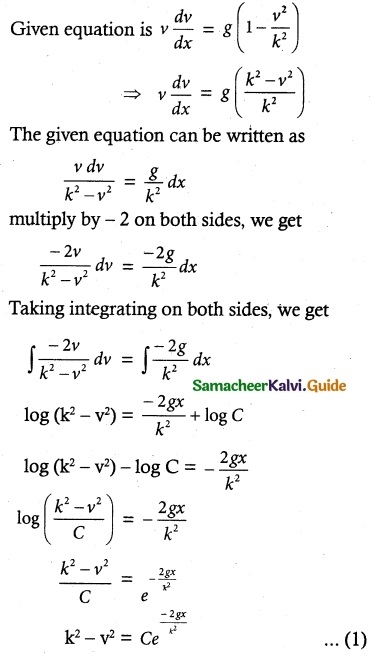
Question 2.
Solve (x³ + y³)dy – x² ydx = 0
Solution:
The given equation can be written as
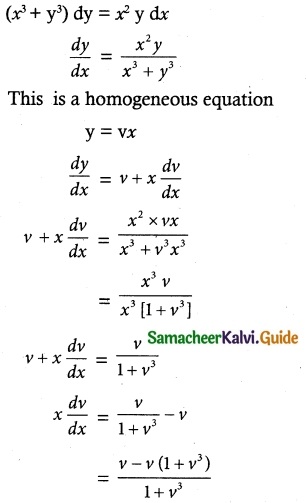
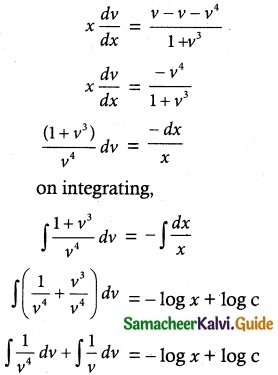
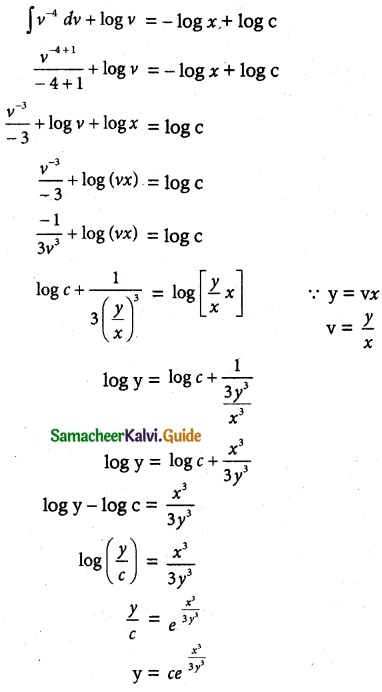
![]()
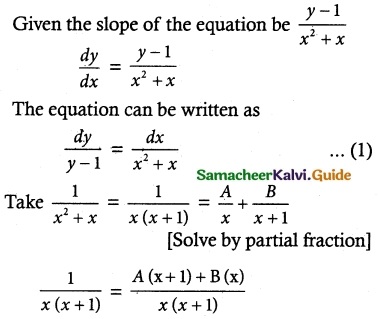
Question 3.
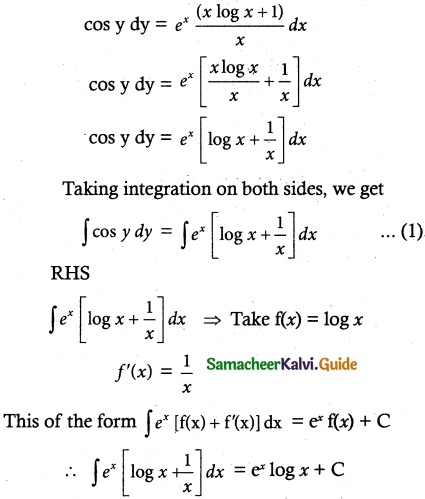
Solve ye\(\frac { x }{ y }\) dx = (x\(\frac { x }{ y }\) + y)dy
Solution:
The given equation can be written as
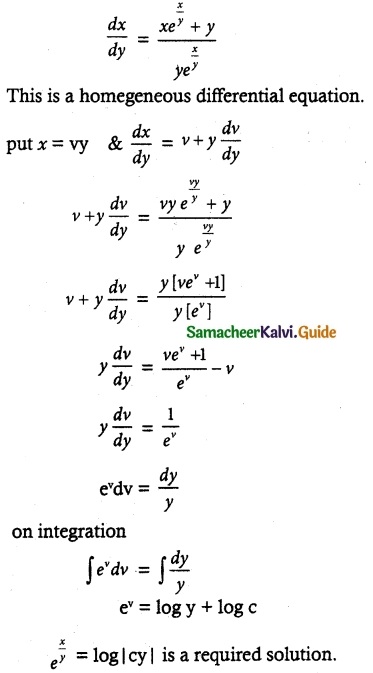
![]()
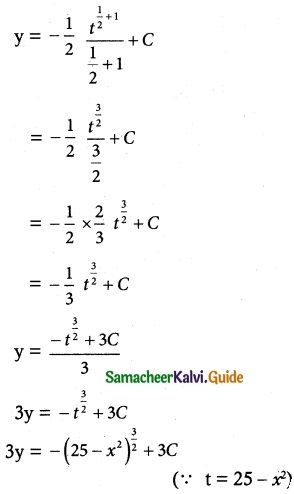
Question 4.
