Students get through the TN Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 6 Joint Stock Company which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 6 Joint Stock Company
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
What is stated in the situation clause in a memorandum?
Answer:
The state in which the registered office of the company is to be situated is stated here. The actual address need not be given.
Question 2.
What are registered companies? Give examples?
Answer:
Companies that are registered under the companies act 1956 are .called registered companies. Tata motors limited, Satyam computer services Ltd, EID parry ltd, etc belong to this category.
![]()
Question 3.
Write a short note on Capital Clause?
Answer:
The capital clause requires to state the company’s authorized share capital, the different categories of shares, and the nominal value (the minimum value per share) of the shares. It is also required to list the company’s assets under this clause.
Question 4.
For what reasons are shares forfeited?
Answer:
- Shares can be forfeited only for non-payment of calls due.
- Shares cannot be forfeited for any other debt due from the shareholder.
Question 5.
How does the company secretaries Act 1980 define a secretary?
Answer:
According to the company secretaries Act 1980, a company secretary is a person who is a member of the institute of company secretaries of India.
Question 6.
What is the consequence of not receiving a minimum subscription?
Answer:
If a minimum subscription is not received within 90 days of the issues of the prospectus money received on the application must be refunded to the applicants.
![]()
Question 7.
What do the Articles of Association deal with?
Answer:
Articles of Association is another important document as it contains the rules and regulations for the internal functioning of the company.
Question 8.
Write a short note on the capital clauses.
Answer:
The amount of share capital with which the company is to be registered and its division into shares of fixed amount are also stated in the capital clause.
Long answer questions
Question 1.
Briefly explain the features of the company form of organization.
Answer:
Salient Features of the company form of organization are –
- Separate legal entity: A company is a person created by law complying with all formalities prescribed under the Companies Act, 1956. It enjoys a separate personality of its own, different from the members composing it. A company can enter into valid Contracts with others including its members and deal with the property in any way it likes. It can sue others in its own name and be sued in its own name by others including its members.
- Perpetual succession – continuity of life: Members may come and go but the company can go on forever” (Lord Gower). This is because the company’s existence does not depend upon the existence of even promoters who were instrumental in its formation Neither change in the membership of the company nor the death of its members has any impact on the x continuity of its life.
- Common seal: Though the separate personality of the company is legally recognized, it needs a human agency to act. Obviously, it cannot sign. Any contract entered into by a company, to be valid, must bear the official seal of the company.
- Limited liability: The liability of the members of a company is generally limited to the value of shares. When once the full value of the shares is paid up, there is no more liability for the shareholders. The feature of limited liability attracts a large number of investors to subscribe to the shares of the company.
- Easy transferability of shares: In the case of public limited companies, their fully paid shares can be transferred to others without any difficulty. However, in the case of private limited companies, the right to transfer the shares is subject to certain restrictions.
![]()
Question 2.
Briefly state the documents to be filed for getting a certificate of incorporation.
Answer:
The promoter has to file the following documents with the Registrar of Companies for getting a certificate of incorporation.
- Memorandum of Association: This document defines the scope of activities of the company. It should contain the name, the place where the registered office is situated, authorized capital, and the objects of the business. It should be printed and duly stamped, signed, and witnessed. A minimum of two persons in the case of a private limited company and seven in the case of a public limited company must sign the document.
- Articles of Association: This contains the regulations connected with the internal management of the company. This document must also be duly stamped and signed by the signatories to the memorandum and witnessed.
- Original letter of approval: Original letter of approval of name be obtained from the Registrar and be filed.
- A list of directors: A list of directors who have consented to be its directors must be filed.
- Written consent to act as directors: The directors have to give their consent in writing to act as their directors. They should also undertake to take the necessary qualification shares and pay for them.
- Notice of the address of the registered office.
- Statutory declaration: A declaration stating that all the requirements of law relating to registration have been complied with is to be filed. This declaration must be given by an Advocate of the Supreme Court or High Court, or by a Chartered Accountant who is engaged in the formation of the company or by a person named in the Articles as a director or secretary of the company. The Registrar will scrutinize all the documents and if he finds them in order, he will issue the Certificate of Incorporation.
Question 3.
Bring out the distinction between a company and a partnership.
