Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Guide Pdf Civics Chapter 1 Forms of Government and Democracy Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Important Questions, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Solutions Civics Chapter 1 Forms of Government and Democracy
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Forms of Government and Democracy Text Book Back Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
A system of government in which one person reigns supreme, usually a king or queen, is called __________
(a) autocracy
(b) monarchy
(c) democracy
(d) republic
Answer:
(b) monarchy
![]()
Question 2.
A system of government with absolute power __________
(a) Aristocracy
(b) Theocracy
(c) Democracy
(d) Autocracy
Answer:
(d) Autocracy
Question 3.
Former Soviet Union is an example for __________
(a) aristocracy
(b) theocracy
(c) oligarchy
(d) republic
Answer:
(c) oligarchy
Question 4.
Select the odd one __________
(a) India
(b) USA
(c) France
(d) Vatican
Answer:
(d) Vatican
![]()
Question 6.
Kudavolai system was followed by __________
(a) Cheras
(b) Pandyas
(c) cholas
(d) Kalabhras
Answer:
(c) cholas
Question 7.
Direct Democracy in olden times existed
(a) In the republics of ancient India
(b) Among the USA (d) Among the UK
(c) In the city-state of ancient Greece
(d) Among the UK
Answer:
(c) In the city-state of ancient Greece
Question 8.
From which language was the term “Democracy” derived?
(a) Greek
(b) Latin
(c) Persian
(d) Arabic
Answer:
(a) Greek
![]()
Question 9.
In democracy the final authority’ rests with __________
(a) The Parliament
(b) The People
(c) The council of Ministers
(d) The President
Answer:
(b) The People
Question 10.
Which one of the country has the Presidential form of government
(a) India
(b) Britain
(c) Canada
(d) the USA
Answer:
(d) the USA
Question 11.
The largest democratic country in the world is __________
(a) Canada
(b) India
(c) USA
(d) China
Answer:
(b) India
![]()
Question 12.
Assertion (A): Direct democracy is practised in Switzerland.
Reason (R): People directly participates in decision making.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) does not explain (A)
(c) (A) is correct and (R) is false
(d) (A) is false and (R) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
Question 13.
Assertion (A): India has a parliamentary form of democracy.
Reason (R): Indian Parliament comprises two houses.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) does not explain (A)
(c) (A) is correct and (R) is false
(d) (A) is false and (R) is true
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
Question 14.
The meaning of Franchise is __________
(a) Right to elect
(b) Right to vote for the poor
(c) Right to vote
(d) Right to vote for the rich
Answer:
(c) Right to vote
Question 15.
The grant of universal franchise creates __________
(a) Social equality
(b) Economic equality
(c) Political equality
(d) Legal equality
Answer:
(c) Political equality
Question 16.
Prime Minister of India is appointed by __________
(a) Lok Sabha
(b) Rajya Sabha
(c) Speaker
(d) President
Answer:
(d) President
Question 17.
The President of India can nominate __________
(a) 12 members to Lok Sabha
(b) 2 members of Rajya Sabha
(c) 12 members to Rajya Sabha
(d) 14 members of Rajya Sabha
Answer:
(c) 12 members to Rajya Sabha
Question 18.
The First general elections after independence in India were held in __________
(a) 1948-49
(b) 1951 – 52
(c) 1957- 58
(d) 1947-48
Answer:
(b) 1951 – 52
II. Fill in the blanks
- The Constitution of India was finally adopted on __________
- The two types of democracy are __________ and __________
- example for direct democracy is __________
- India has a __________ form of democracy.
- __________ was the first Prime Minister of independent India.
- The first general elections were held in British India in the year __________
- The Parliament House in India was designed by _____ and _____
Answer:
- 26th November
- Direct and Indirect
- Switzerland
- Indirect/representative
- Jawaharlal Nehru
- 1920
- Edwin Lutyens and Herbert
III. Match the following
- Autocracy – (i) 18
- Right to vote – (ii) Arthashastra
- Chanakya – (iii) Vatican
- Theocracy -(iv) North Korea
Answer:
- – (iv)
- – (i)
- – (ii)
- – (iii)
IV. Give Short Answers
Question 1.
Give Abraham Lincoln’s definition of democracy.
Answer:
Abraham Lincoln defines democracy as a government of the people, by the people and for the people.
![]()
Question 2.
Mention the forms of democracy.
