Tamilnadu State Board New Syllabus Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Guide Pdf Chapter 24 Environmental Science Text Book Back Questions and Answers, Notes.
Tamilnadu Samacheer Kalvi 9th Science Solutions Chapter 24 Environmental Science
9th Science Guide Environmental Science Text Book Back Questions and Answers
![]()
I. Choose the correct answer:
Question 1.
All the factors of biosphere which affect the ability of organisms to survive and reproduce are called as ………………
(a) biological factors
(b) abiotic factors
(c) biotic factors
(d) physical factors
Answer:
(c) biotic factors
Question 2.
The ice sheets from the north and south poles and the icecaps on the mountains, get converted into water vapour through the process of ………………..
(a) evaporation
(b) condensalion
(c) sublimation
(d) infiltration
Answer:
(c) sublimation
![]()
Question 3.
The atmospheric carbon dioxide enters into the plants through the process of ………………..
(a) photosynthesis
(b) assimilation
(c) respiration
(d) decomposition
Answer:
(a) photosynthesis
Question 4.
Increased amount of ……………….. in the atmosphere, results in greenhouse effect and global warming.
(a) carbon monoxide
(b) sulphur dioxide
(c) nitrogen dioxide
(d) carbon dioxide
Answer:
(d) carbon dioxide
![]()
II. Match the following:
Question 1.
| Microorganism | Role played |
| Nitrosomonas | Nitrogen fixation |
| Azotobacter | Ammonification |
| Pseudomonas species | Nitrification |
| Putrefying bacteria | Denitrification |
Answer:
| Microorganism | Role played |
| Nitrosomonas | Nitrification |
| Azotobacter | Nitrogen fixation |
| Pseudomonas species | Denitrification |
| Putrefying bacteria | Ammonification |
![]()
III. Say true or false. Correct the false statements :
1. Nitrogen is a greenhouse gas.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas.
2. Poorly developed root is an adaptation of mesophytes.
Answer:
False,
Correct statement: Poorly developed root is an adaptation of Hydrophtes.
3. Bats are the only mammals that can fly.
Answer:
True
![]()
4. Earthworms use the remarkable high frequency system called echoes.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Buts use the remarkable high frequency system called echoes.
5. Aestivation is an adaptation to overcome cold condition.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Aestivation is an adaptation to overcome condition.
![]()
IV. Give reason for the following.
Question 1.
Roots grow very deep and reach the layers where water is available. Which type of plants develop the above adaptation? Why?
Answer:
Xerophytes have well developed roots.
Reason: They grow in dry habitat where water is scarcely available.
Question 2.
Why steamlined bodies and presence of setae is considered as adaptations of earthworm?
Answer:
- Streamlined bodies of earthworm helps to live in narrow burrows underground and for easy penetration into the soil.
- Seine helps earthworm to move through the soil and provide anchor in the burrows.
![]()
Question 3.
Why is it impossible for all farmers to construct farm ponds it in their fields?
Answer:
- Farm ponds reduce water flow to other tanks and ponds situated in lower-lying areas.
- Ponds occupy a large portion of farmer’s lands.
V. Answer briefly:
Question 1.
What are the two factors of biosphere?
Answer:
The biosphere is the part of the earth where life exists. All resources of the biosphere can be grouped into two major categories namely:
- Biotic or living factors which include plants, animals and all other living organisms.
- Abiotic or non-living factors which include all factors like temperature, pressure, water, soil, air and sunlight which affect the ability of organisms to survive and reproduce.
Question 2.
How do human activities affect nitrogen cycle?
Answer:
Human activities,
- alters the biodiversity
- changes the food web structure
- destroys the general habitat.
![]()
Question 3.
What is adaptation?
Answer:
Any feature of an organism or its part that enables it to exist under conditions of its habitat is called adaptation.
Question 4.
What are the challenges faced by hydrophytes in their habitat?
Answer:
Challenges faced by hydrophtes:
- More water availability than needed.
- Damaging of water body by water current.
- Regular change of water level.
- Maintenance of buoyancy in water.
Question 5.
Why is it important to conserve water?
Answer:
Importance of water conservation:
- It creates a more efficient use of water resources.
- It ensures that we have enough usable water.
- It helps in decreasing water pollution.
- It helps in increasing energy saving.
![]()
Question 6.
List some of the ways in which you could save water in your home and school?
