Students get through the TN Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 10 Reserve Bank of India which is useful for their exam preparation.
TN State Board 11th Commerce Important Questions Chapter 10 Reserve Bank of India
Very short answer questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by indigenous banker?
Answer:
Indigenous bankers are those who do not come under the control of RBI. For example Moneylenders, Marvadis Chettiars, Pawnbrokers are known as indigenous bankers.
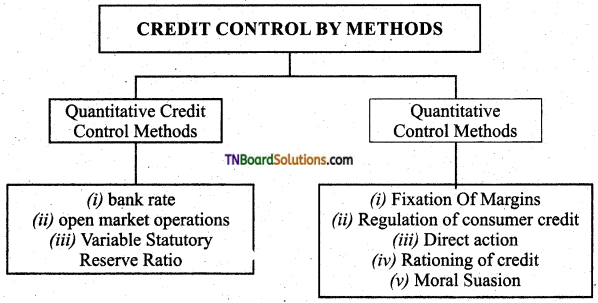
Question 2.
List the credit control methods of Reserve bank of India.
Answer:
Question 3.
Define Scheduled Bank?
Answer:
The banks which fulfill the following conditions are classified into scheduled banks.
- Their paid-up capital and reserves are at least Rs. 5 Lakhs.
- Their operations are not detrimental to the interest of the depositors.
- They are a corporation or Cooperative society and not partnerships or single-owner firms.
![]()
Short answer questions
Question 1.
Who is the sole authority for the issue of currency notes?
Answer:
RBI is the sole authority for the issue of – currency notes in India except for one rupee coin, one rupee note, and subsidiary coins. These notes are printed and issued by the issue department.
Question 2.
Who is the Banker to the Government?
Answer:
RBI acts as the banker and agent of the government. It gives the following services:
Question 3.
Who is called a Banker’s Bank?
Answer:
As per the Banking Regulation Act 1949, every bank has to keep, certain minimum cash balance with RBI. This is called as Cash Reserve Ratio. The scheduled banks can borrow money from the reserve bank of India on eligible securities and by rediscounting bills of exchange. Thus it acts as a banker’s bank.
Long answer questions
Question 1.
What is the main objective of RBI?
Answer:
- To manage and regulate foreign exchange.
- To build a sound and adequate banking and credit structure.
- To promote specialized institutions to increase the term finance to industry.
- To give support to government and planning authorities for the economic development of the country.
- To control and manage the banking system in India.
- To execute the monetary policy of the country.
![]()
For Own Thinking
A Debate on demonetization and – remonetization.
Answer:
Demonetization:
- To crop whip against black money.
- To drive out counterfeit currency in circulation.
- Formalization of cash-dependent business
- Dismantling the financial strength of terrorism and Naxalism. This leads to No black money.
“All must pay correct taxes,
All are equal. ”
Remonetization:
- There were Rs. 17.118 billion value of Rs. 5000 and Rs. 1000 currency notes in circulation before demonetization.
- They consisted of around 2203 Crore: pieces of notes.
- Now remonetization was carried out by issuing new Rs. 2000 and Rs. 500 currency notes to circulate.
‘All economic problems solved now”
For Future teaming
1. Know the Central Banks of Some other Countries. The Central Bank of Russia is the Bank of Russia. The Central Bank of Sri Lanka is the Central Bank of Sri Lanka. The Central Bank of the USA is …..(i)…… The Central Bank of Pakistan is ..(ii)…..
Answer:
(i) Central Bank of America is Federal Reserve.
(ii) Central Bank of Pakistan is the State Bank of Pakistan.
2. Mention the names of Central Banks in three other countries.
Answer:
- Central Bank of Bhutan – Bhutan.
- Reserve Bank of Australia – Australia
- Central Bank of China – China.
- Bank of Canada – Canada.
![]()
3. Understand the concepts of the monetary authority, banking system, financial system.
Answer:
The formal financial system of four segments. These are financial institutions, financial markets, financial instruments, and financial services.
4. Collection of names of RBI Governors.
Answer:
- D. Subbarao. IAS – September 5, 2008
- Raghuram Rajan – September 4, 2013
- Urjit Patel – September 5, 2016.
5. Collection of photocopy of currencies and coins in India.
Answer:

(i) Currency rare Indian 2 rupees.
(ii) Rare 1908 King Edward VII
(iii) My coin collections two rupees.
