Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Guide Pdf Geography Chapter 5 Biosphere Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Important Questions, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Solutions Geography Chapter 5 Biosphere
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Biosphere Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The coldest biome on Earth is __________
(a) Tundra
(b) Taiga
(c) Desert
(d) Oceans
Answer:
(a) Tundra
![]()
Question 2.
This is the smallest unit of biosphere __________
(a) Ecosystems
(b) Biome
(c) Environment
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(d) Ecosystems
Question 3.
Nutrients are recycled in the atmosphere with the help of certain micro organisms, referred to as __________
(a) Producers
(b) Decomposers
(c) Consumers
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(d) None of the above
Question 4.
To which climatic conditions are Xerophytic plants specifically adapted to?
(a) Saline and sandy
(b) Limited moisture availability
(c) Cold temperature
(d) Humid
Answer:
(a) Saline and sandy
Question 5.
Why is the usage of rainforest biomes for large scale agriculture unsustainable?
a) because it is too wet.
b) because the temperature is too warm,
c) because the soil is too thin.
d) because the soil is poor.
Answer:
d) because the soil is poor
Questions 6-8 are assertion type questions. Directions :
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason(R) are true; R explains A
(b) Both assertion(A) and reason(R) are true; R does not explain A
(c) A is true; R is false
(d) Both A and R are false
Question 6.
A: Heterotrophs do not produce their own food.
R : They depend on autotrophs for their nourishment.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason(R) are true; R explains A
Question 7.
A : Hotspots are the regions characterised by numerous endemic plants and animal species
living in a vulnerable environment.
R : To manage and focus on conservation work more effectively, researchers identified hotspots.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason(R) are true; R explains A
![]()
Question 8.
A: The number of gorillas in Africa has plummeted by 60% in the past twenty years.
R : Non intervention of human beings in the forest areas.
Answer:
(c) A is true; R is false
II. Fill in the Blanks
- An area where animals, plants and micro organisms live and interact with one another is known _____
- __________ are also called Heterotrophs.
- __________ is a system of interlocking and independent food chains,
- __________ is an extensive large ecosystem.
- The vegetative type commonly found in desert biomes is called __________
- __________ is an aquatic biome that is found where freshh water and salt water mix
Answer:
- Eco System
- consumers
- Food web
- A Biome
- Xerophytes
- Estuary
III. Answer the following in brief
Question 1.
What is Biosphere?
Answer:
The biosphere is a life-supporting layer that exists on the earth’s surface. This layer on earth encompasses the Lithosphere, Hydrosphere, and Atmosphere. It includes flora and fauna that thrive on or near the earth’s surface.
![]()
Question 2.
What is an ecosystem?
Answer:
- An ecosystem is a community, where all living organisms live and interact with one another and also with their non-living environment such as land, soil, air, water etc.
- Ecosystems range in size from the smallest units (Eg: bark of a tree) that can sustain life to the global ecosystem or ecosphere. (Eg: Cropland, Pond ecosystem, Forest ecosystem, Desert ecosystem etc.).
- Biosphere harbours all ecosystems on the earth and sustains life forms including mankind.
Question 3.
What does the term ‘biodiversity’’ mean?
Answer:
Biodiversity or biological diversity refers to a wide variety of living organisms (plants, animals and other microorganisms) which live in a habitat. It is highly influenced by topography, climate as well as human activities.
Question 4.
What is meant by loss of bio diversity?
Answer:
- The extinction of species (flora and fauna) due to human and natural influences is called loss of biodiversity.
- The biodiversity loss has a great impact on mankind and also affects land, water, air etc.
- Habitat destruction due to deforestation, population explosion, pollution and global warming are the major cause for loss of biodiversity.
- Sometimes, habitat loss is so severe or happens so quickly that it results in a species being eliminated from the planet.
![]()
Question 5.
Mention the various terrestrial biomes.