Answer:
We could save water by
- Using low flow taps.
- Using recycled water for lawns.
- Repairing the leaks in the taps.
- Recycling (or) reusing water wherever it is possible.
Question 7.
What are the uses of recycled water?
Answer:
Uses for recycled water:
Agriculture, Landscape, Public parks, Golf course irrigation, Cooling water for power plants and oil refineries, Toilet flushing, Dust control, and Construction activities.
Question 8.
What is IUCN? What is the vision of IUCN?
Answer:
IUCN: International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources.
VISION: A just world that values and conserves nature.
![]()
VI. Answer in detail:
Question 1.
Describe the processes involved in the water cycle.
Answer:
Water cycle or hydrological cycle is the continuous movement of water on earth. In this process, water moves from one reservoir to another, from river to ocean or from ocean to the atmosphere by processes such as evaporation, sublimation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation, surface runoff and infiltration, during which water converts itself to various forms like liquid, solid and vapour.
- Evaporation: Water evaporates from the surface of the earth and water bodies such as the oceans, seas, lakes, ponds and rivers turn into water vapour.
- Sublimation: Ice sheets and ice caps from north and south poles, and icecaps on mountains get converted into water vapour directly, without converting into liquid.
- Transpiration: Transpiration is the process by which plants release water vapour to atmosphere through small pores in leaves and stems.
- Condensation: At higher altitudes, the temperature is low. The water vapour present there condenses to form very tiny particles of water droplets. These particles come close together to form clouds and fog.
- Precipitation: Due to change in wind or temperature, clouds combine to make bigger droplets, and pour down as precipitation(rain). Precipitation includes drizzle, rain, snow and hail.
- Runoff: As the water pours down, it runs over the surface of earth. Runoff water combines to form channels, rivers, lakes and ends up into seas and oceans.
- Infiltration: Some of the precipitated water moves deep into the soil. Then it moves down and increases the groundwater level.
- Percolation: Some of the precipitated water flows through soil and porous or fractured rock. Infiltration and percolation are two related but different processes describing the movement of water through soil.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain carbon cycle with the help of a flow chart.
Answer:
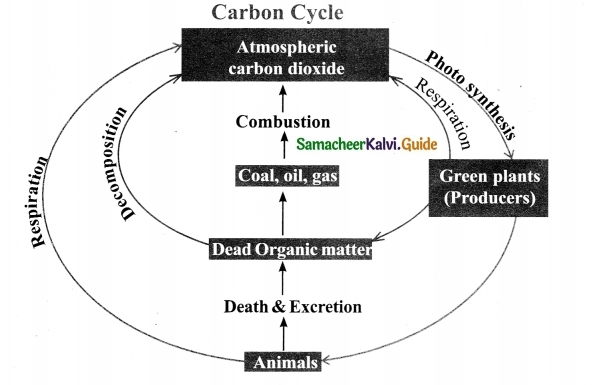
Question 3.
List out the adapatations of xerophytes.
Answer:
The conditions that lead to adaptation of plants in a dry habitat are;
- To absorb as much water as they can get from their surroundings.
- To retain water in their organs for a very long time.
- To reduce the transpiration rate.
- To reduce the consumption of water.
Adaptations of xerophytes:
- They have well-developed roots. Roots grow very deep and reach the layers where water is available as in Calotropis.
- They store water in succulent water-storing parenchymatous tissues, e.g. Opuntia, Aloe vera.
- They have small-sized leaves with a waxy coating, e.g. Acacia. In some plants, leaves are modified into spines, e.g. Opuntia.
- Some of the xerophytes complete their life cycle within a very short period when sufficient moisture is available.
![]()
Question 4.
How does a bat adapt itself to its habitat?
Answer:
Adaptations of BAT:
- Mostly, bats live in caves, which provide protection during the day from most predators and maintain a stable temperature.
- Bats are active at night. This, is a useful adaptation for them, as flight requires a lot of energy during day.
- By Hibernation, bats reduce body temperature with lowered metabolic rate during winter.
- Bats let their internal temperature reduce during rest.
- Bats use echolocation (High frequency ultrasonic sound waves) to identify and locate the prey.
Question 5.
What is water recycling? Explain the conventional wastewater recycling treatment?
Answer:
Water Recycling: Water recycling is reusing treated wastewater for beneficial purposes
such as agricultural and land irrigation, industrial processes, etc.
