Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 4th Science Guide Pdf Term 2 Chapter 3 Plants Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 4th Science Solutions Term 2 Chapter 3 Plants
Samacheer Kalvi 4th Science Guide Plants Text Book Back Questions and Answers
![]()
I. Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
The tip of the leaf is
(a) Blade
(b) Apex
(c) Midrib
(d) Veins
Answer:
(b) Apex
Question 2,
Which one of the following is a primary producer?
(a) Plant
(b) Animal
(c) Human
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Plant
Question 3.
Which flower blooms during winter?
(a) Jasmine
(b) Tulip
(c) December
(d) Fire cracker
Answer:
(c) December
Question 3.
Choose the ornamental plant from the list.
(a) Parthenium
(b) Mango
(c) Travellers palm
(d) Groundnut
Answer:
(c) Travellers palm
Question 4.
Which plant flower is edible?
(a) Cauliflower
(b) Potato
(c) Mint
(d) Cabbage
Answer:
(a) Cauliflower
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks :
Question 1.
During photosynthesis ____________ is produced and stored in the leaf.
Answer:
Food
Question 2.
Green plants have ____________ pigment.
Answer:
Green
Question 3.
Onion is a ____________ part of a plant.
Answer:
Stem
Question 4.
The male part of the flower is ___________.
Answer:
Stamen
Question 5.
An example for edible seed is _____________ .
Answer:
Rice
![]()
III. Answer the following in one or two words :
Question 1.
Which is the female part of the plant?
Answer:
Pistil.
Question 2.
Write the name of any one of the leaf that is used as a food.
Answer:
Cabbage.
Question 3.
Which flower bud is used as spices in food?
Answer:
Cloves.
Question 4.
What are the nutrients present in the seeds?
Answer:
Carbohydrates and proteins.
Question 5.
Write any one of the flower that blooms in summer.
Answer:
Sunflower.
![]()
IV. Answer briefly :
Question 1.
Write the parts of the leaf.
Answer:
- Apex
- Veins
- Midrib
- Blade
- Petiole
Question 2.
Define – Photosynthesis.
Answer:
Photosynthesis is a process by which plants make their food using chlorophyll, water, carbon dioxide in the presence of sunlight.
Question 3.
Write the names of the exotic plants.
Answer:
- Sago palm (Cycas)
- Fern
- Crotons
- Travelers palm
- Boat lily
- Aloevera
Question 4.
Write the names of any two underground stem plant.
Answer:
Potato and Onion are underground stem plants.
Question 5.
Why should we not touch parthenium plant?
Answer:
The pollen of parthenium plant is allergic in nature, so, we do not touch this plant.
![]()
V. Answer detail :
Question 1.
Mask any four parts and describe the parts of a leaf.
Answer:
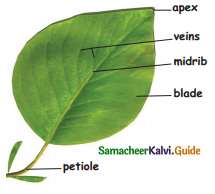
Blade: The broad flat part of the leaf (Lamina).
Apex: The tip of the leaf.
Midrib: The midrib runs along the centre of the leaf.
veins: Veins are branch out from the midrib. They are the framework of hollow tubes that carry water and minerals.
Petiole: This part joins the leaf to the main stem.
Question 2.
Draw a diagram of a flower and explain the parts of a flower.
Answer:
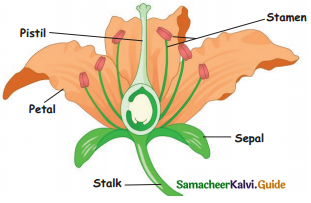
the four visible parts of a flower are explained below.
Sepal: Sepals are leaves that protect the flower while it is still a bud. Sepals are usually green in colour.
Petal: Petals are often bright coloured. Their main job is to attract insects such as bees or butterflies, to the flower. The insects help the flowers in the transfer of pollen grains.
Stamen: Stamen can be seen at the centre of a flower. They contain pollen grains that help the plants to multiply. It is the male part of a flower.
Pistil: Pistil is also seen at the centre of the flower. The pistil uses the pollen to help the flower become the fruit. It is the female part of a flower.
![]()
Samacheer Kalvi 4th Science Guide Plants InText Questions and Answers
Think and Answer (Text Book Page No. 78)
Question 1.
Which part of the leaf collects carbon dioxide?
Answer:
Stomata, the small pores, found at the base of the leaf, collects carbon dioxide.
Question 2.
Which part of the leaf transports water?
Answer:
The vascular tissues, called xylem, transports water from the roots to the leaves.
![]()
Think and Answer (Text Book Page No. 79)
Question 1.
Why would living things not be able to live without plants?
Answer:
Humans and animals depend on plants for their food either directly or indirectly. So, things would not be able to live without plants.
![]()
Try to Answer (Text Book Page No. 79)
Fill in the blanks by rearranging the letters in the bracket :
Question 1.
During photosynthesis plants releases __________ (egxyno).
Answer:
Oxygen
Question 2.
___________ is a primary producer, (tanpl).
Answer:
Plant
Question 3.
Stomata are seen in the ___________ (owler) surface of the leaf.
Answer:
Lower
Question 4.
Pigment involved in the food synthesis is ______ . (phllylochor).
Answer:
Chlorophyll
![]()
Let us do (Text Book Page No. 79)
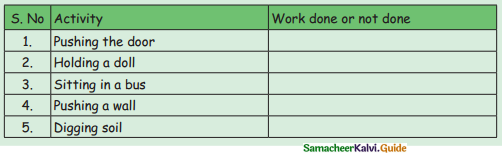
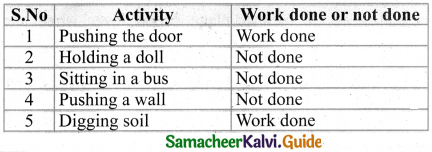
Take two potted plants. Keep one in sunlight and other in a fully covered box. Water them regularly. After a week observe the plants.
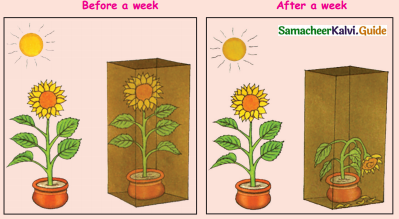

