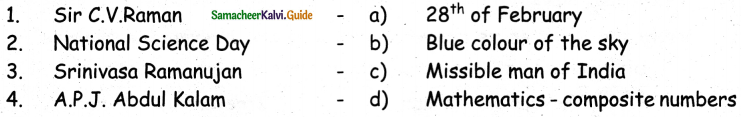Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 5th Science Guide Pdf Term 2 Chapter 3 Plants Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 5th Science Solutions Term 2 Chapter 3 Plants
Samacheer Kalvi 5th Science Guide Plants Text Book Back Questions and Answers
Evaluation
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Male reproductive organ of the flower is _______.
a) sepal
b) petal
c) androecium
d) gynoecium
Answer:
(c) androecium
![]()
Question 2.
Pollination by wind is also known as _______.
a) anemophily
b) hydrophily
c) entamophily
d) ornithophily
Answer:
(a) anemophily
Question 3.
Entamophily is known as _______.
a) pollination by insects
b) pollination by wind
c) pollination by water
d) pollination by animal
Answer:
(a) pollination by insects
Question 4.
Pollination by wind is also known as _______.
a) anemophily
b) hydrophily
c) entamophily
d) ornithophily
Answer:
(a) anemophily
Question 5.
Pollination takes place by wind in _______.
a) grass
b) Vallisneria
c) hydrilla
d) lotus
Answer:
a) grass
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
Spreading of seeds from one place to another is known as _______.
Answer:
Dispersal of seeds
Question 2.
Autochory is known as _______.
Answer:
Self dispersal method
Question 3.
The seed is a fertilized _______.
Answer:
Ovule
Question 4.
Paddy grow well in soil _______.
Answer:
Clay
Question 5.
The soil which contains a bigger sized particle is _______.
Answer:
Sandy soil
![]()
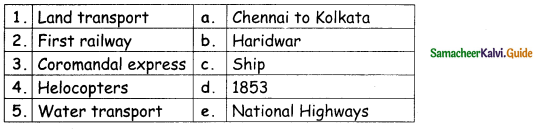
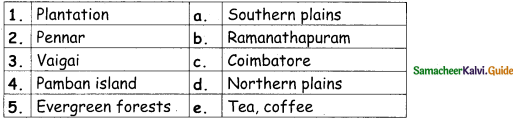
III. Match the following:

Answer:

![]()
IV. Answer briefly:
Question 1.
Define pollination.
Answer:
The transfer of pollen grains from the anther to stigma of a flower is called pollination.
Question 2.
What is germination of seed?
Answer:
The seed is a fertilized ovule. It consists of an embryo, food materials which are protected by the seed coat. During favourable conditions, the seed germinates and gives rise to a new seedling.
Question 3.
How soil is formed?
Answer:
Soil is formed by the breaking of rocks by the action of wind, water and climate. The mixture of rock particles and humus is called the soil.
Question 4.
What is known as vermicompost?
Answer:
The process of decomposing bio-degradable wastes by earthworms is known as vermicompost.
Question 5.
How the seeds are spread by water?
Answer:
Fruits which are dispersed by water have outer coats modified to enable them to float. The mesocarp of coconut is fibrous and is easily carried away by water. They reach different places and grow into a new plant.
E.g. Lotus, Coconut.
![]()
V. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
Write a note on parts of Plants.
Answer:
Parts of a plant
- A plant is made up of many different parts. The three main parts are the roots, the
leaves, and the stem. - Each part has a set of jobs to do to keep the plant healthy.
- The roots absorb water and minerals from the soil and anchor the plant in the ground. The stem supports the plant above ground and carries the water and minerals to the leaves.
- The leaves collect energy from the Sun and make food for the plant, using an amazing process called photosynthesis.
Question 2.
Explain the methods of pollination.
Answer:
- Pollination by Wind (Anemophily): The flowers pollinated by wind are mostly small in size and do not have any attractive colour, smell and nectar. The pollen grains are non-sticky, dry, light and powdery. Hence, they are easily carried by the wind. E.g. Grass, Maize, Pine.
- Pollination by Water (Hydrophily): The flowers of water plants are not colourful and they have no nectar. Pollen grains of these plants have mucilaginous covering to protect them from getting wet. They float in water and reach the other plant. E.g. Vallisneria, Hydrilla, Zosteria.
- Pollination by Insects (Entamophily): This is the most common type of pollination in plants like sunflower, ladies finger, brinjal and pumpkin. Some flowers are large in size and they have a sweet smell. Some of these flowers produce nectar. They attract insects like butterflies and honey bees.
Question 3.
Draw the picture of a flower and label the parts.
Answer:
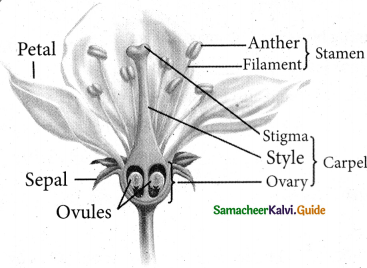
![]()
Activity:
Question 1:
Classify the plants based on the pollination methods.
Vallisneria, Hydrilla, Sunflower, Grass, Brinjal, Maize, Pumpkin.
Answer:
| Hydrophily | Entomophily | Anemophily |
| Vallisneria | Brinjal | Maize |
| Hydrilla | Sunflower | Grass |
| Pumpkin |
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 5th Science Guide Plants Additional Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
Kurinji or Neelakurinji (Strobilanthes kunthianu) blossoms once in _____ years.
(a) 12
(b) 13
(c) 14
(d) 15
Answer:
(a) 12
Question 2.
_______ is the outer part of the flower.
a) Sepal
(b) Petal
(c) Androecium
(d) Gynoecium
Answer:
(a) Sepal
Question 3.
Dicotyledons have seeds with _____ cotyledons.
(a) one
(b) two
(c) three
(d) four
Answer:
(b) two
Question 4.
The example for Self Dispersal Method is ________.
(a) Ladies finger
(b) Coconut
(c) Lotus
(d) Tomato
Answer:
(a) Ladies finger
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks:
Question 1.
Fruit bats, hummingbirds and ants may also act as _____ agents.
Answer:
Pollinating
Question 2.
The zygote develops into an _______.
Answer:
Embryo
Question 3.
_______ is used as food and also for medicinal purposes.
Answer:
Honey
Question 4.
The _______ of coconut is fibrous and is easily carried away by water.
Answer:
Mesocarp
Question 5.
The purplish-blue flowers of blossoms once in 12 years.
Answer:
Neelakurinji
![]()
III. Match the following:
I.