Conventional wastewater recycling treatment : Conventional wastewater treatment consists of combination of physical, chemical and biological processes involving the following stages.
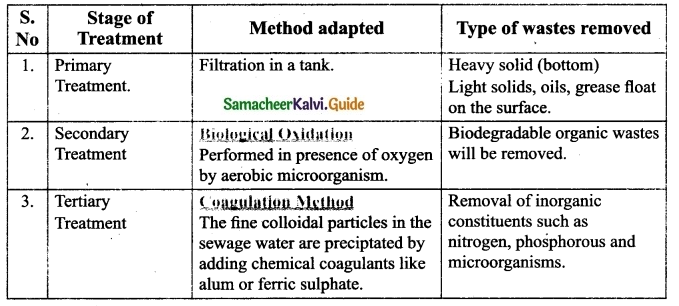
![]()
Intext Activities
ACTIVITY – 1
Create your own water cycle.
Take a small container and place it in the middle of the large bowl. Fill water in the large container and cover it with plastic wrap. Fasten the plastic wrap around the rim of the large container with the rubber band. Place a stone on the top of the plastic wrap. Keep this under sun for few hours. Record your observation.
Aim :
To understand utilisation and recycling of water.
Materials:
A large transparent bowl, plastic wrap, a stone, a smaller container and a rubber band. Procedure:
- The small container is placed in the middle of the large bowl. Water is filled in the large container and it is covered with plastic wrap.
- The plastic wrap is fastened around the rim of the large container with the rubber band.
- The stone is placed on the top of the plastic wrap.
This is placed under the sun for few hours.
Observation :
- When we have a close look at the plastic wrap, water droplets would be formed in the surface of plastic wrap. Thus, can conclude there is condensation process.
- The level of the water in bowl is reduced. It suggests that a part of water is evaporated.
- After sometime, the droplets on the plastic wrap drip into the bowl which indicates the phenonmenon of Precipitation.
Conclusion :
In this activity, the processes such as condensation, evaporation and precipitation have been demonstrated.
[End of the activity]
![]()
9th Science Guide Environmental Science Additional Important Questions and Answers
I. Choose the correct answer :
Question 1.
Which of the following is not an adaptation of hydrophytes?
(a) poorly developed root system
(b) reduced plant body
(c) water storing parenchymatous tissues
(d) finely divided submerged leaves
Answer:
(c) water storing parenchymatous tissues
Question 2.
In some xerophytes, leaves are modified into spines as an adaptation ……………..
(a) to reduce transpiration rate
(b) to store water
(c) to reduce consumption of water
(d) all of the above
Answer:
(d) all of the above
![]()
Question 3.
Identify the incorrect statement with respect to adaptations of earthworm.
(a) Earthworm has a steam lined body with no antennae or fins.
(b) Each segment of earthworm has setae.
(c) Many earthworms become inactive in a process called hibernation, during winter season.
(d) Earthworms remain in its burrow during day time, to avoid sunlight.
Answer:
(c) Many earthworms become inactive in a process called hibernation during, winter season
Question 4.
Which of the following is one of the strategies to conserve water?
(a) Water recycling %
(b) Using large overhead watSr tanks
(c) Increasing the number of bore wells
(d) Watering the plants using hose.
Answer:
(a) Water recycling
Question 5.
Specific constituents such as nitrogen, phosphorus, suspended solids and heavy metals found in the wastewaer are removed during …………….. treatment of water recycling process.
(a) primary
(b) secondary
(c) tertiary
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(c) tertiary
![]()
Question 6.
Free-living soil bacteria such as Pseudomonas sp. are responsible for the ……………..process in the nitrogen cycle.
(a) ammonification
(b) nitrogen fixation
(c) nitrification
(d) denitrification
Answer:
(d) denitrification
Question 7.
Environmental science provides holistic knowledge about ……………..
(a) Natural processes
(b) Effects of human interventions
(b) Solutions to environmental issues
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question 8.
Which one the following is not an abiotic factor?
(a) water
(b) air
(c) soil
(d) None of these
Answer:
(d) None of these
![]()
Question 9.
The process of water cycle that related with the plants is called …………………
(a) Percolation
(b) Evaporation
(c) Transpiration
(d) Precipitation
Answer:
(c) Transpiration
Question 10.