Answer:
The major terrestrial biomes of the world are:
- Tropical Forest Biomes
- Tropical Savanna Biomes
- Desert Biomes
- Temperate Grassland Biomes
- Tundra Biomes
IV. Give reasons for the following
Question 1.
Producers are also called autotrophs.
Answer:
Producers are self-nourishing components of the ecosystem. Hence they are called Autotrophs. They are found both on land and water, e.g. Plants, Algae, Bacteria, etc.
Question 2.
Biosphere provides a stable ecosystem.
Answer:
- Ecosystems range in size from the smallest units that can sustain life to the global ecosystem or ecosphere.
- The biosphere harbours all ecosystems on the earth and sustains life forms including mankind. Therefore Biosphere provides a stable ecosystem.
V. Distinguish between the following.
Question 1.
Producers and Decomposers.
Answer:
Producers:
- Producers are self-nourishing components of the ecosystem.
- Hence they are called Autotrophs.
- They are found both on land and in water. Eg. Plants, Algae, Bacteria etc.
Decomposers:
- Decomposers are some organisms that are incapable of preparing its own food.
- They live on dead and decaying plants and animals.
- Hence they are called Saprotrophs. Eg. Fungus, mushrooms etc.
![]()
Question 2.
Terrestrial biomes and Aquatic biomes.
Answer:
Terrestrial biomes:
- Terrestrial biomes is a group of living organisms that live and interact with one another on land. They are
- mainly determined by temperature and rainfall.
- Some of the major terrestrial biomes of the world are:
- Tropical Forest Biomes
- Tropical Savanna Biomes
- Desert Biomes
- Temperate Grassland Biomes
- Tundra Biomes
Aquatic biomes:
- Aquatic biome is a group of living organisms that live and interact with one. another and its aquatic environment for nutrients and shelter.
- Like terrestrial biomes, aquatic biomes are influenced by a series of abiotic factors.
- It is broadly classified as:
- fresh water biomes and
- marine biomes.
Question 3.
Tropical vegetation and Desert vegetation.
Answer:
Tropical vegetation:
- Tropical forests have the highest biodiversity and primary productivity of any of the terrestrial biomes.
- These regions have very dense forests.
- The chief trees found here are rubber, bamboo, ebony, etc.
Desert vegetation:
- Due to the lack of rainfall and arid conditions, these regions do not possess any vegetation but have a special vegetation type called Xerophytes.
- As the soil is sandy and saline, deserts remain agriculturally unproductive.
- Drought resistant thorny scrubs and bushes, palms are found here.
![]()
Question 4.
Savannas and Tundra.
Answer:
Savannas:
- Tropical Savannas are generally found between tropical forests and deserts.
- Tropical Savanna biomes are found between 10° to 20° North and South latitudes.
- This biome is generally hot and dry and experiences moderate to low rainfall.
- The grass which grow here are tall and sharp.
Tundra:
- 1. Tundra low lands are found where the ground remains frozen.
- 2. Greenland, Arctic and Antarctic region and Northern parts of Asia, Canada, Europe fall in this Biome.
- 3. These regions are also called Barren lands.
- This biome experiences long severe winter and short cool summer.
VI. Answer the following in a paragraph
Question 1.
Explain the various components of the ecosystem.
Answer:
An ecosystem is a community, where all living organisms live and interact with one another and also with their non-living environment such as land, soil, air, water etc. Ecosystems range in size from the smallest units (e.g. bark of a tree) that can sustain life to the global ecosystem or ecosphere. (e.g. Cropland, Pond ecosystem, Forest ecosystem, Desert ecosystem etc.). Biosphere harbours all ecosystems on the earth and sustains life forms including mankind.
Components of the ecosystem:
An ecosystem consists of three basic components, namely
(A) Abiotic components
(B) Biotic components and
(C) Energy component
A) Abiotic Components: Abiotic components include the non-living, inorganic, physical and chemical factors in the environment, e.g. Land, Air, Water, Calcium, Iron etc.
