Students get through the TN Board 12th Economics Important Questions Chapter 2 National Income which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 12th Economics Important Questions Chapter 2 National Income
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
What is depreciation?
Answer:
Fall in value of fixed assets due to normal wear and tear and expected absolescence (disuse) is called depreciation (or consumption of fixed capital).
Question 2.
What are the components of aggregate expenditure?
Answer:
- Private consumption expenditure by households (C)
- Investment expenditure (I)
- Government purchases of goods & services (G)
- Net exports (X – M)
- GDP = C + I + G + (X – M)
![]()
Question 3.
What are Factor Incomes?
Answer:
Factor incomes are Incomes received by factors of production for their contribution to the production process.
Question 4.
What is called Green GNP?
Answer:
GNP would help to attain sustainable use of the natural environment and equitable distributions of benefits of development.
Question 5.
Define: (a) Nominal GNP, (b) Real GNP?
Answer:
- GNP measured at current prices is called nominal GNP
- GNP measured at constant prices is called Real GNP.
Question 6.
What are the uses of National Income accounting?
Answer:
- It reflects the performance of the economy.
- It indicates structural and sectorial changes.
- It shows how National Income is shared among various factors of production.
- It has several uses for economic policy and research.
Question 7.
What are transfer payments?
Answer:
Payments that are made without getting any goods or services in exchange (return) are called transfer payments. Eg: Gifts, old age pension, etc.
![]()
Question 8.
What are the 4 factors of production? What is their remuneration?
Answer:
Land, Labour, capital, and enterprise are the factors of production. Rent, wages, interest, and profit are the reward for factors of production.
Land – labor – capital – an organization
Rent – wages – interest – profit
Question 9.
Name the 3 price indices which are used to calculate price variations.
Answer:
- GDP or GNP deflator
- Consumer price index
- Wholesale price index.
Question 10.
What is GNP Deflator?
Answer:
It is a statistical tool used to measure the average level of prices of all goods and services that make up GNP.
![]()
Question 11.
What is meant by double counting? Why it should be avoided?
Answer:
Counting the same product more than once in calculating National Income is called double counting. It should be avoided to remove the chance of over-estimation.
Question 12.
What do you mean by National Income?
Answer:
It is the total money value of all final goods and services produced in a country during a particular period.
![]()
Question 13.
When do capital gains arise?
Answer:
When capital assets such as a house, other property stocks or shares, etc are sold at a higher price than the price of purchase capital gains arise. It is excluded from National Income.
Question 14.
What is the current price?
Answer:
It is the prevailing market price to calculate the value of output. It may be always higher than the real value.
Question 15.
Where is the production method applied in India?
Answer:
In India, this method is applied to agriculture, mining, and manufacturing including handicrafts.
Question 16.
Give an example of Double counting.
Answer:
Value of cotton enters the value of yam as cost and value of yam in cloth and that of cloth in garments.
![]()
Question 17.
How does the income method approach National income?
Answer:
This method approaches National Income from the distribution side. National Income is calculated by adding up all the income generated in the course of producing National products.
Question 18.
Name the sectors adopted in Income Method to calculate National Income?
Answer:
Small enterprises, banking and insurance, commerce and transport, professions, liberal arts and domestic services, public authorities, house property, and Foreign sector transactions.
Question 19.
What are the items to be included while calculating National Income through Income?
Answer:
The imputed value of rent for self-occupied houses or offices is to be included and the imputed value of services provided by owners of production units (family labour) is to be included.
Question 20.
Why a proper valuation of output is very difficult?
Answer:
In India, a special conceptual problem is posed by the existence of a large, unorganized, and non-monetized subsistence sector where the barter system prevails for transacting goods and services.
![]()
Question 21.
What are the difficulties in assessing depreciation allowance?
Answer:
The deduction of depreciation allowances, accidental damages, repair, and replacement charges from National Income requires a high degree of judgment to assess the depreciation allowance and other charges.
Question 22.
What do you mean by unpaid services?
Answer:
A housewife renders a no. of useful services like preparation of meals, serving, tailoring, mending, washing, cleaning, bringing up children, etc., she is not paid for them and her services are not directly included in National Income.