Solve 2xy dx + (x² + 2y²)dy = 0
Solve ye\(\frac { x }{ y }\) dx = (x\(\frac { x }{ y }\) + y)dy
Solution:
The given differential equation can be written as
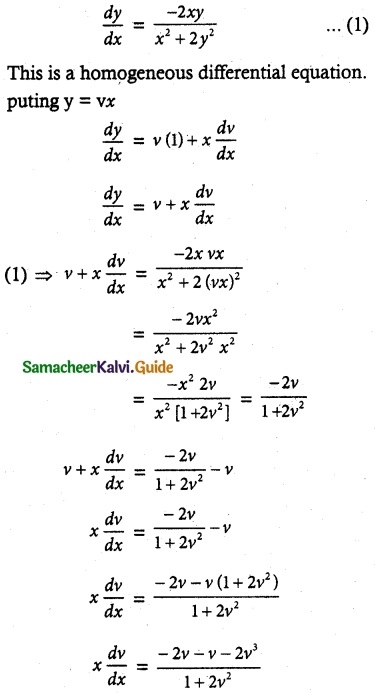
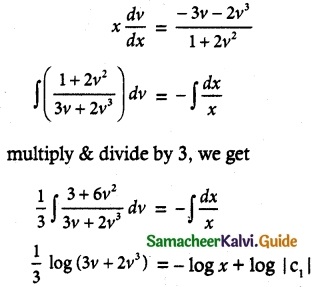
\(\frac { 1 }{ 3 }\) log (3v + 2v³) + log x = log |C1|
log (3v + 2v³) + 3log (x) = 3 log (C1)
log (3v + 2v³) + log (x)³ = log (C1)³
log (3v + 2v³)x³ = log C1³
(3v + 2v³)x³ = C1³
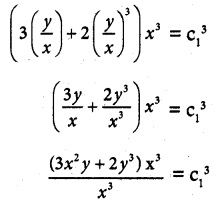
3x²y + 2y³ = C1³
3x²y + 2y³ = C is a required solution.
![]()
Question 5.
(y² – 2xy) dx = (x² – 2xy) dy
Solution:
Given equation is (y² – 2xy) dx = (x² – 2xy) dy
y² – 2xy = (x² – 2xy) \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\)
∴ The equation can written as
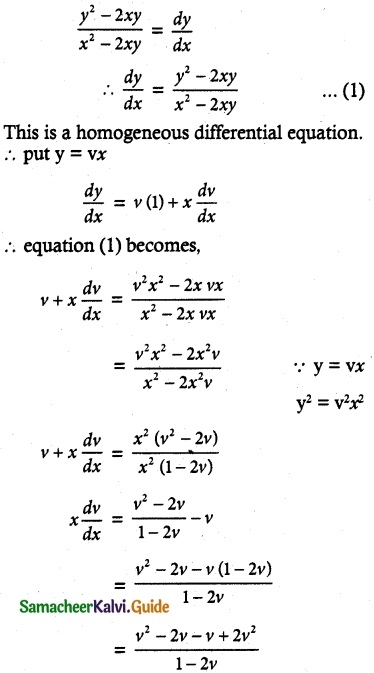
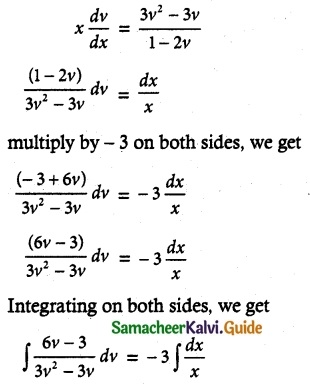
log (3v² – 3v) = – 3 log x + log C
log (3v² – 3v) = – log x³ + log C
= log c – log x³
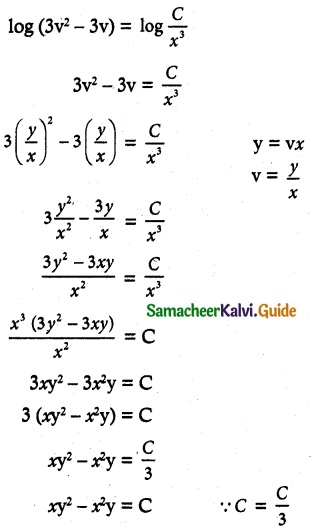
![]()
Question 6.
x \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = y – x cos²(\(\frac { y }{ x }\))
Solution:
Given x \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = y – x cos² \(\frac { y }{ x }\)
The equation can be written as
\(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = \(\frac { y-cos^2 \frac { y }{ x } }{ x }\) …….. (1)
This is a homogeneous differential equation.