B) Biotic Components: Biotic components include plants, animals and microorganisms. Biotic components can be classified into three categories:
- Producers are self-nourishing components of the ecosystem. Hence they are called Autotrophs. They are found both on land and water, e.g. Plants, Algae, Bacteria etc.
- Consumers are those that depend on producers, directly or indirectly. Hence they are called Heterotrophs.
C) Energy Components: All organisms in the biosphere use energy to work and convert one form of energy into another. The Sun is the ultimate source of energy for the biosphere as a whole. The solar energy gets transformed into other forms of energy through the various components in the ecosystem. The producers, consumers and decomposers contribute a lot to the energy flow in an ecosystem.
![]()
Question 2.
Write a paragraph on the functions of an ecosystem.
Answer:
- The living organisms form an interacting set of flora and fauna which are organized into trophic levels, food chains and food webs.
- The functioning of an ecosystem depends on the pattern of the energy flow, as it helps in the distribution and circulation of the organic and inorganic matter within an ecosystem.
- Energy flow generally takes place in a hierarchical order in an ecosystem through various levels.
- These levels are called trophic levels.
- The chain of transformation of energy from one group of organisms to another, through various trophic levels is called a food chain.
- A system of interlocking and interdependent food chains is called a food web.
Question 3.
Explain about the aquatic biomes on Earth.
Answer:
An aquatic biome is a group of living organisms that live and interact with one another and its aquatic environment for nutrients and shelter. Like terrestrial biomes, aquatic biomes are influenced by a series of abiotic factors. It is broadly classified as freshwater biomes and marine biomes.
A. Freshwater Biomes: It comprises lakes, ponds, rivers, streams, wetlands etc. It is influenced by various abiotic components such as the volume of water, water flow, the composition of oxygen, temperature, etc. Humans rely on freshwater biomes for drinking water, crop irrigation, sanitation and industry. Water lily, lotus, duckweeds etc. are the common plants found here. Trout, salmon, turtles, crocodiles etc. are the animals found here.
B. Marine Biomes: They are the largest aquatic biomes on earth. They are continuous bodies of saltwater and provide a wide range of habitats for marine plants and animals. Coral reefs are the second kind of marine biomes within the ocean. Estuaries, coastal areas where salt water and fresh water mix, form a third unique marine biome. As water provides maximum mobility to marine organisms, nutrients are circulated more quickly and efficiently here than the terrestrial biomes. Apart from animals, plants such as kelp, algae, phytoplankton etc. also grow in water. Aquatic biomes are not only important for plants and animals, but also for humans. Humans use aquatic biomes for water, food and leisure activities. Some of the threats and issues to aquatic biomes are overfishing, pollution and a rise in sea level.
![]()
VII. Find out the dates for the following
Question 1.
- World Wild Life Day – _______
- International Day of Forest – _______
- World Water Day – _______
- Earth Day – _______
- World Environment Day – _______
- World Oceans Day – _______
Answer:
- 3rd March
- 21st March
- 22nd March
- 22nd April
- June 5th
- 8th June
VIII. Map Study
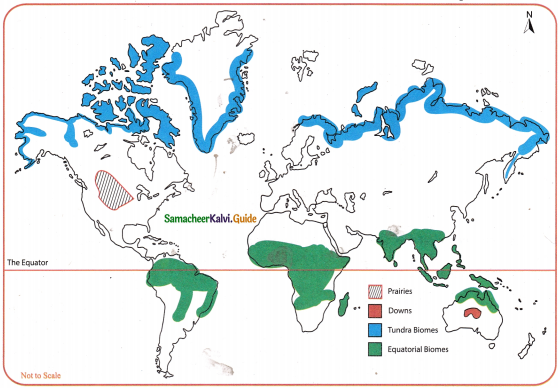
Question 1.
Locate the following on the world outline map.