Question 23.
Why the Income from Illegal activities are not included in National Income?
Answer:
Because such Illegal activities have value and satisfy the wants of the people but they have not considered as productive from the point of view of society.
Question 24.
What is the variation percentage in the estimation of GDP in India?
Answer:
The GDP estimates for India vary from 2 trillion US Dollars to 5 trillion US Dollars. There is at least a 10% margin of error. National Income is overestimated or underestimated by at least 10%.
Question 25.
How is the economy divided under social accounting and sector?
Answer:
(a) Firms
(b) Households
(c) Government
(d) Rest of the world and
(e) Capital sector.
![]()
Question 26.
What do you mean by sector?
Answer:
A sector is a group of individuals or institutions having common interrelated economic transactions.
Question 27.
Give reasons for not including leisure in GNP?
Answer:
Leisure is not included in GNP because it is intangible and subjective. It is very difficult to measure value and it is also impossible to assess the value it.
Question 28.
What are the items that are excluded from GNP?
Answer:
- Financial transactions
- Transfer or second-hand or used goods
- Non-market goods and services
- Illegal activities
- Value of leisure
Question 29.
Does GNP measure National welfare?
Answer:
GNP is considered a good indicator of economic welfare but it is not an adequate measure of national welfare.
Question 30.
Explain components of factor income?
Answer:
- Compensation of employees (wages)
- Rent
- Interest
- Profits = (dividend + profit tax + undistributed profit)
- Mixed Income are called as components.
![]()
Question 31.
Why are exports treated as a part of the domestic products?
Answer:
Because exported goods and services are a part of the domestic output for the production of which domestic resources have been used.
Short answer questions
Question 1.
Methods of measuring National Income – Explain.
Answer:
All goods and services produced in the country must be counted and converted against money value during a year. So whatever is produced is either used for consumption or saving. Thus national output can be calculated at 3 levels that is production, Income, and expenditure.
Question 2.
How the Gross value of the farm output is obtained in India?
Answer:
- The total production of 64 agricultural commodities is estimated. The output of each crop is measured by multiplying the area shown by the average yield per hectare.
- The total output is valued at market price.
- The aggregate value of 64 commodities is taken to measure the gross value of agricultural value
- The net value of the agricultural output is measured by making deductions for the cost of seed, manure, etc.
Question 3.
What are the basic concepts used in measuring National Income?
Answer:
GDP, NNP, NNP at factor cost, Personal Income, Disposable Income, Per capita Income, Real Income, and GDP deflator.
![]()
Question 4.
What do you mean by GDP at market price?
Answer:
GDP is the total market value of the final goods and services produced within the country during a year. It is calculated at market prices. GDP by expenditure method at Market prices = C + I + G + (X-M)
C = Consumption Goods; I = Investment goods;
G = Government purchases (X – M) is net export which can be positive or negative.
Question 5.
Explain Real income.
Answer:
Real Income is the buying power of Nominal Income. Nominal Income is National Income expressed in terms of a general price level of a particular year. The Real Income is derived as National Income = National Income at a constant price. Current price ÷ /P1/ P0.
P1 – Price Index during the current year
P0 – Price Index during the base year
Question 6.
How is National Income calculated under the product method?
Answer:
The product method measures the output of the country. It is also known as the inventory method. Under this method, the value of the output from different sectors like agriculture, industry, trade, and commerce, etc is obtained for the entire economy during a year.
Question 7.
What are the precautions taken while measuring National Income under the expenditure method?
Answer:
Precautions:
- Second-hand goods: This expenditure should not be included.
- Purchase of shares and bonds: This expenditure or purchase should not be included.
- Transfer payments: Expenditures towards old age pension should not be included.
- Expenditure on intermediate goods: Expenditure on seeds, fertilizers by farmers should not be included to avoid double counting.
![]()
Question 8.
Explain statistical problems.
Answer:
There can be statistical problems while calculating National Income. Statistical data may not be perfectly reliable when they are compiled from numerous sources. Skill and efficiency of the statistical staff and co-operation of people at large are important in estimating National Income.
Question 9.
Write a note on National Income and erosion of national wealth.