Case Study
1. Take up a recent newspaper clipping about RBI such as the measures taken to reduce NPA. etc.
Answer:
Central banks are not known to be trigger happy. RBI is no exception. Indeed it has often been criticized for being much too cautious. Especially when it comes to loosening Capital A/c.
2. Arrange for a group discussion on customer grievances and the cases settled by Banking Ombudsman offices.
Answer:
The RBI today said it will bring about a customer grievances redressal mechanism for non-banking finance companies NBFCs by this month-end.
![]()
3. Visit the RBI website www.rbi.org.in to read and have a discussion on any annual report, etc.
Answer:
The asset quality of the banking sector continued to be a concern during 2016-2017. In the aftermath of the assets quality review (QAR) undertaken by the RBI.
Multiple choice questions
1. Which of the following is an example of e-banking:
(a) EFT
(b) Online banking
(c) ATM
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
2. Who can get an overdraft from a bank?
(a) A current A/c Holder
(b) A savings A/c Holder
(c) A fixed Deposit A/c Holder
(d) A Recurring Deposit A/c Holder
Answer:
(a) A current A/c Holder
![]()
3. Give full form of ATM:
(a) Automatic telemoney
(b) Any time money
(c) Automated teller machine
(d) Automatic transfer machine
Answer:
(c) Automated teller machine
4. Name the type of banking under which ATM credit card and EFT facilities are available:
(a) Internet Banking
(b) E – Banking
(c) Modem Banking
(d) Online Banking
Answer:
(b) E – Banking
5. Name the controlling authority to telecom services in India.
(a) TRAI
(b) SEBI
(c) RBI
(d) IRDA
Answer:
(a) TRAI
![]()
6. Which of the following can be used only for e-business?
(a) Cheques
(b) Credit card
(c) Debit card
(d) E-cash
Answer:
(d) E – cash
7. Banks are called as manufactures of:
(a) Money
(b) Loans
(c) Deposit
(d) Overdrafts
Answer:
(a) Money
8. The reserve introduced an electronic clearing service for payment of electricity, bills in 1997;
(a) Chennai
(b) Kolkatta
(c) Delhi
(d) Mumbai
Answer:
(d) Mumbai
9. A bank that occupies a central position in the monetary and banking system of the country and has a superior financial authority is:
(a) Central Bank
(b) Commercial Bank
(c) Exchange Bank
(d) Co-operative bank
Answer:
(a) Central Bank
![]()
10. ……… are those who do not come under the control of RBI,
(a) Indigenous Bank
(b) ICICI
(c) Central bank
(d) exchange bank
Answer:
(a) Indigenous Bank
11. RBI on the basis of functions:
(a) Commercial bank
(b) Co-operation bank
(c) Non-scheduled bank
(d) Private sector bank
Answer:
(a) Commercial bank
12. The head office of the RBI is situated in:
(a) Chennai
(b) Mumbai
(c) Delhi
(d) Kolkatta
Answer:
(b) Mumbai
13. The demonetization in ………. year was a grand success because of the leadership role of the RBI.
(a) 2013-2014
(b) 2014-2015
(c) 2012-2013
(d) 2016-2017
Answer:
(d) 2016-2017
![]()
14. One governor and four deputy governors appointed for a period of ………. years.
(a) one
(b) two
(c) three
(d) four
Answer:
(d) four
15. RBI it also has ………. regional officers.
(a) 20
(b) 19
(c) 21
(d) 24
Answer:
(b) 19
16. The functions of the RBI can be grouped under the heads:
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 5
(d) 6
Answer:
(b) 2
17. This central office has ………. departments in 2017.
(a) 30
(b) 31
(c) 33
(d) 36
Answer:
(c) 33
![]()
18. Emblem of RBI:
(a) Palm tree & tiger
(b) Palm tree lion
(c) Palm tree & zebra
(d) Palm tree kangaroo
Answer:
(a) Palm tree & tiger
19. Foreign exchange management Act:
(a) 2003
(b) 2008
(c) 1999
(d) 2016
Answer:
(c) 1999
20. The rupee symbol was changed from Rs to by the government of India on:
(a) 15.7.2010
(b) 15.4.1987
(c) 15.3.2011
(d) 15.6.2012
Answer:
(a) 15.7.2010
![]()
21. There were ………. billion value of 500 and 1000 currency notes in circulation before Demonetisation.
(a) 16118
(b) 17118
(c) 17211
(d) 16444
Answer:
(b) 17118