Students get through the TN Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 9 Government Organisation which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 9 Government Organisation
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
What was the role of government in the past?
Answer:
In the past the role of government was limited only to the maintenance of law and order.
Question 2.
What factors govern the choice of a particular form of organisation for an industry?
Answer:
The choice of the particular form of organisation depends upon
- the nature of the industry,
- the circumstances of the country and
- the policy of the government.
![]()
Question 3.
Explain the management of public corporation.
Answer:
A Public corporation is an autonomous body corporate created by a special statute of a state or central government. A public corporation is a separate legal entity created for a specific purpose. It is a administrated by a board appointed by public authority to which it is answerable.
Question 4.
How does H. Hansen define public enterprises?
Answer:
According to A.H. Hansen “Public enterprise means state ownership and operation of industrial, agricultural, financial and commercial undertaking.
Question 5.
How can we establish state enterprises?
Answer:
State enterprises are established to implement economic policies of the government the primary objective of the state enterprises is to serve the people and help in creating an environment for industrial activity.
Question 6.
Give some example for government department organisations in india.
Answer:
In India
- Railways post and telegraph,
- BSNL,
- Radio and
- Television as government departments.
![]()
Question 7.
Give the four forms of Govt. Institution.
Answer:
- Departmental understanding
- Public corporation
- Government company
- Board organization.
Question 8.
What are the forms in which government can organize an industrial or commercial unit.
Answer:
The government can organise an industrial or commercial unit in any one of the following form
- Departmental of the government,
- Separate corporation and
- Joint stock company.
Question 9.
Why departmental organisation is suitable for defence industries?
Answer:
Strategic industries like defence and atomic power cannot be better managed other than government departments. Department undertakings can maintain secrecy in their working.
Short answer questions
Question 1.
What necessitated Governments to intervene in industrial sector?
Answer:
Industrial revolution helped all-round growth of industries. Private entrepreneurs worked, only for profit motive. The exploitation of consumers and workers by private entrepreneurs became very common. The development of industries was left to the judgment of private enterprises. Therefore, Government control or intervention became a necessity to safeguard the interests of the general public.
Question 2.
How does the state enterprises bring in balanced economic growth?
Answer:
The aim of Industrialisation is to develop all industries, essential for the country. Also, various regions of the country should be equally developed. Private sector may not establish industries in certain regions, where they do not find opportunities to earn more profit. They cannot be compelled to start their undertakings in backward regions. So government can start industries in backward areas.
![]()
Question 3.
What is a Public Corpqration?
Answer:
Public Corporation is established under a specific statute passed in the parliament. It is also known as-a statutory corporation. The statute defines its objectives, powers and functions. It is an autonomous body fully financed by the government. It has a separate legal existence.
Question 4.
Why does the government enter into those fields where large investments are required?
Answer:
Some undertakings need heavy investment and the gestation period may also be longer. Private industrialists cannot afford to make such, huge investments. In case of railways, ship-building, energy producing concerns, etc., very huge investments is required which is beyond the means of private investors. Hence, government enters these fields and establish its own undertakings.
Question 5.
Write about the provision of public utilities by government.
Answer:
Government undertakes to provide various necessities like electricity, water, coal, gas, transport, communication facilities to the people. The aim is to provide these basic facilities at cheap rates. Private sector cannot be relied upon to provide these services. Moreover, there are chances of public exploitation in these services. So public utilities are provided by government undertakings.
Question 6.
Write a short note on accountability of a public corporation.
Answer:
A public corporation is accountable to the legislature, and also to the ministry mentioned in the special Act. Its accounts are audited by Comptroller and Auditor-General and the Annual report is presented to the Parliament or Legislature.
![]()
Question 7.
Mention the circumstances suitable for government company form of organisation.
Answer:
Government company form of organization . is suitable in the following circumstances.
- When the government wants to take over an existing enterprise in ah emergency.
- When the State wants to establish an undertaking in collaboration with private enterprises or with foreign countries
- When there is a need for flexibility in the operations of the enterprises.
- When the Government wishes to start the enterprises with a view of transferring it to private management later.
Long answer questions
Question 1.
Write a note on government companies.