Answer:
Natural resources are largely damaged for achieving higher GDP. That is there is a reduction of potential for future growth. So while estimating National Income, loss of natural resources should be subtracted from National Income.
Question 10.
What are the difficulties in measuring National Income?
Answer:
- Transfer payments: Pension, insurance, etc.,
- Difficulties in estimating depreciation allowances: Accidental damages, repair, etc…
- Unpaid services: Services of a housewife.
- Income from illegal activities: Smuggling, gambling, etc.,
- Production for self-consumption and changing price: Farmers keep food for self-consumption.
- Capital gains: Stocks & shares etc.,
- Statistical problems: Not perfect and reliable data.
Question 11.
Distinguish between Domestic and National Income.
Answer:
| Domestic income | National income |
| Employee compensation + Rent, Interest and Profits + Mixed Income | Domestic Income + Net Factor Income from abroad. |
![]()
Question 12.
Distinguish between National Income and Net Domestic Product.
Answer:
| National Income (NNPFC) | Net Domestic Product (NDPMP) |
| Employee compensation + Rent Interest and profits + Mixed Income + Net Factor Income from abroad. | Employee compensation + Rent, Interest and Profits + Mixed Income + Net Indirect Taxes. |
Question 13.
Distinguish between NNPMP and NNPFC
Answer:
| NNPMP | NNPFC |
| GNPMp – Depreciation | GNPMp – Depreciation – Net Indirect Taxes |
Question 14.
Distinguish between National Income at current price and National Income at constant price.
Answer:
| National Income at current price | National Income at constant prices |
| It is the sum total of market value – of all final goods and services produced by an economy during a year estimated at current prices of that year. | It is the sum total of market value of all final goods and services produced by an economy during the year but estimated at the price of same base year. |
| It can increase even when there is no flow of goods and services in the economy but only the current prices increase. | It increase only there is an increase in the flow of goods and services. |
![]()
Question 15.
Distinguish between National and Private income.
Answer:
| National Income | Private Income |
| The sum of total factor earned by normal residents of a country within and outside the country during a year. | It consists of Factor Incomes and Transfer Incomes received from all sources by private sector within and outside the country. |
Question 16.
Distinguish between Private and Personal Income.
Answer:
| Private Income | Personal Income |
| It consists of Factor Incomes and Transfer Incomes received from all sources by private sector within an outside the country. | It is the sum of earned incomes and transfer income received by persons from all sources within and outside the country. |
Question 17.
Distinguish between Consumption and Capital goods.
Answer:
| Consumption goods | Capital goods |
| These goods which are consumed by the ultimate consumers to satisfy their wants directly. Eg: Tv, shirt, pen etc., |
These goods which help in the production of other goods and services. Eg: machines, tools etc., |
Question 18.
Distinguish between Intermediate and Final Product.
Answer:
| Intermediate Product | Final Product |
| These products which are used in the production of other products or resale in the same year. Eg: Fuels and raw materials etc., |
These products which are used for final consumption or final investment. Eg: machinery cloth etc., |
![]()
Question 19.
Distinguish between Factor and Transfer payment.
Answer:
| Factor payment | Transfer payment |
| Payments received by the factor of production in return for services. Eg: rent, wages | Payments received by households production units and other sources without rendering any services. Eg: donations, gifts etc., |
Question 20.
Distinguish between Domestic and National Products.
Answer:
| Domestic products | National products |
| It is the gross money value of all final goods and services produced in the domestic territory of a country during a year. It doesn’t include NFIA. | It is the gross money value of all final goods and services produced by the normal residents of a country during a year. It includes NFIA. |
Long answer questions
Question 1.
Explain the types of final goods and services of GNP.
Answer:
GNP is the total measure of the flow of final goods and services at market value resulting from current production in a country during a year including Net Income from abroad.
- The final value of consumer goods and services produced in a year to satisfy the immediate wants of the people – that is Consumption (C).
- Gross Investment is
- such as residential construction and inventories of finished and unfinished goods.
- Goods and services produced or purchased by Government (G)
- Net exports of goods and services that is the difference between the value of exports and imports that is (X – M).