Rain is due to the process of ………………..
(a) Condensation
(b) Precipitation
(b) Sublimation
(d) Run off
Answer:
(b) Precipitation
Question 11.
…………… is the primary nutrient, important for survival of all living organisms.
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Carbon
(c) Hydrogen
(d) Oxygen
Answer:
(a) Nitrogen
![]()
Question 12.
The bacteria present in the root nodules of leguminous plants is .
(a) Nitrobacter
(b) Rhizobium
(c) Pseudomonas sp
(d) Nitrosomonas
Answer:
(b) Rhizobium
Question 13.
In the Nitrification process, the ammonium compounds are oxidised to soluble……………………….
(a) Ammonia
(b) Urea
(c) Nitrites
(d) Nitrates
Answer:
(d) Nitrates
![]()
Question 14.
The atmospheric carbon dioxide enters into the plants through the process of
photosynthesis to form
(a) Proteins
(b) Carbohydrates
(c) Water
(d) Carbon monoxide
Answer:
(b) Carbohydrates
Question 15.
Carbon dioxide is also returned to atmosphere through ……………………..
(a) Decomposition of dead organic matter
(b) Burning fossil fuels
(c) Volcanic activities
(d) All the above
Answer:
(d) All the above
Question 16.
The plants that has air chambers is ……………..
(a) Wolffia
(b) Opuntia
(c) Eichhomia
(d) Acacia
Answer:
(c) Eichhornia
![]()
Question 17.
Which plant is called as “Cindrella of the plant kingdom”?
(a) Hydrilla
(b) Water hyacinth
(c) Calotropis
(d) Aloevera
Answer:
(b) Water hyacinth
Question 18.
Root caps is a characteristic adaptation of ………………….
(a) Xerophytes
(b) Hydrophytes
(c) Mesophytes
(d) All the above
Answer:
(c) Mesophytes
Question 19.
The presence of ………….. in leaves traps the moisture and lessens water loss inMesophytes.
(a) Waxy Cuticle
(b) stomata
(c) stalk
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Waxy Cuticle
![]()
Question 20.
…………………. supports and controls movements during flight of a bat.
(a) Forelimbs
(b) Hind limbs
(c) Tail
(d) Muscles
Answer:
(c) Tail
Question 21.
Find the incorrect statement
(a) Vermicompost is prepared by using earthworms
(b) Vermicompost decomposes the plant and animal waste
(c) Vermicompost is an inorganic compound
(d) Vermicompost contains water soluble nutrients.
Answer:
(c) Vermicompost is an inorganic compound
Question 22.
World Water Day is celebrated on …………………..
(a) 22nd February
(b) 22nd March
(c) 5th June
(d) 03rd December
Answer:
(b) 22nd March
![]()
Question 23.
Which one of the following is not an advantage of farm ponds?
(a) Reduce soil erosion
(b) Recharge ground water
(c) Reduce water flow to other parts
(d) Improve drainage
Answer:
(c) Reduce water flow to other parts
Question 24.
Biological oxidation is the method is used in ……………….
(a) Primary Treatment
(b) Secondary Treatment.
(c) Tertiary Treatment
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Secondary Treatment
![]()
Question 25.
The wastes removed in tertiary treatment are ………………
(a) Suspended solids
(b) Biodegradable organic matter
(c) Inorganic substances
(d) All of these
Answer:
(c) Inorganic substances
Question 26.
India accounts for …………………% of all recorded species.
(a) 2-4%
(b) 5-6%
(c) 6-7%
(d) 7-8%
Answer:
(d) 7 – 8%
![]()
II. Fill in the blanks :
1. …………………is the study of patterns, processes in the natural world and their modifications
by human activities.
Answer:
Environmental Science
2. Biosphere is a …………………. and …………………and system.
Answer:
dynamic, stable
3. Cyclic flow of nutrients between non-living and living factors of the environment are termed as ……………. cycle.
Answer:
Biogeochemical
![]()
4. …………………is the reverse of vapourisation.
Answer:
Condensation
5. Atmosphere is a rich source of ………………….
Answer:
Nitrogen
6. The blue-green algae that take part in nitrogen fixation is also called ………………..
Answer:
Cyanobacteria
![]()
7. …………………….. animals convert plant proteins into animal proteins.