Answer:

![]()
Let us do (Text Book Page No. 81)
Question 1.
List out the flowering and Non-flowering plants in your surrounding.
Flowering plants | Non-flowering plants |
Answer:
| Flowering plants | Non-flowering plants |
| Tomato plant | Fern |
| Mango tree | Mosses |
| Coconut tree | Redwood tree |
![]()
Let us do (Text Book Page No. 82)
Question 1.
List out the places where you see the non-green plants
Answer:
Non-green plants grow on decaying organic matters such as cow-dung, wood, bread, etc. Mushroom, Bracket fungi grow in such places.
![]()
Try to Answer (Text Book Page No. 82)
Fill in the blanks :
Question 1.
__________ is an example for non flowering plant.
Answer:
Algae/Fungi /Fern
Question 2.
Plants are classified based on pigment and ___________ of the plant.
Answer:
Flower
Question 3.
______ depend on other organism to live and get their food.
Answer:
Plants
Question 4.
Autotrophs use _________ , __________ and chlorophyll to prepare their own food.
Answer:
Atmosphere,light
![]()
III. Part of Flower :
Have you seen flowers? Try to answer the questions given below
Question 1.
Which is your favourite flower?
Answer:
Jasmine
Question 2.
What is the colour of the flower?
Answer:
White
Question 3.
How does it smell?
Answer:
A sharp, sweet smell
![]()
Try to Answer (Text Book Page No. 83)
Fill in the blanks :
Question 1.
Sepals _____________ the flower while it is still a bud.
Answer:
Protect
Question 2.
Stamen contains _____________ grains.
Answer:
Pollen
Question 3.
Pistil is ___________ part of a flower.
Answer:
Centre
![]()
Let us do (Text Book Page No. 83)
Bring few hibiscus flowers to the classroom. Distribute the flowers to children. Introduce the parts of the flower to them. Then, ask them to observe and feel the different parts of the flower and tell them to record their observation.
| Parts of flower | What is its colour? |
Answer:
| Parts of flower | What is its colour? |
| petal | Orange – Red |
| Sepal | Green |
| Pistil | Light Green |
| Stamen | Red – Anther Green – Filament |
![]()
Think and Answer (Text Book Page No. 84)
Question 1.
Can you name the four seasons?
Answer:
Spring, Summer, Autumn and Winter.
![]()
Try to Answer (Text Book Page No. 86)
Find the odd one :
Question 1.
December, Tuberose, Tulip.
Answer:
Tulip
Question 2.
Saffron, Tulip, Rose.
Answer:
Rose
Question 3.
Crotons, Boat lily, Rose.
Answer:
Rose
![]()
Try to Answer (Text Book Page No. 88)
Fill in the blanks :
Question 1.
____________ flower is used as food.
Answer:
Banana
Question 2.
____________ part of the potato plant is used as food.
Answer:
Stem
Question 3.
Stem of the stores ____________ food in it.
Answer:
plant
Question 4.
Seeds are rich in ___________ and___________ .
Answer:
Carbohydrates, proteins
![]()