- GNP at a market price i.e. the gross value of final goods and services produced annually in a country that is(C + I + G + (X – M) + (R-P)). GNP at market price = GDP at market prices + Net Factor Income from abroad.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the Income method of Measuring National Income.
Answer:
The income method approaches National Income from the distribution side. In this method, National Income is calculated by adding all Incomes generated in the course of producing the national products.
Steps involved:
- The enterprises are classified into industrial groups.
- Factor Incomes are grouped under Labour Income, Capital Income, and Mixed-Income.
Eg:- Labour Income – Wages and salaries
- Capital Income – Profit and dividend
- Mixed-Income – Farming and other professions
- National Income is calculated as Domestic Income + NFIA
Y – W + r + i + π + (R – P)
W = wages, r = rent, i = interest, n = profit.
This method helps in estimating the contributions of the remaining sector like banking and insurance transports, public authorities, house property, and the foreign sector. Transactions are got from the account of the balance of payments of the country.
Question 3.
What are the precautions taken under the product method?
Answer:
The product method is followed in underdeveloped countries. In this method, the margin of error is more. In India agricultural, mining, manufacturing, and handicrafts sectors follow this method.
Precautions:
- Double counting: The raw material should not be included for the final production of the calculation of National Income. Eg: values of cotton.
- The value of output used for consumption should not be used.
- Durable goods: Sale and purchase of second-hand goods should not be included. Eg: second-hand cars.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain the limitations of National Income as an Index of economic welfare.
Answer:
- Economic welfare depends upon the provided compositions of goods and services.
- Economic welfare will be less when there is higher GDP with environmental hazards. Eg: pollution, air, and water.
- Production of war goods will increase the national output but not economic welfare.
- The Per capita income can be increased by employing women and children for long hours but it will not promote economic welfare.
- The physical quality of life index is considered a better indicator of economic welfare.
Question 5.
How is National income measured through the social accounting method?
Answer:
The social accounting method measures the transactions among various sectors such as firms, households, government, etc., are recorded and their interrelationship is traced. The social accounting framework is useful for economists and policymakers because it represents.
Numerical problems
Question 1.
From the given data calculate Gross Domestic Product at market price.
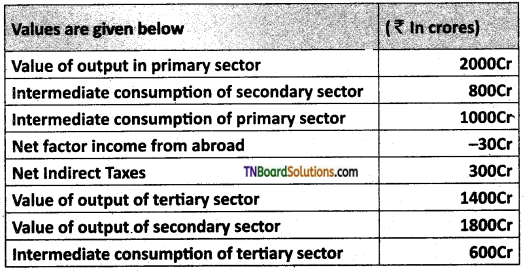
Answer:
GDPMP = (value of output in primary sector) – Intermediate consumption of primary sector + (value of output in secondary sector) – intermediate consumption of secondary sector + (value of output in tertiary sector) – Intermediate consumption of tertiary sector so by substituting the given values
= (2000 – 1000) + (1800- 800) + (1400- 600)
= 1000 + 1000 + 800 = Rs. 2800/- crores
Answer is 2800 crores.
Hence the GDPMP = 2800 Cr.
![]()
Question 2.
Calculate National Income or (NNPFC) by Income method and Expenditure method.
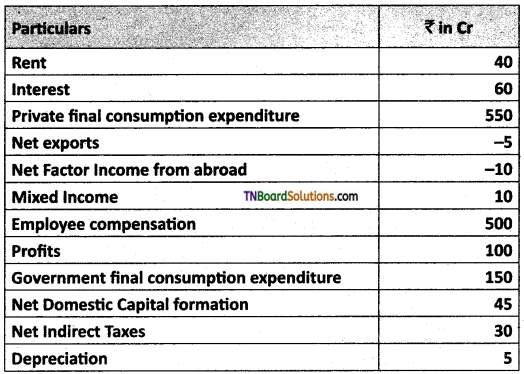
Answer:
Given data’s are:
(i) National Income (Income Method): National Income = Employee compensation + rent + interest + profits + mixed income + Net factor income from abroad = 500 + (100 +40 +60 ) +10 + (-10 ) = Rs. 700cr
(ii) National Income (Expenditure Method):
National Income private final consumption expenditure + government final consumption expenditure + net domestic capital formation + depreciation + net exports + net factor income from abroad – depreciation – net indirect taxes. = 550 + 150 + 45 + (-5) + (-10 ) – 30 = Rs. 700.