Answer:
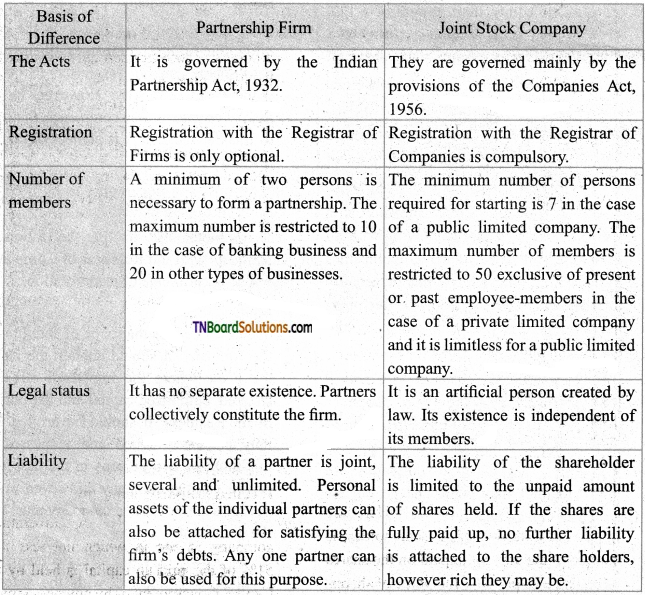
![]()
Question 4.
Discuss briefly the different kinds of companies.
Answer:
Kinds of companies: Companies can be classified on the basis of incorporation, nature of liability, the extent of public interest, ownership, nationality, etc.
On the basis of incorporation: Any company – is to be incorporated under an Act. The provisions of the particular Act under which it is established govern its working. Companies of this kind are of three types. They are –
- Chartered companies: Companies established as a result of a charter granted by the King or Queen of a country are known as chartered companies. The charter issued, governs their functioning, eg: East India Company and Bank of England. In India, such companies do not exist now.
- Statutory companies: Companies established by Special Acts of Parliament or State Legislatures are called statutory companies. The special Acts under which they are established regulate their functioning. Reserve Bank of India, Life Insurance Corporation of India, etc., are of this type.
- Registered companies: Companies that are registered under The Companies Act, 1956 are called registered companies. Tata Motors Limited, Satyam Computer Services Ltd, EID Parry Ltd, etc belong to this category.
On the basis of liabilities:
- Companies limited by shares: Here the maximum liability of a shareholder is limited to the amount unpaid on the shares held. Ofice he pays the full value of shares, he has no further liability.
- Companies limited by guarantee:
company limited by guarantee the liability of a shareholder is limited to the amount he has voluntarily undertaken to contribute to meet any deficiency at the time of its winding up. - Unlimited companies: The liability of the members of unlimited companies is unlimited. Unlimited companies are almost non-existent.
On the basis of nationality:
- Domestic company: Companies registered under the Companies Act, 1956 or under earlier Acts are considered domestic companies.
- Foreign company: A foreign company means a company incorporated outside India but having a place of business in India. It has to furnish to the authorities the full address of the registered or principal office of the company or a list of its directors or names and addresses of the residents in India authorized to receive notices, documents, etc.
On the basis of ownership:
- Holding and subsidiary companies:
A company becomes a holding company of another if it can appoint or remove all or majority of the directors of the latter company or if it holds more than 50% of the equity share capital of the latter or if it can exercise more than 50% of the total voting power of the latter. - The other company which is so controlled is called the subsidiary company.
- Government companies: A Government company is one in which not less than 51% of the paid-up capital is held by the Central Government or by any one or more State Governments or partly by the Central Governments and partly by one or more State Governments, eg: Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited, Steel Authority of India Limited, etc.
A subsidiary of a Government company is also treated as a Government company. Its employees are not Government employees.
![]()
On the basis of a number of members:
- Public Limited Companies: The public is invited to subscribe to the shares of the company usually by issuing a prospectus. Shares are easily transferable. A minimum number of people is seven and there is no limit to the maximum number of shareholders. The name must end with the word ‘limited’.
- Private Limited Companies: A private limited company is a company that has a minimum paid-up capital of rupees one lakh or such higher paid-up capital as may be prescribed.
For Own Thinking
1. Name any 2 Government-owned Joint Stock companies.
Answer:
- Indian Telephone Industries.
- TamilNadu State Transport Corporation Limited.
- TamilNadu Agro Industries Corporation.
2. Name any 2 Joint-stock companies with private ownership.
Answer:
- Nokia
- Nestle
3. Name any 2 Private ownership with Foreign participants.
Answer:
- Marathi Suzuki.
- Ford.
- Hyundai.
For Future Learning
Collect advertisements of three different companies inviting the public to subscribe to their shares. Compare their contents regarding the following points.