Answer:
Herbivorous
8. Carnivorous animals synthesize …………………….. from their food.
Answer:
Protein
9. Charcoal, diamond and graphite are …………………….. forms of carbon.
Answer:
Elemental
![]()
10. All living organisms are made up of carbon-containing molecules like …………………….. and ………………………
Answer:
Proteins, nucleic acids
11. Floating leaves have long …………………….. to enable the leaves move up and down in response to changes in water level.
Answer:
Leaf stalks
12. …………………….. is the plant in which leaves are modified into spines.
Answer:
Opuntia
13. The function of stomata in leaves of mesophytes is to prevent ………………………
Answer:
Transpiration
14. In bats, the excessive heat absorption dining the day is caused by ……………………..
Answer:
Patagium
![]()
15. In bats modified forelimbs serve as ……………..
Answer:
Wings
16. …………………….. of hind limbs in bat provides a tight grasp when the animals are suspended upside down.
Answer:
Tendons
17. Bats are …………………….. blooded animals
Answer:
warm
18. Earthworm belongs to Phylum . ……………………..
Answer:
Annelida
19. Moist skin in earthworm helps in …………………….. of blood.
Answer:
Oxygenation
![]()
20. The theme for World Water Qay 2018 is ………………………
Answer:
Nature for water
21. The microorganism used in file secondary treatment must be separated from treated wastewater by ……………………..
Answer:
Sedimentation
22. There are …………………….. globally identified biodiversity hotspots in India.
Answer:
Four
23. IUCN was founded on …………………….. at Gland, Switzerland.
Answer:
5th October 1948
![]()
III. Match the following :
Question 1.
| Water cycle | Application of fertilizers |
| Nitrogen cycle | Sunlight |
| Carbon cycle | Deforestation |
| Abiotic factor | Volcanic activities |
Answer:
| Water cycle | Deforestation |
| Nitrogen cycle | Application of fertilizers |
| Carbon cycle | Volcanic activities |
| Abiotic factor | Sunlight |
Question 2.
| XeroLyïtes | Broad and thin leaves |
| Mesophytes | Reducedjplant body |
| Hydrophytes | Water hyacinth |
| Green manure | Small sized leaves |
Answer:
| XeroLyïtes | Small sized leaves |
| Mesophytes | Broad and thin leaves |
| Hydrophytes | Reducedjplant body |
| Green manure | Water hyacinth |
Question 3.
| Aestivation | Heat absorption |
| Echolocation | Fall in body temperature |
| Hibernation | Ultrasonic sounds |
| patagium | low metabolism |
Answer:
| Aestivation | low metabolism |
| Echolocation | Ultrasonic sounds |
| Hibernation | Fall in body temperature |
| patagium | Heat absorption |
Question 4.
| Secondary Treatment | Disinfection |
| Grey water | Floatation |
| Primary Treatment | Reusuable waste water |
| Tertiary Treatment | Sedimentation |
Answer:
| Secondary Treatment | Sedimentation |
| Grey water | Reusable waste water |
| Primary Treatment | Floatation |
| Tertiary Treatment | Disinfection |
IV. Say true or false. Correct the false statements :
1. Sublimation is conversion of solid into liquid.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Sublimation is conversion of solid into Gas.
2. Nitrogen is an essential component of protein, DNA and chlorophyll.
Answer:
True.
![]()
3. Plant proteins are excreted in theTorm of urea, uric acid or ammonia.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement : Animal proteins are excreted in the form of urea, uric acid or ammonia %
4. During respiration, plants and animals release carbon into the atmosphere in the form of carbon monoxide.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement : During respiration, plants and animals release carbon into the atmosphere in the form of Carbon dioxide
5. Bats are not blind.
Answer:
True.
![]()
6. Earthworm come out of their burrow during summer season.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Earthworm come out of their burrow during rainy season.
7. Earthworm reacts positively to brighter light.
Answer:
False.
Correct statement: Earthworm reacts negatively to brighter light.
8. Clean and Fresh water is essential for every human activity.
Answer:
True.
9. Nicobar island is one of the biodiversity hotspots in India.
Answer:
True.
![]()
V. Assertion and Reason type questions :
Mark the correct choice as :
(a) If both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion.
(b) If both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion.
(c) If assertion is true but reason is false.
(d) If assertion is false but reason is true.
Question 1.
Assertion (A) : Biosphere is a dynamic and stable system.