Question 3.
Calculate National Income.
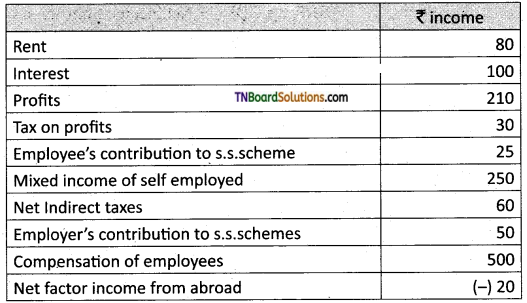
Answer:
Domestic Income = 80 + 100 + 210 + 250 + 500 = 1,140 Cr
National Income = 1,140 + (-20) = 1,120 Cr.
![]()
Question 4.
On the basis of the following real data at current prices of the Indian economy during 1982 -1983.
Find out 1) NNPFC
2) GNPMP
3) GDPMP
4) GNPFC and
5) NDPMP
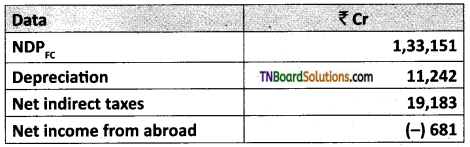
Answer:
1. NNPFC = NDPFC + Net Income from abroad.
= 1,33,151 + (-) 681 = 1,32,470 Cr.
2. NNPMP = NNPFC + Net indirect taxes.
= 1,32,470+ 19,183 = 1,51,653 Cr.
3. GNPNP = NNPMP + Depreciation.
= 1,51,653 + 11,242 = 1,62,895 Cr.
4. GDPMP = GNPMP – Net Income from abroad
= 1,62,895 – (-681) = 1,63,576 Cr.
5. GDPFC = GDPMP – Net indirect taxes.
= 1,63,576 – 19,183 = 1,44,393 Cr.
6. GNPFC = GDPFC + Net Income from abroad
= 1,44,393 +(-681) = 1,43,712 Cr.
7. NDPMP = GDPMP – Depreciation.
= 1,63,576 – 11,242 = 1,52,334 Cr.
![]()
Question 5.
Find out NDP from the given data.
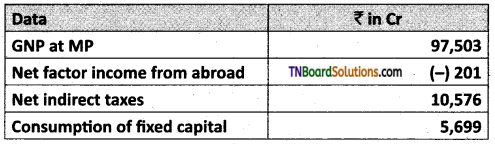
Answer:
NDP at MP = 97,503 – 5,699 – (- 201) = 92,005 Cr
NDPMP = 97,503 – 5,699 – (- 201) = 92,005 Cr.
Question 6.
GNP at MP of an imaginary economy is Rs. 1,20,000 Cr. And its capital stock is worth Rs. 3,00,000 Cr. If capital stock depreciates @ 20% per annum, indirect taxes amount to Rs. 30,000 Cr and subsidies are put at Rs. 15,000 Cr. Then what is the National Income.
Answer:
National Income (NNP at FC) = 12,000 – 60,000 (Dep 20% of 3,00,000) – 30,000 + 15,000.
= 12,000 – 60,000 – 30,000 + 15,000 = 45,000 Cr.
(Depreciation 20% of 3,00,000).
Question 7.
Find GDP at Fc from the following data:
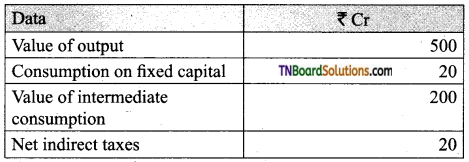
Answer:
GDP at FC = 1-3-4
i.e., Value of output – value of intermediate consumption – Net indirect taxes,
i.e., 500 – 200 – 20 = 280 Cr.
Question 8.
If the NDPFC is Rs. 1,000 Cr and NFIA is Rs. (-) 5 Cr. How much will be National Income (NNPFC)?