Let us do (Text Book Page No. 89)
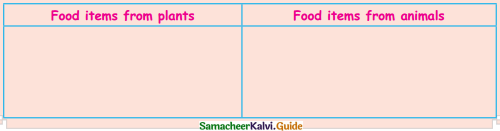
Complete the table to show which parts of the plant we eat.
Question 1.
| Food items | Parts of the plants eaten |
Answer:
| Food items | Parts of the plants eaten |
| Carrot | Root |
| Banana | fruit |
| Mango | fruit |
| Cauliflower | flower |
| Rice | seed |
| Dhal | seed |
| Moringo | leaves |
| Turmeric | stem |
| Onion | stem |
| Cabbage | leaves |
| Jackfruit | fruit |
| Beetroot | root |
Samacheer Kalvi 4th Science Guide Plants Additional Questions and Answers
![]()
I. Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
The ____________ runs along the centre of the leaf
(a) Veins
(b) Midrib
(c) petiole
(d) Lamina
Answer:
(b) Midrib
Question 2.
The largest flower in the world is found in the rain forests of ____________.
(a) India
(b) Australia
(c) Indonesia
(d) South Africa
Answer:
(c) Indonesia
Question 3.
Bamboo plants can grow upto __________ in one day.
(a) 60 cm
(b) 70 cm
(c) 80 cm
(d) 90 cm
Answer:
(d) 90 cm
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks with suitable answer :
Question 1.
The broad flat part of the leaf _____________.
Answer:
Lamina
Question 2.
___________ helps the plants to breathe.
Answer:
Stomata
Question 3.
___________ food is made in their green stems.
Answer:
Cactus
Question 4.
The largest flower in the world is __________.
Answer:
Rafflesia
![]()
III. Write True or False :
Question 1.
The seasons are four.
Answer:
True
Question 2.
Bamboo plants can grow upto 70cm in the day.
Answer:
False
![]()
IV. Answer briefly :
Question 1.
What are primary producers?
Answer:
As plants prepare food for themselves and also for other living things, they are called primary producers.
Question 2.
How are plants classified?
Answer:
Plants are classified in many ways based on stems, life span, seeds, flower and colour. In this session we will study about the classification of plants based on the flower and colour.
![]()
V. Answer briefly :
Question 1.
Differentiate : Flowering plants and Non-flowering plants
Answer:
| Flowering plants | Non-flowering plants |
| 1. Plants bearing flowers are called flowering plants. | Plants without flower that can reproduce are called non-flowering plants |
| 2. It reproduce by sex cells or gametes and produce seeds. Seeds produce new plants. | They reproduce by a special structure called spores.
|
| 3. Example: Mango, Neem, groundnut, paddy. | Algae, Fungi, fern. |
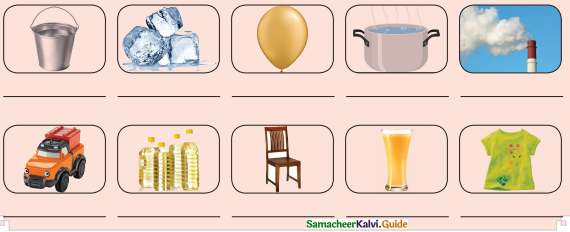
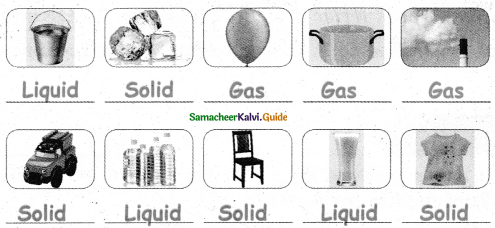
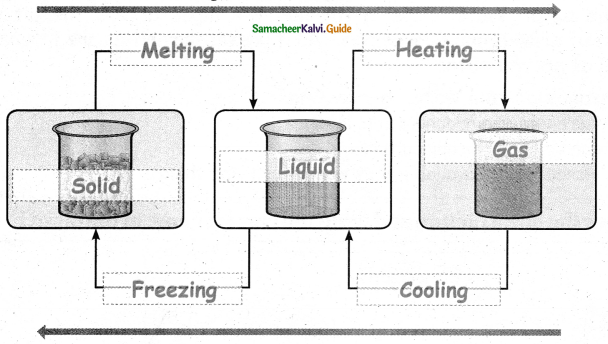
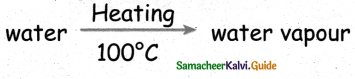
 = ______
= ______
 =________
=________
 = ________
= ________
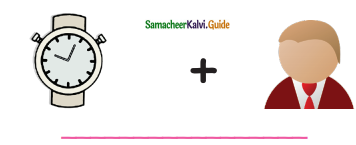
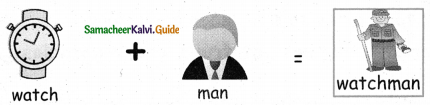