- Prairies
- Downs
- Tundra Biomes
- Equatorial Biomes
IX. Picture Study
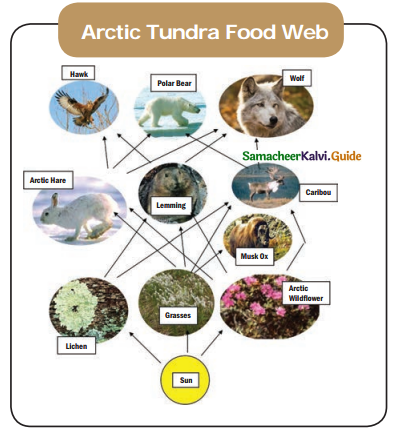
Question 1.
Narrate the given web of Arctic Thundra in your own words
Answer:
- Sun → Lichen → Lemming → Wolf
- Sun → Lichen → Caribou → Wolf
- Sun → Grasses → Arctic Hare → Hawk
- Sun → Grasses → Arctic Hare → Polar Bear
- Sun → Grasses → Arctic Hare → Wolf
- Sun → Grasses → Lemming → Hawk
- Sun → Grasses → Lemming → Wolf
- Sun → Grasses → Musk Ox
- Sun → Artie Wildflower → Leming → Hawk
- Sun → Artie Wildflower → Leming → Wolf
- Sun → Artie Wildflower → Caribou → Polar Bear
- Sun → Artie Wildflower → Caribou → Wolf
Intext Activity
Question 1.
Narrate the forest ecosystem in your own words.
Answer:
- A forest ecosystem is a large area of land that’s covered in trees and other woody plants and filled with living animals. There are three main types of forests: tropical rain forests, deciduous forests, and coniferous forests.
- Tropical rain forests are found near the equator (the center of Earth), where they are warm all year round. It usually rains in rain forests every day, and there are many different species of animals that live in the different levels of the rain forest.
- Deciduous forests are made up of trees that shed their leaves in autumn. Worms, snails, and spiders enjoy their rich soil, and they have warm summers and cold winters. In the winter, animals that live in deciduous forests hibernate, or sleep through the winter, and birds migrate to warmer areas in the world. Raccoons, rabbits, and squirrels are common animals found in deciduous forests.
- Coniferous forests have vegetation composed primarily of cone-bearing needle-leaved or scale-leaved evergreen trees, found in areas that have long winters and moderate to high annual precipitation.
![]()
Question 2.
Find the etymology of Herbivores, carnivores, omnivores and scavengers using dictionary
Answer:
Etymology
- Herbivores Meaning – Plant Eating
- Herba Meaning – Plant / Vorare – Swallow
- Carnivores Meaning – Flesh Eating
- Cami Meaning – Flesh / Vorare – Swallow
- Omnivores Meaning – feeding on a variety of food of both plant and animal origin
- Omni Meaning – All / Vorare – Swallow
- Scavengers Meaning – an animal that feeds on carrion, dead plant material or refuse.
- Scavage Meaning – search or inspect through rubbish things
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Biosphere Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Fill in the Blanks
- All living things large or small are grouped into _________
- The area in which an animal, plant or micro organisms lives is called its _________
- The chain of transformation of energy from one group of organisms to another through various trophic levels is called a _________
- The Extinction of spices is called _________
- In Temperate Grass Lands Biome higher precipitation leads to _________ grass.
- In Temperate Grassland Biomes lower precipitation leads to _________ grass.
- Tundra Biomes are also called _________
- Lakes, ponds, rivers, streams, wetlands together known as _________ biomes.
- In aquatic ecosystem, there is abundant water with limited _________ supply.
- Terrestrial animals use only 1 – 2% of energy to obtain _________
- The wide variety of living organisms that are found on the planet is called _________
- The study about freshwater ecosystem is called _________
- The study of the sources, development and history of a word is called _________
- There are _________ Biosphere Reserves in India.