Answer:
There are two types of democracy. They are
- Direct democracy
- Indirect (Representative) democracy
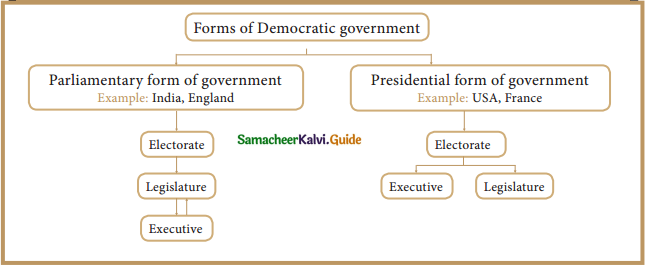
Question 3.
Distinguish between direct and indirect democracy.
Answer:
Direct Democracy: Direct participation of the people
Example: Ancient Greek city-states, Switzerland
Indirect/ Representative Democracy: Indirect participation of the people
Example: India, USA, UK
V. Answer in detail.
Question 1.
What are the challenges to Indian democracy? Explain.
Answer:
Democracy is the dominant form of government in the contemporary world. It has not faced a serious challenge or a rival so far. In the last hundred years, there has been an expansion of democracy all over the world. The various aspects of democracy and its challenges are:
- Illiteracy
- Poverty
- Gender discrimination
- Regionalism
- Casteism, communalism, and religious fundamentalism
- Corruption
- Criminalisation of politics.
- Political violence
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the conditions necessary for the success of democracy in India.
Answer:
There are certain conditions that are necessary for the success of democracy in India. They are:
- Empowerment of the poor and illiterates to enjoy the goodness of democracy.
- Willingness among the elected people not to misuse their powerful position and public wealth.
- Eradication of social evils and dangers from which democracy suffers
- An impartial and efficient press to form public opinion
- Presence of strong public opinion
- The feeling of tolerance and communal harmony among the people
- Awareness among the people of the fundamental rights that they are entitled to enjoy
- Conscious check and vigilance on the working of the elected representatives
- Powerful and responsible opposition
Question 3.
What is your opinion about democracy in India?
Answer:
India has a parliamentary form of democracy. The Indian Parliament comprises the elected representatives of the people and makes the laws for the Country. The participation of people in the decision making and the consent of citizens are the two important elements of the parliamentary form of government in India.
India is the largest democratic country in the world. Democracy in India works on five basic principles. These are sovereign, socialist, secular, democratic, republic.
Every person who is a citizen of India and who is not less than 18 years of age can exercise their right to vote in India, based on universal adult suffrage. There is no discrimination based on a person’s caste, creed, religion, region, gender, and education when it comes to providing the right to vote.
VI. Project and Activity
Question 1.
Discuss in the class what is universal adult franchise? Why is it important?
Answer:
- Students can form different groups with the help of charts. They can bring out the salient features of the adult franchise and how it is implemented in real practice.
- Based on universal adult franchise, every person, who is a citizen of India and who is not less than eighteen years of age, can exercise their right to vote in India.
- There is no discrimination based on a person’s caste, creed, Religion, Gender, and Education when it comes to providing the right to vote.
![]()
Question 2.
“Democracy is the power of the majority which respects minority.” Discuss.
Answer:
- Democracy requires minority rights equally as it does majority rule the minority’s rights must be protected.
- The Indian constitution ensures justice, social, economic, and political, to all citizens.
- India declares herself a secular state
- Article 29 gives the religious and linguistic minorities the right to establish and manage educational institutions of their own.
- No discrimination on grounds of race, religion, caste, language
- Article 30 is vital to the protection and preservation of rights of the minorities
- Article 16 guarantees that in matters of public employment, no discrimination shall be made on the grounds of race, religion, caste or language
- Article 25 of the Indian constitution guarantees freedom of religion to every individual.
- On the whole, minorities of all kinds have very secure rights in India
Question 3.
Conduct a mock election in your class.
Answer:
Activity to be done by the students themselves
Question 4.
A group discussion on the merits and demerits of democracy of India in the classroom.
| Country Name | Type of Government | Characteristics of the country’s government |
Answer:
(a) Merits
- Responsible and accountable government
- Equality and Fraternity
- Sense of responsibility among common people
- Local self-government
- Development and prosperity for all
- Popular sovereignty
- Sense of Co-Operation and fraternal feeling.