Answer:

II.

Answer:

![]()
IV. Answer briefly:
Question 1.
what are the kinds of reproduction?
Answer:
There are two kinds of reproduction that take place in plants. They are sexual reproduction and asexual reproduction. In asexual reproduction, new plants are produced from roots, leaves, stems and buds. In sexual reproduction, new plants are obtained from seeds.
Question 2.
Differentiate between unisexual and bisexual flowers.
Answer:
- The flowers which contain either androecium or gynoecium are called unisexual tlowers.
E.g. Corn, Papaya, Cucumber. - The flowers which contain both androecium and gynoecium are called bisexual flowers.
E.g. Mustard, Rose.
Question 3.
Tabulate the names of the pigment present in petals.
Answer:
| Colour of the petals | Name of the pigment |
| Red, Pink, Blue, Purple | Anthocyanin |
| Yellow, Orange | Carotenoids |
| Green | Chlorophyll |
![]()
Question 4.
What is called fertilization?
Answer:
The process of fusion of male (pollen grains) and female (stigma) gametes is called fertilization. The cell which results after fusion of the gametes is called a zygote. The zygote develops into an embryo.
Question 5.
Label the parts.
Answer:
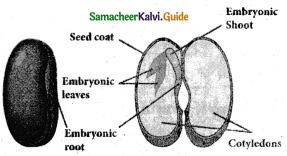
Question 6.
Label the parts.
Answer:
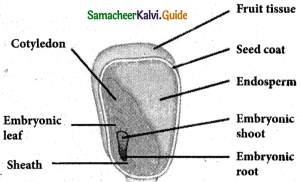
Question 7.
Draw a life cycle of flowering plants.
Answer:
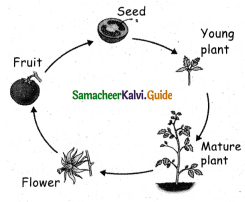
Question 8.
How the seeds are spread by Wind?
Answer:
The seeds which are smaller, lighter and tiny, float in air over a long distance. Some of them proceed with hairs and membranous wing-like structures and so they are carried away easily.
E.g. Cottonseed, Drumstick.
Question 9.
Write a short note on Zoochory.
Answer:
Some fruits are provided with hooks, spines, bristles, stiff hair etc, on their outer coat. These fruits stick on the furry coats or skins of some animals and are carried from one place to another.
E.g. Xanthium, Achyranthus.
Question 10.
Who are the friends of Farmer?
Answer:
Earthworm, honeybee and dragonfly.
![]()
V. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
Write a note on parts of Flower.
Answer:
Flower is the reproductive part of a plant. It is a modified shoot. Flowers have four important parts. They are:
- Sepal: It is the outer part of the flower. Usually, it is small and green in colour. It protects the bud in the early stage.
- Petal: It is often colourful and it attracts insects.
- Androecium: It is the male reproductive part of the flower. It is composed of stamens. Each stamen consists of a stalk called filament and a small bag like structure called anther at the tip. The pollen grains are produced in the anther within the pollen sacs.
- Gynoecium: It is a female part of the flower. It has three parts. They are ovary, style and stigma. The ovary contains the ovules.
Question 2.
Draw a diagram of a leaf and label the parts.
Answer:
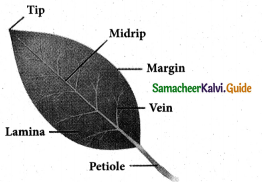
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the types of Soils.
Answer:
- Sandy soil: It contains a greater proportion of big particles. They cannot fit closely together. Water can drain quickly through the spaces between the sand particles. So, sandy soils tend to be light, well aerated and dry.
- Clay soil: It contains a greater proportion of fine particles, packed tightly together. leaving little space for air. It can retain a lot of water in the tiny gaps between the particles. Plants like paddy grow well in this soil.
- Loamy soil: It Contains large and fine particles in almost same proportion. The best topsoil for growing plants is loam. It is a mixture of sand, clay and another type of soil particle known as silt. Silt occurs as a deposit in river beds. It has right water holding capacity for the growth of plants. Clay and loamy soil are suitable for growing wheat, gram and paddy.