Answer:
- Species
- habitat
- Food chain
- Loss of Biodiversity
- tall and soft
- short and soft
- Barren Lands
- Fresh water
- oxygen
- oxygen
- biodiversity
- Limnology
- Etymology
- 18
II. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
The life-supporting layer is known as ________
(a) Atmosphere
(b) Hydrosphere
(c) Lithosphere
(d) Biosphere
Answer:
(d) Biosphere
![]()
Question 2.
The branch of science that deals with an ecosystem are called ________
(a) Etymology
(b) Geology
(c) Limnology
(d) Ecology
Answer:
(d) Ecology
Question 3.
Abiotic components include ________
(a) Non-living things
(b) Living things
(c) only plants
(d) only animals
Answer:
(a) Non-living things
Question 4.
Zebra and goat come under ______ consumers.
(a) Primary
(b) Secondary
(c) Tertiary
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Primary
Question 5.
A healthy ecosystem provides _________
a) clean water
b) enriched soil
c) raw materials
d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Questions 6-8 are assertion type questions:
Directions
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true; R explains A
(b) Both assertion(A) and reason (R) are true; R does not explain A
(c) A is true; R is false
(d) Both A and R are false
![]()
Question 6.
Assertion (A): A stable biosphere has to be conserved.
Reason (R): The loss of biodiversity affects land, water, air etc.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true; R explains A
Question 7.
Assertion (A): In temperate grassland biomes pastoral industry becomes the main occupation.
Reason (R): Apart from wheat cultivation, tall and short soft grass are grown in the
temperate grassland biomes.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true; R explains A
Question 8.
Assertion (A): Biosphere Reserves are established in India.
Reason (R): Today’s loss of biodiversity is habitat alteration caused by human activities.
Answer:
(a) Both assertion (A) and reason(R) are true; R explains A
III. Match the following
- World wild life day – (i) 8th June
- International day of forest – (ii) 22nd April
- World water day – (iii) 3rd March
- Earth day – (iv) 22nd March
- (e) World oceans day – (v) 21st March
Answer:
- – (iii)
- – (v)
- – (iv)
- – (ii)
- – (i)
IV. Give short answers
Question 1.
What is considered a hotspot?
Answer:
An ecological region that has lost more than 70% of its original habitat is considered a hot spot.
![]()
Question 2.
In India where do we find hot spots?
Answer:
Hotspots in India are the Himalayas, Western Ghats, Indo Burma Region and Sundaland.
Question 3.
Mention the human settlement in the Tropical Forest Biomes.
Answer:
- The Tropical Forest Biomes have very dense forests.
- So human settlements are found scattered here,
- They sustain their livelihood through food gathering, fishing, lumbering and shifting cultivation.
Question 4.
What threat is posed by the savanna grasslands?
Answer:
- Of late, parts of the savanna grasslands are being converted into farmlands.
- This poses a great threat to a wide range of fauna.
- For Eg. The population of the big cats like cheetah, lion etc. are dwindling drastically.
Question 5.
What has been identified by the U.S. National Cancer Institute?
Answer:
- The U.S. National Cancer Institute has identified about 70% of the plants used for treating cancer.
- There are found only in rain forests.
Question 6.
Name the common animals found in the Tropical Savanna Biomes.
Answer:
- In the Tropical Savanna biomes the lion, leopard, tiger, deer, zebra, giraffe etc. are the common animals found.
- Flora such as Rhodes grass, red oats grass, lemon grass etc. are found in this biome.
Question 7.
Write about Oasis.
Answer:
- An oasis is a fertile fresh water source found in deserts and semi-arid regions.
- Oases are fed by springs.
- Crops like date palms, figs, citrus fruits, maize etc. are cultivated near these oases.
![]()
Question 8.
Mention the different names of the Temperate grass lands.
Answer:
- Temperate grass lands are called differently in different parts of the world.
- They are Prairies – North America, Steppes – Eurasia Pampas – Argentina and Uruguay Downs – Australia and Newzealand
Question 9.
What is a Biosphere Reserve?