(b) Demerits:
- Indirect or representative nature of democracy
- Lack of educated and experienced voters
- Equal voting right to both wise, average and innocent person
- Freedom to all shades of opinion.
- Delay in decision-making process
VII. HOTS
Question 1.
Will you have the right to equality under a dictatorship? What would be the attitude regarding public opinion in such a country?
Answer:
No; well, a dictatorship is when a country is run by a minority of people and the citizens of that country don’t have a choice of who runs it. If one person has to make all the decisions for a country, they might use their power badly because they have too much responsibility.
Question 2.
How does democracy lead to a peaceful and harmonious life among the citizens? Explain
Answer:
- In a democracy, fundamental rights are safeguarded as basic human freedoms which every Indian citizen has the right to enjoy for proper and harmonious development of personality,
- Democracies usually develop a procedure to conduct their competition.
- This reduces the possibility of tensions becoming explosives or violent.
- The ability to handle social differences, divisions and conflicts with a better manner is a
democratic regime.
VIII. Life Skills
Select a group of countries. Research each country and tell what type of government it has: Aristocracy, Monarchy, Autocracy, Oligarchy, Theocracy, Democracy, Republic. Then, provide characteristics of this country that helped you determine the type of government.
Answer:
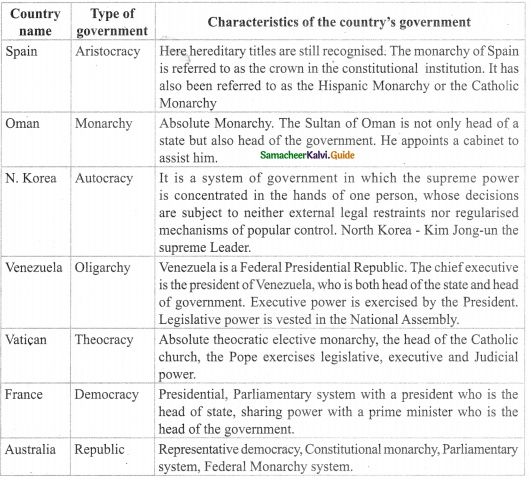
Samacheer Kalvi 9th Social Science Forms of Government and Democracy Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer
Question 1.
A system of government in which power is held by the nobility is called
(a) Monarchy
(b) Oligarchy
(c) Aristocracy
(d) Theocracy
Answer:
(c) Aristocracy
![]()
Question 2.
We find a system of government in which priests rule in the name of God or himself as a God in
(a) North Korea
(b) Vatican
(c) India
(d) Saudi Arabia
Answer:
(b) Vatican
Question 3.
“True Democracy cannot be worked by twenty men sitting at the centre. It has to be worked from below by the people of every village” – This statement was stated by
(a) Prof. Seeley
(b) Lowell
(c) Mahatma
(d) Dicey
Answer:
(c) Mahatma
Question 4.
General Elections were held in British India in
(a) 1910
(b) 1920
(c) 1930
(d) 1940
Answer:
(b) 1920
Question 5.
Freedom to practice any religion or reject all is expressed by the term
(a) Secular
(b) Socialist
(c) Republic
(d) Sovereign
Answer:
(a) Secular
![]()
Question 6.
Assertion (A): Indian President is selected indirectly
Reason (R): India is a Republic.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) does not explain
(c) (A) is correct and (R) is false
(d) (A) is false and (R) is true.
Answer:
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)]
Question 7.
Assertion (A): Lok sabha is called council of states.
Reason (R): People elect representatives to Lok Sabha.
(a) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) explains (A)
(b) Both (A) and (R) are true and (R) does not explain
(c) (A) is correct and (R) is false
(d) (A) is false and (R) is true.
Answer:
(d) (A) is false and (R) is true
II. Fill in the blanks
- According to _________ the Democracy is a government in which everyone has a share
- When people themselves directly express their will on public affairs, the type of government is called _________
- The largest democracy in the world is _________
- The general elections are conducted by the _________ of India
Answer:
- Prof. Seeley
- Direct democracy
- India
- Election Commission
III. Match the following
- Aristocracy – (i) Oman
- Oligarchy – (ii) USA
- Monarchy – (iii) China
- Democracy – (iv) Britain’s Royal family
Answer:
- – (iv)
- – (iii)
- – (i)
- – (ii)
Question 2.