Answer:
NNPFC =NDPFC + NFIA
1,000 + (-5) = 995 Cr.
Question 9.
If Domestic Factor Income is Rs. 200 Cr. And National Income is Rs. 190 Cr. How much will be NFIA (Net Factor Income From Abroad)?
Answer:
NFIA = National Income – Domestic Factor Income = 190 – 200 = – 10 Cr.
![]()
Question 10.
Suppose the GDP at a market price of a country in a particular year was Rs. 1,100 Cr. Net Factor Income from abroad was Rs. 100 Cr. The value of indirect taxes – subsidies was Rs. 150 Cr. And National Income Rs. 850 Cr. Calculate the aggregate value of depreciation.
Answer:
National Income (or NNPFC) = GDPMP – Depreciation + NFIA – Net Indirect Taxes
850 = 1,100 – Depreciation + 1,100 – 150
Depreciation = 1,100 + 100 – 150 – 850
Depreciation = Rs. 200 Cr.
Activity
Question 1.
Compare GDP of different countries since 2001.
Answer:
Advantages of comparing GDP of different countries:
- Helps to develop a deep understanding of one’s own economy in comparison with others.
- Helps to know about our country’s economic backwardness.
- Helps to develop or find a solution to improve our GDP.
- To understand the necessity to work for the development of self and the country.
- To take the right decisions when it comes to the matter of choice of education and job choices.
- Helps to make decisions in life to improve per capita income.
- Comparison of 2 decades (2001 – 2020) will enhance the students to make the dream of Dr A.P.J. Abdul Kalam come true in 2020.
- Helps to build a new India in all-around development in 2020.
![]()
Multiple-choice questions
1. ……….. First introduced the concept of National income.
(a) Adam Smith
(b) Alfred Marshall
(c) Samuel son
(d) Simon Kuznets
Answer:
(d) Simon Kuznets
2. National income is:
(a) Value of good & services in a country during a year
(b) Value of money produced in a country during a year
(c) Value of agricultural products produced in a country during a year
(d) Value of industrial products produced in a country during a year
Answer:
(a) Value of good & services in a country during a year
3. GDP by expenditure method at market prices = ………..
(a) C + L + S + (X + M)
(b) C + S + G + (X – M)
(c) C + I + G + (X – M)
(d) S + I + G + (X – M)
Answer:
(c) C + I + G + (X – M)
4. Net domestic product =
(a) GDP – Depreciation
(b) GNP – Depreciation
(c) GDP – NFIA
(d) NNP – Depreciation
Answer:
(a) GDP – Depreciation
![]()
5. GNP includes ……….. types of final goods and services.
(a) 5
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 3
Answer:
(a) 5
6. The final goods and services produced in a year to satisfy the immediate wants of the people is referred as:
(a) Production
(b) Consumption
(c) Distribution
(d) Exchange
Answer:
(b) Consumption
7. NNP is expressed as:
(a) NNP = GNP – Depreciation
(b) NNP = GDP – Depreciation
(c) NNP = GDP – Transfer payments
(d) NNP = GNP – Transfer payments
Answer:
(a) NNP = GNP – Depreciation
8. Depreciation is also called as:
(a) Personal income
(b) Factor cost
(c) Capital cost
(d) Capital consumption allowance
Answer:
(d) Capital consumption allowance
![]()
9. NNP at factor cost =
(a) NNP at factor price – Indirect taxes + subsidies
(b) NNP at market price – Indirect taxes + subsidies
(c) NNP at market price – Direct taxes + subsidies
(d) NNP at factor price – Direct taxes + subsidies
Answer:
(b) NNP at market price – Indirect taxes + subsidies
10. Personal income is never equal to the National Income because it includes:
(a) Subsidies
(b) Disposable income
(c) Transfer payment
(d) Depreciation
Answer:
(c) Transfer payment
11. Disposal income = Personal income minus:
(a) Savings
(b) Indirect tax
(c) direct tax
(d) Investment
Answer:
(c) direct tax
12. The Average Income of a person of a country in a particular year is called:
(a) Per capita income
(b) National income
(c) personal income
(d) Disposable income
Answer:
(a) Per capita income
![]()
13. Nominal income is National Income expressed in terms of:
(a) Final value of goods
(b) General price level
(c) Current price level
(d) Factor cost
Answer:
(b) General price level
14. Product method is also called as:
(a) Expenditure method
(b) Income method
(c) Inventory method
(d) Factor earning method
Answer:
(c) Inventory method
15. The product method is followed in:
(a) Developed countries
(b) Developing countries
(c) Underdeveloped countries
(d) All the countries
Answer:
