Students get through the TN Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 29 Elements of Contract which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 29 Elements of Contract
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
What is Acceptance?
Answer:
When the person to whom the proposal is made, signifies his assent thereto, the proposal is said to be accepted.
Question 2.
What is an Agreement?
Answer:
Every promise and set of promises forming consideration for each other is an agreement. In short, Agreement = Offer + Acceptance.
Question 3.
What are the classified into agreements categories?
Answer:
The agreements may be classified into two categories:
- Agreement not enforceable by law – Any essential of a valid contract is not available.
- An agreement enforceable by law – All essentials of a valid contract are available.
![]()
Question 4.
What is an implied contract?
Answer:
The implied contract is one, which is not expressly written but understood by the conduct of parties. Where the proposal or acceptance of any promise is made otherwise than in words, the promise is said to be implied, eg: A gets into a public bus, there is an implied contract that he will pay the bus fare.
Question 5.
Explain the Bilateral contract.
Answer:
A contract in which both the parties commit to performing their respective promises is called a bilateral contract, eg: R offers to sell his fiat car to S for Rs. 10,00,000 on acceptance of R’s offer by S, there is a promise by R to Sell the car and there is a promise by S to purchase – the car, there are two promises.
Question 6.
Define Law.
Answer:
Law means a set of rules which governs our, behaviour and relating in a civilized society. So there is no need for Law in an uncivilized society. One to should know the law to which he is subjected because ignorance of the law is no excuse.
Short answer questions
Question 1.
Define free consent.
Answer:
The consent of the parties must be free and genuine. Consent means agreeing upon the same thing in the same sense at the same time i.e. there should be consensus-ad-idem. Consent is said to be free when it is not caused by coercion, undue influence, fraud, misrepresentation or mistake.
![]()
Question 2.
Write a note on (i) Illegal contract, (ii) Unenforceable contract.
Answer:
- Illegal Contract: It is a contract that is forbidden by law. All illegal agreements are Void but all void agreements or contracts are not necessarily illegal. A contract that is immoral or opposed to public policy is illegal in nature.
(a) Unlike illegal agreements there is no punishment to the parties to avoid agreement.
(b) Illegal agreements are void from the very beginning but sometimes valid contracts may subsequently become void. - Unenforceable Contract: Where a contract is unenforceable because of some technical defect i.e. absence in writing barred by imitation etc. If the parties perform the contract it will be valid, but the court will not compel them if they do not.
Question 3.
What is the Indian Contract?
Answer:
The Indian Contract Act occupies the most important place in Commercial Law. Without Contract Act, it would have been difficult to carry on a trade or any other business activity. It is not only the business community that is concerned with the Contract Act, but it also influences the entire society. The main object of the contract action is to Assure that the rights and obligations which arise out of the contract are carried out and in case of failure to do so, the remedies are made available to the affected party.
Question 4.
Write a short note on the executory contract.
Answer:
A contract in which both the parties are yet to fulfil their obligations, it is said to be an executory contract, eg: A agrees to buy B’s cycle by promising to pay cash on 15th June. B agrees to deliver the cycle on 20th June.
Question 5.
Write a short note on a unilateral contract.
Answer:
A unilateral contract is a one-sided contract in which only one party has performed his promise or obligation, the other party has to perform his promise or obligation, eg: X promises to pay Y a sum of? 10,000 for the goods to be delivered by Y. X paid the money and Y is yet to deliver the goods.
![]()
Long answer questions
Question 1.
What is the classification of the type of contracts?
Answer:
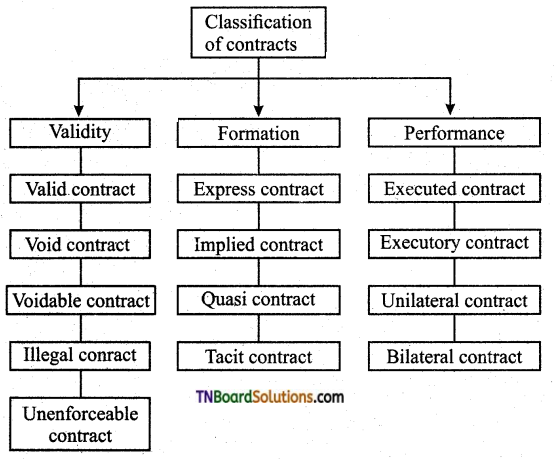
Question 2.
The capacity of parties – Explain (sec-11).