y = vx
\(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) = v (1) + x \(\frac { dv }{ dx }\)
Substituting \(\frac { dy }{ dx }\) value in equation (1), we get
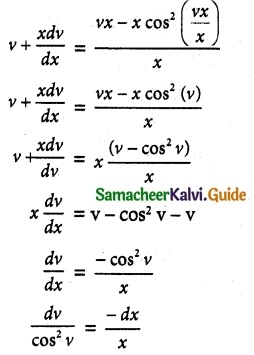
Integrating on both sides, we get
∫ sec² v dx = -∫ \(\frac { dx }{ x }\)
tan v = – log x + log C
tan v = log C – log x
tan v = log(\(\frac { C }{ x }\))
etan v = \(\frac { C }{ x }\)
C = x etan v
C = x etan \(\frac { y }{ x }\)
Is a required equation.
![]()
Question 7.
Solve (1 + 3e\(\frac { y }{ x }\)) dy + 3etan \(\frac { y }{ x }\) (1 – \(\frac { y }{ x }\)) dx = 0, given that y = 0 when x = 1.
Solution:
The given differential equation may be
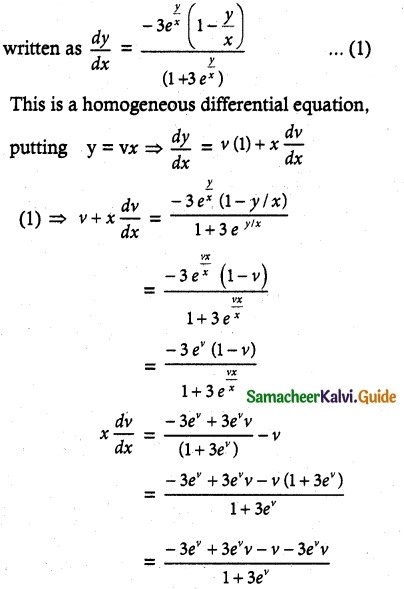
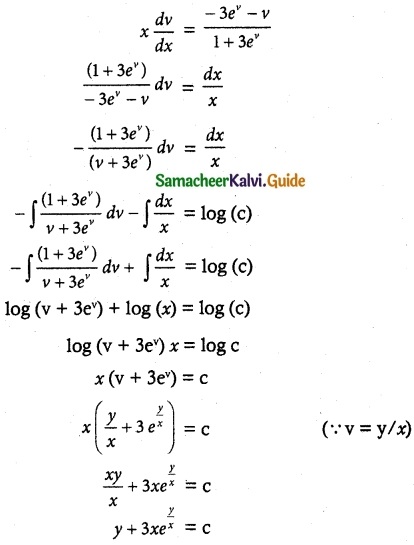
Given that y = 0 when x = 1
0 + 3(1) e° = c
3 = c
∴ y + 3xey/x = 3 is a required solution.
![]()
Question 8.
(x² + y²) dy = xy dx. It is given that y (1) = y(x0) = e. Find the value of x0.
Solution:
The given differential equation is of the form
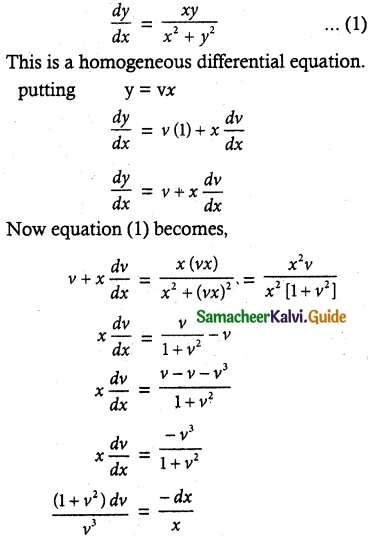
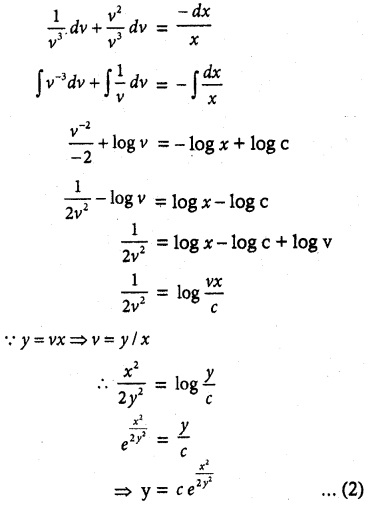
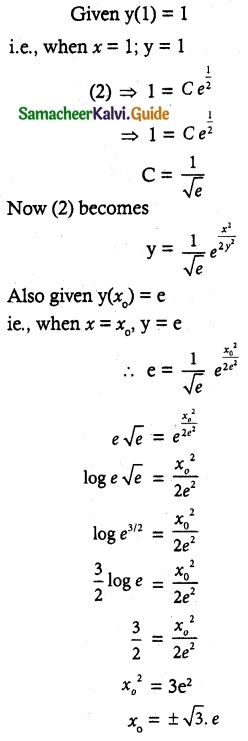
![]()