- Demos – (i) Power
- ratia – (ii) Upper House
- (c) Panchayat – (iii) People
- (d) Rajya Sabha – (iv) Local government
Answer:
- (a) – (iii)
- (b) – (i)
- (c) – (iv)
- (d) – (ii)
IV. Give short answers
Question 1.
What is government?
Answer:
- Government is a group of people that governs a community or unit.
- Forms of Government are
(a) Aristocracy
(b) Monarchy
(c) Autocracy
(d) Oligarchy
(e) Theocracy
(f) Democracy
(g) Republic
Question 2.
What is meant by the Parliamentary form of Government?
Answer:
- India has a parliamentary form of government.
- The Indian parliament comprises the elected representatives of people who make laws for the country.
- The participation of people in the decision making and the consent of citizens are the two important elements of the parliamentary form of government in India.
Question 3.
What is democracy?
Answer:
- Democracy is a form of government that allows people to choose their rulers.
- Only leaders elected by the people should rule the country.
- People have the freedom to express views, freedom to organize and freedom to protest
![]()
Question 4.
Mention the features of Democracy.
Answer:
- Elected representatives of people and final decision-making power to the representatives.
- Free and fair elections.
- Universal adult franchise with each vote having equal value.
- Fundamental rights and protection of individual freedom.
Question 5.
State the importance of the Sixty-first Constitutional Amendment Act.
Answer:
- On 28th March 1989 – the voting age was reduced from 21 to 18 by the sixty-first Constitutional Amendment Act.
- It was passed during the time of Rajiv Gandhi, the late Prime Minister of India
Question 6.
When were the first General elections held in Independent India?
Answer:
- General elections to the first Lok Sabha since independence were held in India between 25th October 1951 and 21st February 1952
- The Indian National Congress (INC) emerged victorious into power by winning 364 of the 489 seats
- Jawaharlal Nehru became the first democratically elected Prime Minister of the country
V. Answer in detail
Question 1.
Write about elections in India
Answer:
- India has a Quasi-federal government, with elected representatives at the federal, state and local levels.
- The general elections are conducted by the Election Commission of India.
- At the National level, the head of the government, the President of India appoints the Prime Minister, who enjoys majority in the Lok Sabha.
- All members of the Lok Sabha, (except two Anglo Indians, who can be nominated by the President of India) are directly elected through the general election
- In India, the general elections take place every five years in normal circumstances.
- Members of the Rajya Sabha, the Upper House of the Indian Parliament, are elected by an Electoral college consisting of elected members of the legislative assemblies of the States and for the Union Territories of India.
- The first – general elections in free india to the first Lok Sabha took place between 25th Oct, 1951 and 21st February 1952
VI. Hots
Question 1.
Is multi party system beneficial for India? Discuss.
Answer:
- In general, a multi party political system ensures that there will never be a single majority.
- The multi party system satisfies the goal of democracy of people being able to influence the decisions.
- India is a huge country. It needs parties that actually have political ideologies.
- Multi party system can be good for countries where development parametric are already very high.
- Constructive criticism by a strong apposition is absolutely essential for parliamentary democracy.
- India is a vast – country with social and geographical diversities. So here the multiparty system allows a variety of interests and opinion to enjoy political representation.
- If people use their voting right in proper manner, definitely multiparty system will help to have multiple ideas to improve the nation.
![]()
Question 2.
Conduct a study on General elections in India
Answer:
- India has a Quasi – federal government with elected representatives at the federal, state and local levels.
- The General elections are conducted by the Election Commission of India
- At the National level, the head of the government, the President of India appoints the Prime Minister.
- All members of Lok Sabha (except two Anglo Indians, who can be nominated by the President of India) are directly elected through General elections.
- It takes place every 5 yrs, in normal circumstances
- Members of the Rajya Sabha, the Upper House of the Indian Parliament, are elected by an Electoral college consisting of elected members of the legislative assemblies of the States and for the Union Territories of India.
VII. Rearrange the jumbled words.
Question 1.
- EDUEFMR
- EINRSVOEG
- NTRYIAFTRE
- OPTCNOREIAO
- WSRAESNEA
Answer:
- FREEDOM
- SOVEREIGN
- FRATERNITY
- CO-OPERATION
- AWARENESS
![]()
Question 2.
- UIPCBL
- IOMSALCIS
- EITNCIZS
- OICDSEIN
Answer:
- PUBLIC
- SOCIALISM
- CITIZENS
- DECISION