(c) Underdeveloped countries
16. Double counting is avoided in the ……….. method.
(a) Income method
(b) Expenditure method
(c) Factor earning method
(d) Value added method
Answer:
(d) Value added method
17. Example for National Income is:
(a) Pension
(b) salary
(c) Profit
(d) Bank savings
Answer:
(a) Pension
![]()
18. GNP =
(a) C + I + G + (X + M)
(b) C + I + S + (X + M)
(c) C + I + G + (X-M)
(d) C + S + I + (X – M)
Answer:
(b) C + I + S + (X + M)
19. National Income by-product method is measured by the value of final goods and services at:
(a) Current market prices
(b) Current factor prices
(c) Current savings
(d) Current income
Answer:
(a) Current market prices
20. The GDP estimates for India varies from 2 trillion US dollar to:
(a) 3 Trillion US dollar
(b) 4 Trillion US dollar
(c) 5 Trillion US dollar
(d) 6 Trillion US dollar
Answer:
(c) 5 Trillion US dollar
21. National disposable income is different from National Income because it also takes into account:
(a) Current transfers
(b) Capital transfers
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) All the above
Answer:
(a) Current transfers
![]()
22. Transfer is:
(a) Gift
(b) Charity
(c) Tax
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
23. Welfare of the people of a country is determined by:
(a) Nominal GDP
(b) Real GDP
(c) Per capita real GDP
(d) Per capita real GDP and Cost of other factors.
Answer:
(d) Per capita real GDP and Cost of other factors.
24. Reduction is the production of junk food:
(a) Reduces welfare
(b) Increase welfare
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Has no effect on welfare
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
25. Given GDPMP = 100
Subsidies = 5
Depreciation = 10 then NDPFC equals:
(a) 95
(b) 100
(c) 105
(d) 115
Answer:
(a) 95
26. Given NDPFC = 80
Indirect tax = 10 and Net factor Incdme to abroad = 10.
What is NNPMP?
(a) 70
(b) 80
(c) 90
(d) 100
Answer:
(d) 100
![]()
27. GDP at MP = 50,720 , NFIA = 2,400 calculate GNP at market price GNP = ………..
(a) 53,120 Cr
(b) 54,120 Cr
(c) 53,000 Cr
(d) 53,720 Cr
Answer:
(a) 53,120 Cr
28. GNP at market price 97,000 , subsidies 9,000 and Indirect Taxes 12,000 calculate GNPFC
(a) 1,00,700
(b) 1,00,000
(c) 9,000
(d) 12,000
Answer:
(b) 1,00,000
Pick the odd one out.
1. Per capita Income is:
(a) The total Income of the country
(b) Dividing National Income by population
(c) GDP/Population
(d) The Average Income of a person of a country
Answer:
(a) The total Income of the country
![]()
2. Net value added at factor cost (F) is:
(a) Market value of output
(b) Total of income payment made to factors of production
(c) NNI – Amount of Indirect tax + subsidies
(d) Value of the net output of the economy
Answer:
(d) Value of the net output of the economy
3. Methods of measuring National Income by:
(a) Value added method
(b) Factor earning method
(c) Disposable Personal Income
(d) Expenditure method
Answer:
(c) Disposable Personal Income
4. Real Income is:
(a) Nominal Income
(b) Real income is National Income expressed in terms of general price level
(c) Buying power of Nominal Income
(d) National Income/ Population
Answer:
(c) Buying power of Nominal Income
![]()
5. GDP deflator is:
(a) Index of price changes of goods and services included in GDP
(b) Difference between the value of exports and imports of goods and services
(c) It is dividing nominal GDP in a given year by the real GDP
(d)
![]()
Answer:
(b) Difference between the value of exports and imports of goods and services