Answer:
- A company owned by central and /or state government is called a Government company. Either whole of the capital or majority of the shares are owned by the government.
- According to Indian Companies Act, 1956, “Government company means any company in which not less than 51 % of the paid-up share capital is held by the central government or by any state governments or government or partly by the central government and partly by one or more state government and includes a company which is a subsidiary of a government company”.
- Government companies are registered both as public limited and private limited companies but the management remains with the government in both cases. Government companies enjoy some privileges which are not available for non¬
government companies. No special statute is required to form government companies. - Government companies enter those . fields where private investment is not forthcoming. Sometimes, government has to take over sick units in private sector.
Question 2.
What are the differences between public and private sector?
Answer:
| Public sector | Private sector |
| Sufficient, unlimited resources; successful in mobilizing savings through banks, bonds etc. | Limited resources; The private sector is not successful in mobilising the resources of the country or from foreign countries for the economic development. |
| Checks concentration of economic power in the hands of few. | Leads to concentration of economic power in the hands of few individuals. |
| Develop those sectors which are neglected bv the private sector. | Develop those industries / sectors in which risk is less and returns is more. |
| Preserves national wealth. | Exploitation of natural resource like forests, mines etc., for personal advantage. |
| Brings in balanced growth; starts industries in backward areas. | Do not establish industries in backward areas. |
| Heavy, basic and defence industries are reserved for public sector. | Consumer goods industries, agriculture are in private sector. |
![]()
Question 3.
Draw a flow chart of state enterprise with example.
Answer:
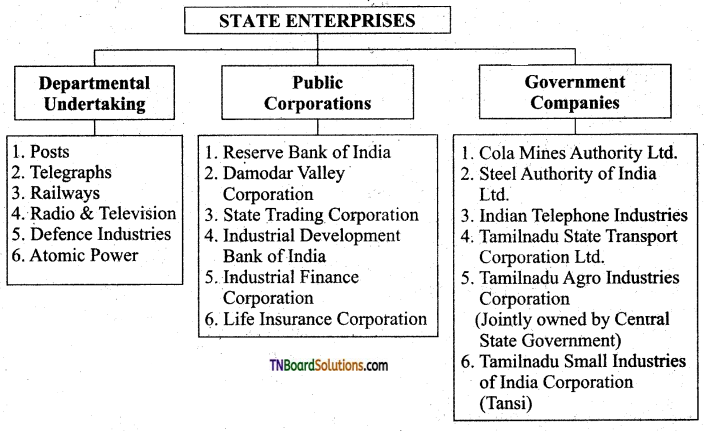
Question 4.
What are the merits and demerits of a government company?
Answer:
Merits of Government Company:
- Easy to form: The formation of a government company is comparatively easy. No prior approval of the parliament/ legislature is required.
- Flexibility in management: There is flexibility in running the business of the company. It can follow flexible policy to suit the changing, business conditions.
- Freedom of action: It enj0ys a large measure of freedom in matters of finance, administration, and personnel. It can plan its own capital structure.
- No government interference: It enjoys greater freedom and authority and is free from the protracted and time-consuming regulations of the Government. So, the government company can work just like any privately owned company.
- Run-on commercial lines: Government companies are run on sound business lines. They earn surpluses to finance their own expansion.
Demerits of Government Company:
- Political interference:
In reality, government companies do not enjoy any autonomy in their activities. The interference of the Ministers has been very frequent. Every Government tries to nominate directors from its own political party and through these, companies are run on political consideration - Minority interest neglected: Since the government is the majority shareholder, the Government is able to impose its will on the management of such a company.
- Lack of interest: The top position officials of the company are not dedicated to the success of the company as they are frequently transferred. The Board of Directors also does not have the necessary skill and experience to run the business on sound business lines.
- Accountability: The Annual Audit Report placed before the Parliament reveal only financial matters. There is no accountability for the operational efficiency, administration, and personnel of the companies.
- Red-tapism: These companies are dependent on the government for taking important policy decisions. Red-tapism in governments affects the working of these companies.
![]()
For Own Thinking
1. Name any two examples of Departmental undertaking business.
Answer:
Examples of Departmental undertaking:
- Radio and Television.
- Post and Telegraph.