Answer:
A Biosphere Reserve is a special ecosystem or specialised environment with flora and fauna that require protection and nurturing. There are 18 Bioshpere Reserves in India.
Question 10.
Explain the following terms
(a) Herbivorous
(b) Carnivorus
(c) Ommivorous
(d) Scavengers
Answer:
(a) Herbivorous: A herbivores is an animal that gets its energy from eating plants and only plants. Many herbivores have special digestive systems that let them digest all kinds of plants including grasses. Eg.-, deer, rabbits, cows, sheep, goats, elephants, giraffes, horses and pandas.
(b) Carnivores: A Carnivore is an animal that gets food from killing and eating other animals. Or they scavenge their dead flesh. Eg., Hyenas, Wolves, Mountains lions, Polar Bears.
(c) Omnivores: An omnivore is a kind of animal that eats either other animals or plants Eg. Raccoons, pigs, rats, chickens, crows etc.
(d) Scavengers: Scavengers feed partly or wholly on the bodies of dead animals. Eg., Jackals, Leopards, Lions, Vulture etc.
V. Distinguish the following
Question 1.
Tropical Grasslands and Temperate grassland.
Answer:
Tropical grasslands:
- Tropical grasslands are generally found between tropical forests and desserts.
- This biome is generally hot and dry and experiences moderate to low rainfall.
- The grass which grow here are tall and sharp.
Temperate grasslands:
- Temperate grasslands are usually found in the interior of the continents and are characterized by large seasonal temperature variations, with warm summer and cold winter.
- The type of grassland in these regions strongly depends upon precipitation.
- Higher precipitation leads to tall and soft grass and lower precipitation leads to short and soft grass.
![]()
VI. Give reasons for the following
Question 1.
In tropical savannas the chief occupation is herding.
Answer:
The tropical savannas biomes are generally hot and dry and experience moderate to low rainfall. Tall and sharp grass is grown. Hence the chief occupation of the people here is herding.
Question 2.
Tropical Forest Biomes have economic importance.
Answer:
- The Amazon basin, Congo basin and Indonesian islands, under this biomie, have very dense forests and so have great economic importance.
- The chief trees found here are rubber, bamboo, ebony etc.
Question 3.
Why do people in Tundra region shift their settlement frequently?
Answer:
The harsh environment makes people change their settlement frequently. People are nomadic, depending on hunting and fishing. The population here is very sparse.
VII. Answer in detail
Question 1.
Write a note on Biodiversity.
Answer:
(a) Biodiversity :
- Biodiversity or biological diversity refers to a wide variety of living organisms (plants, animals and other micro organisms) which live in a habitat.
- It is highly influenced by topography climate as well as human activities.
- It represents the strength of the biological resources of a place on earth.
- In biodiversity, each species, no matter how big or small, has an important role to play in the ecosystem.
- It maintains the ecological balance and facilitates social benefits such as tourism, education, research etc. over an area.
(b) Loss of biodiversity:
- The extinction of species (flora and fauna) due to human and natural influences is called loss of biodiversity.
- The biodiversity loss has a great impact on mankind and also affects land, water, air etc.
- Habitat destruction due to deforestation, population explosion, pollution and global warming are the major cause for loss of biodiversity.
- Sometimes, habitat loss is so severe or happens so quickly that it results in a species being eliminated from the planet.
- Scientists are still trying to decide what caused the mass extinction of dinosaurs.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the need for conservation.
Answer:
- The biosphere extends from the deep ocean trenches to lush rain forests.
- People play an important role in maintaining the flow of energy in the biosphere.
- At the same time, the primary cause of today’s loss of biodiversity is habitat alteration caused by human activities.
- The ever increasing population results in over exploitation of biological resources.
- This has an adverse impact on flora and fauna on earth.
- There are places on earth that are both biologically rich and deeply threatened.
- Hence it is man’s duty to conserve and care for the earth and make it a better place to live in.