Answer:
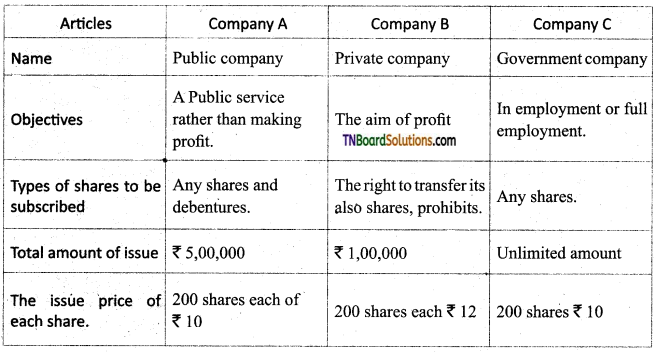
![]()
Case Study
Case 1: Ashok is an industrial designer by training. He had the opportunity to learn the technology of fiberglass manufacture while he was in Germany for his training. He plans to set up a plant for the manufacture of fiberglass in India and is able to interest some financiers and technologists. It is estimated that the initial investment in the plant will be of the order of 50 lakhs. Ashok and others decide to set up a company for this purpose. Should they set up a public limited company for the purpose? If so, how should
they go about it? If not, what alternative would you suggest? What formalities will be required of Ashok and his associates if they choose the alternative form of organization suggested by you?
Answer:
Ashok started the public limited company with a capital of Rs. 50 lakhs.
Incorporation: (a) Registration, (b) Approval for the proposed name.
Filling documents: (a) Memorandum of Association, (b) Articles of Association, (c) List of directors, (d) Written consent to act as a director, (e) Statutory declaration, (j) Registrar check all the documents, (g) Prospectus, (h) Minimum subscription, (i) Statement in lies of the prospectus, (j) Filing further documents.
Ashok followed the above rules regarding forming a company.
Case 2: Collect any 10 items of daily use (Packed items} and list the names of the companies manufacturing those items. Classify those companies as public and private limited companies. Which of them are Multinational Companies?
Answer:
- Sakthi Masala – Private Limited.
- Aachi Masala – Private Limited.
- Aavin milk – Government of Tamil Nadu.
- Arokia – Private Limited.
- Coca-Cola – Multinational company.
- Nestle chocolate – Multinational company.
- Pepsico – Multinational company.
- Lovato – Private Limited company.
- Dairy Milk – Private Limited company.
- Colgate – Private Limited company.
- Hamam Soap – Multinational company.
- Ariel – Private Limited company.
![]()
Multiple choice questions
1. The board of directors of a joint stock company is elected by:
(a) general public
(b) government bodies
(c) share holders
(d) employer
Answer:
(c) share holders
2. Which document is called charter of a company?
(a) Memorandum of association
(b) Prospectus
(c) Articles of association
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(a) Memorandum of association
3. Name the type of company which must have a minimum paid up capital of 5 lakhs:
(a) public company
(b) private company
(c) government company
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(a) public company
4. Registration of a joint stock company is:
(a) compulsory
(b) optional
(c) compulsory for public limited companies for private limited companies
(d) optional for public limited companies and compulsory for private limited companies
Answer:
(a) compulsory
5. The minimum number of members for a public limited company is:
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 1
(d) 10
Answer:
(c) 1
6. The minimum subscription specified in the prospectus must be received with in:
(a) 90 days
(b) 120 days
(c) 130 days
(d) 60 days
Answer:
(a) 90 days
7. Debenture holders of a company are its:
(a) creditors
(b) members
(c) credit customers
(d) borrowers
Answer:
(a) creditors
![]()
8. Where the shares are issued at a discount and the nominal value of the share is Rs. 100 the maximum discount that can be allowed is:
(a) Rs. 5
(b) Rs. 10
(c) Rs. 20
(d) Rs. 15
Answer:
(b) 110
9. Large scale production has become the order of the day with the:
(a) the outbreak of the First World war
(b) the advent of the industrial revolution
(c) break down of feudal system
(d) victory of communism
Answer:
(b) the advent of the industrial revolution
10. A company is created by:
(a) law
(b) the entrepreneur
(c) the government
(d) the rich people
Answer:
(a) law
11. The liability of the members of a company is limited to the:
(a) proportion of capital
(b) value of assets
(c) technical experts
(d) value of shares
Answer:
(d) value of shares
12. Any contract entered into by a company to be a valid must:
(a) be recognized by the government
(b) be accepted by the board of directors
(c) bear the seal of the company
(d) be registered with the registrar of companies
Answer:
(c) bear the seal of the company
![]()
13. Management of a company is entrusted to:
(a) group of exports
(b) government officials
(c) technical experts
(d) the board of directors
Answer:
(d) the board of directors
14. Statutory companies are those which are established by:
(a) special acts of parliament
(b) special acts of parliament or state legislatures
(c) special acts of state legislatures
(d) provisions of the constitution of India
Answer:
(b) special acts of parliament or state legislatures
15. A private company limited can work with just:
(a) two directors
(b) five directors
(c) one director
(d) many directors
Answer:
(a) two directors
16. A company secretary is appointed by:
(a) government
(b) the institute of company secretaries of India
(c) the board of directors
(d) shareholders in annual general meeting