2. Name any two examples of Public corporations. Examples of Public corporation:
Answer:
- RBI – Reserve Bank of India.
- UTI – Unit Trust of India.
3. Name any two examples of Government companies.
Answer:
- Maruti Udyog.
- BHEL – Bharath Heavy Electricals Limited.
For Future Learning
(i) Organise a debate in your class on the motion “Public Enterprises in India have failed to achieve their objectives”. Select a few good speakers for the purpose. State the points for and against the motion.
Answer:
Favorable:
- Excessive government control.
- Interference
- Delay and Redtapism.
- Tax burden to public
- Inefficiency.
Unfavorable:
- Proper use of funds
- Source of income for the government.
- Secrecy.
- Useful to specific industries.
![]()
(ii) Recently a discussion on “The objectives of Public sector undertakings was organized by the Friends Circle, a private cultural, organization of the city of Chennai. One of the participants, Mr. Ramesh happened to be a social worker. He observed, “the objective of Public Enterprises is to serve the Society and not to earn profits”. Mr. Deepesh, an advocate, objected to Mr. Ramesh’s statement and gave his own viewpoint. Thus continued the discussion.
If you have participated in that discussion, what should have been your stand and why?
Answer:
Public enterprises not to earn profit. But run as commercial lines. Defense industries are looking after departmental undertakings. In an emergency situation, the private sector cannot cooperate with the government.
The objective of public sector undertakings is to serve society and not to earn profit.
Case Study
Case 1- You are a newly appointed MD of a foreign sector tourist Bus transport company.
Answer:
The management of the bus Transport undertaking of your city finds that its buses are not able to attract very many tourists. Private Mini-Buses are seen to be preferred by people on certain routes. As a result, the undertaking is incurring losses. Therefore, management wants to reformulate its price policy. As a CEO or MD, what advice can you give to it? Explain.
Answer:
My advice is first to attract the public because people like attractions. Tourist bus transport company earn profit.
Case 2- Mr.Sudhan is studying in B.Com, 1st year. His father, Mr.Somu is a leading businessman in Chennai. Somehow, Mr. Sudhan does not know anything about utilities. But he is to prepare a lesson for his class on this topic. He requests his father for help. His father tells Mr. Sudhan that Public utilities are no different from his own business except that these are controlled by the Government instead of private people. Meanwhile, Mr. Chandrasekaran a friend of Mr. Somu comes there. Mr. Chandrasekaran is an employee of Chennai Electricity Supply Undertaking. Mr. Chandrasekaran intervenes in the conversation going on between Mr. Somu and his son and holds that Mr. Sudhan is not correct; there are other special features of public utilities, too. Perform the characters of Mr, Sudhan, Mr. Somu, and Mr. Chandrasekaran and state your positions.
Answer:
Government undertakes to provide various necessities like electricity, water, coal, gas, transport, communication facilities to the people. Above public utility services given by public enterprises.
Characters of Somu: a businessman.
(i) Private business people pay tax regularly.
(ii) Government employees are paid, servants. So he cannot work efficiently.
Characters of Mr. Chandra Sekar: He is an employee of the Chennai Electricity supply board. He explains electricity is very important to the public electricity board supplies electricity to common people, Industries, and all trade.
Characters of Mr. Sudhan: He is a BCom student. He knows everything from his textbook and also his father is also a businessman. He is getting information about business from his father.
![]()
Multiple choice questions
1. PSE’s are organizations owned by:
(a) joint hindu family
(b) government
(c) foreign companies
(d) private entrepreneurs
Answer:
(b) government
2. Disinvestments of PSE.s implies:
(a) sale of equity shares to private sector/ public
(b) closing down operations
(c) investing in new areas
(d) buying shares of PSE’s
Answer:
(a) sale of equity shares to private sector/ public
3. In which form of public sector enterprise private individuals can also become shareholders?
(a) Departmental undertaking
(b) Government company
(c) Statutory corporation
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Government company
4. Which of the following is most suitable when national security is of utmost importance?
(a) Departmental undertaking
(b) Government company
(c) Statutory corporation
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Departmental undertaking
![]()
5. Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL) is an example of:
(a) statutory corporation
(b) government company
(c) departmental undertaking
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(a) statutory corporation
6. “Which of the following has 51% of the capital from the government?