Answer:
- The parties to a contract must have the capacity (legal ability) to make a valid contract.
- The Indian Contract Act specifies that every person is competent to contract provided.
- He is of the age of majority according to the Law which he is subject to, and
- Who is of sound mind and is not disqualified from contracting by any law.
- To which he is subject to, an alien enemy, foreign sovereigns and accredited representative of a foreign state, insolvents and convicts are not competent to contract.
![]()
For Own Thinking
1. A agrees to pay B (Rs. 20,000). and in consideration, B agrees to unload 10 bags of sugar from a truck in 5 minutes. Is it a Valid contract?
Answer:
- It is hot a valid contract.
- Because unloading time is too short.
2. X writes to Y, As a doctor, you treat my wife without charging, I promise to pay you Rs. 10,000/-. “X” does not pay. Advise Y.
Answer:
As per your promise, I treated your wife. Hence it is left up to you to fulfil your promise to pay me Rs. 10,000/-.
3. P owes Q Rs. 10,000/- for the last 10 years and the payment is time-barred. P signs a pro-note for it. Is it a valid contract? If yes, give a reason.
Answer:
No. It is not a valid contract. The promotion will be renewed every year.
For Future Learning
1. After studying this chapter anyone can enter into a Valid Contract and can also identify the essentials present in the contract.
Answer:
When one person signifies to another his willingness to do or to abstain from doing anything with the accent of that other person.
2. After understanding this chapter entering into Offer and” giving Acceptance becomes easier.
Answer:
An agreement of purity social or domestic nature is not at all a contract. An invitation to dinner does not create any legal relationship and hence, is not a contract.
Offer = proposal
Acceptance = proposal is accepted.
![]()
3. After going through this chapter the value of consideration and the requirement for return payment can be understood better.
Answer:
A contract is an agreement enforceable by law. Every contract is enforceable. A contract includes an agreement.
4. After reviewing this chapter the parties who are allowed to enter and the parties who are not allowed to enter into a contract can be clearly demarcated.
Answer:
Who is allowed to enter into a contract: An agreement includes not only these agreements which can be enforceable by law but also those which may not be enforceable. A minor cannot enter into a contract.
Who are not allowed to enter into a contract: There may be an agreement to do an illegal act. eg: Smuggling goods. Which cannot be enforceable by law.
5. After analysing this chapter an obligation imposed by law – Quasi Contracts are better understood and distinguished from other contracts.
Answer:
Quasi-contract is an obligation of one party to another imposed by law independent Of an agreement between the parties.
Illegal contract: It is a contract that is forbidden by law. All illegal agreement is void but all void agreements or contracts are not necessarily illegal.
Multiple-choice questions
1. The Indian Contract Act occupies the most important place in the ……….. law.
(a) commercial
(b) civil
(c) criminal
(d) labour
Answer:
(a) commercial
![]()
2. The English common law is the basis for the development of the Indian Contract Act:
(a) 1972
(b) 1872
(c) 1982
(d) 1992
Answer:
(b) 1872
3. There are ……… parts of Indian contract Act namely.
(a) two
(b) three
(c) four
(d) five
Answer:
(a) two
4. The Act came into force on 1st September 1872 and applies to the whole of India except the state of:
(a) Andhra
(b) Kerala
(c) Jammu & Kashmir
(d) Madhya Pradesh
Answer:
(c) Jammu & Kashmir
5. Two persons cannot enter into an agreement to do a ………. act.
(a) Criminal act
(b) Commercial law
(c) Civil law
(d) Labour law
Answer:
(a) Criminal act
6. Capacity of parties section:
(a) 12
(b) 19
(c) 10
(d) 11
Answer:
(d) 11
![]()
7. Certain agreements have been expressly declared ……… by the law.
(a) Valid contract
(b) Illegal void
(c) Commercial law
(d) criminal law
Answer:
(b) Illegal void
8. Classification of contract types are:
(a) 5
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 6
Answer:
(c) 3
9. There must be two parties to an agreement namely one party making the offer and the other party accepting it:
(a) Offer and Acceptance
(b) Legal Relationship
(c) Lawful object
(d) Free consent
Answer:
(a) Offer and Acceptance
![]()
10. An agreement of social or domestic nature is not at all a contract:
(a) Free consent
(b) Capacity of parties
(c) Offer and Acceptance
(d) Legal Relationship
Answer:
(d) Legal Relationship