Reason (R) : There is a constant interaction between biotic and abiotic components in the biosphere.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
Question 2.
Assertion (A) : Infiltration and Percolation are two related but different processes.
Reason (R) : They describe the movement of water through atmosphere.
Answer:
(c) Assertion is true but reason is false
Reason (R): They describe the movement of water through Soil.
Question 3.
Assertion (A) : Plants and animals can utilize atmospheric nitrogen.
Reason (R) : Atmosphere is a rich source of nitrogen.
Answer:
(d) Assertion is false but reason is true
Assertion (A) : Plants and animals cannot utilise atmospheric nitrogen.
![]()
Question 4.
Assertion (A) : By increasing the amount of carbon dioxide, earth becomes warmer.
Reason (R) : Carbon dioxide is a green house gas.
Answer:
(a) Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of Assertion
Question 5.
Assertion (A) : The moist skin in earthworm helps in oxygenation of blood.
Reason (R) : The slippery skin of earthworm is kept moist.
Answer:
(b) Both assertion and reason are true but reason is not the correct explanation of assertion
Reason (R) : The slippery skin of earthworm is kept moist as it respires through the skin. Moist skin helps in oxygenation of blood.
![]()
VI. Very Short Answer Questions
Question 1.
Name three Biogeochemical cycles.
Answer:
Some of the important Biogeochemical cycles are :
- Water cycle
- Nitrogen cycle
- Carbon cycle.
Question 2.
List the forms of Precipitation.
Answer:
Precipitation includes
- Drizzle
- Rain
- Snow
- Hail.
![]()
Question 3.
Mention the excretory forms of Animal proteins.
Answer:
- Urea
- Uric acid
- Ammonia
Question 4.
What are the effects of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere?
Answer:
- Green house effect
- Global warming.
Question 5.
How are plants classified on the basis of water availability?
Answer:
On the Basis of water availability, plants have been classified as:
- Hydrophytes
- Xerophytes
- Mesophytes.
![]()
Question 6.
How are bats important to humans?
Answer:
- Bats reduce insect population.
- They help to pollinate plants.
Question 7.
What is the Ideal temperature range of earthworm?
Answer:
The Ideal temperatures range is 60-80°F.
VII. Answer briefly :
Question 1.
Define : Environmental Science.
Answer:
Environmental science is defined as the study of patterns, processes in the natural world and their modifications by human activities.
![]()
Question 2.
What is biogeochemical cycle?
Answer:
The cyclic flow of nutrients between non-living and living factors of the environment are termed as Biogeochemical cycles.
Question 3.
How are clouds and fogs formed?
Answer:
- At higher altitudes, the temperature is low. The water vapour present there condenses to form very tiny particles of water droplets.
- These particles come close together to form clouds and fog.
Question 4.
How is carbon dioxide returned to atmosphere? :
Answer:
Carbon dioxide is returned to the atmosphere through
- decomposition of dead organic matter,
- burning fossil fuels
- volcanic activities.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain briefly the role of earth-worm in soil atmosphere, (or) soil health?
Answer:
- Earthworm facilitates aeration, water infiltration.
- It produces organic matter to increase crop growth.
Question 6.
What is worm castings? How is it useful?
Answer:
- The faecal wastes of earthworm are called worm castings.
- They are rich in nitrogenous content which adds fertility to the soil.
Question 7.
Point out the importance of water conservation.
Answer:
- Water conservation creates more efficient use of the water resources.
- It ensures enough usable water.
- It helps to decrease water pollution.
- It helps in increasing energy saving.
![]()
Question 8.
According to you, which process of water cycle is adversely affected by human activities?
Answer:
Transpiration by which plants release water vapour through small pores in leaves and stems.
Reason : Human activities such as Deforestation, urbanisation.
Question 9.
Identify the given plant. How does it adapt itself to its habitat?

Answer:
Hydrilla:
- Poorly developed Root.
- Narrow (or) finely divided submerged leaves.
![]()
Question 10.
What is grey water? %
Answer:
Grey water is reusable waste water from residential, commercial and industrial bathroom sinks, bath tub, shower drains and washing of clothes.
VIII. Answer in detail :
Question 1.
Draw a neat flow chart of Nitrogen cycle. Briefly explain the various processes involved in nitrogen cycle.