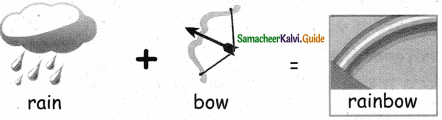

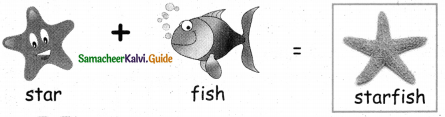

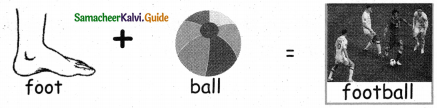

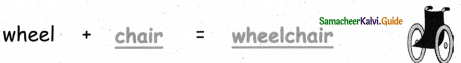
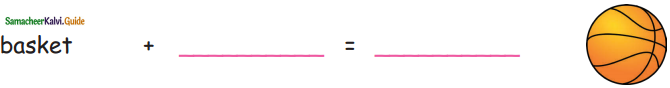


 = ______.
= ______.
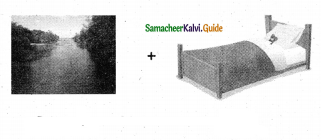 = ______.
= ______.
 = ______.
= ______.
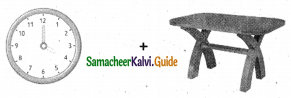 = ______.
= ______.
 = ______.
= ______.