Answer:
(c) the board of directors
17. The overall maximum managerial remuneration in a public limited company shall not exceed:
(a) 11% of net profit
(b) 11% of paid-up capital and free reserves
(c) 5% of net profit
(d) 5% of paid-up capital and free reserve
Answer:
(a) 11% of net profit
![]()
18. The value of qualification shares of a director in a public limited company shall not exceed:
(a) 5000
(b) 500000
(c) 50000
(d) 500
Answer:
(a) 5000
19. Managerial remuneration is paid in the form of:
(a) monthly salary,
(b) commission
(c) percentage of net profit
(d) monthly salary or percentage of net profits or a commission
Answer:
(d) monthly salary or percentage of net profits or a commission
20. The interval between two annual meetings must not be more than months:
(a) 15
(b) 18
(c) 10
(d) 12
Answer:
(a) 15
21. The liability of shareholders of a private limited company is limited to:
(a) the paid-up value of the shares
(b) the amount remaining unpaid on the shares
(c) the extent of private assets
(d) amount called up
Answer:
(b) the amount remaining unpaid on the shares
22. A private limited company can commence business:
(a) immediately on receiving the certificate of incorporation
(b) only after the certificate of commencement of the business is received
(c) on getting name approval from the registrar
(d) on filing all the documents necessary for formation with the Registrar
Answer:
(a) immediately on receiving the certificate of incorporation
23. The existence of a company comes to a close:
(a) on the death of all its promoters
(b) on the death of all the directors of the board
(c) on the transfer of shares by most of its original members
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(d) none of the above
![]()
24. Which of the following documents define the scope of a company’s activities?
(a) Memorandum of Association
(b) Articles of Association
(c) Prospectus
(d) Statutory Declaration
Answer:
(a) Memorandum of Association
25. Which of the following companies must file with the Registrar a statement in lieu of prospectus?
(a) a public limited company which raises funds from the public through issue of shares
(b) a public limited company which has made arrangement for racing its capital from directors and their relatives
(c) a private limited company
(d) all of them
Answer:
(b) a public limited company which has made arrangement for racing its capital from directors and their relatives
26. A preference share has priority in:
(a) dividend only
(b) only in return for capital at the time of winding up
(c) voting rights
(d) both dividend and return of capital on winding up
Answer:
(d) both dividend and return of capital on winding up
27. Shares can be forfeited for:
(a) non-payment of any debt due to the company
(b) not attending three annual general meetings consecutively
(c) for non-payment of call money
(d) for violent activities at the annual general meetings
Answer:
(c) for non-payment of call money
![]()
28. Debenture holders are entitled to receive interest in the following circumstances:
(a) when there are profits
(b) when shareholders also get dividend
(c) every year irrespective of loss
(d) all the above
Answer:
(d) all the above
29. A share certificate discloses:
(a) the name of the shareholder
(b) the number of shares
(c) distinctive number of shares
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
30. Holding companies are those which:
(a) are administered by the multinationals
(b) hold more than 50% of the equity share capital of another company
(c) look after the administration of other companies
(d) are under the direct control of the government of India.
Answer:
(b) hold more than 50% of the equity share capital of another company
31. The minimum paid-up capital of a private limited company should be:
(a) Rs. 5 lakhs
(b) Rs. 10 lakhs
(c) Rs. 25 lakhs
(d) Rs. 1 lakh
Answer:
(d) Rs. 1 lakh
32. Joint-stock companies require:
(a) huge, capital
(b) small capital
(c) no capital
(d) medium capital
Answer:
(a) huge, capital
![]()
33. A private limited company:
(a) should compulsorily hold a statutory meeting
(b) is exempted from holding a statutory meeting
(c) is prohibited from holding a statutory meeting
(d) has to be incorporated with five directors
Answer:
(a) should compulsorily hold statutory meetings
34. The Directors need not retire by rotation in:
(a) Independent Private Limited companies
(b) Joint Stock Companies
(c) Public corporations
(d) Departmental undertakings
Answer:
(b) Joint Stock Companies
35. The first stage of formation of a company is:
(a) location
(b) advertising
(c) promotion
(d) appointment of labor
Answer:
(a) location
36. The objects clause states the:
(a) activities in which the company can engage itself
(b) liability of members is limited
(c) amount of share capital
(d) the situation of the registered office
Answer:
(c) amount of share capital
![]()
37. The share holders’ shares have of a company.
(a) no charge on assets
(b) charge on specific assets
(c) charge on current assets
(d) charge on fixed assets
Answer:
(a) no charge on assets