Answer:
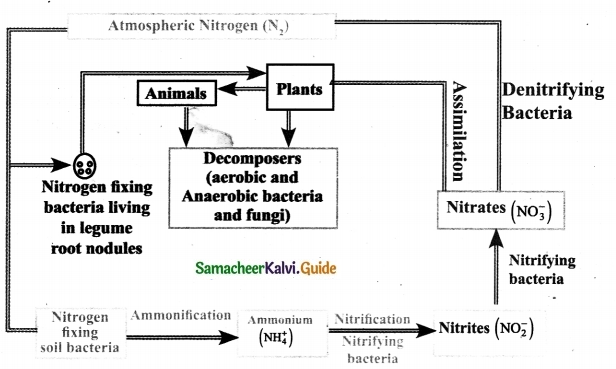
Process involved in nitrogen cycle are explained below :
1. Nitrogen Fixation:
Process : Conversion of atmospheric Nitrogen (inert) into reactive compounds.
Agents : Bacteria and Bluegreen algae (cyanobacteria), (microorganism), Rhizobium.
Occurrence : Root nodules of leguminous plants peas, beans, etc.
2. Nitrogen Assimilation:
Process : Plants absorb nitrate ions and made into organic matter like proteins and nucleic acids.
Agents : Plants, animals.
3. Ammonification :
Process: Decomposition of nitrogenous waste into ammonium compounds.
Micro organism : Putrefying Bacteria, and fungi.
End Products : Urea, Uric acid (or) Ammonia.
4. Nitrification
Process: Ammonium compounds are oxidised to soluble nitrates.
Bacteria : Nitrification is caused by nitrifying bacteria.
5. Denitrification:
Process: Reduction of nitrate ions of soil into gaseous nitrogen which enters into the atmosphere.
Bacteria : Pseudomonas sp.
![]()
Question 2.
Write the adaptations of mesophytes.
Answer:
- The roots of mesophytes are well developed with root caps.
- They have straight as well as branched stems.
- Broad and thin leaves with waxy cuticles.
- Waxy cuticles traps the moisture and lessens water loss.
- Leaves have stomata which close in extreme heat and wind to prevent transpiration.
![]()
Question 3.
Discuss the adaptations of earthworm with its applications.
Answer:
adaption : of Earthworm :
1. Stream-lined body:
Adaptation : Earthworm has cylindrical, elongated and segmented body.
Application : 1. To live in burrows, 2. Easy penetration into soil.
2. Skin: .
Adaptation : Mucus covers skin, 2. slippery moist skin.
Application : 1. It does not allow soil particle to stick on the skin.
2. Respiration through skin and oxygenation of blood.
3. Burrowing:
Adaptation : 1. Circular and longitudinal muscles in body.
2. Each segment of the lower surface of the body has number of bristles called setae.
Application: 1. Movement and subsoil burrowing.
2. To move through the soil and provide anchor in the burrows.
4. Aestivation
Adaptation : 1. During dry (or) hot condition, Earthworms moves deep into the soil and become inactive.
2. It secrets mucus and lowers metabolic rate.
Application: To reduce water loss.
5. Nocturnality:
Adaptation : Earthworm sense light through light-sensitive cells in the skin.
Remains in burrow during day.
Application : To detect light and changes in light intensity.
![]()
Question 4.
Describe layout of a Farm pond.
Answer:
1. Farm pond is a dugout structure with definite shape and size.
2. They have proper inlet and outlet structures for collecting the surface run off flowing from the farm area.
3. The size and depth of the pond depend upon
- The amount of land available.
- The type of soil
- Water requirement of farmers
- The cost of excavation
4. The stored water is used forinigation.
Question 5.
What are all the strategies used to support water conservation?
Answer:
Water conservation strategies
- Rain water harvesting.
- Improved Irrigation techniques.
- Use of traditional water harvesting structures.
- Minimising domestic water consumption.
- Awareness on water conservation.
- Construction of farm ponds.
- Recycling of water.
![]()
Question 6.
List out any five advantages of Farm ponds.
Answer:
The advantages of farm ponds are-
- They provide water to growing crops, without waiting for rainfall.
- They reduce soil erosion.
- They recharge ground water.
- They improve drainage.
- The excavated soil can be used to enrich soil in fields and levelling lands.
- They promote fish rearing.
- They provide water for domestic purposes and livestock.