(a) Government Company
(b) Departmental Undertaking
(c) Statutory Corporation
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Government Company
7. Which year brought a drastic change in the role of the public sector in India?
(a) 1951
(b) 1991
(c) 1956
(d) 2001
Answer:
(b) 1991
8. Memorandum of understanding (mou) is a term used in the context of:
(a) public-private partnership
(b) joint venture
(c) the changing role of the Public sector
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(d) all of the above
9. Since 1991 number of …….. has increased in India:
(a) departmental undertaking
(b) government company
(c) statutory corporation
(d) global enterprises
Answer:
(d) global enterprises
![]()
10. Which of the following is controlled and managed as per provisions of the statute under which it has been formed?
(a) Departmental undertaking
(b) Statutory corporation
(c) Government company
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Statutory corporation
11. State enterprise is an undertaking owned and controlled by the:
(a) local government
(b) state government
(c) central government
(d) local or state or central government.
Answer:
(d) local or state or central government.
12. Example for the departmental undertaking is:
(a) industrial development bank of India
(b) all India radio and television
(c) state trading corporation
(d) Tamil Nadu state transport corporation
Answer:
(b) all India radio and television
13. Indian telephone industry is an example of:
(a) departmental organization
(b) public corporation
(c) government company
(d) joint venture
Answer:
(a) departmental organization
14. Red-Tapism affects the working of the:
(a) government companies
(b) departmental organization
(c) private companies
(d) foreign companies in India
Answer:
(a) government companies
![]()
15. Departmental undertaking can maintain in their working:
(a) cost-effectiveness
(b) secrecy
(c) discipline (irregularity)
Answer:
(b) secrecy
16. Government companies are managed by:
(a) ministers
(b) members of parliament
(c) board of directors
(d) higher officials
Answer:
(c) board of directors
17. A public corporation is accountable to the:
(a) board of directors
(b) government officials
(c) ministers
(d) legislature
Answer:
(d) legislature
18. If defense industries are owned by private individuals:
(a) profits will go the private entrepreneurs
(b) the security of the country will be safe
(c) defense secrets will be given out
(d) the country’s defense will be safe.
Answer:
(c) defense secrets will be given out
![]()
19. Government companies provide healthy competition to the:
(a) private sector
(b) public corporation
(c) co-operative society
(d) foreign companies
Answer:
(a) private sector
20. There is no competition to the business of:
(a) partnership
(b) joint-stock company
(c) sole trading concern
(d) departmental organization
Answer:
(d) departmental organization
21. Government companies are registered under:
(a) a special statute of government
(b) companies act, 1956
(c) royal charter
(d) order of the Government
Answer:
(b) companies act, 1956
22. In a public corporation the management has:
(a) limited freedom
(b) no freedom of action
(c) controlled freedom
(d) unrestricted freedom of action
Answer:
(c) controlled freedom
![]()
23. For the efficient working of state enterprise the form of organization generally considered suitable is:
(a) departmental organization
(b) public corporation
(c) government company
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) public corporation
24. Public can also subscribe to the share capital of:
(a) public corporation
(b) departmental undertaking
(c) government company
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) government company
25. In a government company the share capital of the government must hot be less than:
(a) 51%
(b) 60%
(c) 75%
(d) 90%
Answer:
(a) 51%
26. State enterprises are established to:
(a) implement economic policies of the government
(b) earn profit
(c) prevent the entry of private enterprises
(d) establish socialist society
Answer:
(a) implement economic policies of the government
![]()
27. This is an undertaking owned and controlled by Government:
(a) Sole tradership
(b) Partnership
(c) State enterprises
(d) Joint-stock companies
Answer:
(c) State enterprises
28. The aim of industrialization is to:
(a) achieve economic development
(b) develop all industries
(c) raise the income of the people
(d) raise the employment opportunities
Answer:
(b) develop all industries
29. The public corporation is managed by:
(a) board of directors
(b) civil servants
(c) directors
(d) managing Committee
Answer:
(a) board of directors
![]()
30. Government companies are managed by:
(a) Ministers
(b) Members of Parliament
(c) Board of Directors
(d) Higher officials
Answer:
(c) Board of Directors